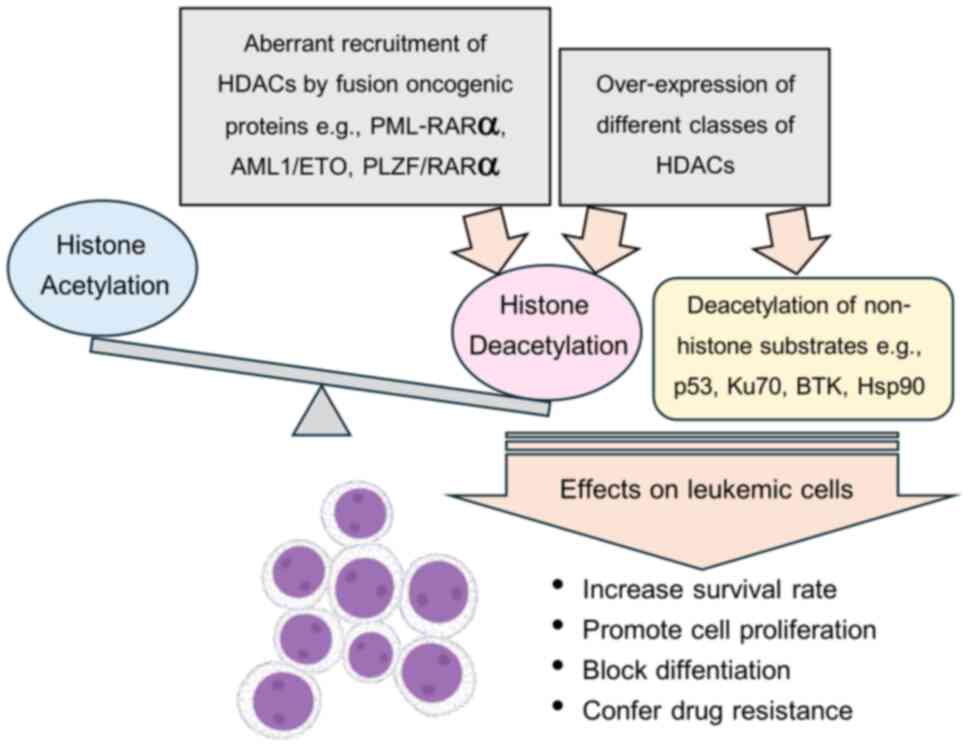
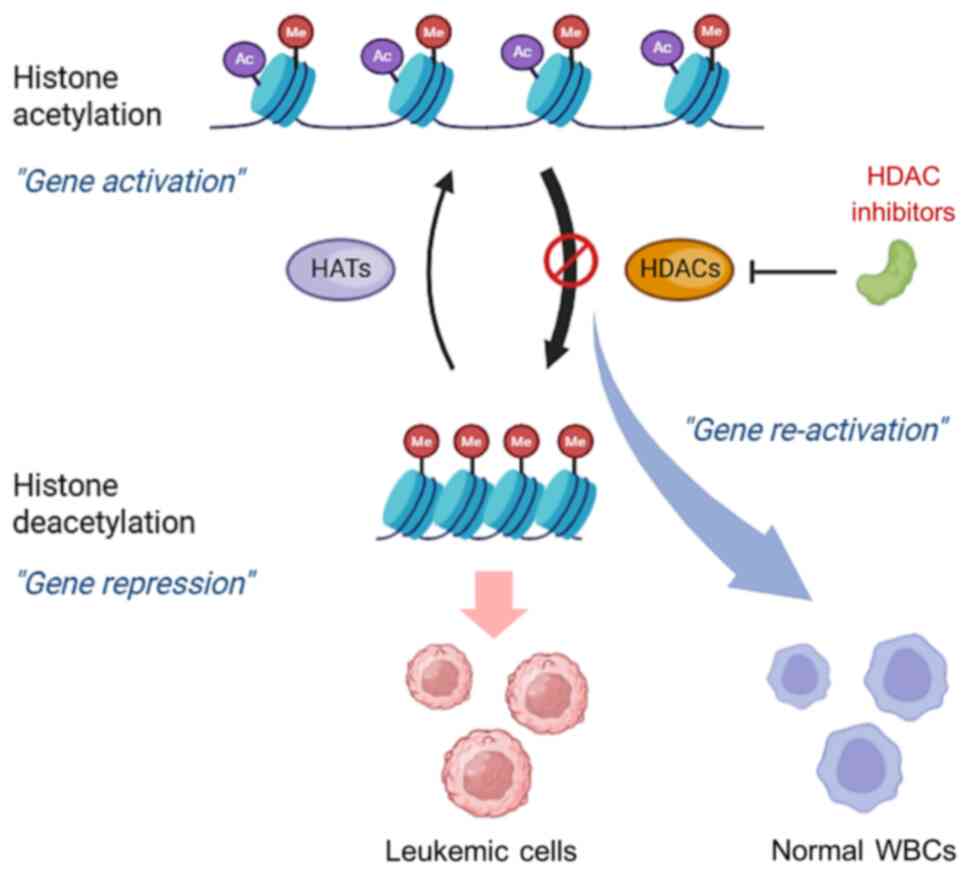
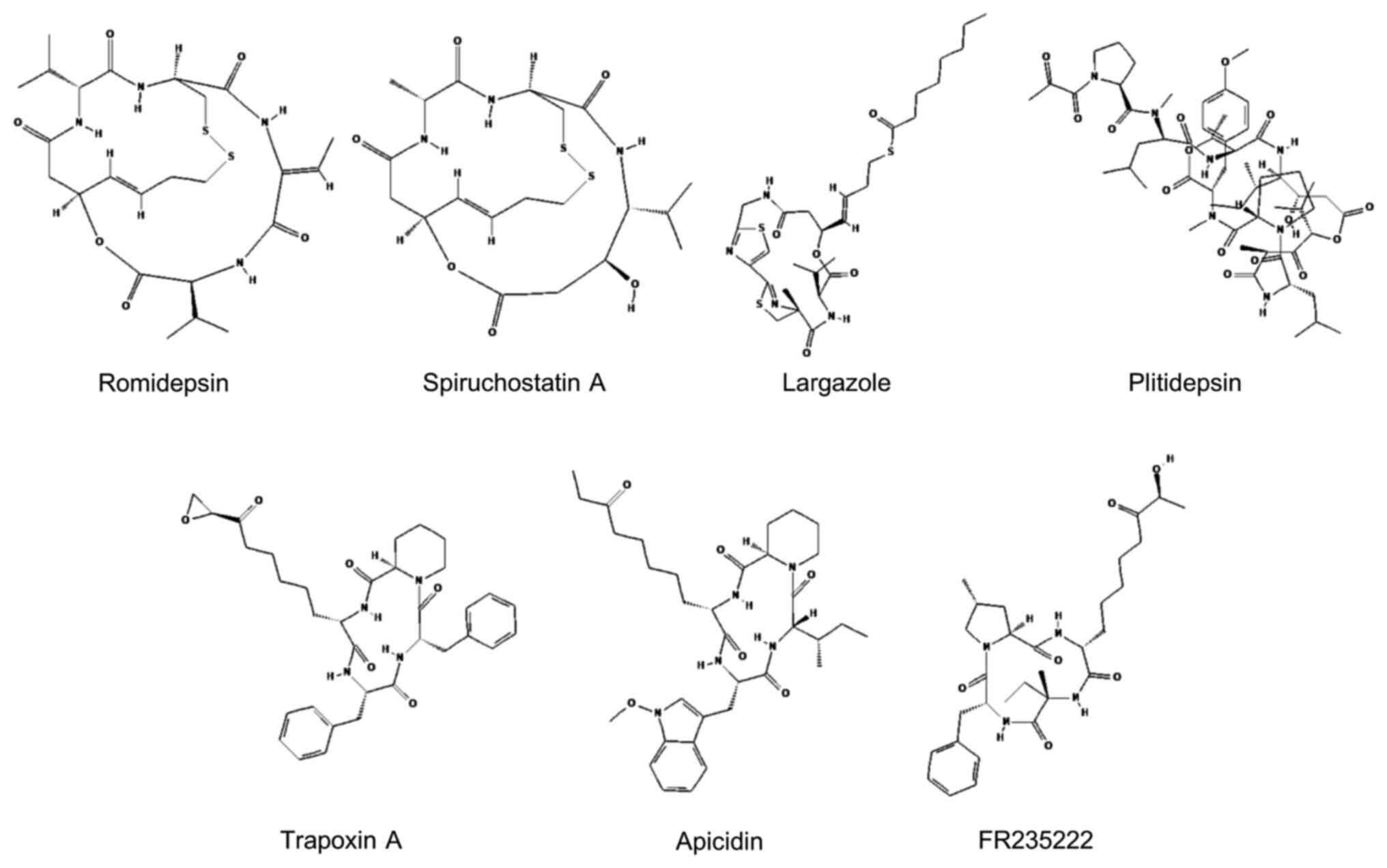
|
1
|
Brown G: Introduction and Classification
of Leukemias. Leukemia Stem Cells: Methods and Protocols. Cobaleda
C and Sánchez-García I: Springer; New York, NY: pp. 3–23. 2021
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Daltveit DS, Morgan E, Colombet M,
Steliarova-Foucher E, Bendahhou K, Marcos-Gragera R, Rongshou Z,
Smith A, Wei H and Soerjomataram I: Global patterns of leukemia by
subtype, age, and sex in 185 countries in 2022. Leukemia.
39:412–419. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Du M, Chen W, Liu K, Wang L, Hu Y, Mao Y,
Sun X, Luo Y, Shi J, Shao K, et al: The global burden of leukemia
and its attributable factors in 204 countries and territories:
Findings from the Global Burden of Disease 2019 study and
projections to 2030. J Oncol. 2022:16127022022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dong Y, Shi O, Zeng Q, Lu X, Wang W, Li Y
and Wang Q: Leukemia incidence trends at the global, regional, and
national level between 1990 and 2017. Exp Hematol Oncol. 9:142020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sharma R and Jani C: Mapping incidence and
mortality of leukemia and its subtypes in 21 world regions in last
three decades and projections to 2030. Ann Hematol. 101:1523–1534.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Briot T, Roger E, Thépot S and Lagarce F:
Advances in treatment formulations for acute myeloid leukemia. Drug
