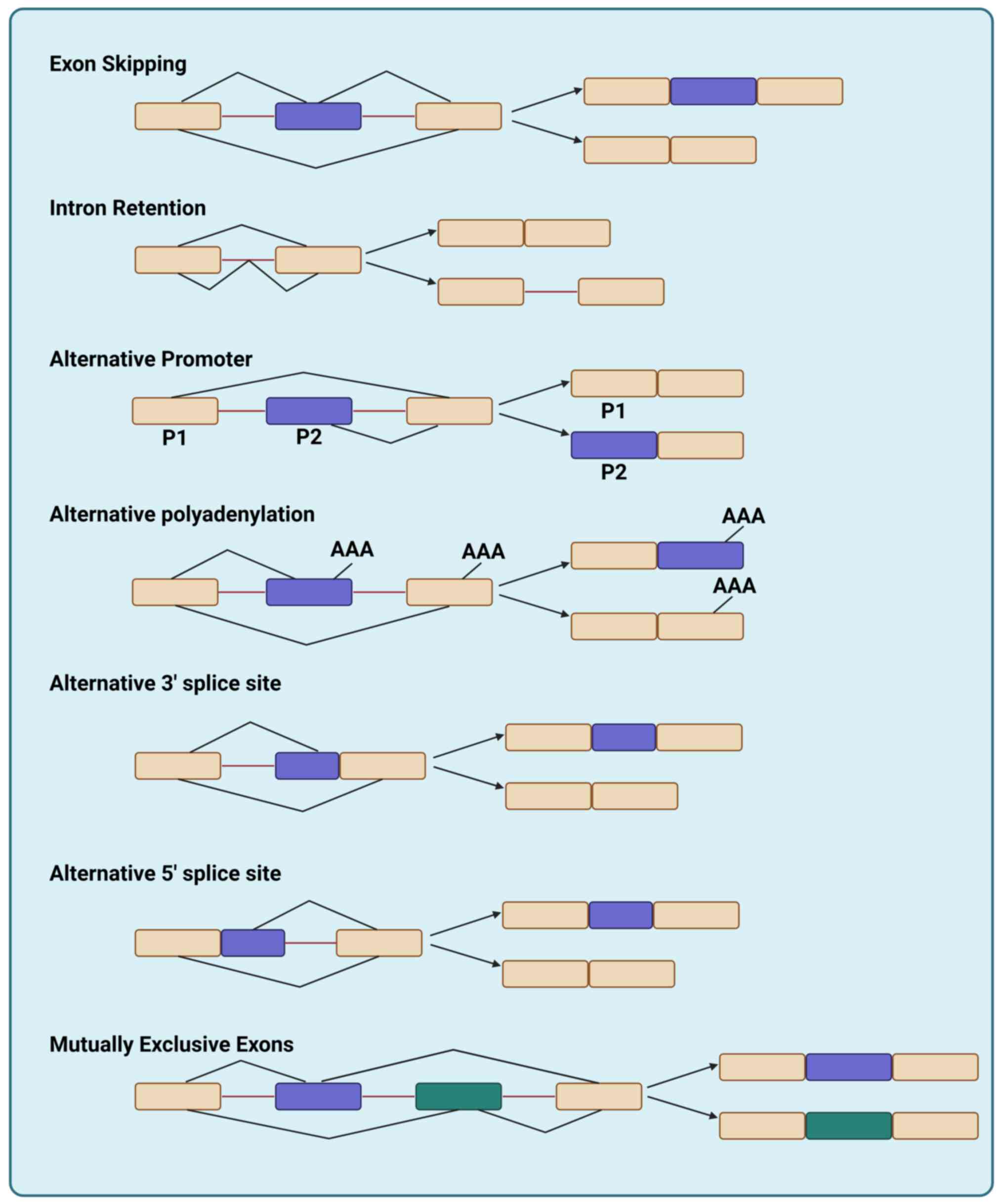
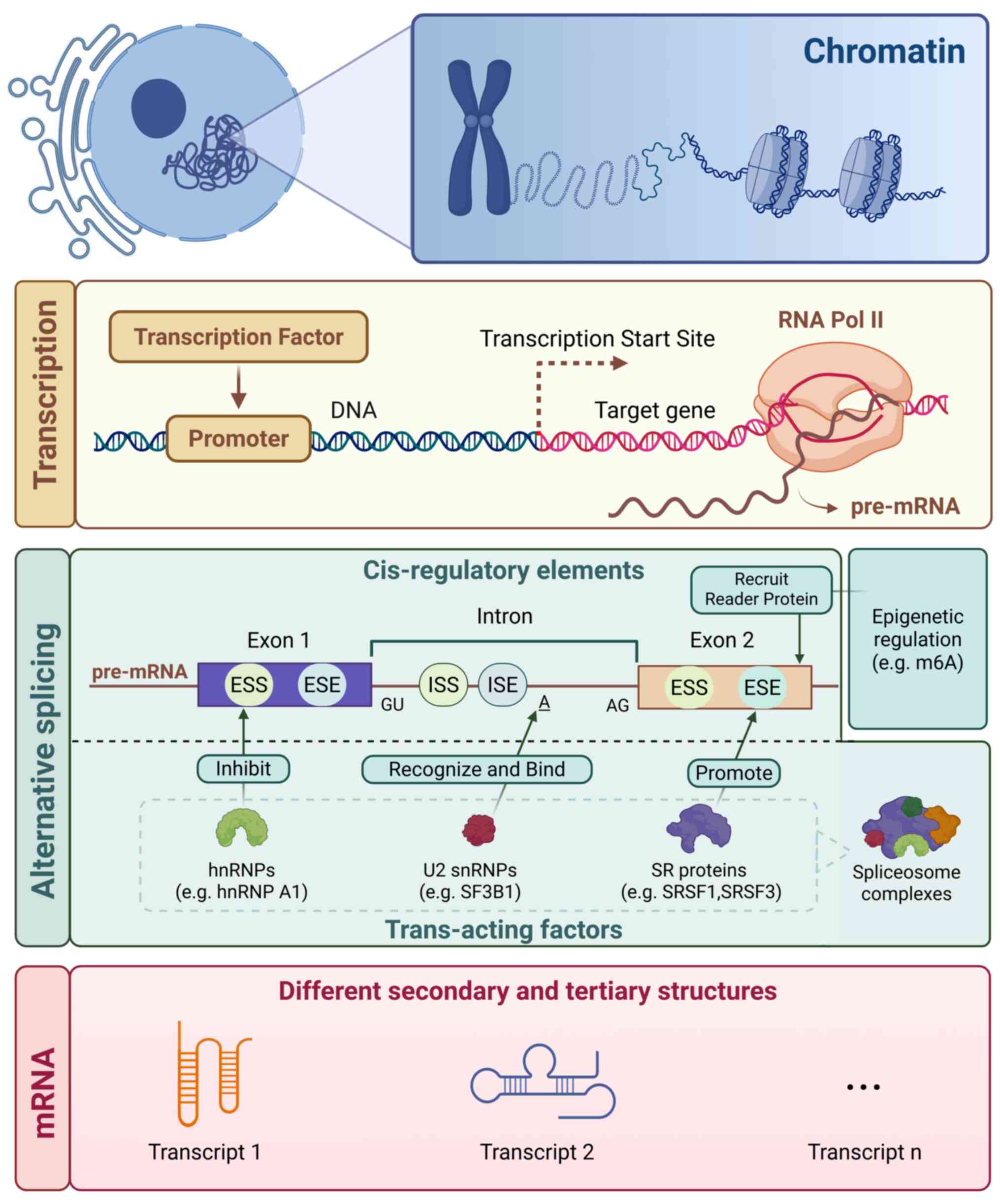
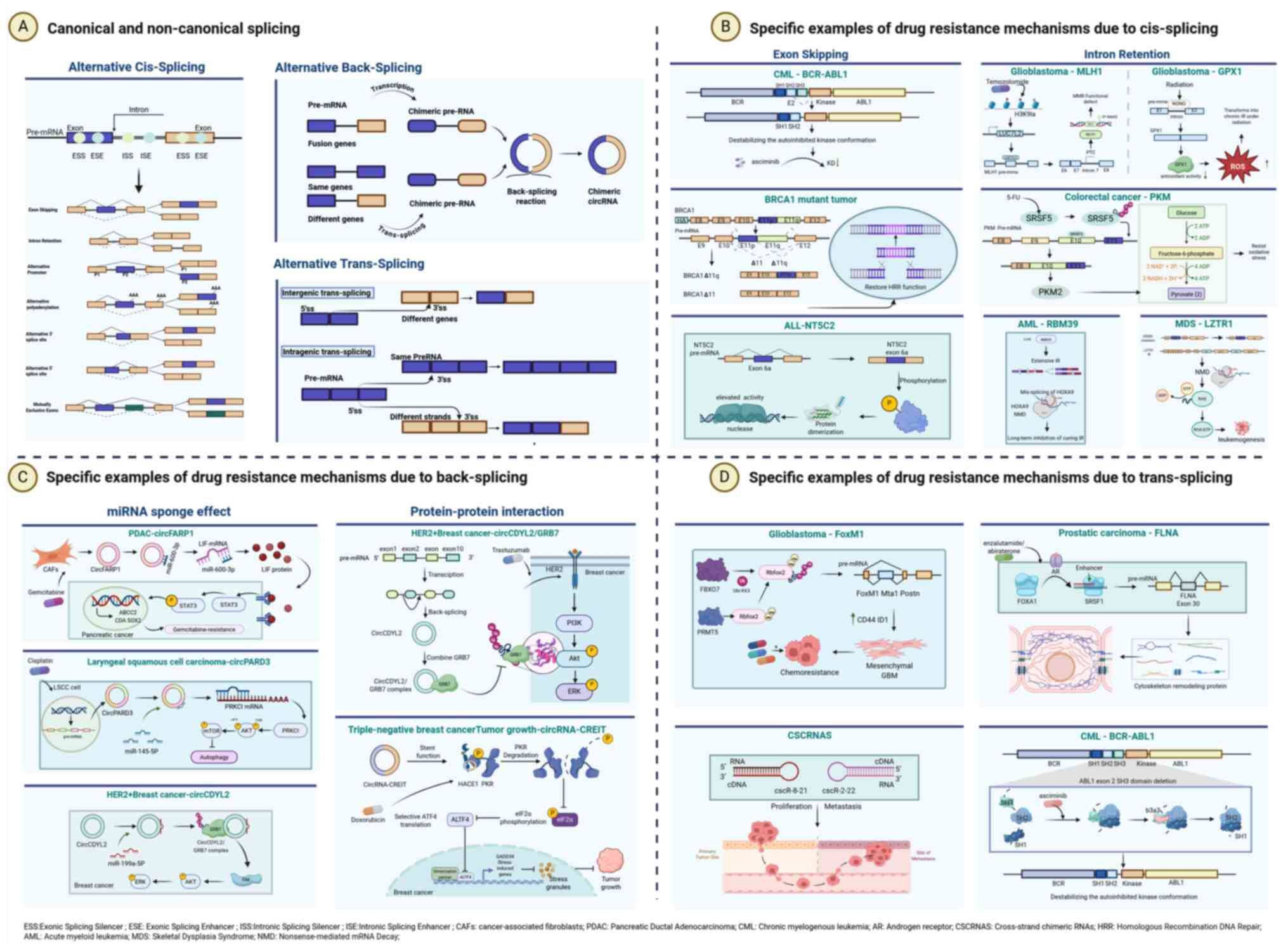
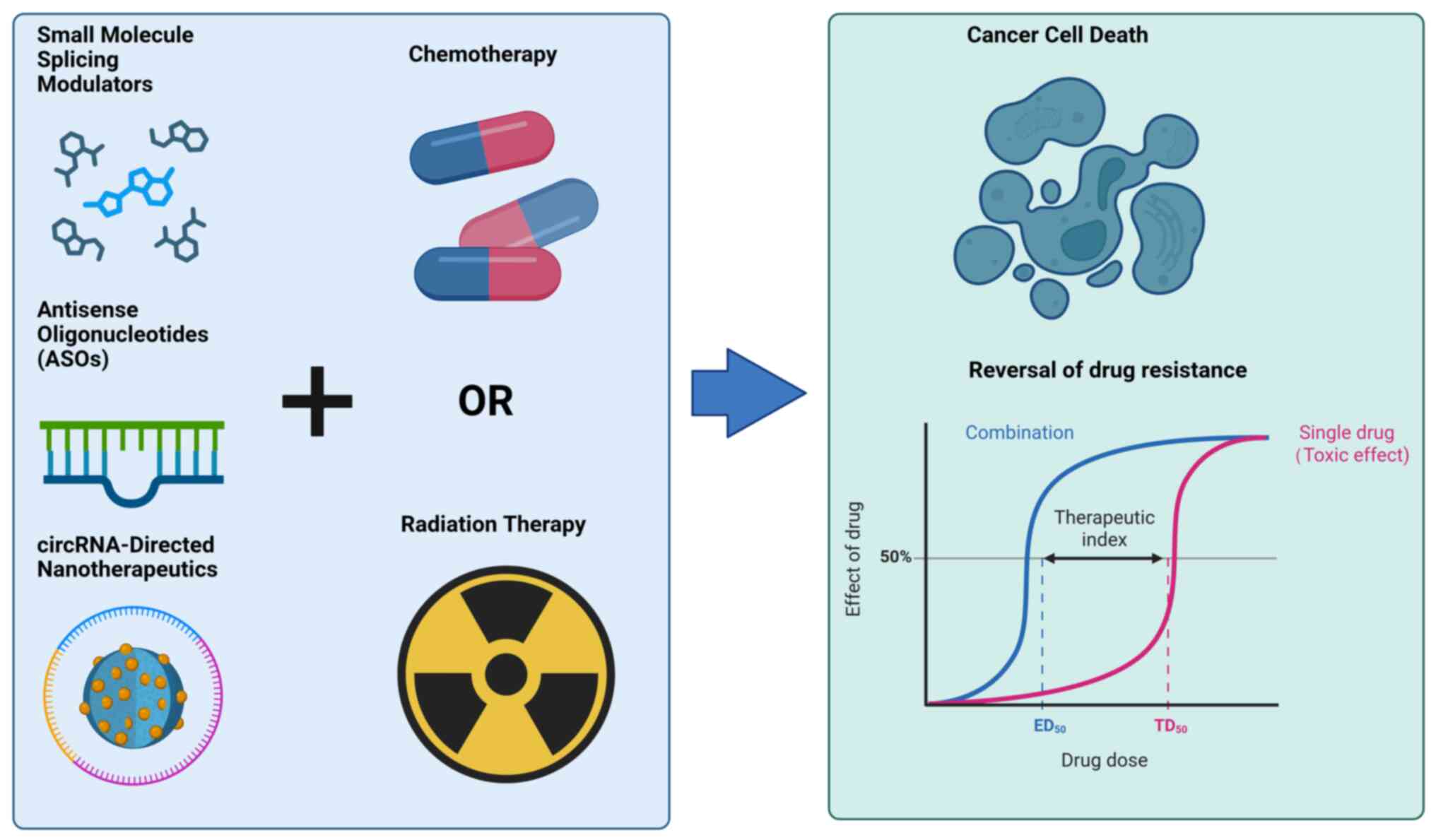
|
1
|
Yang Q, Zhao J, Zhang W, Chen D and Wang
Y: Aberrant alternative splicing in breast cancer. J Mol Cell Biol.
11:920–929. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Marasco LE and Kornblihtt AR: The
physiology of alternative splicing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
24:242–254. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li S, Chen Y, Xie Y, Zhan H, Zeng Y, Zeng
K, Wang L, Zhan Z, Li C, Zhao L, et al: FBXO7 confers mesenchymal
properties and chemoresistance in glioblastoma by controlling
Rbfox2-mediated alternative splicing. Adv Sci. 10:e23035612023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu M, Zhang S, Zhou H, Hu X, Li J, Fu B,
