|
1
|
Wang Q, Shao X, Zhang Y, Zhu M, Wang FXC,
Mu J, Li J, Yao H and Chen K: Role of tumor microenvironment in
cancer progression and therapeutic strategy. Cancer Med.
12:11149–11165. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang Y and Zhang Z: The history and
advances in cancer immunotherapy: Understanding the characteristics
of tumor-infiltrating immune cells and their therapeutic
implications. Cell Mol Immunol. 17:807–821. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Esfahani K, Roudaia L, Buhlaiga N, Del
Rincon SV, Papneja N and Miller WH Jr: A review of cancer
immunotherapy: From the past, to the present, to the future. Curr
Oncol. 27:S87–S97. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang H, Kaur G, Sankin AI, Chen F, Guan F
and Zang X: Immune checkpoint blockade and CAR-T cell therapy in
hematologic malignancies. J Hematol Oncol. 12:592019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
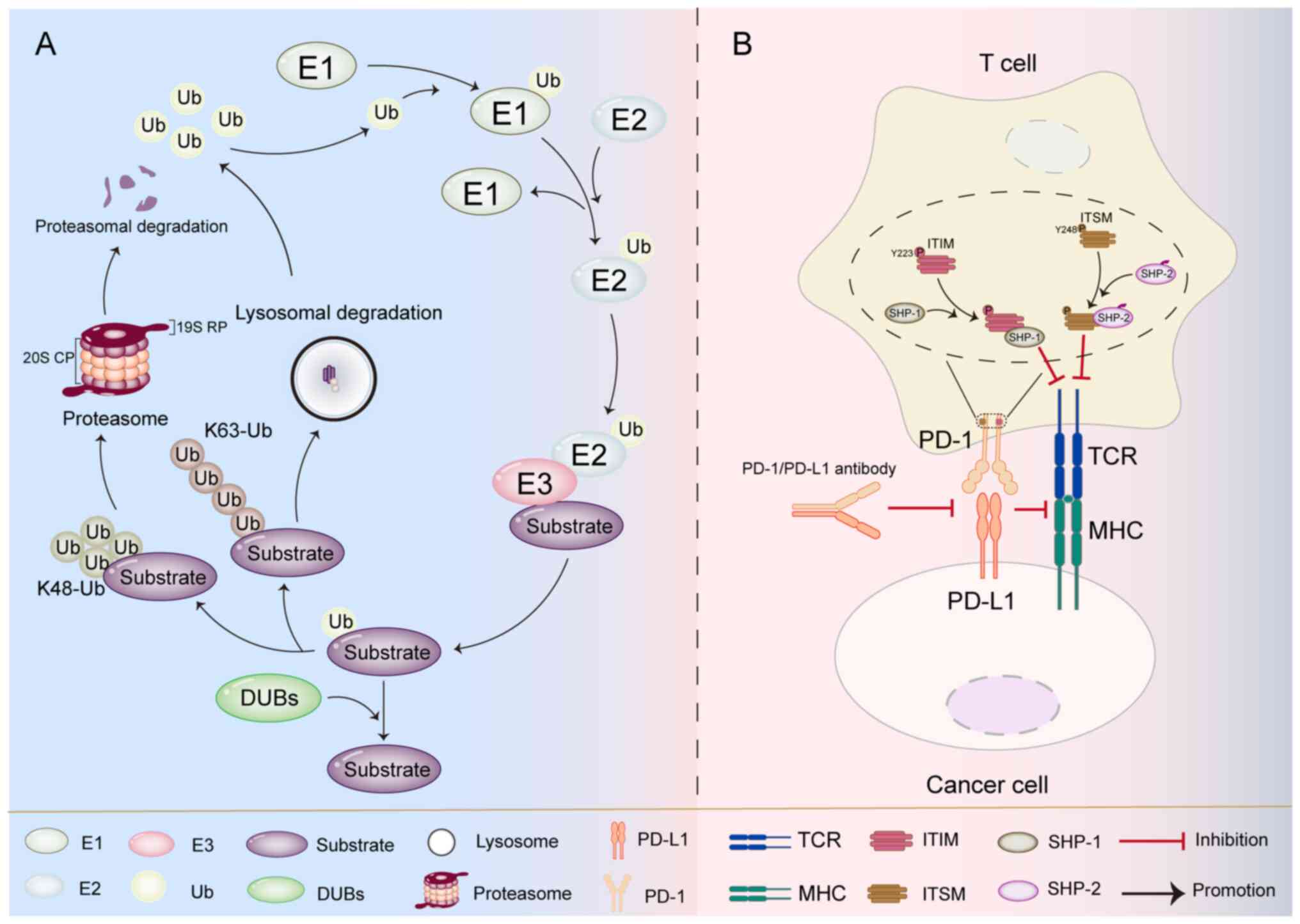
|
|
5
|
Byun DJ, Wolchok JD, Rosenberg LM and
Girotra M: Cancer immunotherapy-immune checkpoint blockade and
associated endocrinopathies. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 13:195–207. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Naimi A, Mohammed RN, Raji A, Chupradit S,
Yumashev AV, Suksatan W, Shalaby MN, Thangavelu L, Kamrava S,
Shomali N, et al: Tumor immunotherapies by immune checkpoint
inhibitors (ICIs); the pros and cons. Cell Commun Signal.
