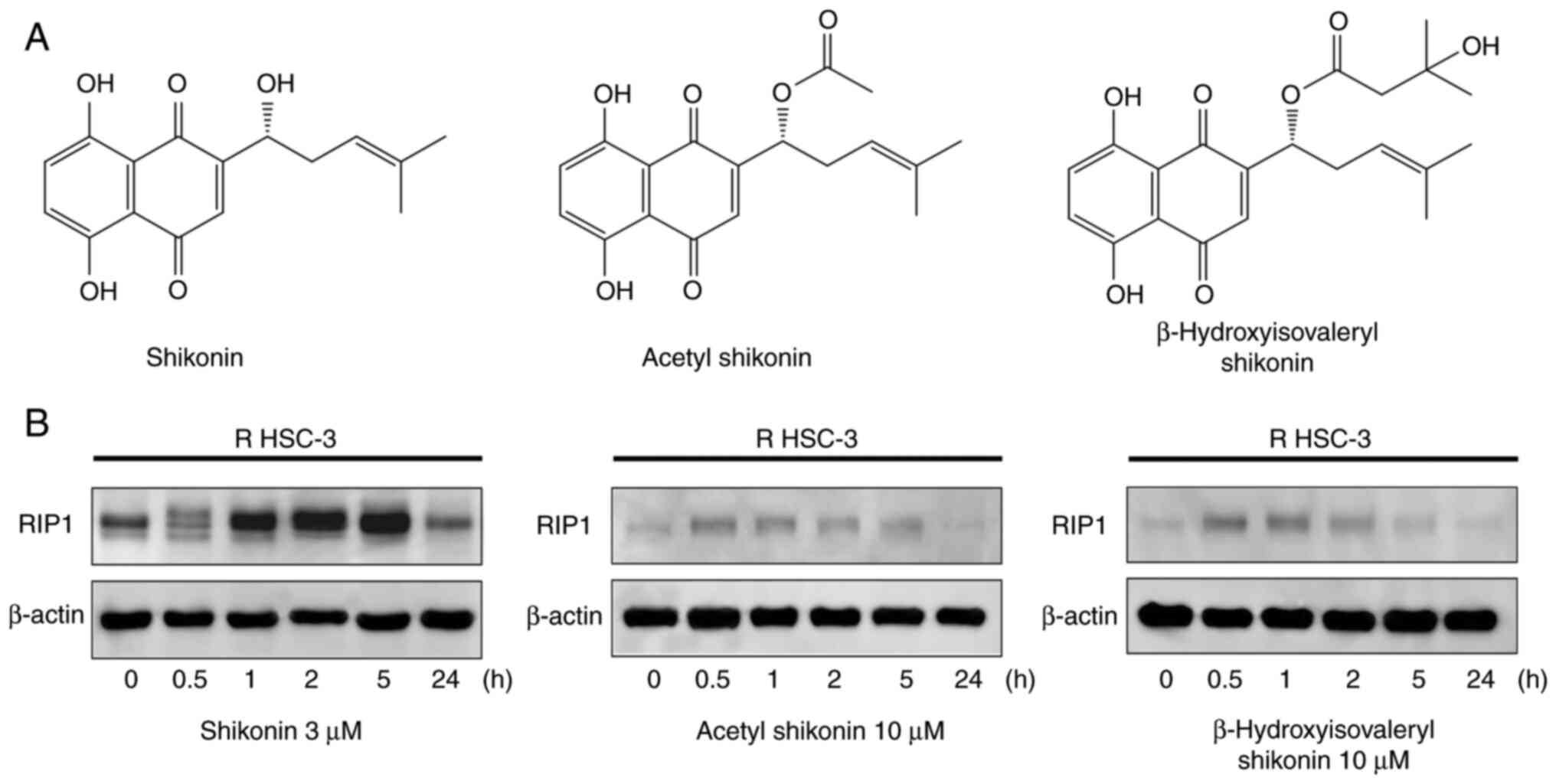
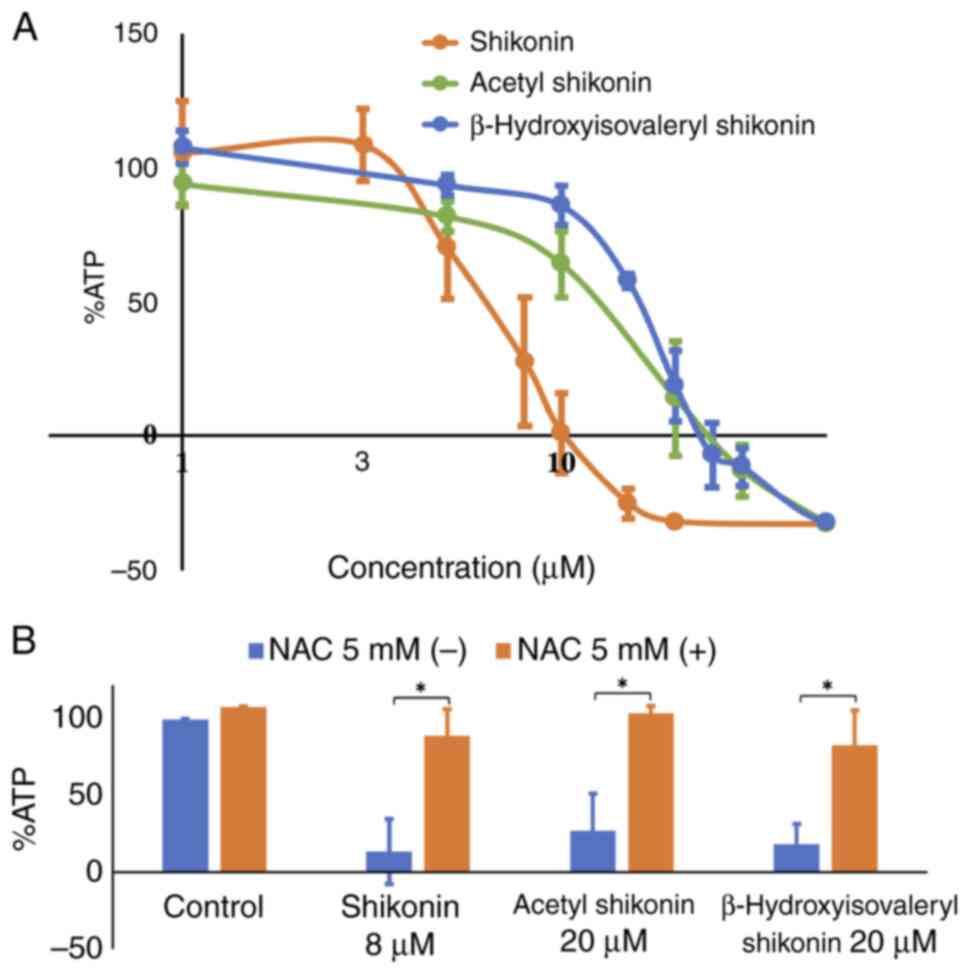
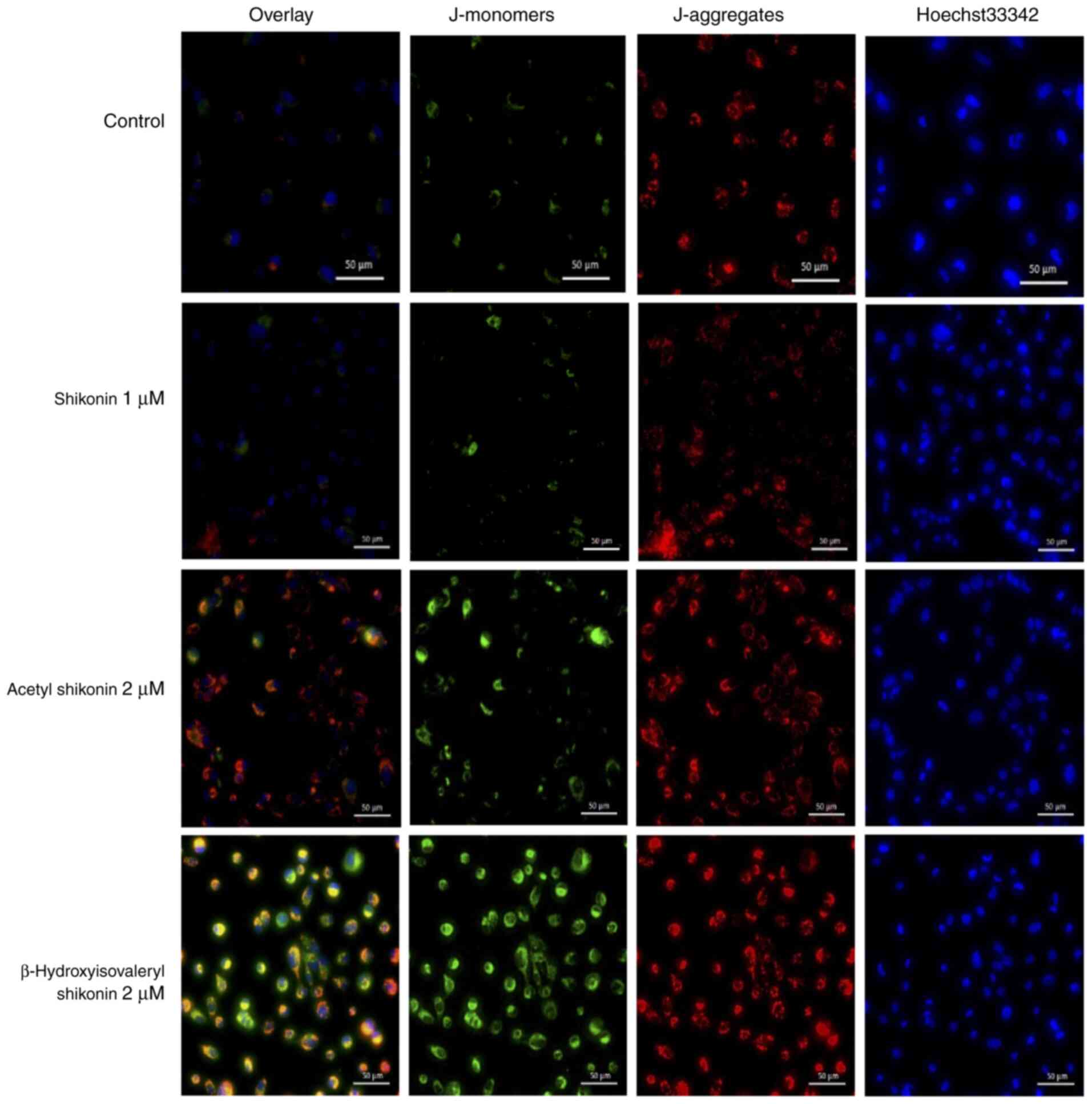
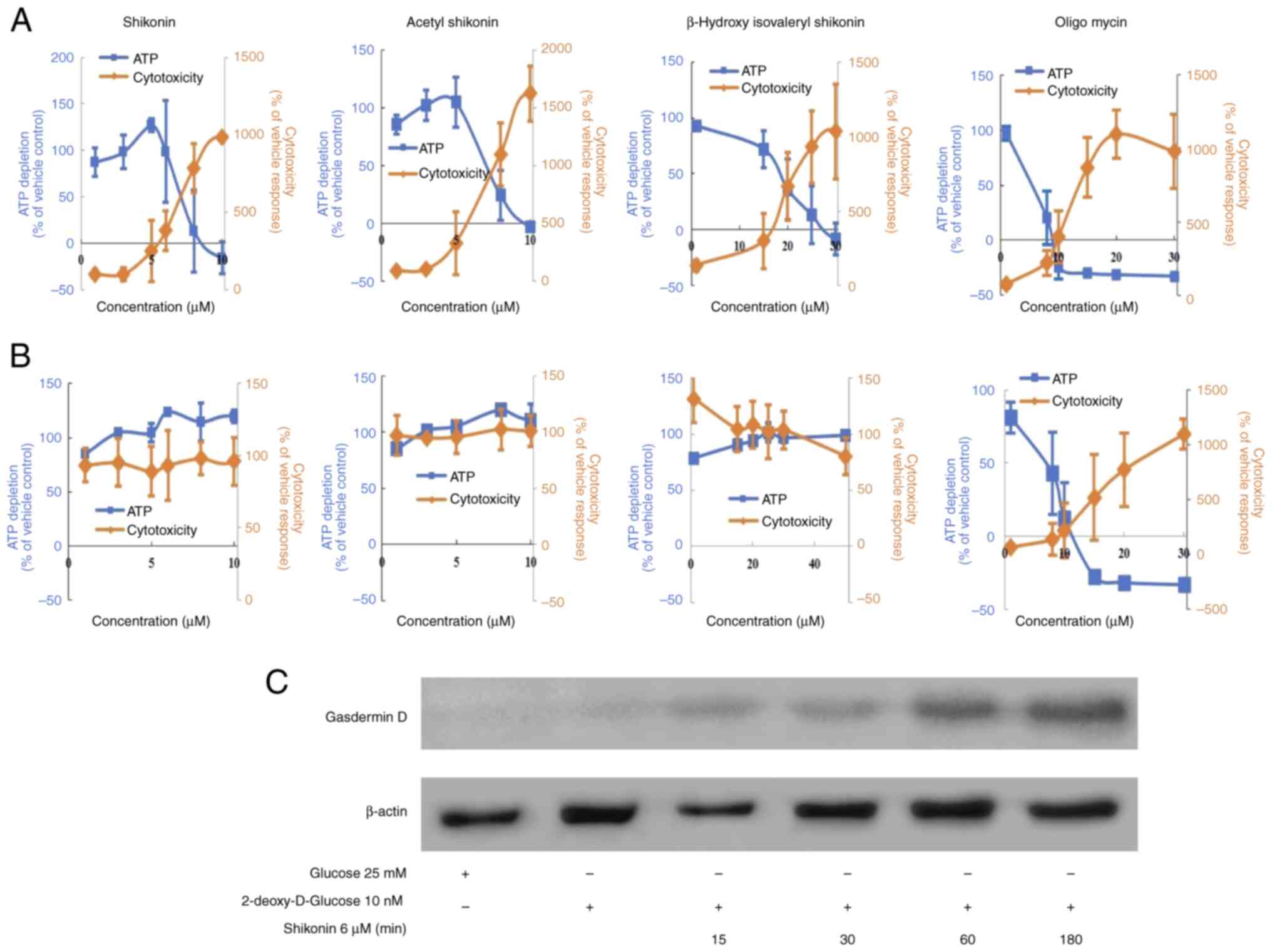
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Argiris A, Karamouzis MV, Raben D and
Ferris RL: Head and neck cancer. Lancet. 371:1695–1709. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Price KA and Cohen EE: Current treatment
options for metastatic head and neck cancer. Curr Treat Options
Oncol. 13:35–46. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chang JH, Wu CC, Yuan KS, Wu ATH and Wu
SY: Locoregionally recurrent head and neck squamous cell carcinoma:
