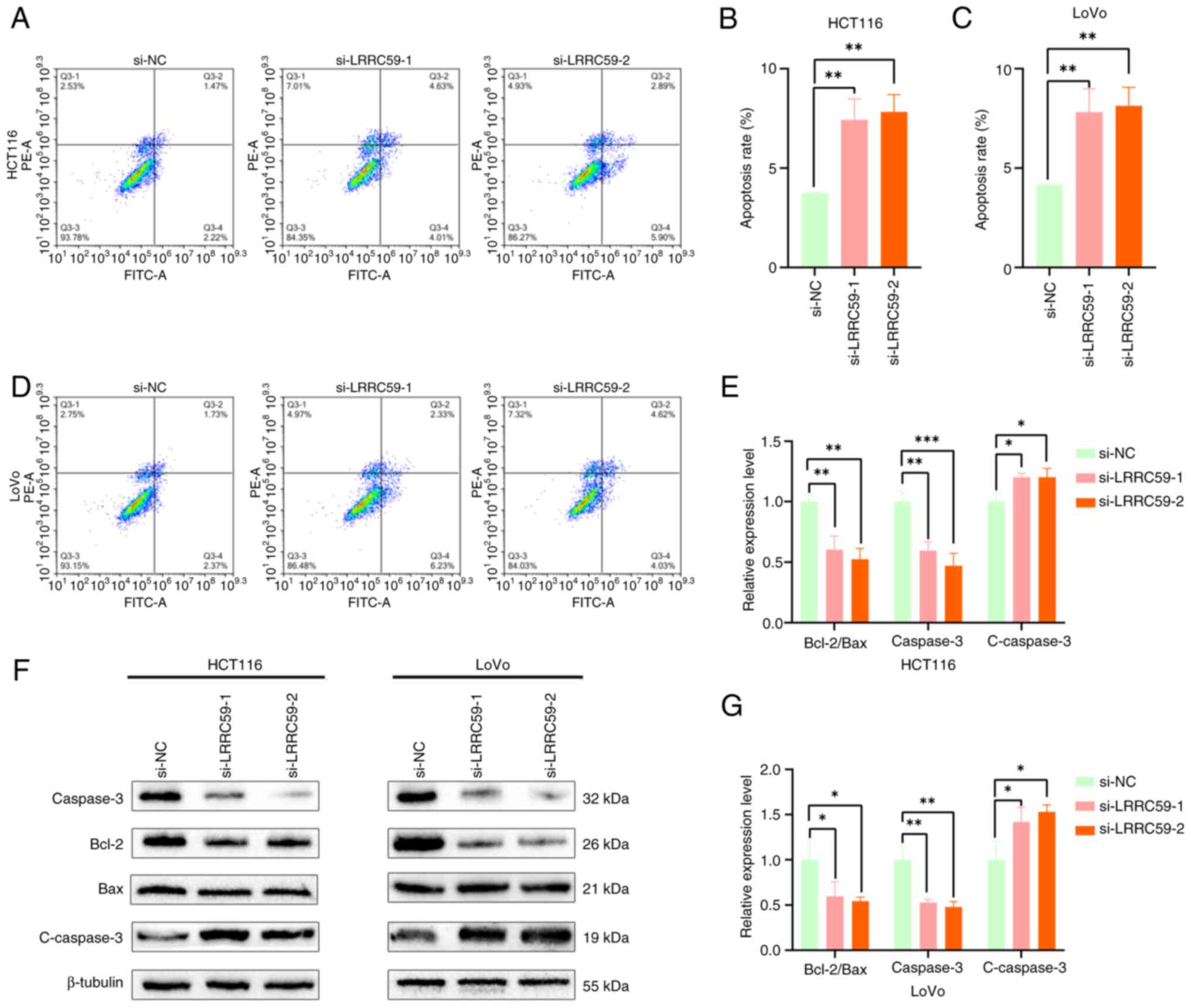
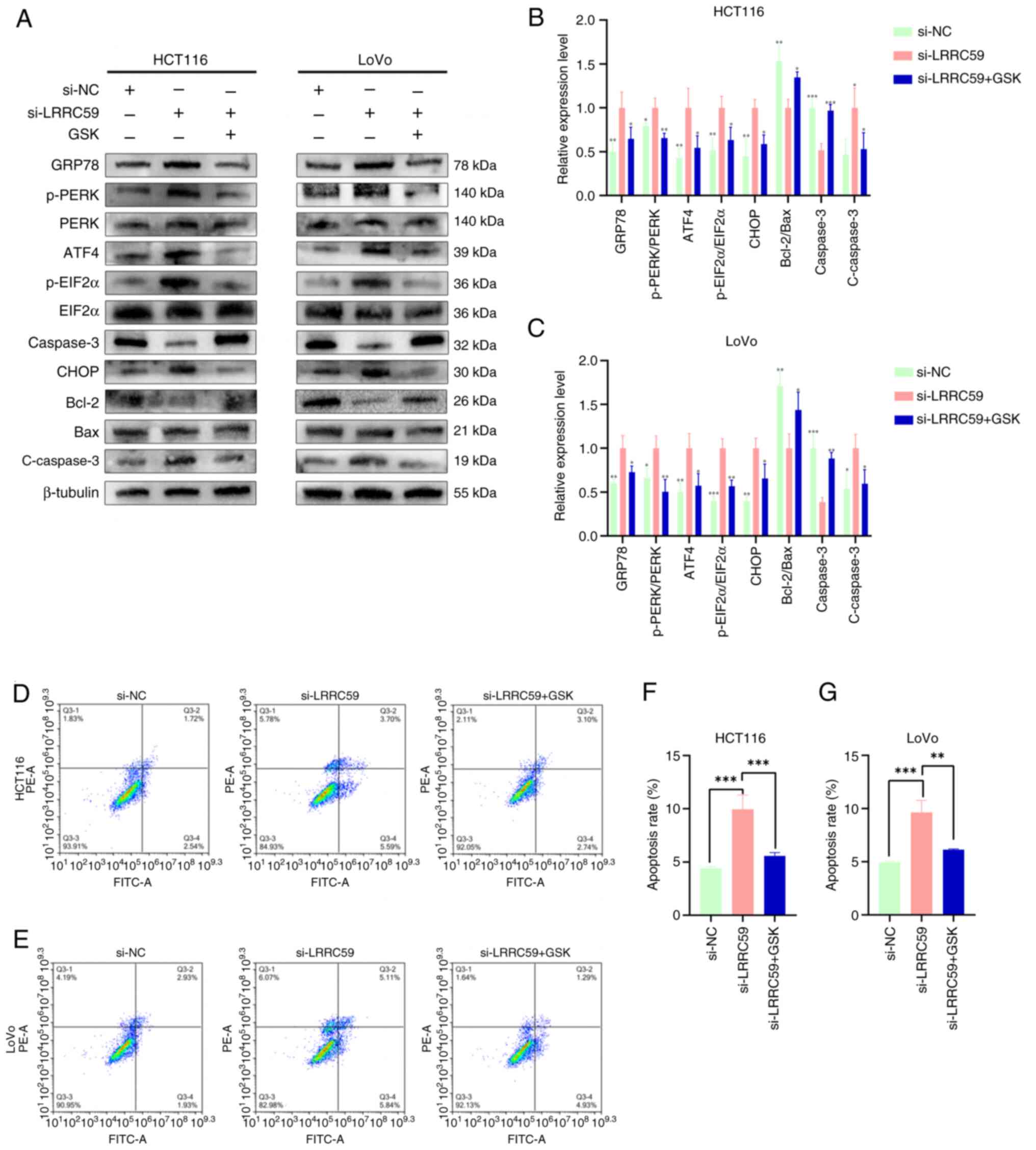
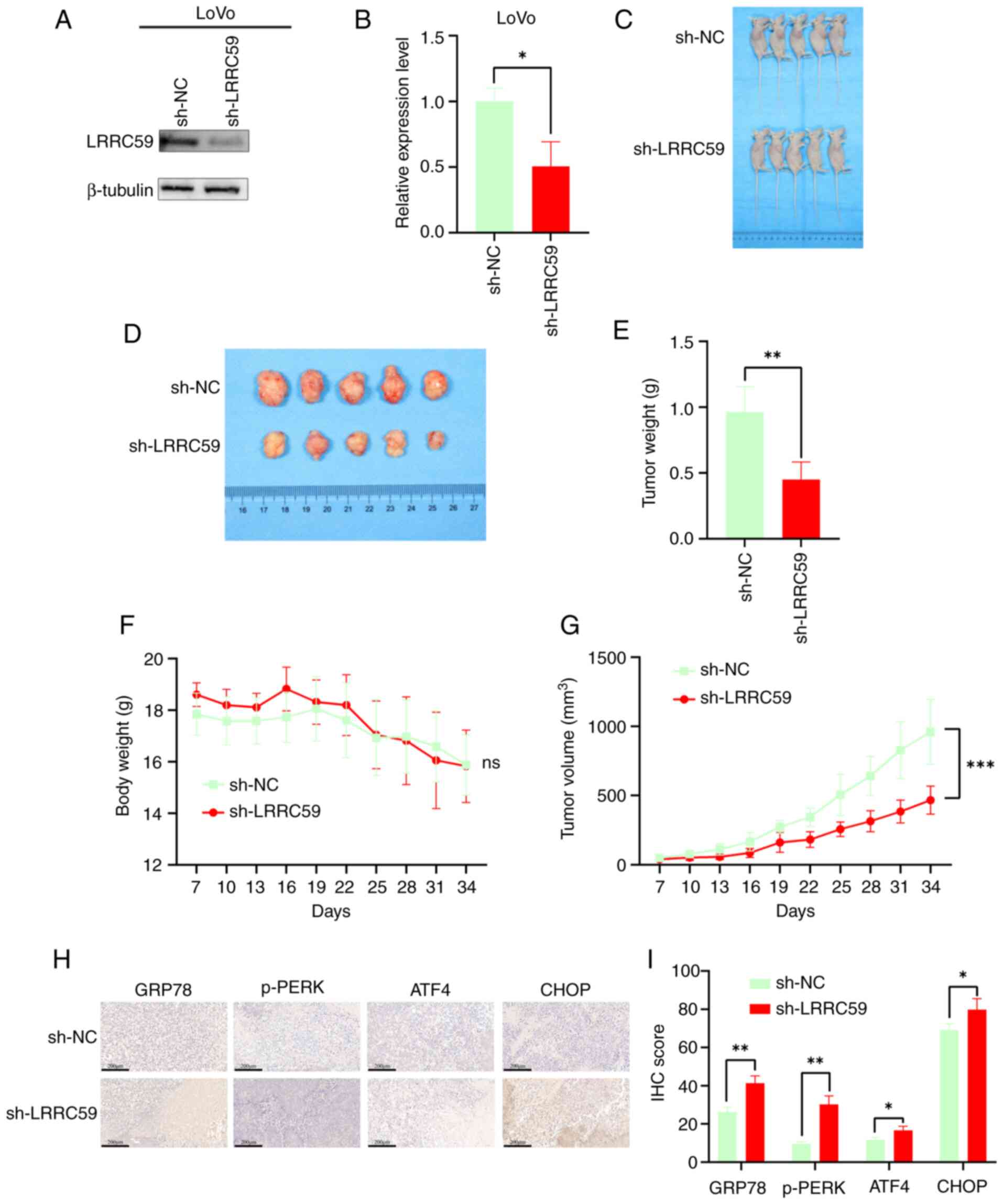
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA
and Jemal A: Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin.
73:233–254. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Morgan E, Arnold M, Gini A, Lorenzoni V,
Cabasag CJ, Laversanne M, Vignat J, Ferlay J, Murphy N and Bray F:
Global burden of colorectal cancer in 2020 and 2040: Incidence and
mortality estimates from GLOBOCAN. Gut. 72:338–344. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Leowattana W, Leowattana P and Leowattana
T: Systemic treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 29:1569–1588. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ichimura T, Shindo Y, Uda Y, Ohsumi T,
Omata S and Sugano H: Anti-(p34 protein) antibodies inhibit
ribosome binding to and protein translocation across the rough
microsomal membrane. FEBS Lett. 326:241–245. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ohsumi T, Ichimura T, Sugano H, Omata S,
Isobe T and Kuwano R: Ribosome-binding protein p34 is a member of
the leucine-rich-repeat-protein superfamily. Biochem J.
294:465–472. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ichimura T, Ohsumi T, Shindo Y, Ohwada T,
Yagame H, Momose Y, Omata S and Sugano H: Isolation and some
properties of a 34-kDa-membrane protein that may be responsible for
ribosome binding in rat liver rough microsomes. FEBS Lett.