Wei M, Huang H and Wu H: The interplay between non-coding RNAs and
alternative splicing: From regulatory mechanism to therapeutic
implications in cancer. Theranostics. 13:2616–2631. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bauer M, Schöbel CM, Wickenhauser C,
Seliger B and Jasinski-Bergner S: Deciphering the role of
alternative splicing in neoplastic diseases for immune-oncological
therapies. Front Immunol. 15:13869932024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu X and Hurst LD: Determinants of the
usage of splice-associated cis-motifs predict the distribution of
human pathogenic SNPs. Mol Biol Evol. 33:518–529. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Venkataramany AS, Schieffer KM, Lee K,
Cottrell CE, Wang PY, Mardis ER, Cripe TP and Chandler DS:
Alternative RNA splicing defects in pediatric cancers: New insights
in tumorigenesis and potential therapeutic vulnerabilities. Ann
Oncol. 33:578–592. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ruta V, Naro C, Pieraccioli M, Leccese A,
Archibugi L, Cesari E, Panzeri V, Allgöwer C, Arcidiacono PG,
Falconi M, et al: An alternative splicing signature defines the
basal-like phenotype and predicts worse clinical outcome in
pancreatic cancer. Cell Rep Med. 5:1014112024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huan L, Guo T, Wu Y, Xu L, Huang S, Xu Y,
Liang L and He X: Hypoxia induced LUCAT1/PTBP1 axis modulates
cancer cell viability and chemotherapy response. Mol Cancer.