Discov Today. 23:1936–1949. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Škubník J, Pavlíčková VS, Ruml T and
Rimpelová S: Vincristine in combination therapy of cancer: Emerging
trends in clinics. Biology (Basel). 10:8492021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Park SB, Goldstein D, Krishnan AV, Lin CS,
Friedlander ML, Cassidy J, Koltzenburg M and Kiernan MC:
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity: A critical analysis.
CA Cancer J Clin. 63:419–437. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mort MK, Sen JM, Morris AL, DeGregory KA,
McLoughlin EM, Mort JF, Dunn SP, Abuannadi M and Keng MK:
Evaluation of cardiomyopathy in acute myeloid leukemia patients
treated with anthracyclines. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 26:680–687. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wallace KB: Doxorubicin-induced cardiac
mitochondrionopathy. Pharmacol Toxicol. 93:105–115. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pogorzala M, Kubicka M, Rafinska B,
Wysocki M and Styczynski J: Drug-resistance profile in
multiple-relapsed childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Anticancer Res. 35:5667–5670. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xia CQ and Smith PG: Drug efflux
transporters and multidrug resistance in acute leukemia:
Therapeutic impact and novel approaches to mediation. Mol
Pharmacol. 82:1008–1021. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kantarjian HM, Keating MJ and Freireich
EJ: Toward the potential cure of leukemias in the next decade.