296:7–10. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pallai R, Bhaskar A, Barnett-Bernodat N,
Gallo-Ebert C, Pusey M, Nickels JT Jr and Rice LM: Leucine-rich
repeat-containing protein 59 mediates nuclear import of cancerous
inhibitor of PP2A in prostate cancer cells. Tumour Biol.
36:6383–6390. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li D, Xing Y, Tian T, Guo Y and Qian J:
Overexpression of LRRC59 is associated with poor prognosis and
promotes cell proliferation and invasion in lung adenocarcinoma.
Onco Targets Ther. 13:6453–6463. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pei L, Zhu Q, Zhuang X, Ruan H, Zhao Z,
Qin H and Lin Q: Identification of leucine-rich repeat-containing
protein 59 (LRRC59) located in the endoplasmic reticulum as a novel
prognostic factor for urothelial carcinoma. Transl Oncol.
23:1014742022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen X and Cubillos-Ruiz JR: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress signals in the tumour and its microenvironment.
Nat Rev Cancer. 21:71–88. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Walter P and Ron D: The unfolded protein
response: From stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science.
334:1081–1086. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hetz C, Zhang K and Kaufman RJ:
Mechanisms, regulation and functions of the unfolded protein
response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 21:421–438. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shore GC, Papa FR and Oakes SA: Signaling
cell death from the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 23:143–149. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Long D, Chen K, Yang Y and Tian X:
Unfolded protein response activated by endoplasmic reticulum stress
in pancreatic cancer: Potential therapeutical target. Front Biosci
(Landmark Ed). 26:1689–1696. 2021. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song M and Cubillos-Ruiz JR: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress responses in intratumoral immune cells:
Implications for cancer immunotherapy. Trends Immunol. 40:128–141.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Geng J, Guo Y, Xie M, Li Z, Wang P, Zhu D,
Li J and Cui X: Characteristics of endoplasmic reticulum stress in
colorectal cancer for predicting prognosis and developing treatment
options. Cancer Med. 12:12000–12017. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou F, Gao H, Shang L, Li J, Zhang M,
Wang S, Li R, Ye L and Yang S: Oridonin promotes endoplasmic
reticulum stress via TP53-repressed TCF4 transactivation in
colorectal cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 42:1502023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li F, Dong Q, Kai Z, Pan Q and Liu C:
CYP8B1 is a prognostic biomarker with important functional
implications in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 54:1042025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ma H, Suleman M, Zhang F, Cao T, Wen S,
Sun D, Chen L, Jiang B, Wang Y, Lin F, et al: Pirin inhibits
FAS-mediated apoptosis to support colorectal cancer survival. Adv
Sci (Weinh). 11:e23014762024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu H, Wang T, Nie H, Sun Q, Jin C, Yang S,
Chen Z, Wang X, Tang J, Feng Y and Sun Y: USP36 promotes colorectal
cancer progression through inhibition of p53 signaling pathway via
stabilizing RBM28. Oncogene. 43:3442–3455. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao L, Sun X, Hou C, Yang Y, Wang P, Xu
Z, Chen Z, Zhang X, Wu G, Chen H, et al: CPNE7 promotes colorectal
tumorigenesis by interacting with NONO to initiate ZFP42
transcription. Cell Death Dis. 15:8962024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim J, Jeong Y, Shin YM, Kim SE and Shin
SJ: FL118 enhances therapeutic efficacy in colorectal cancer by
inhibiting the homologous recombination repair pathway through
survivin-RAD51 downregulation. Cancers (Basel). 16:33852024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang Z, Wang L, Zhao L, Wang Q, Yang C,
Zhang M, Wang B, Jiang K, Ye Y, Wang S and Shen Z:
N6-methyladenosine demethylase ALKBH5 suppresses colorectal cancer
progression potentially by decreasing PHF20 mRNA methylation. Clin
Transl Med. 12:e9402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu H, Zheng S, Zhang J, Xu S and Miao Z:
Cadmium induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in
pig pancreas via the increase of Th1 cells. Toxicology.
457:1527902021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee H, Lee YS, Harenda Q, Pietrzak S,
Oktay HZ, Schreiber S, Liao Y, Sonthalia S, Ciecko AE, Chen YG, et
al: Beta cell dedifferentiation induced by IRE1α deletion prevents
type 1 diabetes. Cell Metab. 31:822–836.e825. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim TW, Lee SY, Kim M, Cheon C and Ko SG:
Kaempferol induces autophagic cell death via IRE1-JNK-CHOP pathway
and inhibition of G9a in gastric cancer cells. Cell Death Dis.