19:112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nesic K, Krais JJ, Wang Y, Vandenberg CJ,
Patel P, Cai KQ, Kwan T, Lieschke E, Ho GY, Barker HE, et al: BRCA1
secondary splice-site mutations drive exon-skipping and PARP
inhibitor resistance. Mol Cancer. 23:1582024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bradley RK and Anczuków O: RNA splicing
dysregulation and the hallmarks of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
23:135–155. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kahles A, Lehmann KV, Toussaint NC, Hüser
M, Stark SG, Sachsenberg T, Stegle O, Kohlbacher O and Sander C;
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network; Rätsch G, : Comprehensive
analysis of alternative splicing across tumors from 8,705 patients.
Cancer Cell. 34:211–224.e6. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li F, Xiong Y, Yang M, Chen P, Zhang J,
Wang Q, Xu M, Wang Y, He Z, Zhao X, et al: c-mpl-del, a c-mpl
alternative splicing isoform, promotes AMKL progression and
chemoresistance. Cell Death Dis. 13:8692022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhen N, Zhu J, Mao S, Zhang Q, Gu S, Ma J,
Zhang Y, Yin M, Li H, Huang N, et al: Alternative splicing of
lncRNAs from SNHG family alters snoRNA expression and induces
chemoresistance in hepatoblastoma. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol.
16:735–755. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ule J and Blencowe BJ: Alternative
splicing regulatory networks: functions, mechanisms, and evolution.
Mol Cell. 76:329–345. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Duan C, Zhang Y, Li L, Liu K, Yao X, Wu X,
Li B, Mao X, Wu H, Liu H, et al: Identification of alternative
splicing associated with clinical features: From pan-cancers to
genitourinary tumors. Front Oncol. 13:12499322023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim P, Yang M, Yiya K, Zhao W and Zhou X:
ExonSkipDB: Functional annotation of exon skipping event in human.
Nucleic Acids Res. 48:D896–D907. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mazieres J, Paik PK, Garassino MC, Le X,
Sakai H, Veillon R, Smit EF, Cortot AB, Raskin J, Viteri S, et al:
Tepotinib treatment in patients with MET exon 14-skipping non-small
cell lung cancer: Long-term follow-up of the VISION phase 2
nonrandomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 9:1260–1266. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mazieres J, Vioix H, Pfeiffer BM, Campden
RI, Chen Z, Heeg B and Cortot AB: MET exon 14 skipping in NSCLC: A
systematic literature review of epidemiology, clinical
characteristics, and outcomes. Clin Lung Cancer. 24:483–497. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen S, Yang C, Wang ZW, Hu JF, Pan JJ,
Liao CY, Zhang JQ, Chen JZ, Huang Y, Huang L, et al: CLK1/SRSF5
pathway induces aberrant exon skipping of METTL14 and cyclin L2 and
promotes growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer. J Hematol
Oncol. 14:602021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang K, Wei J, Zhang S, Fei L, Guo L, Liu
X, Ji Y, Chen W, Ciamponi FE, Chen W, et al: A chemical screen
identifies PRMT5 as a therapeutic vulnerability for
paclitaxel-resistant triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Chem Biol.
31:1942–1957.e6. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ambeskovic A, McCall MN, Woodsmith J, Juhl
H and Land H: Exon-skipping-based subtyping of colorectal cancers.
Gastroenterology. 167:1358–1370.e12. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hsu TYT, Simon LM, Neill NJ, Marcotte R,
Sayad A, Bland CS, Echeverria GV, Sun T, Kurley SJ, Tyagi S, et al:
The spliceosome is a therapeutic vulnerability in MYC-driven
cancer. Nature. 525:384–388. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Koedoot E, van Steijn E, Vermeer M,
González-Prieto R, Vertegaal ACO, Martens JWM, Le Dévédec SE and
van de Water B: Splicing factors control triple-negative breast
cancer cell mitosis through SUN2 interaction and sororin intron
retention. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 40:822021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Grabski DF, Broseus L, Kumari B, Rekosh D,
Hammarskjold M and Ritchie W: Intron retention and its impact on
gene expression and protein diversity: A review and a practical
guide. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 12:e16312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Monteuuis G, Schmitz U, Petrova V, Kearney
PS and Rasko JEJ: Holding on to junk bonds: intron retention in
cancer and therapy. Cancer Res. 81:779–789. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang M, Chen C, Lu Z, Cai Y, Li Y, Zhang
F, Liu Y, Chen S, Zhang H, Yang S, et al: Genetic control of
alternative splicing and its distinct role in colorectal cancer
mechanisms. Gastroenterology. 165:1151–1167. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang D, Hu Q, Liu X, Ji Y, Chao HP, Liu
Y, Tracz A, Kirk J, Buonamici S, Zhu P, et al: Intron retention is
a hallmark and spliceosome represents a therapeutic vulnerability
in aggressive prostate cancer. Nat Commun. 11:20892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Demircioğlu D, Cukuroglu E, Kindermans M,
Nandi T, Calabrese C, Fonseca NA, Kahles A, Lehmann KV, Stegle O,
Brazma A, et al: A pan-cancer transcriptome analysis reveals
pervasive regulation through alternative promoters. Cell.