20:442022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dong H, Strome SE, Salomao DR, Tamura H,
Hirano F, Flies DB, Roche PC, Lu J, Zhu G, Tamada K, et al:
Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: A potential
mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med. 8:793–800. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gauen LK, Zhu Y, Letourneur F, Hu Q, Bolen
JB, Matis LA, Klausner RD and Shaw AS: Interactions of p59fyn and
ZAP-70 with T-cell receptor activation motifs: Defining the nature
of a signalling motif. Mol Cell Biol. 14:3729–3741. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Straus DB and Weiss A: Genetic evidence
for the involvement of the lck tyrosine kinase in signal
transduction through the T cell antigen receptor. Cell. 70:585–593.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang H, Dai Z, Wu W, Wang Z, Zhang N,
Zhang L, Zeng WJ, Liu Z and Cheng Q: Regulatory mechanisms of
immune checkpoints PD-L1 and CTLA-4 in cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 40:1842021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tang Q, Chen Y, Li X, Long S, Shi Y, Yu Y,
Wu W, Han L and Wang S: The role of PD-1/PD-L1 and application of
immune-checkpoint inhibitors in human cancers. Front Immunol.
13:9644422022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Butte MJ, Keir ME, Phamduy TB, Sharpe AH
and Freeman GJ: Programmed death-1 ligand 1 interacts specifically
with the B7-1 costimulatory molecule to inhibit T cell responses.
Immunity. 27:111–122. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Paik J: Nivolumab plus relatlimab: First
approval. Drugs. 82:925–931. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Harrington KJ, Burtness B, Greil R,
Soulières D, Tahara M, de Castro G Jr, Psyrri A, Brana I, Basté N,
Bratland Å, et al: Pembrolizumab with or without chemotherapy in
recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma:
Updated results of the phase III KEYNOTE-048 study. J Clin Oncol.
41:790–802. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Powles T, Park SH, Voog E, Caserta C,
Valderrama BP, Gurney H, Kalofonos H, Radulović S, Demey W, Ullén
A, et al: Avelumab maintenance therapy for advanced or metastatic
urothelial carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 383:1218–1230. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kiasari BA, Abbasi A, Darestani NG, Adabi
N, Moradian A, Yazdani Y, Hosseini GS, Gholami N and Janati S:
Combination therapy with nivolumab (anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody):
A new era in tumor immunotherapy. Int Immunopharmacol.
113:1093652022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Scheffner M, Werness BA, Huibregtse JM,
Levine AJ and Howley PM: The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human
papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53.
Cell. 63:1129–1136. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Joazeiro CA, Wing SS, Huang H, Leverson
JD, Hunter T and Liu YC: The tyrosine kinase negative regulator
c-Cbl as a RING-type, E2-dependent ubiquitin-protein ligase.
Science. 286:309–312. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Han D, Wang L, Jiang S and Yang Q: The
ubiquitin-proteasome system in breast cancer. Trends Mol Med.
29:599–621. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Eldridge AG and O'Brien T: Therapeutic
strategies within the ubiquitin proteasome system. Cell Death
Differ. 17:4–13. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fang S and Weissman AM: A field guide to
ubiquitylation. Cell Mol Life Sci. 61:1546–1561. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pfoh R, Lacdao IK and Saridakis V:
Deubiquitinases and the new therapeutic opportunities offered to
cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 22:T35–T54. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hochstrasser M: Ubiquitin-dependent
protein degradation. Annu Rev Genet. 30:405–439. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hofmann K and Falquet L: A
ubiquitin-interacting motif conserved in components of the
proteasomal and lysosomal protein degradation systems. Trends
Biochem Sci. 26:347–350. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Park J, Cho J and Song EJ:
Ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) as a target for anticancer
treatment. Arch Pharm Res. 43:1144–1161. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
McKeon JE, Sha D, Li L and Chin LS:
Parkin-mediated K63-polyubiquitination targets ubiquitin C-terminal
hydrolase L1 for degradation by the autophagy-lysosome system. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 72:1811–1824. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pickart CM and Eddins MJ: Ubiquitin:
Structures, functions, mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1695:55–72. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Groll M, Ditzel L, Löwe J, Stock D,
Bochtler M, Bartunik HD and Huber R: Structure of 20S proteasome
from yeast at 2.4 A resolution. Nature. 386:463–471. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bedford L, Paine S, Sheppard PW, Mayer RJ
and Roelofs J: Assembly, structure, and function of the 26S
proteasome. Trends Cell Biol. 20:391–401. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Meng X, Liu X, Guo X, Jiang S, Chen T, Hu
Z, Liu H, Bai Y, Xue M, Hu R, et al: FBXO38 mediates PD-1
ubiquitination and regulates anti-tumour immunity of T cells.