9:8752018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pallai R, Bhaskar A, Barnett-Bernodat N,
Gallo-Ebert C, Nickels JT Jr and Rice LM: Cancerous inhibitor of
protein phosphatase 2A promotes premature chromosome segregation
and aneuploidy in prostate cancer cells through association with
shugoshin. Tumour Biol. 36:6067–6074. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Maurizio E, Wiśniewski JR, Ciani Y, Amato
A, Arnoldo L, Penzo C, Pegoraro S, Giancotti V, Zambelli A, Piazza
S, et al: Translating proteomic into functional data: An high
mobility group A1 (HMGA1) proteomic signature has prognostic value
in breast cancer. Mol Cell Proteomics. 15:109–123. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pan B, Cheng J, Tan W, Wu X, Fan Q, Fan L,
Jiang M, Yu R, Cheng X and Deng Y: Pan-cancer analysis of LRRC59
with a focus on prognostic and immunological roles in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY). 16:8171–8197.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen H, Zhao T, Fan J, Yu Z, Ge Y, Zhu H,
Dong P, Zhang F, Zhang L, Xue X and Lin X: Construction of a
prognostic model for colorectal adenocarcinoma based on Zn
transport-related genes identified by single-cell sequencing and
weighted co-expression network analysis. Front Oncol.
13:12074992023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xian H, Yang S, Jin S, Zhang Y and Cui J:
LRRC59 modulates type I interferon signaling by restraining the
SQSTM1/p62-mediated autophagic degradation of pattern recognition
receptor DDX58/RIG-I. Autophagy. 16:408–418. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhen Y, Sørensen V, Skjerpen CS, Haugsten
EM, Jin Y, Wälchli S, Olsnes S and Wiedlocha A: Nuclear import of
exogenous FGF1 requires the ER-protein LRRC59 and the importins
Kpnα1 and Kpnβ1. Traffic. 13:650–664. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu N, Zhang J, Sun S, Yang L, Zhou Z, Sun
Q and Niu J: Expression and clinical significance of fibroblast
growth factor 1 in gastric adenocarcinoma. Onco Targets Ther.
8:615–621. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Oakes SA: Endoplasmic reticulum stress
signaling in cancer cells. Am J Pathol. 190:934–946. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang J, Pan H, Wang J, Wang T, Huo X, Ma
Y, Lu Z, Sun B and Jiang H: Unfolded protein response in colorectal
cancer. Cell Biosci. 11:262021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Urra H, Dufey E, Avril T, Chevet E and
Hetz C: Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the hallmarks of cancer.
Trends Cancer. 2:252–262. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Harding HP, Novoa I, Zhang Y, Zeng H, Wek
R, Schapira M and Ron D: Regulated translation initiation controls
stress-induced gene expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell.
6:1099–1108. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Han D, Lerner AG, Vande Walle L, Upton JP,
Xu W, Hagen A, Backes BJ, Oakes SA and Papa FR: IRE1alpha kinase
activation modes control alternate endoribonuclease outputs to
determine divergent cell fates. Cell. 138:562–575. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
4Hollien J, Lin JH, Li H, Stevens N,
Walter P and Weissman JS: Regulated Ire1-dependent decay of
messenger RNAs in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 186:323–331. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hollien J and Weissman JS: Decay of
endoplasmic reticulum-localized mRNAs during the unfolded protein
response. Science. 313:104–107. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lee AH, Iwakoshi NN and Glimcher LH: XBP-1
regulates a subset of endoplasmic reticulum resident chaperone
genes in the unfolded protein response. Mol Cell Biol.
