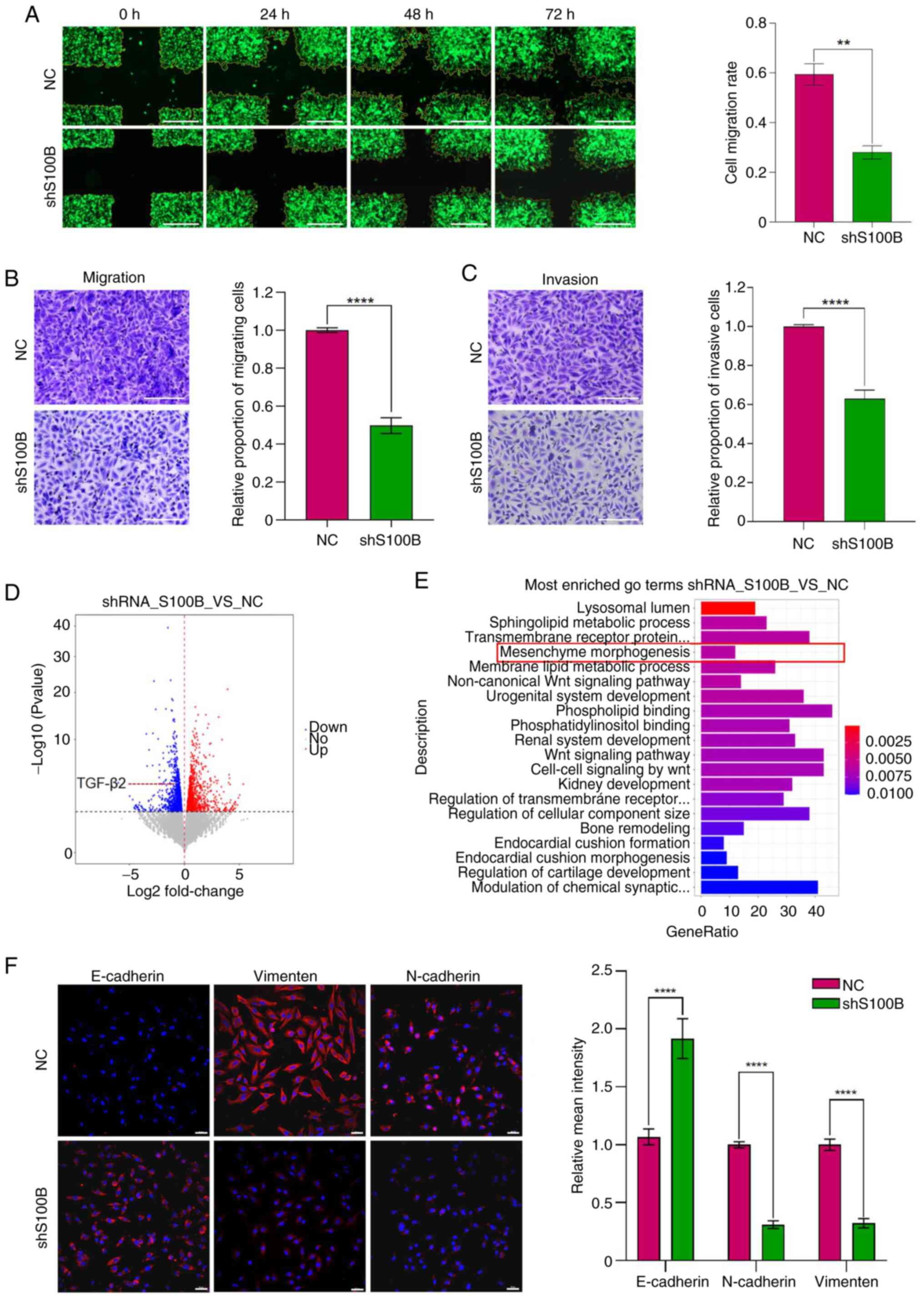
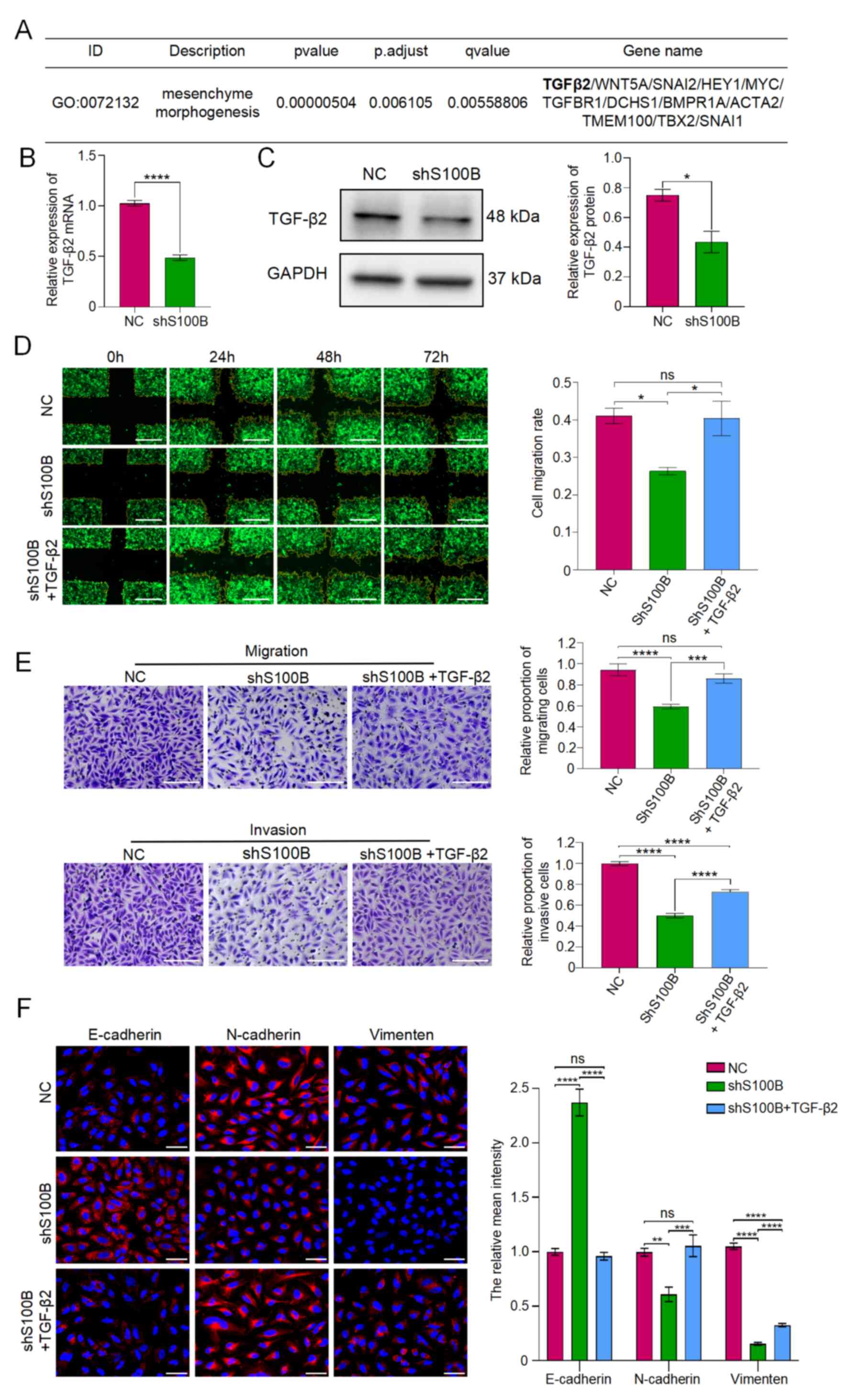
|
1
|
Tan AC, Ashley DM, López GY, Malinzak M,
Friedman HS and Khasraw M: Management of glioblastoma: State of the
art and future directions. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:299–312.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Louis DN, Perry A, Wesseling P, Brat DJ,
Cree IA, Figarella-Branger D, Hawkins C, Ng HK, Pfister SM,
Reifenberger G, et al: The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the
central nervous system: A summary. Neuro Oncol. 23:1231–1251. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sahm F, Capper D, Jeibmann A, Habel A,
Paulus W, Troost D and von Deimling A: Addressing diffuse glioma as
a systemic brain disease with single-cell analysis. Arch Neurol.