Incidence, survival, prognostic factors, and treatment outcomes.
Oncotarget. 8:55600–55612. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sugimoto Y, Tsukahara S, Sato S, Suzuki M,
Nunoi H, Malech HL, Gottesman MM and Tsuruo T: Drug-selected
co-expression of P-glycoprotein and gp91 in vivo from an
MDR1-bicistronic retrovirus vector Ha-MDR-IRES-gp91. J Gene Med.
5:366–376. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Murakami K, Umemura N, Adachi M, Motoki M
and Ohkoshi E: ABCG2, CD44 and SOX9 are increased with the
acquisition of drug resistance and involved in cancer stem cell
activities in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Exp Ther
Med. 24:7222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Smith ER, Wang JQ, Yang DH and Xu XX:
Paclitaxel resistance related to nuclear envelope structural
sturdiness. Drug Resist Updat. 65:1008812022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kanda Y: Investigation of the freely
available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone
Marrow Transplant. 48:452–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ofengeim D and Yuan J: Regulation of RIP1
kinase signalling at the crossroads of inflammation and cell death.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:727–736. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xie Y, Zhao G, Lei X, Cui N and Wang H:
Advances in the regulatory mechanisms of mTOR in necroptosis. Front
Immunol. 14:12974082023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Murphy MP: How mitochondria produce
reactive oxygen species. Biochem J. 417:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Butow RA and Avadhani NG: Mitochondrial
signaling: The retrograde response. Mol Cell. 14:1–15. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sena LA and Chandel NS: Physiological
roles of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Mol Cell.
