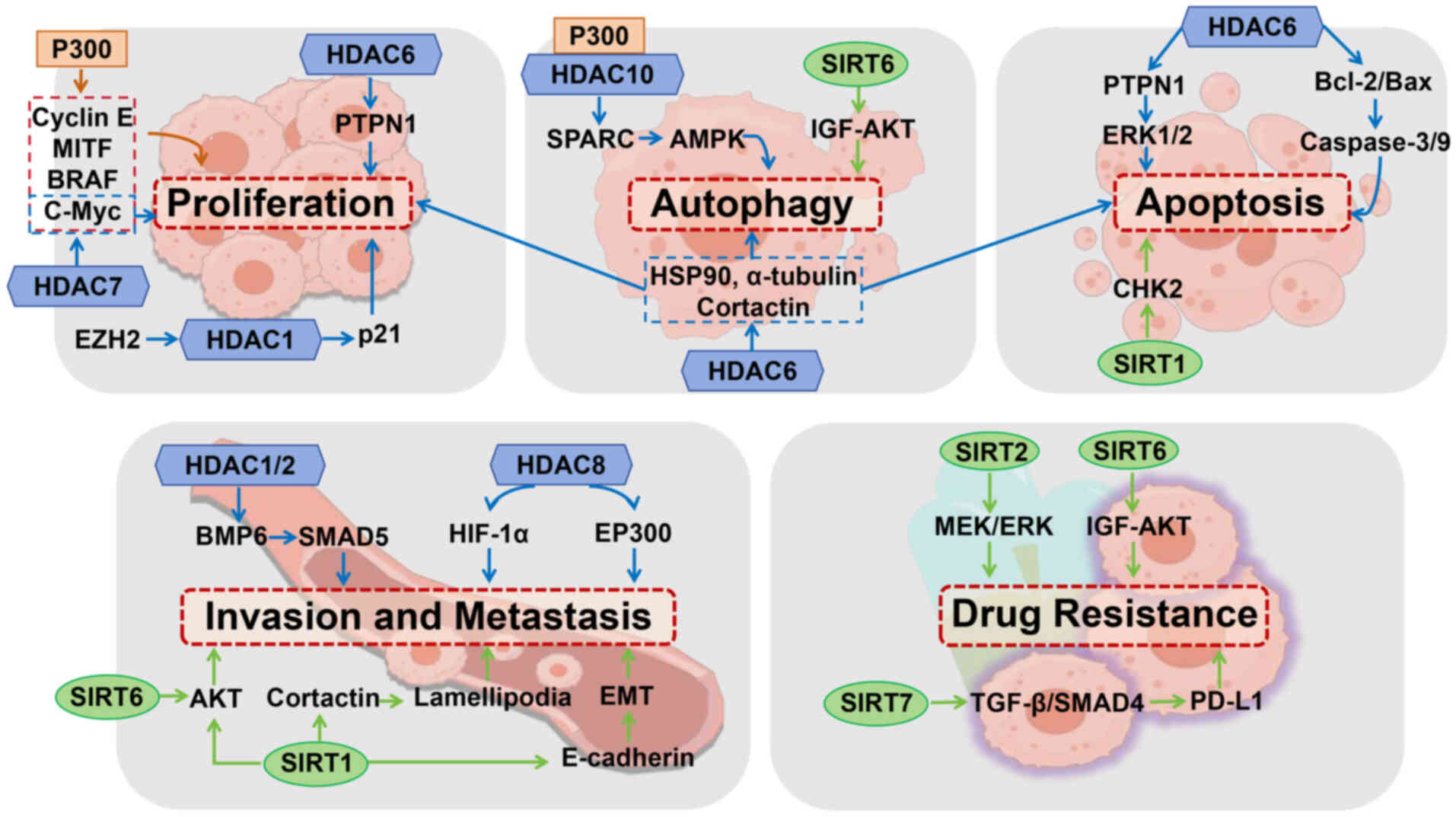
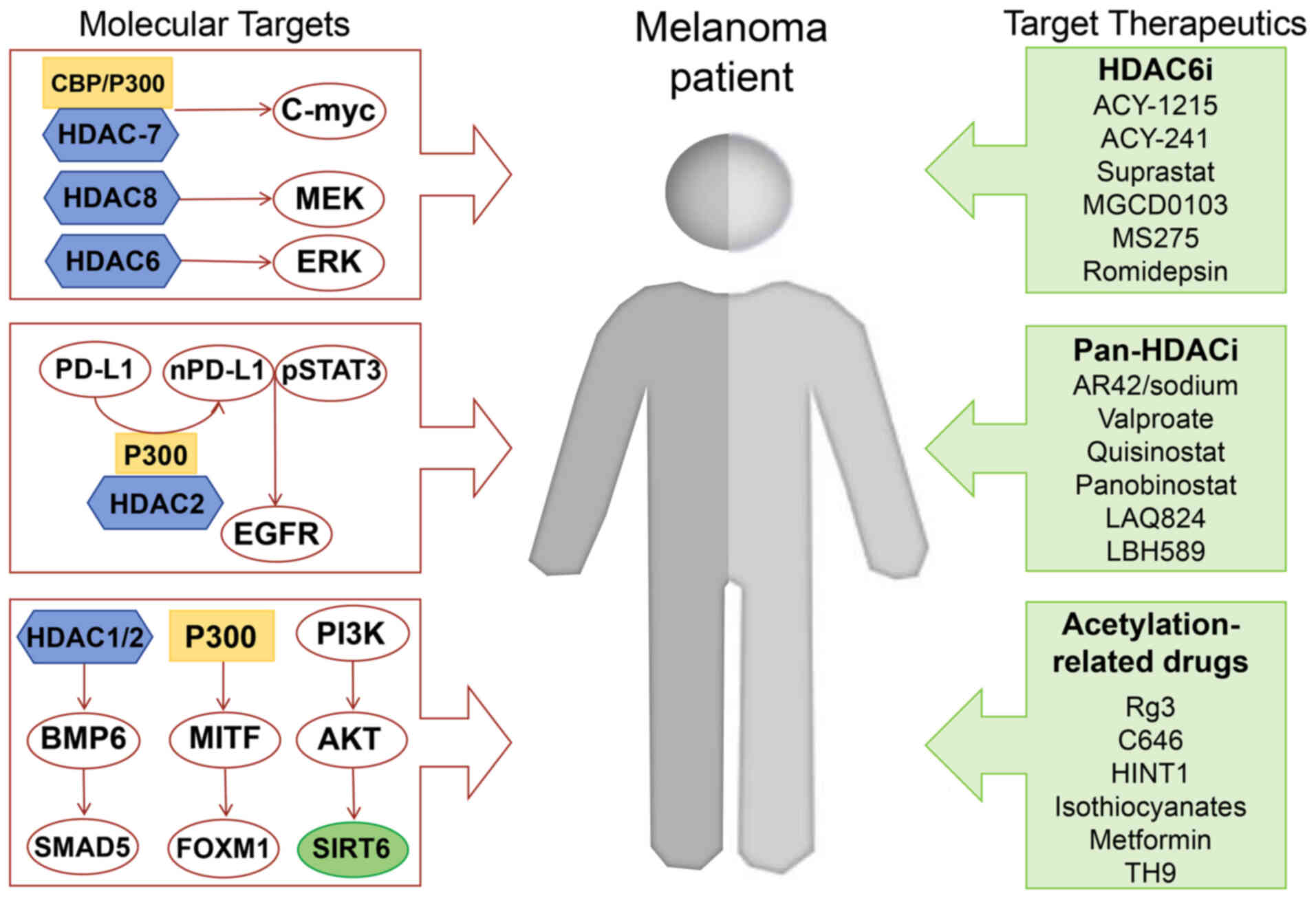
|
1
|
Fateeva A, Eddy K and Chen S: Current
state of melanoma therapy and next steps: Battling therapeutic
resistance. Cancers (Basel). 16:15712024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Urban K, Mehrmal S, Uppal P, Giesey RL and
Delost GR: The global burden of skin cancer: A longitudinal
analysis from the global burden of disease study, 1990–2017. JAAD
Int. 2:98–108. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Arnold M, Singh D, Laversanne M, Vignat J,
Vaccarella S, Meheus F, Cust AE, de Vries E, Whiteman DC and Bray
F: Global burden of cutaneous melanoma in 2020 and projections to
2040. JAMA Dermatol. 158:495–503. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Beasley GM and Terando AM: Articles from
2022 to 2023 to inform your cancer practice: Melanoma. Ann Surg
Oncol. 31:1851–1856. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yuan J, Li X and Yu S: Global, regional,
and national incidence trend analysis of malignant skin melanoma
between 1990 and 2019, and projections until 2034. Cancer Control.
