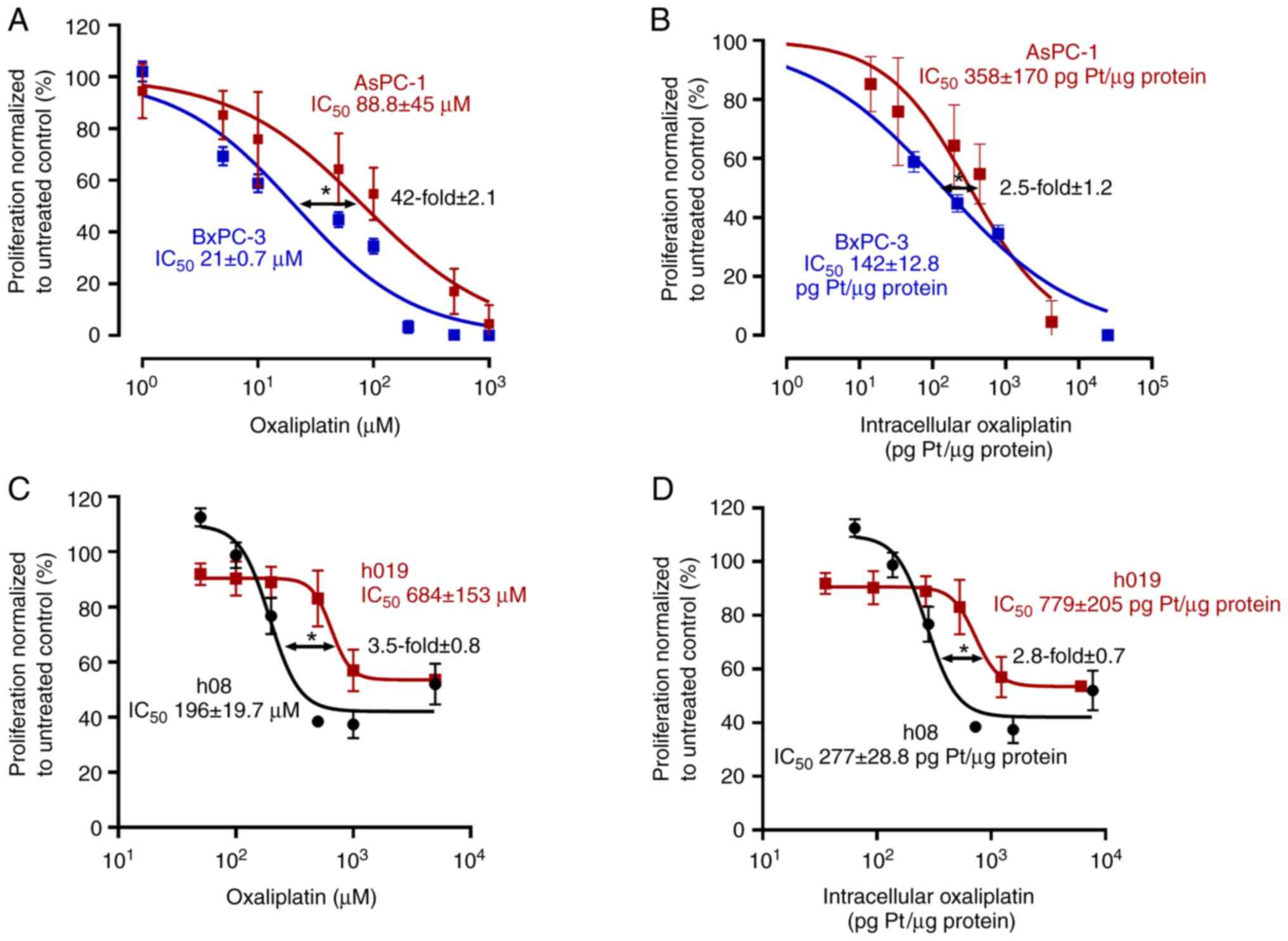
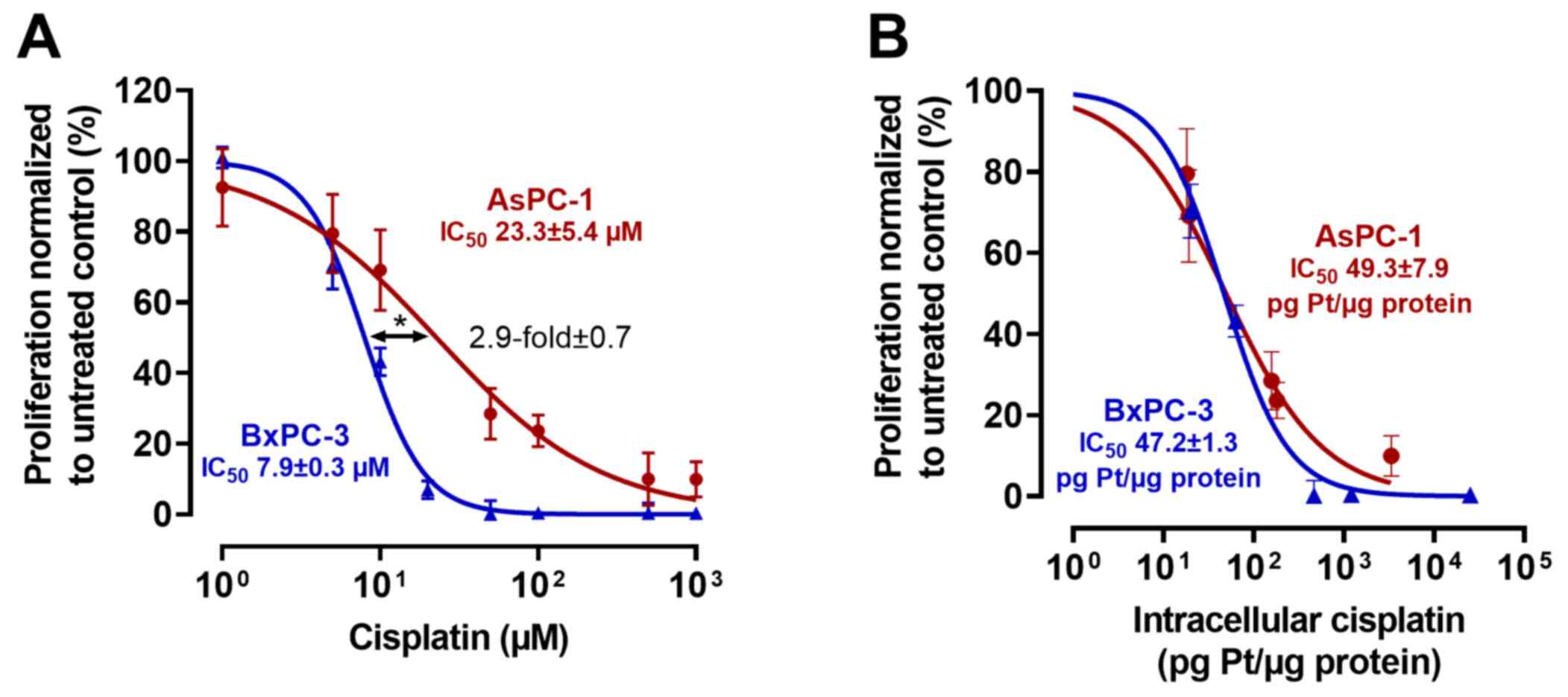
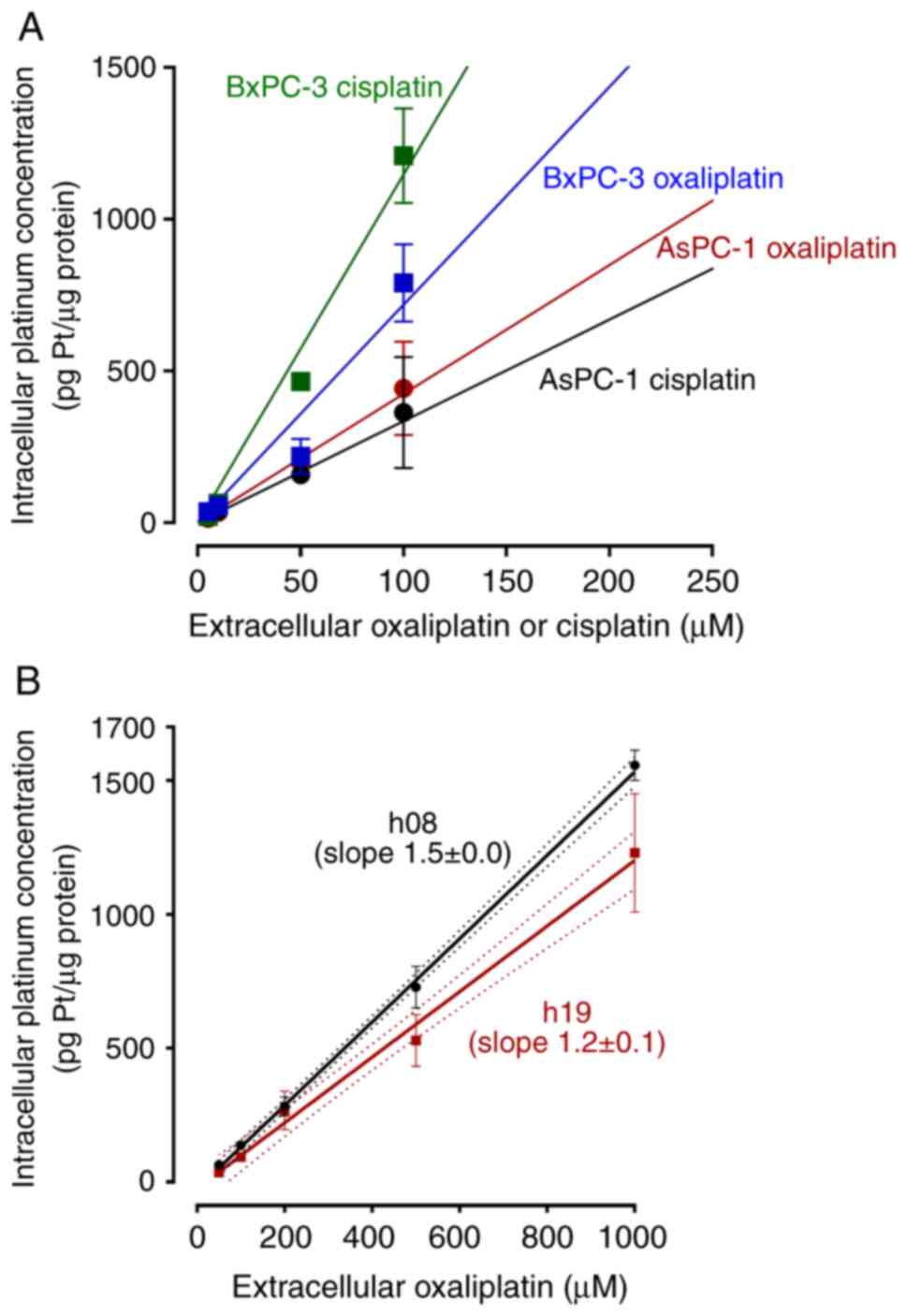
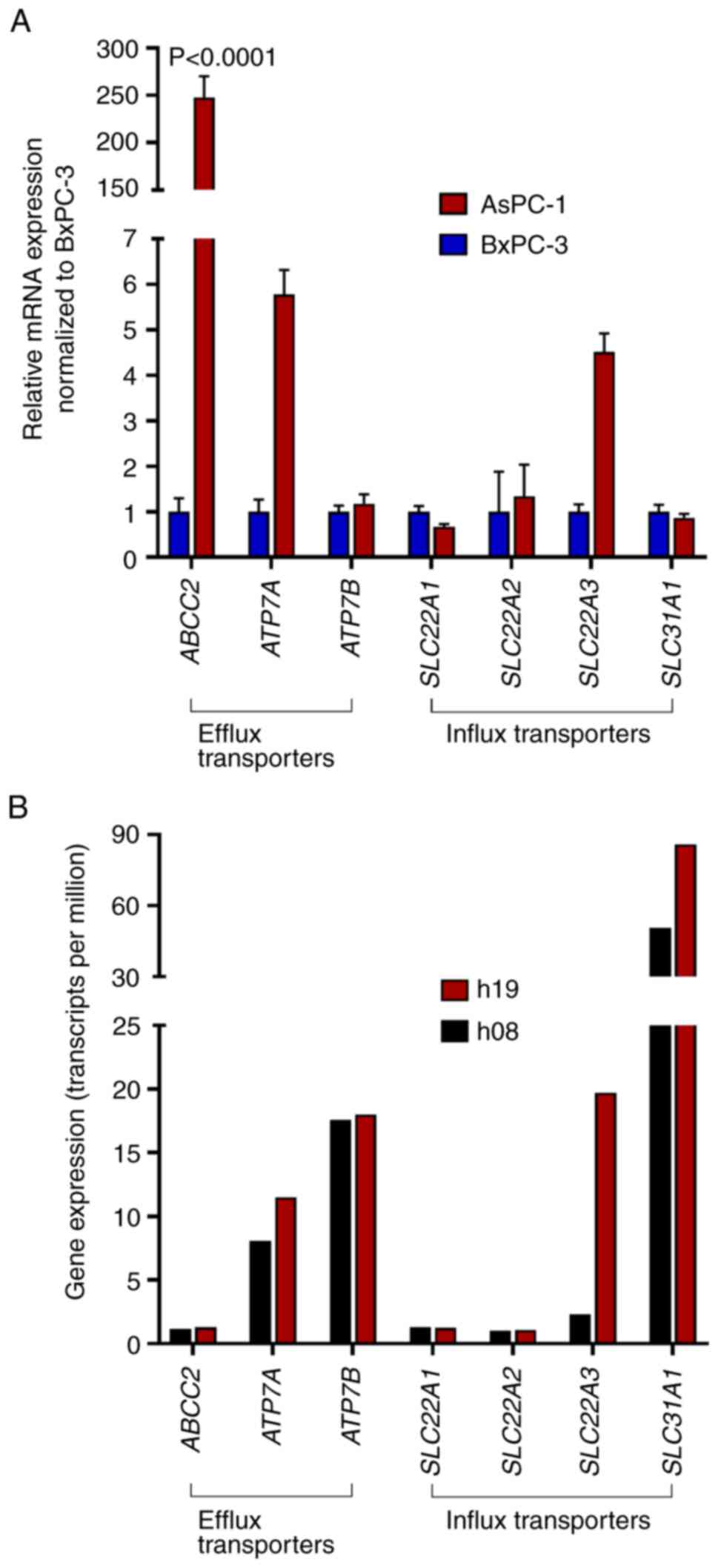