Cancer. 124:4301–4313. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bhansali RS, Pratz KW and Lai C: Recent
advances in targeted therapies in acute myeloid leukemia. J Hematol
Oncol. 16:292023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brivio E, Baruchel A, Beishuizen A,
Bourquin JP, Brown PA, Cooper T, Gore L, Kolb EA, Locatelli F,
Maude SL, et al: Targeted inhibitors and antibody immunotherapies:
Novel therapies for paediatric leukaemia and lymphoma. Eur J
Cancer. 164:1–17. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Das AB, Smith-Díaz CC and Vissers MCM:
Emerging epigenetic therapeutics for myeloid leukemia: Modulating
demethylase activity with ascorbate. Haematologica. 106:14–25.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang X, Wang H, Zhang Y and Wang X:
Advances in epigenetic alterations of chronic lymphocytic leukemia:
From pathogenesis to treatment. Clin Exp Med. 24:542024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bian J and Zhang L, Han Y, Wang C and
Zhang L: Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Potent anti-leukemic
agents. Curr Med Chem. 22:2065–2074. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gaál Z, Oláh É, Rejtő L, Erdődi F and
Csernoch L: Strong correlation between the expression levels of
HDAC4 and SIRT6 in hematological malignancies of the adults. Pathol
Oncol Res. 23:493–504. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang F, Li Z, Zhou J, Wang G, Zhang W, Xu
J and Liang A: SIRT1 regulates the phosphorylation and degradation
of P27 by deacetylating CDK2 to promote T-cell acute lymphoblastic
leukemia progression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 40:2592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Merarchi M, Sethi G, Shanmugam MK, Fan L,
Arfuso F and Ahn KS: Role of natural products in modulating histone
deacetylases in cancer. Molecules. 24:10472019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Singh AK, Bishayee A and Pandey AK:
Targeting histone deacetylases with natural and synthetic agents:
An emerging anticancer strategy. Nutrients. 10:7312018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Janssens Y, Wynendaele E, Vanden Berghe W
and De Spiegeleer B: Peptides as epigenetic modulators: Therapeutic
implications. Clin Epigenetics. 11:1012019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang XJ and Seto E: HATs and HDACs: From
structure, function and regulation to novel strategies for therapy
and prevention. Oncogene. 26:5310–5318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gray SG and Teh BT: Histone
acetylation/deacetylation and cancer: An ‘open’ and ‘shut’ case?
Curr Mol Med. 1:401–429. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lawson M, Uciechowska U, Schemies J, Rumpf
T, Jung M and Sippl W: Inhibitors to understand molecular
mechanisms of NAD(+)-dependent deacetylases (sirtuins). Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1799:726–739. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Seto E and Yoshida M: Erasers of histone
acetylation: The histone deacetylase enzymes. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 6:a0187132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Asmamaw MD, He A, Zhang LR, Liu HM and Gao
Y: Histone deacetylase complexes: Structure, regulation and
function. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1879:1891502024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Duan Z, Zarebski A, Montoya-Durango D,
Grimes HL and Horwitz M: Gfi1 coordinates epigenetic repression of
p21 Cip/WAF1 by recruitment of histone lysine methyltransferase G9a
and histone deacetylase 1. Mol Cell biol. 25:10338–10351. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fujiwara T, Lee HY, Sanalkumar R and
Bresnick EH: Building multifunctionality into a complex containing
master regulators of hematopoiesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:20429–20434. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
van Oorschot R, Hansen M, Koornneef JM,
Marneth AE, Bergevoet SM, van Bergen MGJM, van Alphen FPJ, van der
Zwaan C, Martens JHA, Vermeulen M, et al: Molecular mechanisms of
bleeding disorder associated GFI1BQ287* mutation and its affected
pathways in megakaryocytes and platelets. Haematologica.
104:1460–1472. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Calderon A, Mestvirishvili T, Boccalatte
F, Ruggles KV and David G: Chromatin accessibility and cell cycle
progression are controlled by the HDAC-associated Sin3B protein in
murine hematopoietic stem cells. Epigenetics Chromatin. 17:22024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wada T, Kikuchi J, Nishimura N, Shimizu R,
Kitamura T and Furukawa Y: Expression levels of histone
deacetylases determine the cell fate of hematopoietic progenitors.
J Biol Chem. 284:30673–30683. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang P, Wang Z and Liu J: Role of HDACs in
normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Mol Cancer. 19:52020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yan B, Yang J, Kim MY, Luo H, Cesari N,
Yang T, Strouboulis J, Zhang J, Hardison R, Huang S and Qiu Y:
HDAC1 is required for GATA-1 transcription activity, global
chromatin occupancy and hematopoiesis. Nucleic Acids Res.
49:9783–9798. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Iwasaki H, Mizuno S, Arinobu Y, Ozawa H,
Mori Y, Shigematsu H, Takatsu K, Tenen DG and Akashi K: The order
of expression of transcription factors directs hierarchical
specification of hematopoietic lineages. Genes Dev. 20:3010–3021.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yamamura K, Ohishi K, Katayama N, Yu Z,
Kato K, Masuya M, Fujieda A, Sugimoto Y, Miyata E, Shibasaki T, et
al: Pleiotropic role of histone deacetylases in the regulation of
human adult erythropoiesis. Br J Haematol. 135:242–253. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Das Gupta K, Shakespear MR, Iyer A,
Fairlie DP and Sweet MJ: Histone deacetylases in
monocyte/macrophage development, activation and metabolism:
refining HDAC targets for inflammatory and infectious diseases.
Clin Transl Immunol. 5:e622016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Heideman MR, Lancini C, Proost N, Yanover
E, Jacobs H and Dannenberg JH: Sin3a-associated Hdac1 and Hdac2 are
essential for hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis and contribute
differentially to hematopoiesis. Haematologica. 99:1292–1303. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu B, Ohishi K, Yamamura K, Suzuki K,
Monma F, Ino K, Nishii K, Masuya M, Sekine T, Heike Y, et al: A
potential activity of valproic acid in the stimulation of
interleukin-3−mediated megakaryopoiesis and erythropoiesis. Exp
Hematol. 38:685–695. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yamaguchi T, Cubizolles F, Zhang Y,
Reichert N, Kohler H, Seiser C and Matthias P: Histone deacetylases
1 and 2 act in concert to promote the G1-to-S progression. Genes
Dev. 24:455–469. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Boucheron N, Tschismarov R, Göschl L,
Moser MA, Lagger S, Sakaguchi S, Winter M, Lenz F, Vitko D,
Breitwieser FP, et al: CD4+ T cell lineage integrity is controlled
by the histone deacetylases HDAC1 and HDAC2. Nat Immunol.