31:107327482412273402024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gracia-Hernandez M, Munoz Z and Villagra
A: Enhancing therapeutic approaches for melanoma patients targeting
epigenetic modifiers. Cancers (Basel). 13:61802021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang L and Yan Y: Emerging roles of
post-translational modifications in skin diseases: Current
knowledge, challenges and future perspectives. J Inflamm Res.
15:965–975. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Reolid A, Muñoz-Aceituno E, Abad-Santos F,
Ovejero-Benito MC and Daudén E: Epigenetics in non-tumor
immune-mediated skin diseases. Mol Diagn Ther. 25:137–161. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Centeno PP, Pavet V and Marais R: The
journey from melanocytes to melanoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 23:372–390.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shain AH and Bastian BC: From melanocytes
to melanomas. Nat Rev Cancer. 16:345–358. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Elder DE, Bastian BC, Cree IA, Massi D and
Scolyer RA: The 2018 World Health Organization classification of
cutaneous, mucosal, and uveal melanoma: Detailed analysis of 9
distinct subtypes defined by their evolutionary pathway. Arch
Pathol Lab Med. 144:500–522. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Long GV, Swetter SM, Menzies AM,
Gershenwald JE and Scolyer RA: Cutaneous melanoma. Lancet.
402:485–502. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gelmi MC, Houtzagers LE, Strub T, Krossa I
and Jager MJ: MITF in normal melanocytes, cutaneous and uveal
melanoma: A delicate balance. Int J Mol Sci. 23:60012022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Slominski RM, Raman C, Chen JY and
Slominski AT: How cancer hijacks the body's homeostasis through the
neuroendocrine system. Trends Neurosci. 46:263–275. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Slominski RM, Kim TK, Janjetovic Z,
Brożyna AA, Podgorska E, Dixon KM, Mason RS, Tuckey RC, Sharma R,
Crossman DK, et al: Malignant melanoma: An overview, new
perspectives, and vitamin D signaling. Cancers (Basel).
16:22622024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Slominski RM, Chen JY, Raman C and
Slominski AT: Photo-neuro-immuno-endocrinology: How the ultraviolet
radiation regulates the body, brain, and immune system. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 121:e23083741212024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Slominski RM, Raman C, Jetten AM and
Slominski AT: Neuro-immuno-endocrinology of the skin: how
environment regulates body homeostasis. Nat Rev Endocrinol.
21:495–509. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Slominski RM, Sarna T, Płonka PM, Raman C,
Brożyna AA and Slominski AT: Melanoma, melanin, and melanogenesis:
The Yin and Yang RELATIONSHIP. Front Oncol. 12:8424962022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wacker M and Holick MF: Sunlight and
vitamin D: A global perspective for health. Dermatoendocrinol.
5:51–108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Menzies KJ, Zhang H, Katsyuba E and Auwerx
J: Protein acetylation in metabolism-metabolites and cofactors. Nat
Rev Endocrinol. 12:43–60. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Weinert BT, Narita T, Satpathy S,
Srinivasan B, Hansen BK, Schölz C, Hamilton WB, Zucconi BE, Wang
WW, Liu WR, et al: Time-resolved analysis reveals rapid dynamics
and broad scope of the CBP/p300 acetylome. Cell. 174:231–244.e12.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shvedunova M and Akhtar A: Modulation of
cellular processes by histone and non-histone protein acetylation.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 23:329–349. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Parveen R, Harihar D and Chatterji BP:
Recent histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy. Cancer.
129:3372–3380. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee HY, Hsu MJ, Chang HH, Chang WC, Huang
WC and Cho EC: Enhancing anti-cancer capacity: Novel class I/II
HDAC inhibitors modulate EMT, cell cycle, and apoptosis pathways.
Bioorg Med Chem. 109:1177922024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu Y, Tong X, Hu W and Chen D: HDAC11: A
novel target for improved cancer therapy. Biomed Pharmacother.