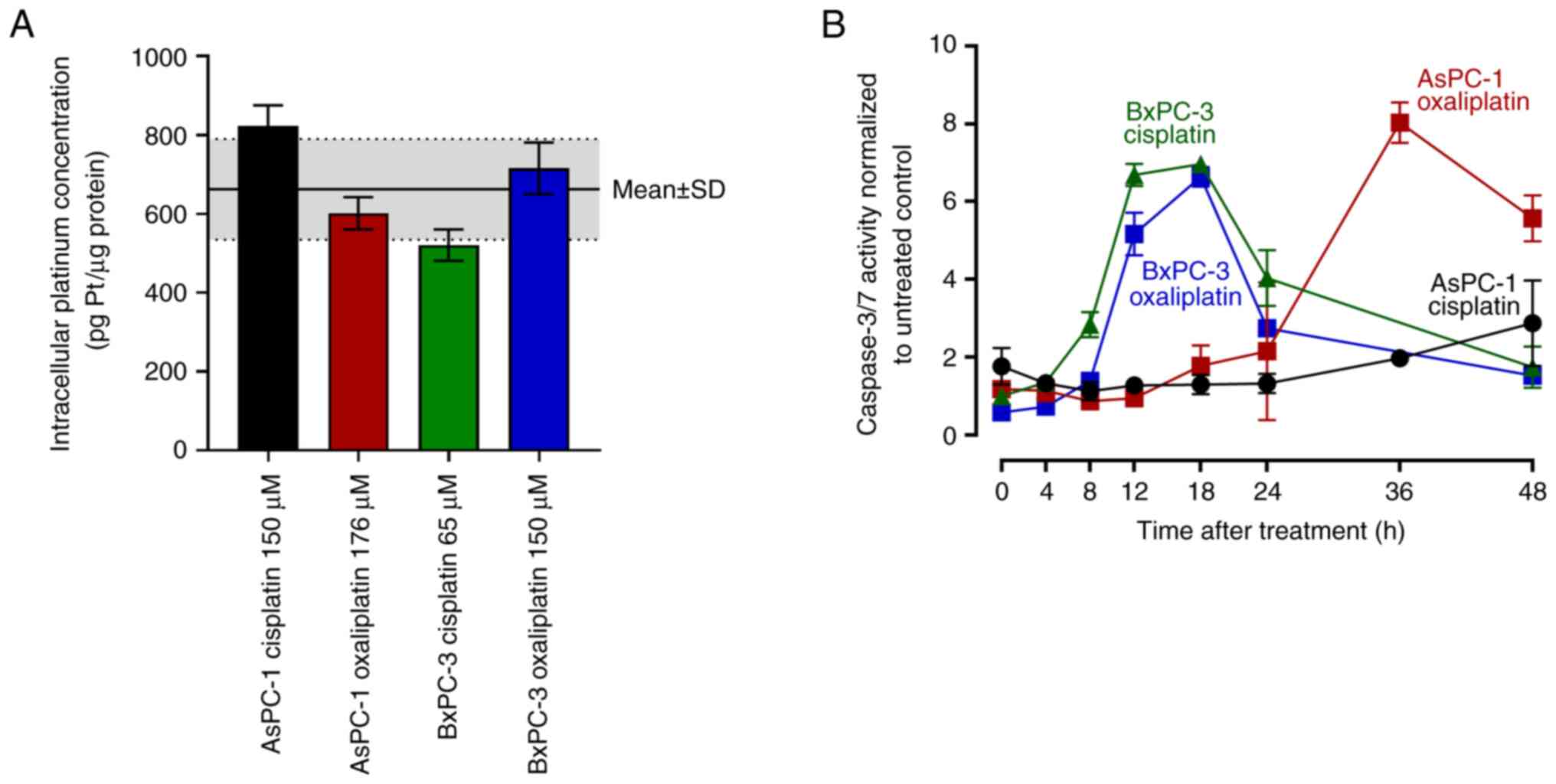
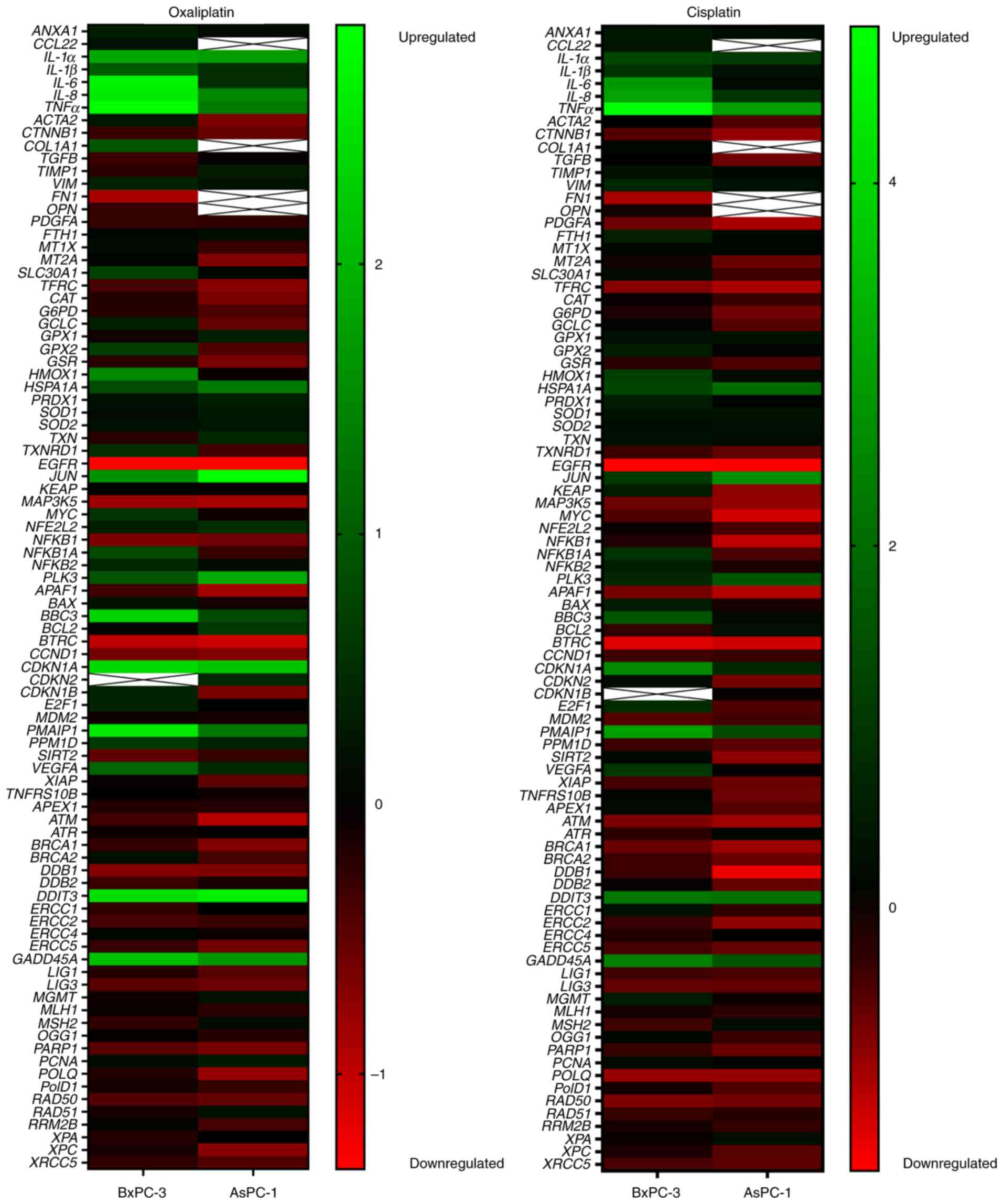
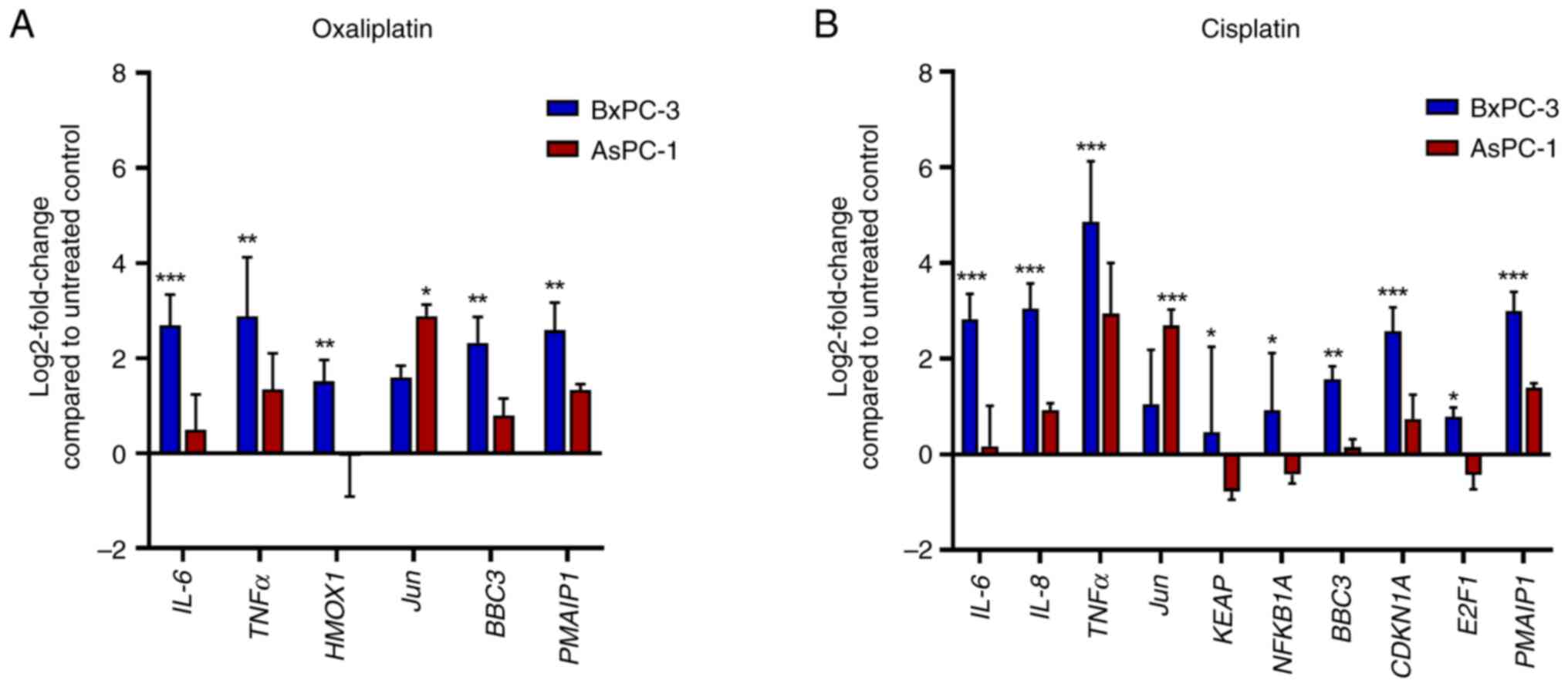
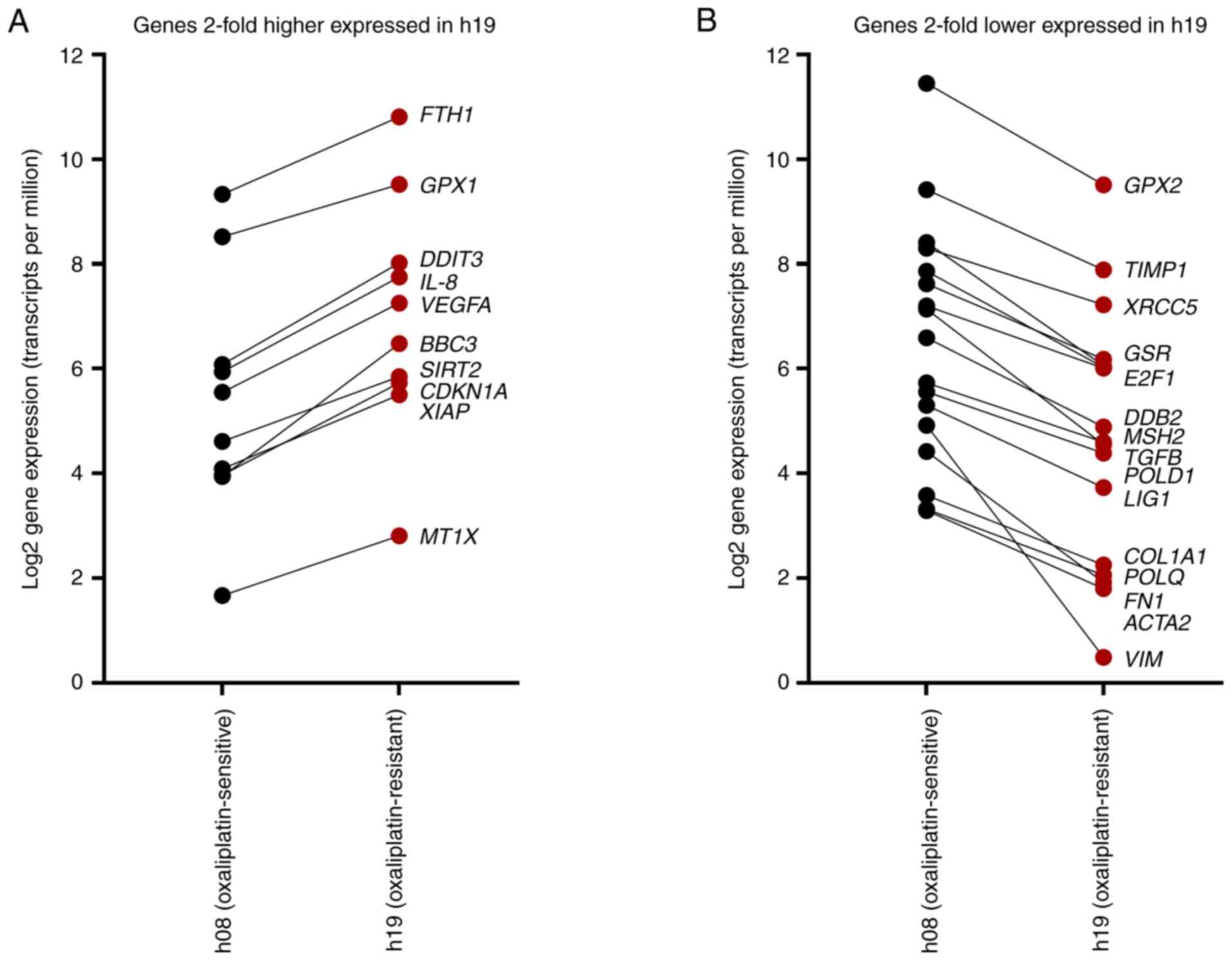
|
1
|
Neoptolemos JP, Kleeff J, Michl P,
Costello E, Greenhalf W and Palmer DH: Therapeutic developments in
pancreatic cancer: Current and future perspectives. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15:333–348. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hu ZI and O'Reilly EM: Therapeutic
developments in pancreatic cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
21:7–24. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gresham GK, Wells GA, Gill S, Cameron C
and Jonker DJ: Chemotherapy regimens for advanced pancreatic
cancer: A systematic review and network Meta-analysis. BMC Cancer.