Nature. 564:130–135. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
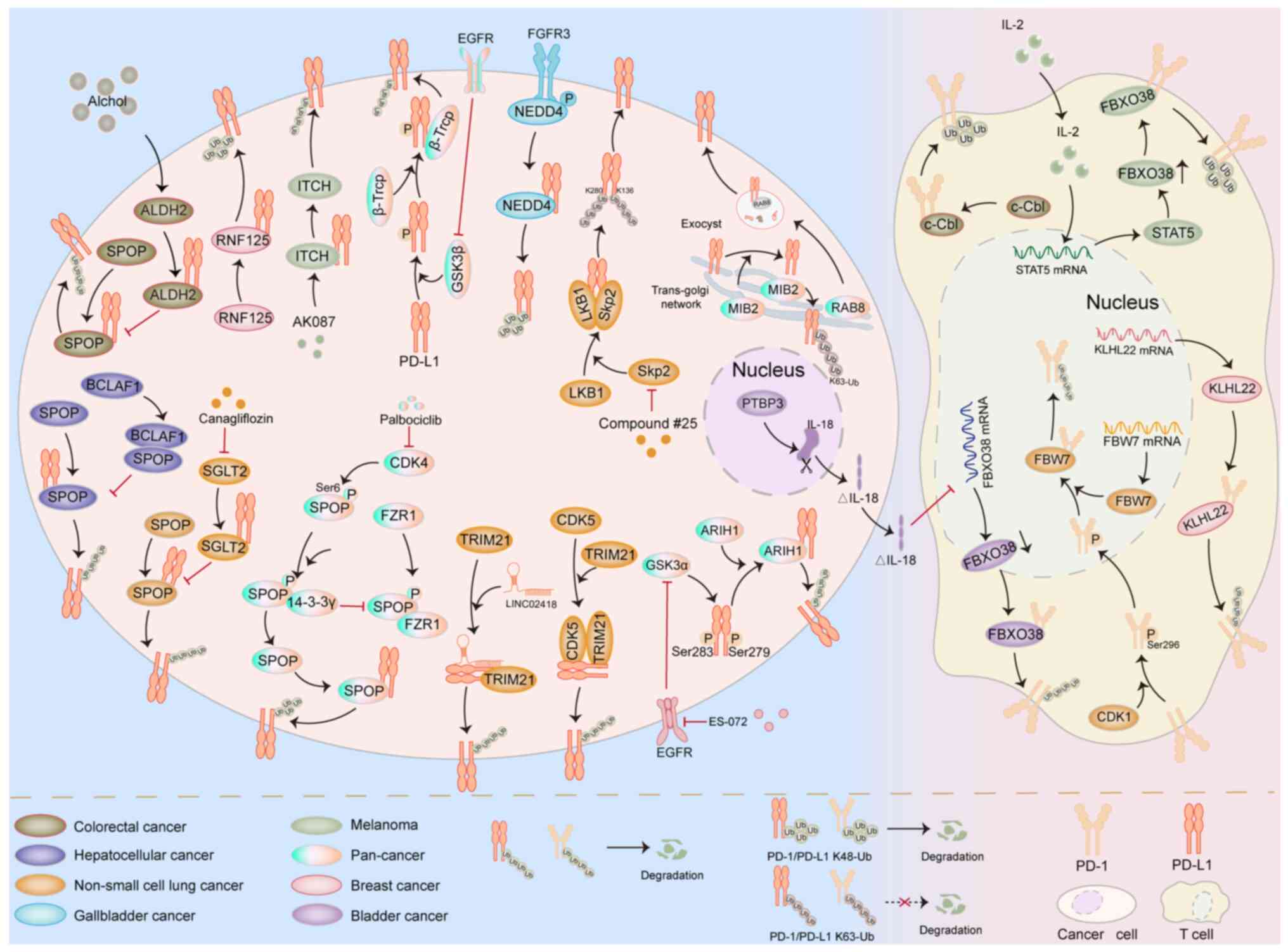
|
|
31
|
Zhang H, Xia Y, Wang F, Luo M, Yang K,
Liang S, An S, Wu S, Yang C, Chen D, et al: Aldehyde dehydrogenase
2 mediates alcohol-induced colorectal cancer immune escape through
stabilizing PD-L1 expression. Adv Sci (Weinh). 8:20034042021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yu Z, Wu X, Zhu J, Yan H, Li Y, Zhang H,
Zhong Y, Lin M, Ye G, Li X, et al: BCLAF1 binds SPOP to stabilize
PD-L1 and promotes the development and immune escape of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Mol Life Sci. 81:822024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang J, Bu X, Wang H, Zhu Y, Geng Y,
Nihira NT, Tan Y, Ci Y, Wu F, Dai X, et al: Cyclin D-CDK4 kinase
destabilizes PD-L1 via cullin 3-SPOP to control cancer immune
surveillance. Nature. 553:91–95. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ding L, Chen X, Zhang W, Dai X, Guo H, Pan
X, Xu Y, Feng J, Yuan M, Gao X, et al: Canagliflozin primes
antitumor immunity by triggering PD-L1 degradation in endocytic
recycling. J Clin Invest. 133:e1547542023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun Z, Mai H, Xue C, Fan Z, Li J, Chen H,
Huo N, Kang X, Tang C, Fang L, et al:
Hsa-LINC02418/mmu-4930573I07Rik regulated by METTL3 dictates
anti-PD-L1 immunotherapeutic efficacy via enhancement of
Trim21-mediated PD-L1 ubiquitination. J Immunother Cancer.