15:439–448. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ni L, Wang L, Yao C, Ni Z, Liu F, Gong C,
Zhu X, Yan X, Watowich SS, Lee DA and Zhu S: The histone
deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid inhibits NKG2D expression in
natural killer cells through suppression of STAT3 and HDAC3. Sci
Rep. 7:452662017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lemercier C, Brocard MP, Puvion-Dutilleul
F, Kao HY, Albagli O and Khochbin S: Class II histone deacetylases
are directly recruited by BCL6 transcriptional repressor. J Biol
Chem. 277:22045–22052. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kasler HG and Verdin E: Histone
deacetylase 7 functions as a key regulator of genes involved in
both positive and negative selection of thymocytes. Mol Cell Biol.
27:5184–5200. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li J, Li X, Sun W, Zhang J, Yan Q, Wu J,
Jin J, Lu R and Miao D: Specific overexpression of SIRT1 in
mesenchymal stem cells rescues hematopoiesis niche in BMI1 knockout
mice through promoting CXCL12 expression. Int J Biol Sci.
18:2091–2103. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Skokowa J, Lan D, Thakur BK, Wang F, Gupta
K, Cario G, Brechlin AM, Schambach A, Hinrichsen L, Meyer G, et al:
NAMPT is essential for the G-CSF-induced myeloid differentiation
via a NAD(+)-sirtuin-1-dependent pathway. Nat Med. 15:151–158.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ou X, Chae HD, Wang RH, Shelley WC, Cooper
S, Taylor T, Kim YJ, Deng CX, Yoder MC and Broxmeyer HE: SIRT1
deficiency compromises mouse embryonic stem cell hematopoietic
differentiation, and embryonic and adult hematopoiesis in the
mouse. Blood. 117:440–450. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Brown K, Xie S, Qiu X, Mohrin M, Shin J,
Liu Y, Zhang D, Scadden DT and Chen D: SIRT3 reverses
aging-associated degeneration. Cell Rep. 3:319–327. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kaiser A, Schmidt M, Huber O, Frietsch JJ,
Scholl S, Heidel FH, Hochhaus A, Müller JP and Ernst T: SIRT7: An
influence factor in healthy aging and the development of
age-dependent myeloid stem-cell disorders. Leukemia. 34:2206–2216.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Luo H, Mu WC, Karki R, Chiang HH, Mohrin
M, Shin JJ, Ohkubo R, Ito K, Kanneganti TD and Chen D:
Mitochondrial stress-Initiated aberrant activation of the NLRP3
inflammasome regulates the functional deterioration of
hematopoietic stem cell aging. Cell Rep. 26:945–954.e4. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sahakian E, Chen J, Powers JJ, Chen X,
Maharaj K, Deng SL, Achille AN, Lienlaf M, Wang HW, Cheng F, et al:
Essential role for histone deacetylase 11 (HDAC11) in neutrophil
biology. J Leukoc Biol. 102:475–486. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Grignani F, De Matteis S, Nervi C,
Tomassoni L, Gelmetti V, Cioce M, Fanelli M, Ruthardt M, Ferrara
FF, Zamir I, et al: Fusion proteins of the retinoic acid
receptor-alpha recruit histone deacetylase in promyelocytic
leukaemia. Nature. 391:815–818. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Gelmetti V, Zhang J, Fanelli M, Minucci S,
Pelicci PG and Lazar MA: Aberrant recruitment of the nuclear
receptor corepressor-histone deacetylase complex by the acute
myeloid leukemia fusion partner ETO. Mol Cell Biol. 18:7185–7191.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Girard N, Tremblay M, Humbert M, Grondin
B, Haman A, Labrecque J, Chen B, Chen Z, Chen SJ and Hoang T:
RARα-PLZF oncogene inhibits C/EBPα function in myeloid cells. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:13522–13527. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang J, Hug BA, Huang EY, Chen CW,
Gelmetti V, Maccarana M, Minucci S, Pelicci PG and Lazar MA:
Oligomerization of ETO is obligatory for corepressor interaction.
Mol Cell Biol. 21:156–163. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Vishwakarma BA, Nguyen N, Makishima H,
Hosono N, Gudmundsson KO, Negi V, Oakley K, Han Y, Przychodzen B,
Maciejewski JP and Du Y: Runx1 repression by histone deacetylation
is critical for Setbp1-induced mouse myeloid leukemia development.
Leukemia. 30:200–208. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Nakata S, Yoshida T, Horinaka M, Shiraishi
T, Wakada M and Sakai T: Histone deacetylase inhibitors upregulate
death receptor 5/TRAIL-R2 and sensitize apoptosis induced by
TRAIL/APO2-L in human malignant tumor cells. Oncogene.
23:6261–6271. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yoo CB and Jones PA: Epigenetic therapy of
cancer: past, present and future. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 5:37–50.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Mehrpouri M, Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi A and
Bashash D: The contributory roles of histone deacetylases (HDACs)
in hematopoiesis regulation and possibilities for pharmacologic
interventions in hematologic malignancies. Int Immunopharmacol.
100:1081142021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Van Damme M, Crompot E, Meuleman N, Mineur
P, Bron D, Lagneaux L and Stamatopoulos B: HDAC isoenzyme
expression is deregulated in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B-cells
and has a complex prognostic significance. Epigenetics.