27:4712014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chan K, Shah K, Lien K, Coyle D, Lam H and
Ko YJ: A Bayesian meta–analysis of multiple treatment comparisons
of systemic regimens for advanced pancreatic cancer. PLoS One.
9:e1087492014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Springfeld C, Jäger D, Büchler MW, Strobel
O, Hackert T, Palmer DH and Neoptolemos JP: Chemotherapy for
pancreatic cancer. Presse Med. 48:e159–e174. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Martinez-Balibrea E, Martínez-Cardús A,
Ginés A, Ruiz de Porras V, Moutinho C, Layos L, Manzano JL, Bugés
C, Bystrup S, Esteller M and Abad A: Tumor-related molecular
mechanisms of oxaliplatin resistance. Mol Cancer Ther.
14:1767–1776. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Burger H, Loos WJ, Eechoute K, Verweij J,
Mathijssen RH and Wiemer EA: Drug transporters of Platinum-based
anticancer agents and their clinical significance. Drug Resist
Updat. 14:22–34. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Buß I, Hamacher A, Sarin N, Kassack MU and
Kalayda GV: Relevance of copper transporter 1 and organic cation
transporters 1–3 for oxaliplatin uptake and drug resistance in
colorectal cancer cells. Metallomics. 10:414–425. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Martin LP, Hamilton TC and Schilder RJ:
Platinum resistance: The role of DNA repair pathways. Clin Cancer
Res. 14:1291–1295. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Grierson PM, Dodhiawala PB, Cheng Y, Chen
TH, Khawar IA, Wei Q, Zhang D, Li L, Herndon J, Monahan JB, et al:
The MK2/Hsp27 axis is a major survival mechanism for pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma under genotoxic stress. Sci Transl Med.
13:eabb54452021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Melisi D, Xia Q, Paradiso G, Ling J,
Moccia T, Carbone C, Budillon A, Abbruzzese JL and Chiao PJ:
Modulation of pancreatic cancer chemoresistance by inhibition of
TAK1. J Natl Cancer Inst. 103:1190–1204. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Muniz VP, Askeland RW, Zhang X, Reed SM,
Tompkins VS, Hagen J, McDowell BD, Button A, Smith BJ, Weydert JA,
et al: RABL6A promotes oxaliplatin resistance in tumor cells and is
a new marker of survival for resected pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma patients. Genes Cancer. 4:273–284. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jing W, Song N, Liu Y, Qu X, Hou K, Yang X
and Che X: DNA methyltransferase 3a modulates chemosensitivity to
gemcitabine and oxaliplatin via CHK1 and AKT in p53-deficient
pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 17:117–124. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pishvaian MJ, Biankin AV, Bailey P, Chang
DK, Laheru D, Wolfgang CL and Brody JR: BRCA2 secondary
mutation-mediated resistance to platinum and PARP Inhibitor-based
therapy in pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 116:1021–1026. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lal S, Burkhart RA, Beeharry N,
Bhattacharjee V, Londin ER, Cozzitorto JA, Romeo C, Jimbo M, Norris
ZA, Yeo CJ, et al: HuR posttranscriptionally regulates WEE1:
Implications for the DNA damage response in pancreatic cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 74:1128–1140. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xia R, Hu C, Ye Y, Zhang X, Li T, He R,
Zheng S, Wen X and Chen R: HNF1A regulates oxaliplatin resistance
in pancreatic cancer by targeting 53BP1. Int J Oncol. 62:452023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
An J, Kurilov R, Peccerella T, Bergmann F,
Edderkaoui M, Lim A, Zhou X, Pfütze K, Schulz A, Wolf S, et al:
Metavert synergises with standard cytotoxics in human PDAC
organoids and is associated with transcriptomic signatures of
therapeutic response. Transl Oncol. 49:1021092024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Peters T, Lindenmaier H, Haefeli WE and
Weiss J: Interaction of the mitotic kinesin Eg5 inhibitor monastrol
with P-glycoprotein. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol.