11:e0074152023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gao L, Xia L, Ji W, Zhang Y, Xia W and Lu
S: Knockdown of CDK5 down-regulates PD-L1 via the
ubiquitination-proteasome pathway and improves antitumor immunity
in lung adenocarcinoma. Transl Oncol. 14:1011482021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wu Y, Zhang C, Liu X, He Z, Shan B, Zeng
Q, Zhao Q, Zhu H, Liao H, Cen X, et al: ARIH1 signaling promotes
anti-tumor immunity by targeting PD-L1 for proteasomal degradation.
Nat Commun. 12:23462021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wei M, Mo Y, Liu J, Zhai J, Li H, Xu Y,
Peng Y, Tang Z, Wei T, Yang X, et al: Ubiquitin ligase RNF125
targets PD-L1 for ubiquitination and degradation. Front Oncol.
12:8356032022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yang Z, Wang Y, Liu S, Deng W, Lomeli SH,
Moriceau G, Wohlschlegel J, Piva M and Lo RS: Enhancing PD-L1
degradation by ITCH during MAPK inhibitor therapy suppresses
acquired resistance. Cancer Discov. 12:1942–1959. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Doble BW and Woodgett JR: GSK-3: Tricks of
the trade for a multi-tasking kinase. J Cell Sci. 116:1175–1186.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li CW, Lim SO, Xia W, Lee HH, Chan LC, Kuo
CW, Khoo KH, Chang SS, Cha JH, Kim T, et al: Glycosylation and
stabilization of programmed death ligand-1 suppresses T-cell
activity. Nat Commun. 7:126322016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jing W, Wang G, Cui Z, Xiong G, Jiang X,
Li Y, Li W, Han B, Chen S and Shi B: FGFR3 destabilizes PD-L1 via