7:1403–1412. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Verbeek TCAI, Vrenken KS, Arentsen-Peters
STCJM, Castro PG, van de Ven M, van Tellingen O, Pieters R and Stam
RW: Selective inhibition of HDAC class IIA as therapeutic
intervention for KMT2A-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Commun Biol. 7:12572024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Gu W and Roeder RG: Activation of p53
sequence-specific DNA binding by acetylation of the p53 C-terminal
domain. Cell. 90:595–606. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Molica M, Mazzone C, Niscola P and de
Fabritiis P: TP53 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia: Still a
daunting challenge? Front Oncol. 10:6108202021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kuo YH, Qi J and Cook GJ: Regain control
of p53: Targeting leukemia stem cells by isoform-specific HDAC
inhibition. Exp Hematol. 44:315–321. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Qi J, Singh S, Hua WK, Cai Q, Chao SW, Li
L, Liu H, Ho Y, McDonald T, Lin A, et al: HDAC8 inhibition
specifically targets inv(16) acute myeloid leukemic stem cells by
restoring p53 acetylation. Cell Stem Cell. 17:597–610. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Lee SM, Bae JH, Kim MJ, Lee HS, Lee MK,
Chung BS, Kim DW, Kang CD and Kim SH: Bcr-Abl-independent
imatinib-resistant K562 cells show aberrant protein acetylation and
increased sensitivity to histone deacetylase inhibitors. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 322:1084–1092. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Burgess M, Chen YCE, Mapp S, Blumenthal A,
Mollee P, Gill D and Saunders NA: HDAC7 is an actionable driver of
therapeutic antibody resistance by macrophages from CLL patients.
Oncogene. 39:5756–5767. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Micelli C and Rastelli G: Histone
deacetylases: Structural determinants of inhibitor selectivity.
Drug Discov Today. 20:718–735. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zhang L, Zhang J, Jiang Q, Zhang L and
Song W: Zinc binding groups for histone deacetylase inhibitors. J
Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 33:714–721. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Rajak H, Singh A, Dewangan PK, Patel V,
Jain DK, Tiwari SK, Veerasamy R and Sharma PC: Peptide based
aacrocycles: Selective histone deacetylase inhibitors with
antiproliferative activity. Curr Med Chem. 20:1887–1903. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Curcio A, Rocca R, Alcaro S and Artese A:
The histone deacetylase family: Structural features and application
of combined computational methods. Pharmaceuticals (Basel).
17:6202024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Davie JR: Inhibition of histone
deacetylase activity by butyrate. J Nutr. 133 (7
Suppl):2485S–2493S. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Luu M, Riester Z, Baldrich A, Reichardt N,
Yuille S, Busetti A, Klein M, Wempe A, Leister H, Raifer H, et al:
Microbial short-chain fatty acids modulate CD8(+) T cell responses
and improve adoptive immunotherapy for cancer. Nat Commun.
12:40772021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Ozkan AD, Eskiler GG, Kazan N and Turna O:
Histone deacetylase inhibitor sodium butyrate regulates the
activation of toll-like receptor 4/interferon regulatory factor-3
signaling pathways in prostate cancer cells. J Cancer Res Ther.
19:1812–1817. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Sampathkumar SG, Jones MB, Meledeo MA,
Campbell CT, Choi SS, Hida K, Gomutputra P, Sheh A, Gilmartin T,
Head SR and Yarema KJ: Targeting glycosylation pathways and the
cell cycle: Sugar-dependent activity of butyrate-carbohydrate
cancer prodrugs. Chem Biol. 13:1265–1275. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Steliou K, Boosalis MS, Perrine SP,
Sangerman J and Faller DV: Butyrate histone deacetylase inhibitors.
Biores Open Access. 1:192–198. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Tang R, Faussat AM, Majdak P, Perrot JY,
Chaoui D, Legrand O and Marie JP: Valproic acid inhibits
proliferation and induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells
expressing P-gp and MRP1. Leukemia. 18:1246–1251. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Zapotocky M, Mejstrikova E, Smetana K,
Stary J, Trka J and Starkova J: Valproic acid triggers
differentiation and apoptosis in AML1/ETO-positive leukemic cells
specifically. Cancer Lett. 319:144–153. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Fredly H, Gjertsen BT and Bruserud Ø:
Histone deacetylase inhibition in the treatment of acute myeloid
leukemia: The effects of valproic acid on leukemic cells, and the
clinical and experimental evidence for combining valproic acid with
other antileukemic agents. Clin Epigenetics. 5:122013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Garcia-Manero G, Kantarjian HM,
Sanchez-Gonzalez B, Yang H, Rosner G, Verstovsek S, Rytting M,
Wierda WG, Ravandi F, Koller C, et al: Phase 1/2 study of the
combination of 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine with valproic acid in
patients with leukemia. Blood. 108:3271–3279. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Peiffer L, Poll-Wolbeck SJ, Flamme H,
Gehrke I, Hallek M and Kreuzer KA: Trichostatin A effectively
induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells via
inhibition of Wnt signaling and histone deacetylation. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 140:1283–1293. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Khan N, Jeffers M, Kumar S, Hackett C,
Boldog F, Khramtsov N, Qian X, Mills E, Berghs SC, Carey N, et al:
Determination of the class and isoform selectivity of
small-molecule histone deacetylase inhibitors. Biochem J.
409:581–589. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Duvic M, Talpur R, Ni X, Zhang C, Hazarika
P, Kelly C, Chiao JH, Reilly JF, Ricker JL, Richon VM and Frankel
SR: Phase 2 trial of oral vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic
acid, SAHA) for refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). Blood.
109:31–39. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Campbell P and Thomas CM: Belinostat for
the treatment of relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma.
J Oncol Pharm Pract. 23:143–147. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Laubach JP, Moreau P, San-Miguel JF and
Richardson PG: Panobinostat for the treatment of multiple myeloma.