23:7448–7459. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ameri K and Harris AL: Activating
transcription factor 4. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 40:14–21. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shi Y, Jiang B and Zhao J: Induction
mechanisms of autophagy and endoplasmic reticulum stress in
intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury, inflammatory bowel disease,
and colorectal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 170:1159842024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sisinni L, Pietrafesa M, Lepore S,
Maddalena F, Condelli V, Esposito F and Landriscina M: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress and unfolded protein response in breast cancer:
The balance between apoptosis and autophagy and its role in drug
resistance. Int J Mol Sci. 20:8572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ji X, Chen Z, Lin W, Wu Q, Wu Y, Hong Y,
Tong H, Wang C and Zhang Y: Esculin induces endoplasmic reticulum
stress and drives apoptosis and ferroptosis in colorectal cancer
via PERK regulating eIF2α/CHOP and Nrf2/HO-1 cascades. J
Ethnopharmacol. 328:1181392024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Qu J, Zeng C, Zou T, Chen X, Yang X and
Lin Z: Autophagy induction by trichodermic acid attenuates
endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in colon cancer
cells. Int J Mol Sci. 22:55662021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang G, Han J, Wang G, Wu X, Huang Y, Wu M
and Chen Y: ERO1α mediates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced
apoptosis via microRNA-101/EZH2 axis in colon cancer RKO and HT-29
cells. Hum Cell. 34:932–944. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Piao MJ, Han X, Kang KA, Fernando PDSM,
Herath HMUL and Hyun JW: The endoplasmic reticulum stress response
mediates shikonin-induced apoptosis of 5-fluorouracil-resistant
colorectal cancer cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 30:265–273. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Quan JH, Gao FF, Chu JQ, Cha GH, Yuk JM,
Wu W and Lee YH: Silver nanoparticles induce apoptosis via
NOX4-derived mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and
endoplasmic reticulum stress in colorectal cancer cells.
Nanomedicine (Lond). 16:1357–1375. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Urano F, Wang X, Bertolotti A, Zhang Y,
Chung P, Harding HP and Ron D: Coupling of stress in the ER to
activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase
IRE1. Science. 287:664–666. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tabas I and Ron D: Integrating the
mechanisms of apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Nat Cell Biol. 13:184–190. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhou R, Wang W, Li B, Li Z, Huang J and Li
X: Endo-plasmic reticulum stress in cancer. MedComm (2020).
6:e702632025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Guo YJ, Zhu MY, Wang ZY, Chen HY, Qing YJ,
Wang HZ, Xu JY, Hui H and Li H: Therapeutic effect of V8 affecting
mitophagy and endoplasmic reticulum stress in acute myeloid
leukemia mediated by ROS and CHOP signaling. FASEB J.
39:e706222025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhang P, Liu H, Yu Y, Peng S, Zeng A and
Song L: Terpenoids mediated cell apoptotsis in cervical cancer:
Mechanisms, advances and prospects. Fitoterapia. 180:1063232024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhou N, Liu Q, Wang X, He L, Zhang T, Zhou
H, Zhu X, Zhou T, Deng G and Qiu C: The combination of
hydroxychloroquine and 2-deoxyglucose enhances apoptosis in breast
cancer cells by blocking protective autophagy and sustaining
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Discov. 8:2862022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liang L, Zhu Z, Jiang X, Tang Y, Li J,
Zhang Z, Ding B, Li X, Yu M and Gan Y: Endoplasmic
reticulum-targeted strategies for programmed cell death in cancer
therapy: Approaches and prospects. J Control Release.
385:1140592025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Liu Z, Deng X, Wang Z, Guo Y, Hameed MMA,
El-Newehy M, Zhang J, Shi X and Shen M: A biomimetic therapeutic
nanovaccine based on dendrimer-drug conjugates coated with
metal-phenolic networks for combination therapy of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma: An in vitro investigation. J Mater Chem B.
13:5440–5452. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yeap JW, Ali IAH, Ibrahim B and Tan ML:
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and emerging ER
stress-related therapeutic targets. Pulm Pharmacol Ther.
81:1022182023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Harding HP, Zeng H, Zhang Y, Jungries R,
Chung P, Plesken H, Sabatini DD and Ron D: Diabetes mellitus and
exocrine pancreatic dysfunction in perk-/- mice reveals a role for
translational control in secretory cell survival. Mol Cell.
7:1153–1163. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhang P, McGrath B, Li S, Frank A, Zambito
F, Reinert J, Gannon M, Ma K, McNaughton K and Cavener DR: The PERK
eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha kinase is required for the
development of the skeletal system, postnatal growth, and the
function and viability of the pancreas. Mol Cell Biol.
22:3864–3874. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yuan Z, Wang Y, Xu S, Zhang M and Tang J:
Construction of a prognostic model for colon cancer by combining
endoplasmic reticulum stress responsive genes. J Proteomics.
309:1052842024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|