NEDD4 to control T-cell-mediated bladder cancer immune
surveillance. Cancer Res. 82:114–129. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yu X, Li W, Liu H, Wang X, Coarfa C, Cheng
C, Yu X, Zeng Z, Cao Y, Young KH and Li Y: PD-L1 translocation to
the plasma membrane enables tumor immune evasion through MIB2
ubiquitination. J Clin Invest. 133:e1604562023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
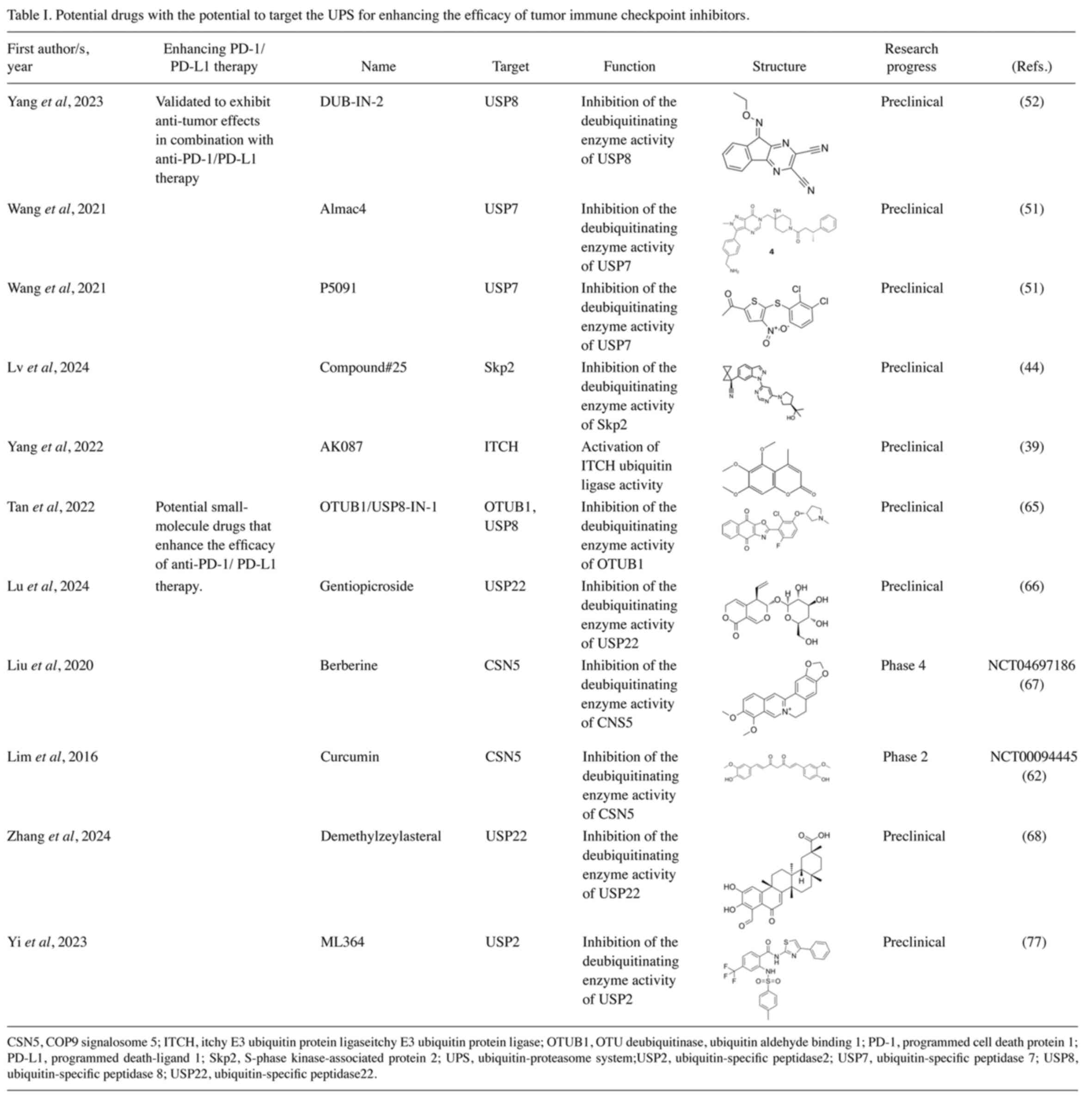
44
|
Lv L, Miao Q, Zhan S, Chen P, Liu W, Lv J,
Yan W, Wang D, Liu H, Yin J, et al: LKB1 dictates sensitivity to
immunotherapy through Skp2-mediated ubiquitination of PD-L1 protein
in non-small cell lung cancer. J Immunother Cancer. 12:e0094442024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhao C, Zhao JW, Zhang YH, Zhu YD, Yang
ZY, Liu SL, Tang QY, Yang Y, Wang HK, Shu YJ, et al: PTBP3 Mediates
IL-18 exon skipping to promote immune escape in gallbladder cancer.
Adv Sci (Weinh). 11:e24066332024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhou XA, Zhou J, Zhao L, Yu G, Zhan J, Shi
C, Yuan R, Wang Y, Chen C, Zhang W, et al: KLHL22 maintains PD-1
homeostasis and prevents excessive T cell suppression. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 117:28239–28250. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu J, Wei L, Hu N, Wang D, Ni J, Zhang S,
Liu H, Lv T, Yin J, Ye M and Song Y: FBW7-mediated ubiquitination
and destruction of PD-1 protein primes sensitivity to anti-PD-1
immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. J Immunother Cancer.