Clin Cancer Res. 21:4767–4773. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Wagner JM, Hackanson B, Lübbert M and Jung
M: Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors in recent clinical trials
for cancer therapy. Clin Epigenetics. 1:117–136. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Batlevi CL, Crump M, Andreadis C, Rizzieri
D, Assouline SE, Fox S, van der Jagt RHC, Copeland A, Potvin D,
Chao R and Younes A: A phase 2 study of mocetinostat, a histone
deacetylase inhibitor, in relapsed or refractory lymphoma. Br J
Haematol. 178:434–441. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Carraway HE, Sawalha Y, Gojo I, Lee MJ,
Lee S, Tomita Y, Yuno A, Greer J, Smith BD, Pratz KW, et al: Phase
1 study of the histone deacetylase inhibitor entinostat plus
clofarabine for poor-risk Philadelphia chromosome-negative (newly
diagnosed older adults or adults with relapsed refractory disease)
acute lymphoblastic leukemia or biphenotypic leukemia. Leuk Res.
110:1067072021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Maolanon AR, Kristensen HM, Leman LJ,
Ghadiri MR and Olsen CA: Natural and synthetic macrocyclic
inhibitors of the histone deacetylase enzymes. Chembiochem.
18:5–49. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Ueda H, Manda T, Matsumoto S, Mukumoto S,
Nishigaki F, Kawamura I and Shimomura K: FR901228, a novel
antitumor bicyclic depsipeptide produced by Chromobacterium
violaceum No. 968. III. Antitumor activities on experimental tumors
in mice. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 47:315–323. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Furumai R, Matsuyama A, Kobashi N, Lee KH,
Nishiyama M, Nakajima H, Tanaka A, Komatsu Y, Nishino N, Yoshida M
and Horinouchi S: FK228 (depsipeptide) as a natural prodrug that
inhibits class I histone deacetylases. Cancer Res. 62:4916–4921.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Murata M, Towatari M, Kosugi H, Tanimoto
M, Ueda R, Saito H and Naoe T: Apoptotic cytotoxic effects of a
histone deacetylase inhibitor, FK228, on malignant lymphoid cells.
Jpn J Cancer Res. 91:1154–1160. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Campas-Moya C: Romidepsin for the
treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Drugs Today (Barc).
45:787–795. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Coiffier B, Pro B, Prince HM, Foss F,
Sokol L, Greenwood M, Caballero D, Morschhauser F, Wilhelm M,
Pinter-Brown L, et al: Romidepsin for the treatment of
relapsed/refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma: Pivotal study
update demonstrates durable responses. J Hematol Oncol. 7:112014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Savickiene J, Treigyte G, Borutinskaite V,
Navakauskiene R and Magnusson KE: The histone deacetylase inhibitor
FK228 distinctly sensitizes the human leukemia cells to retinoic
acid-induced differentiation. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1091:368–384. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Kosugi H, Ito M, Yamamoto Y, Towatari M,
Ito M, Ueda R, Saito H and Naoe T: In vivo effects of a histone
deacetylase inhibitor, FK228, on human acute promyelocytic leukemia
in NOD/Shi-scid/scid mice. Jpn J Cancer Res. 92:529–536. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Okabe S, Tauchi T, Nakajima A, Sashida G,
Gotoh A, Broxmeyer HE, Ohyashiki JH and Ohyashiki K: Depsipeptide
(FK228) preferentially induces apoptosis in BCR/ABL-expressing cell
lines and cells from patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in
blast crisis. Stem Cells Dev. 16:503–514. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Klisovic MI, Maghraby EA, Parthun MR,
Guimond M, Sklenar AR, Whitman SP, Chan KK, Murphy T, Anon J,
Archer KJ, et al: Depsipeptide (FR 901228) promotes histone
acetylation, gene transcription, apoptosis and its activity is
enhanced by DNA methyltransferase inhibitors in AML1/ETO-positive
leukemic cells. Leukemia. 17:350–358. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Shaker S, Bernstein M, Momparler LF and
Momparler RL: Preclinical evaluation of antineoplastic activity of
inhibitors of DNA methylation (5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine) and histone
deacetylation (trichostatin A, depsipeptide) in combination against
myeloid leukemic cells. Leuk Res. 27:437–444. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Brunvand MW and Carson J: Complete
remission with romidepsin in a patient with T-cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia refractory to induction hyper-CVAD. Hematol
Oncol. 36:340–343. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Cox WPJ, Evander N, Van Ingen Schenau DS,
Stoll GR, Anderson N, De Groot L, Grünewald KJT, Hagelaar R, Butler
M, Kuiper RP, et al: Histone deacetylase inhibition sensitizes
p53-deficient B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia to
chemotherapy. Haematologica. 109:1755–1765. 2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Foley N, Riedell PA, Bartlett NL, Cashen
AF, Kahl BS, Fehniger TA, Fischer A, Moreno C, Liu J, Carson KR and
Mehta-Shah N: A phase I study of romidepsin in combination with
gemcitabine, oxaliplatin, and dexamethasone in patients with
relapsed or refractory aggressive lymphomas enriched for T-Cell
lymphomas. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 25:328–336. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Seiser T, Kamena F and Cramer N: Synthesis
and biological activity of largazole and derivatives. Angew Chem
Int Ed Engl. 47:6483–6485. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Bowers A, West N, Taunton J, Schreiber SL,
Bradner JE and Williams RM: Total synthesis and biological mode of
action of largazole: A potent class I histone deacetylase
inhibitor. J Am Chem Soc. 130:11219–11222. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Taori K, Paul VJ and Luesch H: Structure
and activity of largazole, a potent antiproliferative agent from
the floridian marine cyanobacterium symploca sp. J Am Chem Soc.
130:1806–1807. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Souto JA, Vaz E, Lepore I, Pöppler AC,
Franci G, Alvarez R, Altucci L and de Lera AR: Synthesis and
biological characterization of the histone deacetylase inhibitor
largazole and C7-modified analogues. J Med Chem. 53:4654–4667.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Zhang B, Ruan ZW, Luo D, Zhu Y, Ding T,
Sui Q and Lei X: Unexpected enhancement of HDACs inhibition by MeS
substitution at C-2 position of fluoro largazole. Mar Drugs.