178:1465–1477.e17. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Suzawa K, Offin M, Lu D, Kurzatkowski C,
Vojnic M, Smith RS, Sabari JK, Tai H, Mattar M, Khodos I, et al:
Activation of KRAS mediates resistance to targeted therapy in MET
exon 14-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
25:1248–1260. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lévesque E, Labriet A, Hovington H, Allain
ÉP, Melo-Garcia L, Rouleau M, Brisson H, Turcotte V, Caron P,
Villeneuve L, et al: Alternative promoters control
UGT2B17-dependent androgen catabolism in prostate cancer and its
influence on progression. Br J Cancer. 122:1068–1076. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nepal C and Andersen JB: Alternative
promoters in CpG depleted regions are prevalently associated with
epigenetic misregulation of liver cancer transcriptomes. Nat
Commun. 14:27122023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Veiga DFT, Nesta A, Zhao Y, Mays AD, Huynh
R, Rossi R, Wu TC, Palucka K, Anczukow O, Beck CR and Banchereau J:
A comprehensive long-read isoform analysis platform and sequencing
resource for breast cancer. Sci Adv. 8:eabg67112022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ryan M, Wong WC, Brown R, Akbani R, Su X,
Broom B, Melott J and Weinstein J: TCGASpliceSeq a compendium of
alternative mRNA splicing in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 44((D1)):
D1018–D1022. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rogalska ME, Mancini E, Bonnal S, Gohr A,
Dunyak BM, Arecco N, Smith PG, Vaillancourt FH and Valcárcel J:
Transcriptome-wide splicing network reveals specialized regulatory
functions of the core spliceosome. Science. 386:551–560. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Torres-Diz M, Reglero C, Falkenstein CD,
Castro A, Hayer KE, Radens CM, Quesnel-Vallières M, Ang Z, Sehgal
P, Li MM, et al: An alternatively spliced gain-of-function NT5C2
isoform contributes to chemoresistance in acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Cancer Res. 84:3327–3336. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lin CC, Chang TC, Wang Y, Guo L, Gao Y,
Bikorimana E, Lemoff A, Fang YV, Zhang H, Zhang Y, et al: PRMT5 is
an actionable therapeutic target in CDK4/6 inhibitor-resistant
ER+/RB-deficient breast cancer. Nat Commun. 15:22872024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sun Q, Han Y, He J, Wang J, Ma X, Ning Q,
Zhao Q, Jin Q, Yang L, Li S, et al: Long-read sequencing reveals
the landscape of aberrant alternative splicing and novel
therapeutic target in colorectal cancer. Genome Med. 15:762023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Song X, Tiek D, Miki S, Huang T, Lu M,
Goenka A, Iglesia R, Yu X, Wu R, Walker M, et al: RNA splicing
analysis deciphers developmental hierarchies and reveals
therapeutic targets in adult glioma. J Clin Invest.
134:e1737892024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sciarrillo R, Wojtuszkiewicz A, Assaraf
YG, Jansen G, Kaspers GJL, Giovannetti E and Cloos J: The role of
alternative splicing in cancer: From oncogenesis to drug
resistance. Drug Resist Updat. 53:1007282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Baralle FE and Giudice J: Alternative
splicing as a regulator of development and tissue identity. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 18:437–451. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dou Z, Zhao D, Chen X, Xu C, Jin X, Zhang
X, Wang Y, Xie X, Li Q, Di C and Zhang H: Aberrant bcl-x splicing
in cancer: From molecular mechanism to therapeutic modulation. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 40:1942021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Preissl S, Gaulton KJ and Ren B:
Characterizing cis-regulatory elements using single-cell
epigenomics. Nat Rev Genet. 24:21–43. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Soni K, Jagtap PKA, Martínez-Lumbreras S,
Bonnal S, Geerlof A, Stehle R, Simon B, Valcárcel J and Sattler M:
Structural basis for specific RNA recognition by the alternative
splicing factor RBM5. Nat Commun. 14:42332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dvinge H and Bradley RK: Widespread intron
retention diversifies most cancer transcriptomes. Genome Med.
7:452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sinnakannu JR, Lee KL, Cheng S, Li J, Yu
M, Tan SP, Ong CCH, Li H, Than H, Anczuków-Camarda O, et al: SRSF1
mediates cytokine-induced impaired imatinib sensitivity in chronic
myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 34:1787–1798. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fuentes-Fayos AC, Pérez-Gómez JM, G-García
ME, Jiménez-Vacas JM, Blanco-Acevedo C, Sánchez-Sánchez R, Solivera
J, Breunig JJ, Gahete MD, Castaño JP and Luque RM: SF3B1 inhibition
disrupts malignancy and prolongs survival in glioblastoma patients
through BCL2L1 splicing and mTOR/ß-catenin pathways imbalances. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 41:392022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Taketo K, Konno M, Asai A, Koseki J,
Toratani M, Satoh T, Doki Y, Mori M, Ishii H and Ogawa K: The
epitranscriptome m6A writer METTL3 promotes chemo- and
radioresistance in pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
52:621–629. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang N, Hu Y and Wang Z: Regulation of
alternative splicing: Functional interplay with epigenetic
modifications and its implication to cancer. Wiley Interdiscip Rev
RNA. 12:e18152023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lei Y and Lai M: Epigenetic regulation and
therapeutic targeting of alternative splicing dysregulation in
cancer. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 18:7132025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ilango S, Paital B, Jayachandran P, Padma
PR and Nirmaladevi R: Epigenetic alterations in cancer. Front
Biosci (Landmark Ed). 25:1058–1109. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bao B, Tian M, Wang X, Yang C, Qu J, Zhou
S, Cheng Y, Tong Q and Zheng L: SNORA37/CMTR1/ELAVL1 feedback loop
drives gastric cancer progression via facilitating CD44 alternative
splicing. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 44:152025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sun L, Zhang H and Gao P: Metabolic
reprogramming and epigenetic modifications on the path to cancer.