10:e0051162022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lyle C, Richards S, Yasuda K, Napoleon MA,
Walker J, Arinze N, Belghasem M, Vellard I, Yin W, Ravid JD, et al:
c-Cbl targets PD-1 in immune cells for proteasomal degradation and
modulates colorectal tumor growth. Sci Rep. 9:202572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Clague MJ, Urbé S and Komander D: Breaking
the chains: Deubiquitylating enzyme specificity begets function.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:338–352. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Gao H, Yin J, Ji C, Yu X, Xue J, Guan X,
Zhang S, Liu X and Xing F: Targeting ubiquitin specific proteases
(USPs) in cancer immunotherapy: From basic research to preclinical
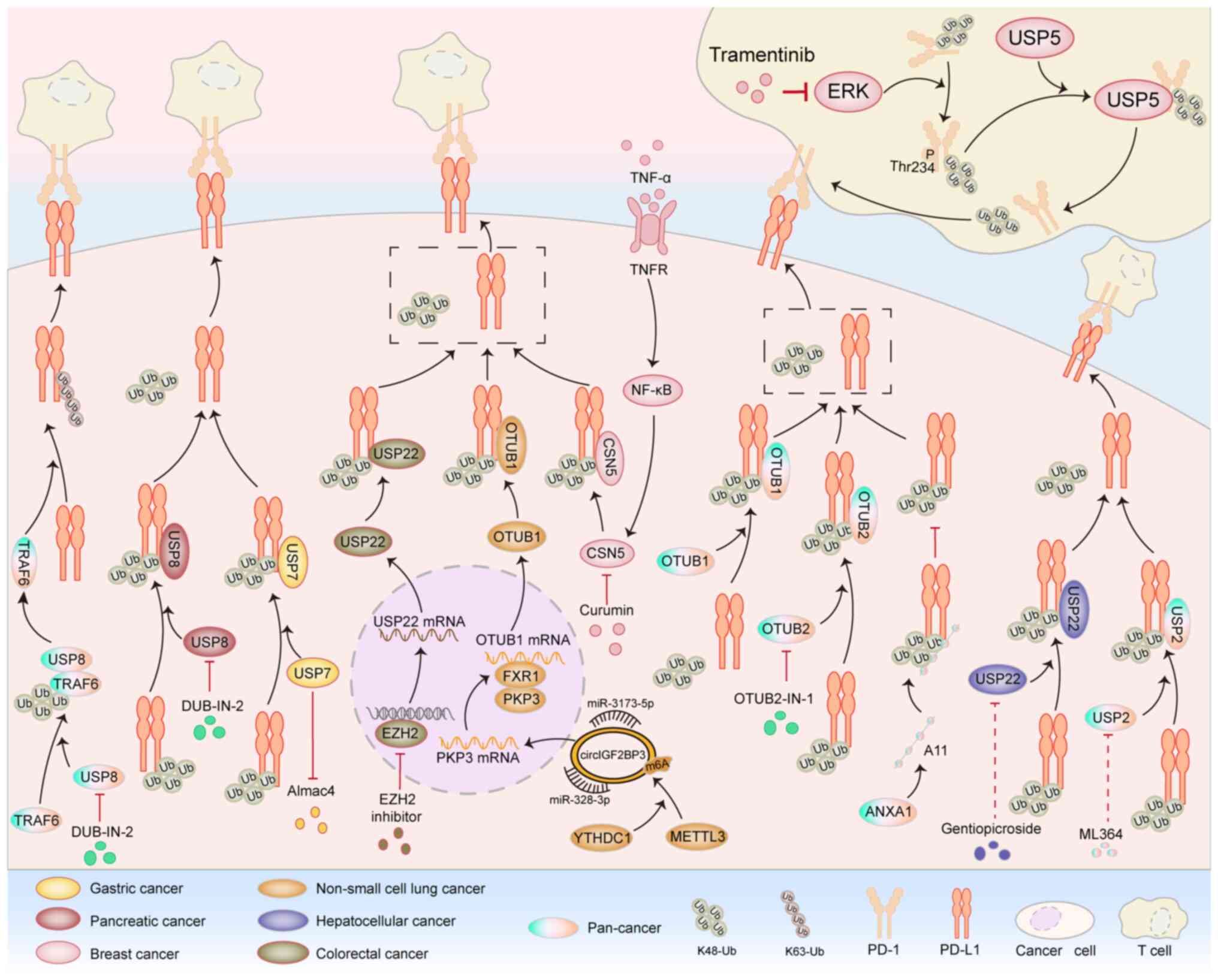
application. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 42:2252023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang Z, Kang W, Li O, Qi F, Wang J, You Y,
He P, Suo Z, Zheng Y and Liu HM: Abrogation of USP7 is an
alternative strategy to downregulate PD-L1 and sensitize gastric
cancer cells to T cells killing. Acta Pharm Sin B. 11:694–707.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yang H, Zhang X, Lao M, Sun K, He L, Xu J,
Duan Y, Chen Y, Ying H, Li M, et al: Targeting ubiquitin-specific
protease 8 sensitizes anti-programmed death-ligand 1 immunotherapy
of pancreatic cancer. Cell Death Differ. 30:560–575. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Xiong W, Gao X, Zhang T, Jiang B, Hu MM,
Bu X, Gao Y, Zhang LZ, Xiao BL, He C, et al: USP8 inhibition
reshapes an inflamed tumor microenvironment that potentiates the
immunotherapy. Nat Commun. 13:17002022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kuang Z, Liu X, Zhang N, Dong J, Sun C,
Yin M, Wang Y, Liu L, Xiao D, Zhou X, et al: USP2 promotes tumor
immune evasion via deubiquitination and stabilization of PD-L1.