18:3442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Wang M, Sun XY, Zhou YC, Zhang KJ, Lu YZ,
Liu J, Huang YC, Wang GZ, Jiang S and Zhou GB: Suppression of
Musashi-2 by the small compound largazole exerts inhibitory effects
on malignant cells. Int J Oncol. 56:1274–1283. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Yurek-George A, Habens F, Brimmell M,
Packham G and Ganesan A: Total synthesis of spiruchostatin A, a
potent histone deacetylase inhibitor. J Am Chem Soc. 126:1030–1031.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Narita K, Fukui Y, Sano Y, Yamori T, Ito
A, Yoshida M and Katoh T: Total synthesis of bicyclic depsipeptides
spiruchostatins C and D and investigation of their histone
deacetylase inhibitory and antiproliferative activities. Eur J Med
Chem. 60:295–304. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Kanno S, Maeda N, Tomizawa A, Yomogida S,
Katoh T and Ishikawa M: Involvement of p21waf1/cip1 expression in
the cytotoxicity of the potent histone deacetylase inhibitor
spiruchostatin B towards susceptible NALM-6 human B cell leukemia
cells. Int J Oncol. 40:1391–1396. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Rehman MU, Jawaid P, Yoshihisa Y, Li P,
Zhao QL, Narita K, Katoh T, Kondo T and Shimizu T: Spiruchostatin A
and B, novel histone deacetylase inhibitors, induce apoptosis
through reactive oxygen species-mitochondria pathway in human
lymphoma U937 cells. Chem Biol Interact. 221:24–34. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Yao L: Aplidin PharmaMar. IDrugs.
6:246–250. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Erba E, Bassano L, Di Liberti G, Muradore
I, Chiorino G, Ubezio P, Vignati S, Codegoni A, Desiderio MA,
Faircloth G, et al: Cell cycle phase perturbations and apoptosis in
tumour cells induced by aplidine. Br J Cancer. 86:1510–1517. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Erba E, Serafini M, Gaipa G, Tognon G,
Marchini S, Celli N, Rotilio D, Broggini M, Jimeno J, Faircloth GT,
et al: Effect of aplidin in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cells. Br
J Cancer. 89:763–773. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Bresters D, Broekhuizen AJ, Kaaijk P,
Faircloth GT, Jimeno J and Kaspers GJ: In vitro cytotoxicity of
aplidin and crossresistance with other cytotoxic drugs in childhood
leukemic and normal bone marrow and blood samples: A rational basis
for clinical development. Leukemia. 17:1338–1343. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Gómez SG, Bueren JA, Faircloth GT, Jimeno
J and Albella B: In vitro toxicity of three new antitumoral drugs
(trabectedin, aplidin, and kahalalide F) on hematopoietic
progenitors and stem cells. Exp Hematol. 31:1104–1111. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Gajate C, An F and Mollinedo F: Rapid and
selective apoptosis in human leukemic cells induced by Aplidine
through a Fas/CD95- and mitochondrial-mediated mechanism. Clin
Cancer Res. 9:1535–1545. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Mitsiades CS, Ocio EM, Pandiella A, Maiso
P, Gajate C, Garayoa M, Vilanova D, Montero JC, Mitsiades N,
McMullan CJ, et al: Aplidin, a marine organism-derived compound
with potent antimyeloma activity in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res.
68:5216–5225. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Muñoz-Alonso MJ, Álvarez E,
Guillén-Navarro MJ, Pollán M, Avilés P, Galmarini CM and Muñoz A:
c-Jun N-terminal kinase phosphorylation is a biomarker of
plitidepsin activity. Mar Drugs. 11:1677–1692. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Broggini M, Marchini SV, Galliera E,
Borsotti P, Taraboletti G, Erba E, Sironi M, Jimeno J, Faircloth
GT, Giavazzi R and D'Incalci M: Aplidine, a new anticancer agent of
marine origin, inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
secretion and blocks VEGF-VEGFR-1 (flt-1) autocrine loop in human
leukemia cells MOLT-4. Leukemia. 17:52–59. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Morande PE, Zanetti SR, Borge M, Nannini
P, Jancic C, Bezares RF, Bitsmans A, González M, Rodríguez AL,
Galmarini CM, et al: The cytotoxic activity of Aplidin in chronic
lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is mediated by a direct effect on
leukemic cells and an indirect effect on monocyte-derived cells.
Invest New Drugs. 30:1830–1840. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Barboza NM, Medina DJ, Budak-Alpdogan T,
Aracil M, Jimeno JM, Bertino JR and Banerjee D: Plitidepsin
(Aplidin) is a potent inhibitor of diffuse large cell and Burkitt
lymphoma and is synergistic with rituximab. Cancer Biol Ther.
13:114–122. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Humeniuk R, Menon LG, Mishra PJ, Saydam G,
Longo-Sorbello GS, Elisseyeff Y, Lewis LD, Aracil M, Jimeno J,
Bertino JR and Banerjee D: Aplidin synergizes with cytosine
arabinoside: Functional relevance of mitochondria in
Aplidin-induced cytotoxicity. Leukemia. 21:2399–2405. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Spicka I, Ocio EM, Oakervee HE, Greil R,
Banh RH, Huang SY, D'Rozario JM, Dimopoulos MA, Martínez S,
Extremera S, et al: Randomized phase III study (ADMYRE) of
plitidepsin in combination with dexamethasone vs. dexamethasone
alone in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Ann
Hematol. 98:2139–2150. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Mateos MV, Prosper F, Martin Sánchez J,
Ocio EM, Oriol A, Motlló C, Michot JM, Jarque I, Iglesias R, Solé
M, et al: Phase I study of plitidepsin in combination with
bortezomib and dexamethasone in patients with relapsed/refractory
multiple myeloma. Cancer Med. 12:3999–4009. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Itazaki H, Nagashima K, Sugita K, Yoshida
H, Kawamura Y, Yasuda Y, Matsumoto K, Ishii K, Uotani N, Nakai H,
et al: Isolation and structural elucidation of new
cyclotetrapeptides, trapoxins A and B, having detransformation
activities as antitumor agents. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 43:1524–1532.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Furumai R, Komatsu Y, Nishino N, Khochbin
S, Yoshida M and Horinouchi S: Potent histone deacetylase
inhibitors built from trichostatin A and cyclic tetrapeptide
antibiotics including trapoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:87–92.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Kijima M, Yoshida M, Sugita K, Horinouchi
S and Beppu T: Trapoxin, an antitumor cyclic tetrapeptide, is an
irreversible inhibitor of mammalian histone deacetylase. J Biol
Chem. 268:22429–22435. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Kosugi H, Towatari M, Hatano S, Kitamura
K, Kiyoi H, Kinoshita T, Tanimoto M, Murate T, Kawashima K, Saito H
and Naoe T: Histone deacetylase inhibitors are the potent
inducer/enhancer of differentiation in acute myeloid leukemia: A
new approach to anti-leukemia therapy. Leukemia. 13:1316–1324.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Maeda T, Towatari M, Kosugi H and Saito H:
Up-regulation of costimulatory/adhesion molecules by histone
deacetylase inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood.