372:291–299. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fischer BM, Neumann D, Piberger AL, Risnes
SF, Köberle B and Hartwig A: Use of high-throughput RT-qPCR to
assess modulations of gene expression profiles related to genomic
stability and interactions by cadmium. Arch Toxicol. 90:2745–2761.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rose F, Köberle B, Honnen S, Bay C,
Burhenne J, Weiss J, Haefeli WE and Theile D: RNA is a
pro-apoptotic target of cisplatin in cancer cell lines and C.
elegans. Biomed Pharmacother. 173:1164502024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pfaffl MW: A new mathematical model for
relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res.
29:e452001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Albermann N, Schmitz-Winnenthal FH,
Z'graggen K, Volk C, Hoffmann MM, Haefeli WE and Weiss J:
Expression of the drug transporters MDR1/ABCB1, MRP1/ABCC1,
MRP2/ABCC2, BCRP/ABCG2, and PXR in peripheral blood mononuclear
cells and their relationship with the expression in intestine and
liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 70:949–958. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Weiss J, Herzog M and Haefeli WE:
Differential modulation of the expression of important drug
metabolising enzymes and transporters by endothelin-1 receptor
antagonists ambrisentan and bosentan in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol.
660:298–304. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Theile D, Ketabi-Kiyanvash N, Herold-Mende
C, Dyckhoff G, Efferth T, Bertholet V, Haefeli WE and Weiss J:
Evaluation of drug transporters' significance for multidrug
resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck.
33:959–968. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F,
Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A and Speleman F: Accurate
normalization of Real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric
averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol.
3:RESEARCH00342002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kuo SH, Yang SH, Wei MF, Lee HW, Tien YW,
Cheng AL and Yeh KH: Contribution of nuclear BCL10 expression to
tumor progression and poor prognosis of advanced and/or metastatic
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by activating NF-κB-related
signaling. Cancer Cell Int. 21:4362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee JH, Lee SH, Lee SK, Choi JH, Lim S,
Kim MS, Lee KM, Lee MW, Ku JL, Kim DH, et al: Antiproliferative
activity of krukovine by regulating transmembrane protein 139
(TMEM139) in Oxaliplatin-resistant pancreatic cancer cells. Cancers
(Basel). 15:26422023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Noordhuis P, Laan AC, van de Born K,
Honeywell RJ and Peters GJ: Coexisting molecular determinants of
acquired oxaliplatin resistance in human colorectal and ovarian
cancer cell lines. Int J Mol Sci. 20:36192019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Biswas R, Bugde P, He J, Merien F, Lu J,
Liu DX, Myint K, Liu J, McKeage M and Li Y: Transport-mediated
oxaliplatin resistance associated with endogenous overexpression of
MRP2 in Caco-2 and PANC-1 Cells. Cancers (Basel). 11:13302019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Myint K, Biswas R, Li Y, Jong N, Jamieson
S, Liu J, Han C, Squire C, Merien F, Lu J, et al: Identification of
MRP2 as a targetable factor limiting oxaliplatin accumulation and
response in gastrointestinal cancer. Sci Rep. 9:22452019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mohelnikova-Duchonova B, Brynychova V,
Hlavac V, Kocik M, Oliverius M, Hlavsa J, Honsova E, Mazanec J,
Kala Z, Melichar B and Soucek P: The association between the
expression of solute carrier transporters and the prognosis of
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 72:669–682. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cervenkova L, Vycital O, Bruha J,
Rosendorf J, Palek R, Liska V, Daum O, Mohelnikova-Duchonova B and
Soucek P: Protein expression of ABCC2 and SLC22A3 associates with
prognosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep. 9:197822019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Deer EL, González-Hernández J, Coursen JD,
Shea JE, Ngatia J, Scaife CL, Firpo MA and Mulvihill SJ: Phenotype
and genotype of pancreatic cancer cell lines. Pancreas. 39:425–435.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sugimoto H, Nakamura M, Yoda H, Hiraoka K,
Shinohara K, Sang M, Fujiwara K, Shimozato O, Nagase H and Ozaki T:
Silencing of RUNX2 enhances gemcitabine sensitivity of
p53-deficient human pancreatic cancer AsPC-1 cells through the
stimulation of TAp63-mediated cell death. Cell Death Dis.
6:e19142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Detjen KM, Farwig K, Welzel M, Wiedenmann
B and Rosewicz S: Interferon gamma inhibits growth of human
pancreatic carcinoma cells via caspase-1 dependent induction of
apoptosis. Gut. 49:251–262. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|