Cell Death Differ. 30:2249–2264. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Huang X, Zhang Q, Lou Y, Wang J, Zhao X,
Wang L, Zhang X, Li S, Zhao Y, Chen Q, et al: USP22 deubiquitinates
CD274 to suppress anticancer immunity. Cancer Immunol Res.
7:1580–1590. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Huang J, Yin Q, Wang Y, Zhou X, Guo Y,
Tang Y, Cheng R, Yu X, Zhang J, Huang C, et al: EZH2 inhibition
enhances PD-L1 protein stability through USP22-mediated
deubiquitination in colorectal cancer. Adv Sci (Weinh).
11:e23080452024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yu ZZ, Liu YY, Zhu W, Xiao D, Huang W, Lu
SS, Yi H, Zeng T, Feng XP, Yuan L, et al: ANXA1-derived peptide for
targeting PD-L1 degradation inhibits tumor immune evasion in
multiple cancers. J Immunother Cancer. 11:e0063452023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Sivakumar D, Kumar V, Naumann M and Stein
M: Activation and selectivity of OTUB-1 and OTUB-2
deubiquitinylases. J Biol Chem. 295:6972–6982. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhu D, Xu R, Huang X, Tang Z, Tian Y,
Zhang J and Zheng X: Deubiquitinating enzyme OTUB1 promotes cancer
cell immunosuppression via preventing ER-associated degradation of
immune checkpoint protein PD-L1. Cell Death Differ. 28:1773–1789.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ren W, Xu Z, Chang Y, Ju F, Wu H, Liang Z,
Zhao M, Wang N, Lin Y, Xu C, et al: Pharmaceutical targeting of
OTUB2 sensitizes tumors to cytotoxic T cells via degradation of
PD-L1. Nat Commun. 15:92024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Liu Z, Wang T, She Y, Wu K, Gu S, Li L,
Dong C, Chen C and Zhou Y: N6-methyladenosine-modified
circIGF2BP3 inhibits CD8(+) T-cell responses to facilitate tumor
immune evasion by promoting the deubiquitination of PD-L1 in
non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer. 20:1052021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lim SO, Li CW, Xia W, Cha JH, Chan LC, Wu
Y, Chang SS, Lin WC, Hsu JM, Hsu YH, et al: Deubiquitination and
stabilization of PD-L1 by CSN5. Cancer Cell. 30:925–939. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Xiao X, Shi J, He C, Bu X, Sun Y, Gao M,
Xiang B, Xiong W, Dai P, Mao Q, et al: ERK and USP5 govern PD-1
homeostasis via deubiquitination to modulate tumor immunotherapy.
Nat Commun. 14:28592023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Ding P, Ma Z, Fan Y, Feng Y, Shao C, Pan
M, Zhang Y, Huang D, Han J, Hu Y and Yan X: Emerging role of
ubiquitination/deubiquitination modification of PD-1/PD-L1 in
cancer immunotherapy. Genes Dis. 10:848–863. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Tan L, Shan H, Han C, Zhang Z, Shen J,
Zhang X, Xiang H, Lu K, Qi C, Li Y, et al: Discovery of potent
OTUB1/usp8 dual inhibitors targeting proteostasis in non-small-cell
lung cancer. J Med Chem. 65:13645–13659. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Lu W, Chu P, Tang A, Si L and Fang D: The
secoiridoid glycoside Gentiopicroside is a USP22 inhibitor with
potent antitumor immunotherapeutic activity. Biomed Pharmacother.
177:1169742024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Liu Y, Liu X, Zhang N, Yin M, Dong J, Zeng
Q, Mao G, Song D, Liu L and Deng H: Berberine diminishes cancer
cell PD-L1 expression and facilitates antitumor immunity via
inhibiting the deubiquitination activity of CSN5. Acta Pharm Sin B.
10:2299–2312. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhang Y, Huang Y, Yu D, Xu M, Hu H, Zhang
Q, Cai M, Geng X, Zhang H, Xia J, et al: Demethylzeylasteral
induces PD-L1 ubiquitin-proteasome degradation and promotes
antitumor immunity via targeting USP22. Acta Pharm Sin B.
14:4312–4328. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Denis M, Grasselly C, Choffour PA,
Wierinckx A, Mathé D, Chettab K, Tourette A, Talhi N, Bourguignon
A, Birzele F, et al: In vivo syngeneic tumor models with acquired
resistance to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapies. Cancer Immunol Res.
10:1013–1027. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Laine A and Ronai Z: Ubiquitin chains in
the ladder of MAPK signaling. Sci STKE. 26:re52005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Çetin G, Klafack S, Studencka-Turski M,
Krüger E and Ebstein F: The ubiquitin-proteasome system in immune
cells. Biomolecules. 11:602021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Han M, Guo Y, Li Y, Zeng Q, Zhu W and
Jiang J: SMURF2 facilitates ubiquitin-mediated degradation of ID2
to attenuate lung cancer cell proliferation. Int J Biol Sci.