Protein Cell. 13:877–919. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hogg SJ, Beavis PA, Dawson MA and
Johnstone RW: Targeting the epigenetic regulation of antitumour
immunity. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 19:776–800. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wang Y, Wei J, Feng L, Li O, Huang L, Zhou
S, Xu Y, An K, Zhang Y, Chen R, et al: Aberrant m5C
hypermethylation mediates intrinsic resistance to gefitinib through
NSUN2/YBX1/QSOX1 axis in EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer.
Mol Cancer. 22:812023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bian Z, Yang F, Xu P, Gao G, Yang C, Cao
Y, Yao S, Wang X, Yin Y, Fei B and Huang Z: LINC01852 inhibits the
tumorigenesis and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer by
suppressing SRSF5-mediated alternative splicing of PKM. Mol Cancer.
23:232024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wickland DP, McNinch C, Jessen E, Necela
B, Shreeder B, Lin Y, Knutson KL and Asmann YW: Comprehensive
profiling of cancer neoantigens from aberrant RNA splicing. J
Immunother Cancer. 12:e0089882024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Leyte-Vidal A, DeFilippis R, Outhwaite IR,
Kwan I, Lee JY, Leavitt C, Miller KB, Rea D, Rangwala AM, Lou K, et
al: Absence of ABL1 exon 2-encoded SH3 residues in BCR::ABL1
destabilizes the autoinhibited kinase conformation and confers
resistance to asciminib. Leukemia. 38:2046–2050. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Monteuuis G, Wong JJL, Bailey CG, Schmitz
U and Rasko JEJ: The changing paradigm of intron retention:
Regulation, ramifications and recipes. Nucleic Acids Res.
47:11497–11513. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wong JJL and Schmitz U: Intron retention:
Importance, challenges, and opportunities. Trends Genet.
38:789–792. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Tan ZW, Fei G, Paulo JA, Bellaousov S,
Martin SES, Duveau DY, Thomas CJ, Gygi SP, Boutz PL and Walker S:
O-GlcNAc regulates gene expression by controlling detained intron
splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 48:5656–5669. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yue Q, Wang Z, Shen Y, Lan Y, Zhong X, Luo
X, Yang T, Zhang M, Zuo B, Zeng T, et al: Histone H3K9 lactylation
confers temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma via LUC7L2-mediated
MLH1 intron retention. Adv Sci (Weinh). 11:23092902024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wang X, Han M, Wang S, Sun Y, Zhao W, Xue
Z, Liang X, Huang B, Li G, Chen A, et al: Targeting the splicing
factor NONO inhibits GBM progression through GPX1 intron retention.
Theranostics. 12:5451–5469. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wang E, Lu SX, Pastore A, Chen X, Imig J,
Lee SCW, Hockemeyer K, Ghebrechristos YE, Yoshimi A, Inoue D, et
al: Targeting an RNA-binding protein network in acute myeloid
leukemia. Cancer Cell. 35:369–384.e7. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Inoue D, Polaski JT, Taylor J, Castel P,
Chen S, Kobayashi S, Hogg SJ, Hayashi Y, Pineda JMB, El Marabti E,
et al: Minor intron retention drives clonal hematopoietic disorders
and diverse cancer predisposition. Nat Genet. 53:707–718. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Xu Z, Chen Y, Ma L, Chen Y, Liu J, Guo Y,
Yu T, Zhang L, Zhu L and Shu Y: Role of exosomal non-coding RNAs
from tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages in the tumor
microenvironment. Mol Ther. 30:3133–3154. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Chen LL: The expanding regulatory
mechanisms and cellular functions of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 21:475–490. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Liu CX and Chen LL: Circular RNAs:
Characterization, cellular roles, and applications. Cell.
185:2016–2034. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Chen R, Wang SK, Belk JA, Amaya L, Li Z,
Cardenas A, Abe BT, Chen CK, Wender PA and Chang HY: Engineering
circular RNA for enhanced protein production. Nat Biotechnol.
41:262–272. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Pitolli C, Marini A, Sette C and
Pagliarini V: Non-canonical splicing and its implications in brain
physiology and cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 23:28112022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Xue W, Ma XK and Yang L: Fast and furious:
insights of back splicing regulation during nascent RNA synthesis.
Sci China Life Sci. 64:1050–1061. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Xu B, Meng Y and Jin Y: RNA structures in
alternative splicing and back-splicing. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA.
12:e16262021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ling Y, Liang G, Lin Q, Fang X, Luo Q, Cen
Y, Mehrpour M, Hamai A, Liu Z, Shi Y, et al: circCDYL2 promotes
trastuzumab resistance via sustaining HER2 downstream signaling in
breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 21:82022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Wang X, Chen T, Li C, Li W, Zhou X, Li Y,
Luo D, Zhang N, Chen B, Wang L, et al: CircRNA-CREIT inhibits
stress granule assembly and overcomes doxorubicin resistance in
TNBC by destabilizing PKR. J Hematol Oncol. 15:1222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Enuka Y, Lauriola M, Feldman ME, Sas-Chen
A, Ulitsky I and Yarden Y: Circular RNAs are long-lived and display
only minimal early alterations in response to a growth factor.