166:1154182023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jia G, Liu J, Hou X, Jiang Y and Li X:
Biological function and small molecule inhibitors of histone
deacetylase 11. Eur J Med Chem. 276:1166342024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Strub T, Ballotti R and Bertolotto C: The
‘ART’ of epigenetics in melanoma: From histone ‘alterations, to
resistance and therapies’. Theranostics. 10:1777–1797. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cintra Lopes Carapeto F, Neves Comodo A,
Germano A, Pereira Guimarães D, Barcelos D, Fernandes M and Landman
G: Marker protein expression combined with expression heterogeneity
is a powerful indicator of malignancy in acral lentiginous
melanomas. Am J Dermatopathol. 39:114–120. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Comodo-Navarro AN, Fernandes M, Barcelos
D, Carapeto FCL, Guimarães DP, de Sousa Moraes L, Cerutti J,
Iwamura ESM and Landman G: Intratumor heterogeneity of KIT gene
mutations in acral lentiginous melanoma. Am J Dermatopathol.
42:265–271. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cheng PF: Medical bioinformatics in
melanoma. Curr Opin Oncol. 30:113–117. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Castillo JJAQ, Silva W, Barcelos D and
Landman G: Molecular landscape of acral melanoma: an integrative
review. Surg Exp Pathol. 8:172025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wang L, Guo W, Ma J, Dai W, Liu L, Guo S,
Chen J, Wang H, Yang Y, Yi X, et al: Aberrant SIRT6 expression
contributes to melanoma growth: Role of the autophagy paradox and
IGF-AKT signaling. Autophagy. 14:518–533. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Strub T, Ghiraldini FG, Carcamo S, Li M,
Wroblewska A, Singh R, Goldberg MS, Hasson D, Wang Z, Gallagher SJ,
et al: SIRT6 haploinsufficiency induces BRAFV600E
melanoma cell resistance to MAPK inhibitors via IGF signalling. Nat
Commun. 9:34402018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Manickavinayaham S, Vélez-Cruz R, Biswas
AK, Bedford E, Klein BJ, Kutateladze TG, Liu B, Bedford MT and
Johnson DG: E2F1 acetylation directs p300/CBP-mediated histone
acetylation at DNA double-strand breaks to facilitate repair. Nat
Commun. 10:49512019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim E, Zucconi BE, Wu M, Nocco SE, Meyers
DJ, McGee JS, Venkatesh S, Cohen DL, Gonzalez EC, Ryu B, et al:
MITF expression predicts therapeutic vulnerability to p300
inhibition in human melanoma. Cancer Res. 79:2649–2661. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dai X, Zhang X, Yin Q, Hu J, Guo J, Gao Y,
Snell AH, Inuzuka H, Wan L and Wei W: Acetylation-dependent
regulation of BRAF oncogenic function. Cell Rep. 38:1102502022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vervoorts J, Lüscher-Firzlaff JM, Rottmann
S, Lilischkis R, Walsemann G, Dohmann K, Austen M and Lüscher B:
Stimulation of c-MYC transcriptional activity and acetylation by
recruitment of the cofactor CBP. EMBO Rep. 4:484–490. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fan T, Jiang S, Chung N, Alikhan A, Ni C,
Lee C-CR and Hornyak TJ: EZH2-dependent suppression of a cellular
senescence phenotype in melanoma cells by inhibition of p21/CDKN1A
expression. Mol Cancer Res. 9:418–429. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kovacs JJ, Murphy PJM, Gaillard S, Zhao X,
Wu JT, Nicchitta CV, Yoshida M, Toft DO, Pratt WB and Yao TP: HDAC6
regulates Hsp90 acetylation and chaperone-dependent activation of
glucocorticoid receptor. Mol Cell. 18:601–607. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pulya S, Amin SA, Adhikari N, Biswas S,
Jha T and Ghosh B: HDAC6 as privileged target in drug discovery: A
perspective. Pharmacol Res. 163:1052742021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu J, Luan W, Zhang Y, Gu J, Shi Y, Yang
Y, Feng Z and Qi F: HDAC6 interacts with PTPN1 to enhance melanoma
cells progression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 495:2630–2636. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bai J, Lei Y, An G and He L:
Down-regulation of deacetylase HDAC6 inhibits the melanoma cell
line A375.S2 growth through ROS-dependent mitochondrial pathway.