69:523–526. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Omuro A and DeAngelis LM: Glioblastoma and
other malignant gliomas: A clinical review. JAMA. 310:1842–1850.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Alexander BM and Cloughesy TF: Adult
glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 35:2402–2409. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
McKinnon C, Nandhabalan M, Murray SA and
Plaha P: Glioblastoma: Clinical presentation, diagnosis, and
management. BMJ. 374:n15602021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Donato R, Cannon BR, Sorci G, Riuzzi F,
Hsu K, Weber DJ and Geczy CL: Functions of S100 proteins. Curr Mol
Med. 13:24–57. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schafer BW and Heizmann CW: The S100
family of EF-hand calcium-binding proteins: Functions and
pathology. Trends Biochem Sci. 21:134–140. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Donato R, Sorci G, Riuzzi F, Arcuri C,
Bianchi R, Brozzi F, Tubaro C and Giambanco I: S100B's double life:
intracellular regulator and extracellular signal. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1793:1008–1022. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xiong TF, Pan FQ and Li D: Expression and
clinical significance of S100 family genes in patients with
melanoma. Melanoma Res. 29:23–29. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yen MC, Huang YC, Kan JY, Kuo PL, Hou MF
and Hsu YL: S100B expression in breast cancer as a predictive
marker for cancer metastasis. Int J Oncol. 52:433–440.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang T, Cheng J, Yang Y, Qi W, Zhao Y,
Long H, Xie R and Zhu B: S100B mediates stemness of ovarian cancer
stem-like cells through inhibiting p53. Stem Cells. 35:325–336.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin J, Yang Q, Yan Z, Markowitz J, Wilder
PT, Carrier F and Weber DJ: Inhibiting S100B restores p53 levels in
primary malignant melanoma cancer cells. J Biol Chem.
279:34071–34077. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Roy Choudhury S, Heflin B, Taylor E, Koss
B, Avaritt NL and Tackett AJ: CRISPR/dCas9-KRAB-mediated
suppression of S100b restores p53-mediated apoptosis in melanoma
cells. Cells. 12:7302023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu H, Li W, Yue H, Bai Y, Li J, Lu X and
Wang J: S100B induces angiogenesis via the clathrin/FOXO1/β-catenin
signaling pathway and contributes to bevacizumab resistance in
epithelial ovarian cancer. J Adv Res. May 31–2025.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun D, Wang J, Han Y, Dong X, Ge J, Zheng
R, Shi X, Wang B, Li Z, Ren P, et al: TISCH: A comprehensive web
resource enabling interactive single-cell transcriptome
visualization of tumor microenvironment. Nucleic Acids Res. 49(D1):
D1420–D1430. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide
for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wen PY and Kesari S: Malignant gliomas in
adults. N Engl J Med. 359:492–507. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent
MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Allgeier A, Fisher B,
Belanger K, et al: Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and
adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in
glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of
the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 10:459–466. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, de Blank PM,
Finlay JL, Gurney JG, McKean-Cowdin R, Stearns DS, Wolff JE, Liu M,
Wolinsky Y, et al: American brain tumor association adolescent and
young adult primary brain and central nervous system tumors
diagnosed in the United States in 2008–2012. Neuro Oncol. 18 (Suppl
1):i1–i50. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Witthayanuwat S, Pesee M, Supaadirek C,
Supakalin N, Thamronganantasakul K and Krusun S: Survival analysis
of glioblastoma multiforme. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 19:2613–2617.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tan B, Shen L, Yang K, Huang D, Li X, Li
Y, Zhao L, Chen J, Yi Q, Xu H, et al: C6 glioma-conditioned medium
induces malignant transformation of mesenchymal stem cells:
Possible role of S100B/RAGE pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
495:78–85. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hu Y, Song J, Wang Z, Kan J, Ge Y, Wang D,
Zhang R, Zhang W and Liu Y: A novel S100 family-based signature
associated with prognosis and immune microenvironment in glioma. J
Oncol. 2021:35865892021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang H, Zhang L, Zhang IY, Chen X, Da