Nucleic Acids Res. 44:1370–1383. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW,
Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB and Kjems J: The biogenesis, biology and
characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 20:675–691. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Rybak-Wolf A, Stottmeister C, Glažar P,
Jens M, Pino N, Giusti S, Hanan M, Behm M, Bartok O, Ashwal-Fluss
R, et al: Circular RNAs in the mammalian brain are highly abundant,
conserved, and dynamically expressed. Mol Cell. 58:870–885. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F,
Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer
M, et al: Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with
regulatory potency. Nature. 495:333–338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Gao W, Guo H, Niu M, Zheng X, Zhang Y, Xue
X, Bo Y, Guan X, Li Z, Guo Y, et al: circPARD3 drives malignant
progression and chemoresistance of laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma by inhibiting autophagy through the PRKCI-akt-mTOR
pathway. Mol Cancer. 19:1662020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Chen L and Shan G: CircRNA in cancer:
Fundamental mechanism and clinical potential. Cancer Lett.
505:49–57. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Hu C, Xia R, Zhang X, Li T, Ye Y, Li G, He
R, Li Z, Lin Q, Zheng S and Chen R: circFARP1 enables
cancer-associated fibroblasts to promote gemcitabine resistance in
pancreatic cancer via the LIF/STAT3 axis. Mol Cancer. 21:242022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Hong EM, Ingemarsdotter CK and Lever AML:
Therapeutic applications of trans -splicing. Br Med Bull. 136:4–20.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Berger A, Maire S, Gaillard M, Sahel J,
Hantraye P and Bemelmans A: mRNA trans-splicing in gene therapy for
genetic diseases. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 7:487–498. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Zhang J, Xu X, Deng H, Liu L, Xiang Y and
Feng J: Overcoming cancer drug-resistance calls for novel
strategies targeting abnormal alternative splicing. Pharmacol Ther.
261:1086972024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Dhungel BP, Monteuuis G, Giardina C, Tabar
MS, Feng Y, Metierre C, Ho S, Nagarajah R, Fontaine ARM, Shah JS,
et al: The fusion of CLEC12A and MIR223HG arises from a
trans-splicing event in normal and transformed human cells. Int J
Mol Sci. 22:121782021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Lee G and Muir TW: Distinct phases of
cellular signaling revealed by time-resolved protein synthesis. Nat
Chem Biol. 20:1353–1360. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Brunmeir R, Ying L, Yan J, Hee YT, Lin B,
Kaur H, Leong QZ, Teo WW, Choong G, Jen WY, et al: EZH2 modulates
mRNA splicing and exerts part of its oncogenic function through
repression of splicing factors in CML. Leukemia. 39:650–662. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Del Giudice M, Foster JG, Peirone S,
Rissone A, Caizzi L, Gaudino F, Parlato C, Anselmi F, Arkell R,
Guarrera S, et al: FOXA1 regulates alternative splicing in prostate
cancer. Cell Rep. 40:1114042022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Wang Y, Zou Q, Li F, Zhao W, Xu H, Zhang
W, Deng H and Yang X: Identification of the cross-strand chimeric
RNAs generated by fusions of bi-directional transcripts. Nat
Commun. 12:46452021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Tu J, Huo Z, Yu Y, Zhu D, Xu A, Huang MF,
Hu R, Wang R, Gingold JA, Chen YH, et al: Hereditary retinoblastoma
iPSC model reveals aberrant spliceosome function driving bone
malignancies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 119:e21178571192022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Allen I, Hassan H, Walburga Y, Huntley C,
Loong L, Rahman T, Allen S, Garrett A, Torr B, Bacon A, et al:
Second primary cancer risks after breast cancer in BRCA1 and BRCA2
pathogenic variant carriers. J Clin Oncol. 43:651–661. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Esplin ED, Hanson C, Wu S, Horning AM,
Barapour N, Nevins SA, Jiang L, Contrepois K, Lee H, Guha TK, et
al: Multiomic analysis of familial adenomatous polyposis reveals
molecular pathways associated with early tumorigenesis. Nat Cancer.
5:1737–1753. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Yadav S, Boddicker NJ, Na J, Polley EC, Hu
C, Hart SN, Gnanaolivu RD, Larson N, Holtegaard S, Huang H, et al:
Contralateral breast cancer risk among carriers of germline
pathogenic variants in ATM, BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2, and PALB2. J Clin
Oncol. 41:1703–1713. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Pacheco AG and Lou H: Alternative splicing
of exon 23a in neurofibromatosis type 1 pre-mRNA: Its contribution
to the protein structure and function of neurofibromin. Wiley
Interdiscip Rev RNA. 16:e700212025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Choe JH, Kawase T, Xu A, Guzman A,
Obradovic AZ, Low-Calle AM, Alaghebandan B, Raghavan A, Long K,
Hwang PM, et al: Li-fraumeni syndrome-associated dimer-forming
mutant p53 promotes transactivation-independent mitochondrial cell
death. Cancer Discov. 13:1250–1273. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Kim WJ, Crosse EI, De Neef E, Etxeberria
I, Sabio EY, Wang E, Bewersdorf JP, Lin KT, Lu SX, Belleville A, et
al: Mis-splicing-derived neoantigens and cognate TCRs in splicing
factor mutant leukemias. Cell. 188:3422–3440.e24. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Lu SX, De Neef E, Thomas JD, Sabio E,
Rousseau B, Gigoux M, Knorr DA, Greenbaum B, Elhanati Y, Hogg SJ,
et al: Pharmacologic modulation of RNA splicing enhances antitumor
immunity. Cell. 184:4032–4047.e31. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Zhang Y, Qian J, Gu C and Yang Y:
Alternative splicing and cancer: A systematic review. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 6:782021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Garcia-Cabau C, Bartomeu A, Tesei G,
Cheung KC, Pose-Utrilla J, Picó S, Balaceanu A, Duran-Arqué B,
Fernández-Alfara M, Martín J, et al: Mis-splicing of a neuronal
microexon promotes CPEB4 aggregation in ASD. Nature. 637:496–503.