PLoS One. 10:e01212472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ling H, Li Y, Peng C, Yang S and Seto E:
HDAC10 blockade upregulates SPARC expression thereby repressing
melanoma cell growth and BRAF inhibitor resistance. bioRxiv
[Preprint]. 2023.12.05.570182. 2023.
|
|
44
|
Yuan W, Fang W, Zhang R, Lyu H, Xiao S,
Guo D, Ali DW, Michalak M, Chen XZ, Zhou C and Tang J: Therapeutic
strategies targeting AMPK-dependent autophagy in cancer cells.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 1870:1195372023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ling H, Li Y, Peng C, Yang S and Seto E:
HDAC10 inhibition represses melanoma cell growth and BRAF inhibitor
resistance via upregulating SPARC expression. NAR Cancer.
6:zcae0182024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Mustofa MK, Tanoue Y, Tateishi C, Vaziri C
and Tateishi S: Roles of Chk2/CHEK2 in guarding against
environmentally induced DNA damage and replication-stress. Environ
Mol Mutagen. 61:730–735. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang W, Feng Y, Guo Q, Guo W, Xu H, Li X,
Yi F, Guan Y, Geng N, Wang P, et al: SIRT1 modulates cell cycle
progression by regulating CHK2 acetylation-phosphorylation. Cell
Death Differ. 27:482–496. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Guo QQ, Wang SS, Zhang SS, Xu HD, Li XM,
Guan Y, Yi F, Zhou TT, Jiang B, Bai N, et al: ATM-CHK2-Beclin 1
axis promotes autophagy to maintain ROS homeostasis under oxidative
stress. EMBO J. 39:e1031112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mendelson K, Martin TC, Nguyen CB, Hsu M,
Xu J, Lang C, Dummer R, Saenger Y, Messina JL, Sondak VK, et al:
Differential histone acetylation and super-enhancer regulation
underlie melanoma cell dedifferentiation. JCI Insight.
9:e1666112024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Min D, Byun J, Lee EJ, Khan AA, Liu C,
Loudig O, Hu W, Zhao Y, Herlyn M, Tycko B, et al: Epigenetic
silencing of BMP6 by the SIN3A-HDAC1/2 repressor complex drives
melanoma metastasis via FAM83G/PAWS1. Mol Cancer Res. 20:217–230.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hornig E, Heppt MV, Graf SA, Ruzicka T and
Berking C: Inhibition of histone deacetylases in melanoma-a
perspective from bench to bedside. Exp Dermatol. 25:831–838. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kim JY, Cho H, Yoo J, Kim GW, Jeon YH, Lee
SW and Kwon SH: HDAC8 deacetylates HIF-1α and enhances its protein
stability to promote tumor growth and migration in melanoma.
Cancers (Basel). 15:11232023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Emmons MF, Bennett RL, Riva A, Gupta K,
Carvalho LADC, Zhang C, Macaulay R, Dupéré-Richér D, Fang B, Seto
E, et al: HDAC8-mediated inhibition of EP300 drives a
transcriptional state that increases melanoma brain metastasis. Nat
Commun. 14:77592023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kong F, Ma L, Wang X, You H, Zheng K and
Tang R: Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition by protein
lysine acetylation. Cell Commun Signal. 20:572022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Sun T, Jiao L, Wang Y, Yu Y and Ming L:
SIRT1 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition by promoting
autophagic degradation of E-cadherin in melanoma cells. Cell Death
Dis. 9:1362018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kunimoto R, Jimbow K, Tanimura A, Sato M,
Horimoto K, Hayashi T, Hisahara S, Sugino T, Hirobe T, Yamashita T
and Horio Y: SIRT1 regulates lamellipodium extension and migration
of melanoma cells. J Invest Dermatol. 134:1693–1700. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Porta C, Paglino C and Mosca A: Targeting
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in cancer. Front Oncol. 4:642014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yang Y, Liu Y, Wang Y, Chao Y, Zhang J,
Jia Y, Tie J and Hu D: Regulation of SIRT1 and its roles in
inflammation. Front Immunol. 13:8311682022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Bajpe PK, Prahallad A, Horlings H,
Nagtegaal I, Beijersbergen R and Bernards R: A chromatin modifier
genetic screen identifies SIRT2 as a modulator of response to
targeted therapies through the regulation of MEK kinase activity.