48:158–167. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Warburg O: On the origin of cancer cells.
Science. 123:309–314. 1956. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pfeiffer T, Schuster S and Bonhoeffer S:
Cooperation and competition in the evolution of ATP-producing
pathways. Science. 292:504–507. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Marroquin LD, Hynes J, Dykens JA, Jamieson
JD and Will Y: Circumventing the Crabtree effect: Replacing media
glucose with galactose increases susceptibility of HepG2 cells to
mitochondrial toxicants. Toxicol Sci. 97:539–547. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Niles AL, Moravec RA, Eric Hesselberth P,
Scurria MA, Daily WJ and Riss TL: A homogeneous assay to measure
live and dead cells in the same sample by detecting different
protease markers. Anal Biochem. 366:197–206. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Miao R, Jiang C, Chang WY, Zhang H, An J,
Ho F, Chen P, Zhang H, Junqueira C, Amgalan D, et al: Gasdermin D
permeabilization of mitochondrial inner and outer membranes
accelerates and enhances pyroptosis. Immunity. 56:2523–2541.e8.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rickard JA, O'Donnell JA, Evans JM,
Lalaoui N, Poh AR, Rogers T, Vince JE, Lawlor KE, Ninnis RL,
Anderton H, et al: RIPK1 regulates RIPK3-MLKL-driven systemic
inflammation and emergency hematopoiesis. Cell. 157:1175–1188.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dillon CP, Weinlich R, Rodriguez DA,
Cripps JG, Quarato G, Gurung P, Verbist KC, Brewer TL, Llambi F,
Gong YN, et al: RIPK1 blocks early postnatal lethality mediated by
caspase-8 and RIPK3. Cell. 157:1189–1202. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang Z, Zhou T, Sun X, Zheng Y, Cheng B,
Li M, Liu X and He C: Necroptosis in microglia contributes to
neuroinflammation and retinal degeneration through TLR4 activation.
Cell Death Differ. 25:180–189. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu Z, Jiang N, Su W and Zhuo Y:
Necroptosis: A novel pathway in neuroinflammation. Front Pharmacol.
12:7015642021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wellenstein MD and de Visser KE:
Cancer-cell-intrinsic mechanisms shaping the tumor immune
landscape. Immunity. 48:399–416. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gardai SJ, McPhillips KA, Frasch SC,
Janssen WJ, Starefeldt A, Murphy-Ullrich JE, Bratton DL, Oldenborg
PA, Michalak M and Henson PM: Cell-surface calreticulin initiates
clearance of viable or apoptotic cells through trans-activation of
LRP on the phagocyte. Cell. 123:321–334. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tesniere A, Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Joza
N, Panaretakis T, Kepp O, Schlemmer F, Zitvogel L and Kroemer G:
Immunogenic cancer cell death: A key-lock paradigm. Curr Opin
Immunol. 20:504–511. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee MJ, Kao SH, Hunag JE, Sheu GT, Yeh CW,
Hseu YC, Wang CJ and Hsu LS: Shikonin time-dependently induced
necrosis or apoptosis in gastric cancer cells via generation of
reactive oxygen species. Chem Biol Interact. 211:44–53. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Forrester SJ, Kikuchi DS, Hernandes MS, Xu
Q and Griendling KK: Reactive oxygen species in metabolic and
inflammatory signaling. Circ Res. 122:877–902. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li J, Pang J, Liu Z, Ge X, Zhen Y, Jiang
CC, Liu Y, Huo Q, Sun Y and Liu H: Shikonin induces programmed
death of fibroblast synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis by
inhibiting energy pathways. Sci Rep. 11:182632021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu XN, Yang ZH, Wang XK, Zhang Y, Wan H,
Song Y, Chen X, Shao J and Han J: Distinct roles of RIP1-RIP3
hetero- and RIP3-RIP3 homo-interaction in mediating necroptosis.