19:3324–3340. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Cui H, Wang Q, Lei Z, Feng M, Zhao Z, Wang
Y and Wei G: DTL promotes cancer progression by PDCD4
ubiquitin-dependent degradation. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:3502019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Chen Y, Xian M, Ying W, Liu J, Bing S,
Wang X, Yu J, Xu X, Xiang S, Shao X, et al: Succinate dehydrogenase
deficiency-driven succinate accumulation induces drug resistance in
acute myeloid leukemia via ubiquitin-cullin regulation. Nat Commun.
15:98202024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Reichelt J, Sachs W, Frömbling S, Fehlert
J, Studencka-Turski M, Betz A, Loreth D, Blume L, Witt S, Pohl S,
et al: Non-functional ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 drives
podocyte injury through impairing proteasomes in autoimmune
glomerulonephritis. Nat Commun. 14:21142023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Fuseya Y, Kadoba K, Liu X, Suetsugu H,
Iwasaki T, Ohmura K, Sumida T, Kochi Y, Morinobu A, Terao C and
Iwai K: Attenuation of HOIL-1L ligase activity promotes systemic
autoimmune disorders by augmenting linear ubiquitin signaling. JCI
Insight. 9:e1711082024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Yi J, Tavana O, Li H, Wang D, Baer RJ and
Gu W: Targeting USP2 regulation of VPRBP-mediated degradation of
p53 and PD-L1 for cancer therapy. Nat Commun. 14:19412023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zhang XZ, Li FH and Wang XJ: Regulation of
tripartite motif-containing proteins on immune response and viral
evasion. Front Microbiol. 12:7948822021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Gao X, Cao Y, Li H, Yu F, Xi J, Zhang J,
Zhuang R, Xu Y and Xu L: Mechanisms underlying altered
ubiquitin-proteasome system activity during heart failure and
pharmacological interventions. Eur J Med Chem. 292:1177252025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Yamaguchi H, Hsu JM, Yang WH and Hung MC:
Mechanisms regulating PD-L1 expression in cancers and associated
opportunities for novel small-molecule therapeutics. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 19:287–305. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhong G, Chang X, Xie W and Zhou X:
Targeted protein degradation: Advances in drug discovery and
clinical practice. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 9:3082024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Wang C, Zhang Y, Chen W, Wu Y and Xing D:
New-generation advanced PROTACs as potential therapeutic agents in
cancer therapy. Mol Cancer. 23:1102024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Dong T, Niu H, Chu Z, Zhou C, Gao Y, Jia
M, Sun B, Zheng X, Zhang W, Zhang J, et al: Targeting VPS18 hampers
retromer trafficking of PD-L1 and augments immunotherapy. Sci Adv.
10:eadp49172024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Shende S, Rathored J and Budhbaware T:
Role of metabolic transformation in cancer immunotherapy
resistance: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications.
Discov Oncol. 16:4532025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Raina K, Lu J, Qian Y, Altieri M, Gordon
D, Rossi AM, Wang J, Chen X, Dong H, Siu K, et al: PROTAC-induced
BET protein degradation as a therapy for castration-resistant
prostate cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:7124–7129. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Xiao M, Zhao J, Wang Q, Liu J and Ma L:
Recent advances of degradation technologies based on PROTAC
mechanism. Biomolecules. 12:12572022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Chen Y, Tandon I, Heelan W, Wang Y, Tang W
and Hu Q: Proteolysis-targeting chimera (PROTAC) delivery system:
Advancing protein degraders towards clinical translation. Chem Soc
Rev. 51:5330–5350. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Sun C, Liu S, Lau JW, Yang H, Chen Y and
Xing B: Enzyme-Activated orthogonal proteolysis chimeras for tumor
microenvironment-responsive immunomodulation. Angew Chem Int Ed
Engl. 64:e2024230572025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Zhou Y, Li C, Chen X, Zhao Y, Liao Y,
Huang P, Wu W, Nieto NS, Li L and Tang W: Development of folate
receptor targeting chimeras for cancer selective degradation of
extracellular proteins. Nat Commun. 15:86952024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
He Y, Zheng Y, Zhu C, Lei P, Yu J, Tang C,
Chen H and Diao X: Radioactive ADME demonstrates ARV-110′s high
druggability despite low oral bioavailability. J Med Chem.
67:14277–14291. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Gough SM, Flanagan JJ, Teh J, Andreoli M,
Rousseau E, Pannone M, Bookbinder M, Willard R, Davenport K,
Bortolon E, et al: Oral estrogen receptor PROTAC vepdegestrant
(ARV-471) is highly efficacious as monotherapy and in combination
with CDK4/6 or PI3K/mTOR pathway inhibitors in preclinical ER+
breast cancer models. Clin Cancer Res. 30:3549–3563. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|