Oncogene. 34:531–536. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhao N, Guo Y, Liu P, Chen Y and Wang Y:
Sirtuin 2 promotes cell stemness and MEK/ERK signaling pathway
while reduces chemosensitivity in endometrial cancer. Arch Gynecol
Obstet. 305:693–701. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wang QL and Guo SJ: Sirtuins function as
the modulators in aging-related diseases in common or respectively.
Chin Med J (Engl). 128:1671–1678. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Yi X, Wang H, Yang Y, Wang H, Zhang H, Guo
S, Chen J, Du J, Tian Y, Ma J, et al: SIRT7 orchestrates melanoma
progression by simultaneously promoting cell survival and immune
evasion via UPR activation. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
8:1072023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Yu J, Zhuang A, Gu X, Hua Y, Yang L, Ge S,
Ruan J, Chai P, Jia R and Fan X: Nuclear PD-L1 promotes
EGR1-mediated angiogenesis and accelerates tumorigenesis. Cell
Discov. 9:332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Gao Y, Nihira NT, Bu X, Chu C, Zhang J,
Kolodziejczyk A, Fan Y, Chan NT, Ma L, Liu J, et al:
Acetylation-dependent regulation of PD-L1 nuclear translocation
dictates the efficacy of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Nat Cell Biol.
22:1064–1075. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wilmott JS, Colebatch AJ, Kakavand H,
Shang P, Carlino MS, Thompson JF, Long GV, Scolyer RA and Hersey P:
Expression of the class 1 histone deacetylases HDAC8 and 3 are
associated with improved survival of patients with metastatic
melanoma. Mod Pathol. 28:884–894. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
López-Bañuelos L and Vega L: Inhibition of
acetylation, is it enough to fight cancer? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
176:1037522022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Pan S and Chen R: Pathological implication
of protein post-translational modifications in cancer. Mol Aspects
Med. 86:1010972022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
He W, Li Q and Li X: Acetyl-CoA regulates
lipid metabolism and histone acetylation modification in cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1878:1888372023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Krumm A, Barckhausen C, Kücük P,
Tomaszowski KH, Loquai C, Fahrer J, Krämer OH, Kaina B and Roos WP:
Enhanced histone deacetylase activity in malignant melanoma
provokes RAD51 and FANCD2-triggered drug resistance. Cancer Res.
76:3067–3077. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Hess L, Moos V, Lauber AA, Reiter W,
Schuster M, Hartl N, Lackner D, Boenke T, Koren A, Guzzardo PM, et
al: A toolbox for class I HDACs reveals isoform specific roles in
gene regulation and protein acetylation. PLoS Genet.
18:e10103762022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Chen G, Cheng Y, Tang Y, Martinka M and Li
G: Role of Tip60 in human melanoma cell migration, metastasis, and
patient survival. J Invest Dermatol. 132:2632–2641. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Karst AM, Dai DL, Martinka M and Li G:
PUMA expression is significantly reduced in human cutaneous
melanomas. Oncogene. 24:1111–1116. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhang Y, Subbaiah VK, Rajagopalan D, Tham
CY, Abdullah LN, Toh TB, Gong M, Tan TZ, Jadhav SP, Pandey AK, et
al: TIP60 inhibits metastasis by ablating DNMT1-SNAIL2-driven
epithelial-mesenchymal transition program. J Mol Cell Biol.
8:384–399. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhang X, Bustos MA, Shoji Y, Ramos RI,
Iida Y, Gentry R, Takeshima TL and Hoon DSB: Acetylated DNMT1
downregulation and related regulatory factors influence metastatic
melanoma patients survival. Cancers (Basel). 13:46912021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Bhandaru M, Ardekani GS, Zhang G, Martinka
M, McElwee KJ, Li G and Rotte A: A combination of p300 and Braf
expression in the diagnosis and prognosis of melanoma. BMC Cancer.