Cell Death Differ. 21:1709–1720. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Christofferson DE and Yuan J: Necroptosis
as an alternative form of programmed cell death. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 22:263–268. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Smith CC and Yellon DM: Necroptosis,
necrostatins and tissue injury. J Cell Mol Med. 15:1797–1806. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Degterev A, Hitomi J, Germscheid M, Ch'en
IL, Korkina O, Teng X, Abbott D, Cuny GD, Yuan C, Wagner G, et al:
Identification of RIP1 kinase as a specific cellular target of
necrostatins. Nat Chem Biol. 4:313–321. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cho YS, Challa S, Moquin D, Genga R, Ray
TD, Guildford M and Chan FK: Phosphorylation-driven assembly of the
RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates programmed necrosis and virus-induced
inflammation. Cell. 137:1112–1123. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sun L, Wang H, Wang Z, He S, Chen S, Liao
D, Wang L, Yan J, Liu W, Lei X and Wang X: Mixed lineage kinase
domain-like protein mediates necrosis signaling downstream of RIP3
kinase. Cell. 148:213–227. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Linkermann A and Green DR: Necroptosis. N
Engl J Med. 370:455–465. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao J, Jitkaew S, Cai Z, Choksi S, Li Q,
Luo J and Liu ZG: Mixed lineage kinase domain-like is a key
receptor interacting protein 3 downstream component of TNF-induced
necrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:5322–5327. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang H, Sun L, Su L, Rizo J, Liu L, Wang
LF, Wang FS and Wang X: Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein
MLKL causes necrotic membrane disruption upon phosphorylation by
RIP3. Mol Cell. 54:133–146. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Moreno-Gonzalez G, Vandenabeele P and
Krysko DV: Necroptosis: A novel cell death modality and its
potential relevance for critical care medicine. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 194:415–428. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Quarato G, Guy CS, Grace CR, Llambi F,
Nourse A, Rodriguez DA, Wakefield R, Frase S, Moldoveanu T and
Green DR: Sequential engagement of distinct MLKL
Phosphatidylinositol-binding sites executes necroptosis. Mol Cell.
61:589–601. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dhuriya YK and Sharma D: Necroptosis: A
regulated inflammatory mode of cell death. J Neuroinflammation.
15:1992018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Green DR: The coming decade of cell death
research: Five riddles. Cell. 177:1094–1107. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Aaes TL, Kaczmarek A, Delvaeye T, De
Craene B, De Koker S, Heyndrickx L, Delrue I, Taminau J, Wiernicki
B, De Groote P, et al: Vaccination with necroptotic cancer cells
induces efficient anti-tumor immunity. Cell Rep. 15:274–287. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gong YN, Guy C, Crawford JC and Green DR:
Biological events and molecular signaling following MLKL activation
during necroptosis. Cell Cycle. 16:1748–1760. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Grootjans S, Vanden Berghe T and
Vandenabeele P: Initiation and execution mechanisms of necroptosis:
An overview. Cell Death Differ. 24:1184–1195. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Aaronson SA, Abrams
JM, Adam D, Agostinis P, Alnemri ES, Altucci L, Amelio I, Andrews
DW, et al: Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of
the nomenclature committee on cell death 2018. Cell Death Differ.
25:486–541. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang Y, Liu L, Jin L, Yi X, Dang E, Yang
Y, Li C and Gao T: Oxidative stress-induced calreticulin expression
and translocation: New insights into the destruction of
melanocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 134:183–191. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Obeid M, Tesniere A, Ghiringhelli F, Fimia
GM, Apetoh L, Perfettini JL, Castedo M, Mignot G, Panaretakis T,
Casares N, et al: Calreticulin exposure dictates the immunogenicity
of cancer cell death. Nat Med. 13:54–61. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang X, Wu S, Liu F, Ke D, Wang X, Pan D,
Xu W, Zhou L and He W: An Immunogenic cell death-related
classification predicts prognosis and response to immunotherapy in
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Front Immunol.
12:7814662021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bauza-Thorbrugge M, Peris E, Zamani S,
Micallef P, Paul A, Bartesaghi S, Benrick A and Wernstedt Asterholm
I: NRF2 is essential for adaptative browning of white adipocytes.
Redox Biol. 68:1029512023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chen S, Ren Q, Zhang J, Ye Y, Zhang Z, Xu
Y, Guo M, Ji H, Xu C, Gu C, et al: N-acetyl-L-cysteine protects
against cadmium-induced neuronal apoptosis by inhibiting
ROS-dependent activation of Akt/mTOR pathway in mouse brain.
Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 40:759–777. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|