Fonseca A, Wu S, Ren H, Badie S, Sadeghi S, Ouyang M, et al: S100B
promotes glioma growth through chemoattraction of myeloid-derived
macrophages. Clin Cancer Res. 19:3764–3775. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gao H, Zhang IY, Zhang L, Song Y, Liu S,
Ren H, Liu H, Zhou H, Su Y, Yang Y and Badie B: S100B suppression
alters polarization of infiltrating myeloid-derived cells in
gliomas and inhibits tumor growth. Cancer Lett. 439:91–100. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kahlert UD, Joseph JV and Kruyt FAE: EMT-
and MET-related processes in nonepithelial tumors: Importance for
disease progression, prognosis, and therapeutic opportunities. Mol
Oncol. 11:860–877. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xie C, Zhou M, Lin J, Wu Z, Ding S, Luo J,
Zhan Z, Cai Y, Xue S and Song Y: EEF1D promotes glioma
proliferation, migration, and invasion through EMT and PI3K/Akt
pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2020:78047062020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dongre A and Weinberg RA: New insights
into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
implications for cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:69–84. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Miettinen PJ, Ebner R, Lopez AR and
Derynck R: TGF-beta induced transdifferentiation of mammary
epithelial cells to mesenchymal cells: Involvement of type I
receptors. J Cell Biol. 127:2021–2036. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Piek E, Moustakas A, Kurisaki A, Heldin CH
and ten Dijke P: TGF-(beta) type I receptor/ALK-5 and Smad proteins
mediate epithelial to mesenchymal transdifferentiation in NMuMG
breast epithelial cells. J Cell Sci. 112:4557–4568. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Valcourt U, Kowanetz M, Niimi H, Heldin CH
and Moustakas A: TGF-beta and the Smad signaling pathway support
transcriptomic reprogramming during epithelial-mesenchymal cell
transition. Mol Biol Cell. 16:1987–2002. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gao J, Zhu Y, Nilsson M and Sundfeldt K:
TGF-β isoforms induce EMT independent migration of ovarian cancer
cells. Cancer Cell Int. 14:722014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Su J, Morgani SM, David CJ, Wang Q, Er EE,
Huang YH, Basnet H, Zou Y, Shu W, Soni RK, et al: TGF-beta
orchestrates fibrogenic and developmental EMTs via the RAS effector
RREB1. Nature. 577:566–571. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu J, Lamouille S and Derynck R:
TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res.
19:156–172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Leung DHL, Phon BWS, Sivalingam M,
Radhakrishnan AK and Kamarudin MNA: Regulation of EMT markers,
extracellular matrix, and associated signalling pathways by long
non-coding RNAs in glioblastoma mesenchymal transition: A scoping
review. Biology (Basel). 12:8182023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Joseph JV, Conroy S, Tomar T,
Eggens-Meijer E, Bhat K, Copray S, Walenkamp AM, Boddeke E,
Balasubramanyian V, Wagemakers M, et al: TGF-β is an inducer of
ZEB1-dependent mesenchymal transdifferentiation in glioblastoma
that is associated with tumor invasion. Cell Death Dis.
5:e14432014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen J, Hu J, Li X, Zong S, Zhang G, Guo Z
and Jing Z: Enhydrin suppresses the malignant phenotype of GBM via
Jun/Smad7/TGF-β1 signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol.
226:1163802024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Corbet C, Bastien E, Santiago de Jesus JP,
Dierge E, Martherus R, Vander Linden C, Doix B, Degavre C, Guilbaud
C, Petit L, et al: TGFβ2-induced formation of lipid droplets
supports acidosis-driven EMT and the metastatic spreading of cancer
cells. Nat Commun. 11:4542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Song C and Zhou C: HOXA10 mediates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition to promote gastric cancer
metastasis partly via modulation of TGFB2/Smad/METTL3 signaling
axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 40:622021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Almstedt E, Rosén E, Gloger M, Stockgard
R, Hekmati N, Koltowska K, Krona C and Nelander S: Real-time
evaluation of glioblastoma growth in patient-specific zebrafish
xenografts. Neuro Oncol. 24:726–738. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Larsson S, Kettunen P and Carén H:
Orthotopic transplantation of human paediatric high-grade glioma in
zebrafish larvae. Brain Sci. 12:6252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|