14:3982014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Rotte A, Bhandaru M, Cheng Y, Sjoestroem
C, Martinka M and Li G: Decreased expression of nuclear p300 is
associated with disease progression and worse prognosis of melanoma
patients. PLoS One. 8:e754052013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Roos WP and Krumm A: The multifaceted
influence of histone deacetylases on DNA damage signalling and DNA
repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:10017–10030. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Booth L, Roberts JL, Sander C, Lee J,
Kirkwood JM, Poklepovic A and Dent P: The HDAC inhibitor AR42
interacts with pazopanib to kill trametinib/dabrafenib-resistant
melanoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget. 8:16367–16386.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Booth L, Roberts JL, Poklepovic A,
Kirkwood J and Dent P: HDAC inhibitors enhance the immunotherapy
response of melanoma cells. Oncotarget. 8:83155–83170. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Woods DM, Sodré AL, Villagra A, Sarnaik A,
Sotomayor EM and Weber J: HDAC inhibition upregulates PD-1 ligands
in melanoma and augments immunotherapy with PD-1 blockade. Cancer
Immunol Res. 3:1375–1385. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Beg AA and Gray JE: HDAC inhibitors with
PD-1 blockade: A promising strategy for treatment of multiple
cancer types? Epigenomics. 8:1015–1017. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Noonepalle S, Shen S, Ptáček J, Tavares
MT, Zhang G, Stránský J, Pavlíček J, Ferreira GM, Hadley M, Pelaez
G, et al: Rational design of suprastat: A novel selective histone
deacetylase 6 inhibitor with the ability to potentiate
immunotherapy in melanoma models. J Med Chem. 63:10246–10262. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Peng X, Yu Z, Surineni G, Deng B, Zhang M,
Li C, Sun Z, Pan W, Liu Y, Liu S, et al: Discovery of novel
benzohydroxamate-based histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) inhibitors
with the ability to potentiate anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in
melanoma. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 38:22014082023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Li F, Zhao X, Zhang Y, Shao P, Ma X,
Paradee WJ, Liu C, Wang J and Xue HH: TFH cells depend
on Tcf1-intrinsic HDAC activity to suppress CTLA4 and guard B-cell
help function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 118:e20145621182021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
van der Waart AB, van de Weem NMP, Maas F,
Kramer CSM, Kester MGD, Falkenburg JHF, Schaap N, Jansen JH, van
der Voort R, Gattinoni L, et al: Inhibition of Akt signaling
promotes the generation of superior tumor-reactive T cells for
adoptive immunotherapy. Blood. 124:3490–3500. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Kreidieh F and Wong MK: New standards in
the treatment of advanced metastatic melanoma: Immunotherapy and
BRAF-targeted therapies as emerging paradigms. Curr Pharm Des. May
26–2025.(Epub ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Zhang F, Zhou X, DiSpirito JR, Wang C,
Wang Y and Shen H: Epigenetic manipulation restores functions of
defective CD8+ T cells from chronic viral infection. Mol
Ther. 22:1698–1706. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Blake MK, O'Connell P and Aldhamen YA:
Fundamentals to therapeutics: Epigenetic modulation of
CD8+ T Cell exhaustion in the tumor microenvironment.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 10:10821952023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Vo DD, Prins RM, Begley JL, Donahue TR,
Morris LF, Bruhn KW, de la Rocha P, Yang MY, Mok S, Garban HJ, et
al: Enhanced antitumor activity induced by adoptive T-cell transfer
and adjunctive use of the histone deacetylase inhibitor LAQ824.
Cancer Res. 69:8693–8699. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Wang J, Hasan F, Frey AC, Li HS, Park J,
Pan K, Haymaker C, Bernatchez C, Lee DA, Watowich SS and Yee C:
Histone deacetylase inhibitors and IL21 cooperate to reprogram
human effector CD8+ T cells to memory T cells. Cancer Immunol Res.
8:794–805. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Lisiero DN, Soto H, Everson RG, Liau LM
and Prins RM: The histone deacetylase inhibitor, LBH589, promotes
the systemic cytokine and effector responses of adoptively
transferred CD8+ T cells. J Immunother Cancer. 2:82014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Heijkants R, Willekens K, Schoonderwoerd
M, Teunisse A, Nieveen M, Radaelli E, Hawinkels L, Marine JC and
Jochemsen A: Combined inhibition of CDK and HDAC as a promising
therapeutic strategy for both cutaneous and uveal metastatic
melanoma. Oncotarget. 9:6174–6187. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Gallagher SJ, Gunatilake D, Beaumont KA,
Sharp DM, Tiffen JC, Heinemann A, Weninger W, Haass NK, Wilmott JS,
Madore J, et al: HDAC inhibitors restore BRAF-inhibitor sensitivity
by altering PI3K and survival signalling in a subset of melanoma.