96:3847–3856. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Park JS, Lee KR, Kim JC, Lim SH, Seo JA
and Lee YW: A hemorrhagic factor (Apicidin) produced by toxic
Fusarium isolates from soybean seeds. Appl Environ Microbiol.
65:126–130. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Han JW, Ahn SH, Park SH, Wang SY, Bae GU,
Seo DW, Kwon HK, Hong S, Lee HY, Lee YW and Lee HW: Apicidin, a
histone deacetylase inhibitor, inhibits proliferation of tumor
cells via induction of p21WAF1/Cip1 and gelsolin. Cancer Res.
60:6068–6074. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Cheong JW, Chong SY, Kim JY, Eom JI, Jeung
HK, Maeng HY, Lee ST and Min YH: Induction of apoptosis by
apicidin, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, via the activation of
mitochondria-dependent caspase cascades in human Bcr-Abl-positive
leukemia cells. Clin Cancer Res. 9:5018–5027. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Kim JS, Jeung HK, Cheong JW, Maeng H, Lee
ST, Hahn JS, Ko YW and Min YH: Apicidin potentiates the
imatinib-induced apoptosis of Bcr-Abl-positive human leukaemia
cells by enhancing the activation of mitochondria-dependent caspase
cascades. Br J Haematol. 124:166–178. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Ferrante F, Giaimo BD, Bartkuhn M,
Zimmermann T, Close V, Mertens D, Nist A, Stiewe T, Meier-Soelch J,
Kracht M, et al: HDAC3 functions as a positive regulator in Notch
signal transduction. Nucleic Acids Res. 48:3496–3512. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Mori H, Urano Y, Abe F, Furukawa S,
Furukawa S, Tsurumi Y, Sakamoto K, Hashimoto M, Takase S, Hino M
and Fujii T: FR235222, a fungal metabolite, is a novel
immunosuppressant that inhibits mammalian histone deacetylase
(HDAC). I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and biological
activities. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 56:72–79. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Petrella A, D'Acunto CW, Rodriquez M,
Festa M, Tosco A, Bruno I, Terracciano S, Taddei M, Paloma LG and
Parente L: Effects of FR235222, a novel HDAC inhibitor, in
proliferation and apoptosis of human leukaemia cell lines: Role of
annexin A1. Eur J Cancer. 44:740–749. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
D'Acunto CW, Carratù A, Rodriquez M,
Taddei M, Parente L and Petrella A: LGP1, A histone deacetylase
inhibitor analogue of FR235222, sensitizes promyelocytic leukaemia
U937 cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. Anticancer Res. 30:887–894.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Fuentes-Baile M, García-Morales P,
Pérez-Valenciano E, Mata-Balaguer T, Menéndez-Gutiérrez MP, de Juan
Romero C, Rodríguez-Lescure Á, Martín-Orozco E, Mallavia R, Barberá
VM and Saceda M: Insights into histone deacetylase
inhibitors-induced cell death in cancer cell lines. Biomed
Pharmacother. 191:1185412025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Li Z, Qiu H, Lu W, Duan N, Fan S, Zhou R,
Li X, Zhang H, Liu N and Yang F: Design and synthesis of
thiazole-based hydroxamate histone deacetylase inhibitors with
potent antitumor efficacy by inducing apoptosis, pyroptosis and
cell cycle arrest. Sci Rep. 15:245892025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Aroonthongsawat P, Manocheewa S, Srisawat
C, Punnakitikashem P and Suwanwong Y: Enhancement of the in vitro
anti-leukemic effect of the histone deacetylase inhibitor
romidepsin using Poly-(D, L-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles as
a drug carrier. Eur J Pharm Sci. 207:1070432025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Pal I, Illendula A, Joyner AM, Manavalan
JS, Deddens TM, Sabzevari A, Damera DP, Zuberi S, Marchi E, Fox TE,
et al: Nanoromidepsin, a polymer nanoparticle of the HDAC
inhibitor, improves safety and efficacy in models of T-cell
lymphoma. Blood. Sep 2–2025.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Xiao W, Jiang W, Chen Z, Huang Y, Mao J,
Zheng W, Hu Y and Shi J: Advance in peptide-based drug development:
delivery platforms, therapeutics and vaccines. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 10:742025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Rizwan A, Aqeel A and Farooqi H: Decoding
HDACs and its inhibitors-artificial intelligence assisted smart
software based super computational modelling technology in
targeting cancer and neurological disorders of the brain. Netw
Modeling Anal Health Inform Bioinform. 14:1042025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Wang D, Li W, Zhao R, Chen L, Liu N, Tian
Y, Zhao H, Xie M, Lu F, Fang Q, et al: Stabilized peptide HDAC
inhibitors derived from HDAC1 substrate H3K56 for the treatment of
cancer stem-like cells in vivo. Cancer Res. 79:1769–1783. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|