Int J Cancer. 142:1926–1937. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Badamchi-Zadeh A, Moynihan KD, Larocca RA,
Aid M, Provine NM, Iampietro MJ, Kinnear E, Penaloza-MacMaster P,
Abbink P, Blass E, et al: Combined HDAC and BET inhibition enhances
melanoma vaccine immunogenicity and efficacy. J Immunol.
201:2744–2752. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Shan X, Fu YS, Aziz F, Wang XQ, Yan Q and
Liu JW: Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits melanoma cell proliferation
through down-regulation of histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) and
increase of p53 acetylation. PLoS One. 9:e1154012014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Yan G, Eller MS, Elm C, Larocca CA, Ryu B,
Panova IP, Dancy BM, Bowers EM, Meyers D, Lareau L, et al:
Selective inhibition of p300 HAT blocks cell cycle progression,
induces cellular senescence, and inhibits the DNA damage response
in melanoma cells. J Invest Dermatol. 133:2444–2452. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
van den Bosch T, Boichenko A, Leus NGJ,
Ourailidou ME, Wapenaar H, Rotili D, Mai A, Imhof A, Bischoff R,
Haisma HJ and Dekker FJ: The histone acetyltransferase p300
inhibitor C646 reduces pro-inflammatory gene expression and
inhibits histone deacetylases. Biochem Pharmacol. 102:130–140.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Chen YF, Rahman A, Sax JL, Atala
Pleshinger MJ, Friedrich RM and Adams DJ: C646 degrades exportin-1
to modulate p300 chromatin occupancy and function. Cell Chem Biol.
31:1363–1372.e8. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Mitsiogianni M, Anestopoulos I, Kyriakou
S, Trafalis DT, Franco R, Pappa A and Panayiotidis MI: Benzyl and
phenethyl isothiocyanates as promising epigenetic drug compounds by
modulating histone acetylation and methylation marks in malignant
melanoma. Invest New Drugs. 39:1460–1468. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Okonkwo A, Mitra J, Johnson GS, Li L,
Dashwood WM, Hegde ML, Yue C, Dashwood RH and Rajendran P:
Heterocyclic analogs of sulforaphane trigger DNA damage and impede
DNA repair in colon cancer cells: Interplay of HATs and HDACs. Mol
Nutr Food Res. 62:e18002282018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Mitsiogianni M, Mantso T, Trafalis DT,
Vasantha Rupasinghe HP, Zoumpourlis V, Franco R, Botaitis S, Pappa
A and Panayiotidis MI: Allyl isothiocyanate regulates lysine
acetylation and methylation marks in an experimental model of
malignant melanoma. Eur J Nutr. 59:557–569. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Mitsiogianni M, Trafalis DT, Franco R,
Zoumpourlis V, Pappa A and Panayiotidis MI: Sulforaphane and iberin
are potent epigenetic modulators of histone acetylation and
methylation in malignant melanoma. Eur J Nutr. 60:147–158. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Li K, Zhang TT, Wang F, Cui B, Zhao CX, Yu
JJ, Lv XX, Zhang XW, Yang ZN, Huang B, et al: Metformin suppresses
melanoma progression by inhibiting KAT5-mediated SMAD3 acetylation,
transcriptional activity and TRIB3 expression. Oncogene.
37:2967–2981. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Chen J, Huang Z, Chen Y, Tian H, Chai P,
Shen Y, Yao Y, Xu S, Ge S and Jia R: Lactate and lactylation in
cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 10:382025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Zhang D, Tang Z, Huang H, Zhou G, Cui C,
Weng Y, Liu W, Kim S, Lee S, Perez-Neut M, et al: Metabolic
regulation of gene expression by histone lactylation. Nature.
574:575–580. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Zhao L, Qi H, Lv H, Liu W, Zhang R and
Yang A: Lactylation in health and disease: Physiological or
pathological? Theranostics. 15:1787–1821. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Dai X, Lv X, Thompson EW and Ostrikov KK:
Histone lactylation: Epigenetic mark of glycolytic switch. Trends
Genet. 38:124–127. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Yang K, Fan M, Wang X, Xu J, Wang Y, Tu F,
Gill PS, Ha T, Liu L, Williams DL and Li C: Lactate promotes
macrophage HMGB1 lactylation, acetylation, and exosomal release in
polymicrobial sepsis. Cell Death Differ. 29:133–146. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|