2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Kowalski MH, Wessels HH, Linder J,
Dalgarno C, Mascio I, Choudhary S, Hartman A, Hao Y, Kundaje A and
Satija R: Multiplexed single-cell characterization of alternative
polyadenylation regulators. Cell. 187:4408–4425.e23. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
The Tabula Sapiens Consortium, . Jones RC,
Karkanias J, Krasnow MA, Pisco AO, Quake SR, Salzman J, Yosef N,
Bulthaup B, Brown P, et al: The tabula sapiens: A multiple-organ,
single-cell transcriptomic atlas of humans. Science.
376:eabl48962022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Zhu C, Lian Y, Wang C, Wu P, Li X, Gao Y,
Fan S, Ai L, Fang L, Pan H, et al: Single-cell transcriptomics
dissects hematopoietic cell destruction and T-cell engagement in
aplastic anemia. Blood. 138:23–33. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Augspach A, Drake KD, Roma L, Qian E, Lee
SR, Clarke D, Kumar S, Jaquet M, Gallon J, Bolis M, et al: Minor
intron splicing is critical for survival of lethal prostate cancer.
Mol Cell. 83:1983–2002.e11. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Bai R, Yuan M, Zhang P, Luo T, Shi Y and
Wan R: Structural basis of U12-type intron engagement by the fully
assembled human minor spliceosome. Science. 383:1245–1252. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Bai R, Wan R, Wang L, Xu K, Zhang Q, Lei J
and Shi Y: Structure of the activated human minor spliceosome.
Science. 371:eabg08792021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Lee SCW and Abdel-Wahab O: Therapeutic
targeting of splicing in cancer. Nat Med. 22:976–986. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Steensma DP, Wermke M, Klimek VM,
Greenberg PL, Font P, Komrokji RS, Yang J, Brunner AM, Carraway HE,
Ades L, et al: Phase I first-in-human dose escalation study of the
oral SF3B1 modulator H3B-8800 in myeloid neoplasms. Leukemia.
35:3542–3550. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Seiler M, Yoshimi A, Darman R, Chan B,
Keaney G, Thomas M, Agrawal AA, Caleb B, Csibi A, Sean E, et al:
H3B-8800, an orally available small-molecule splicing modulator,
induces lethality in spliceosome-mutant cancers. Nat Med.
24:497–504. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Chi KN, Higano CS, Blumenstein B, Ferrero
JM, Reeves J, Feyerabend S, Gravis G, Merseburger AS, Stenzl A,
Bergman AM, et al: Custirsen in combination with docetaxel and
prednisone for patients with metastatic castration-resistant
prostate cancer (SYNERGY trial): A phase 3, multicentre,
open-label, randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 18:473–485. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Aird D, Teng T, Huang CL, Pazolli E, Banka
D, Cheung-Ong K, Eifert C, Furman C, Wu ZJ, Seiler M, et al:
Sensitivity to splicing modulation of BCL2 family genes defines
cancer therapeutic strategies for splicing modulators. Nat Commun.
10:1372019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Klein IA, Boija A, Afeyan LK, Hawken SW,
Fan M, Dall'Agnese A, Oksuz O, Henninger JE, Shrinivas K, Sabari
BR, et al: Partitioning of cancer therapeutics in nuclear
condensates. Science. 368:1386–1392. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Lan Q, Liu PY, Bell JL, Wang JY,
Hüttelmaier S, Zhang XD, Zhang L and Liu T: The emerging roles of
RNA m6A methylation and demethylation as critical regulators of
tumorigenesis, drug sensitivity, and resistance. Cancer Res.
81:3431–3440. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Salton M, Kasprzak WK, Voss T, Shapiro BA,
Poulikakos PI and Misteli T: Inhibition of vemurafenib-resistant
melanoma by interference with pre-mRNA splicing. Nat Commun.
6:71032015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Ramasamy T, Ruttala HB, Munusamy S,
Chakraborty N and Kim JO: Nano drug delivery systems for antisense
oligonucleotides (ASO) therapeutics. J Control Release.
352:861–878. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Ma WK, Voss DM, Scharner J, Costa ASH, Lin
KT, Jeon HY, Wilkinson JE, Jackson M, Rigo F, Bennett CF and
Krainer AR: ASO-based PKM splice-switching therapy inhibits
hepatocellular carcinoma growth. Cancer Res. 82:900–915. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Kobayashi Y, Chhoeu C, Li J, Price KS,
Kiedrowski LA, Hutchins JL, Hardin AI, Wei Z, Hong F, Bahcall M, et
al: Silent mutations reveal therapeutic vulnerability in RAS Q61
cancers. Nature. 603:335–342. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Zhao C, Zhao J, Zhang Y, Zhu YD, Yang ZY,
Liu SL, Tang QY, Yang Y, Wang HK, Shu YJ, et al: PTBP3 mediates
IL-18 exon skipping to promote immune escape in gallbladder cancer.
Adv Sci. 11:24066332024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Ang Z, Paruzzo L, Hayer KE, Schmidt C, Diz
MT, Xu F, Zankharia U, Zhang Y, Soldan S, Zheng S, et al:
Alternative splicing of its 5′ UTR limits CD20 mRNA translation and
enables resistance to CD20-directed immunotherapies. Blood.
142:1724–1739. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Wang Z, Wang S, Qin J, Zhang X, Lu G, Liu
H, Guo H, Wu L, Shender VO, Shao C, et al: Splicing factor BUD31
promotes ovarian cancer progression through sustaining the
expression of anti-apoptotic BCL2L12. Nat Commun. 13:62462022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Hu Y, Revenko A, Barsoumian H, Bertolet G,
Fowlkes NW, Maazi H, Green MM, He K, Sezen D, Voss TA, et al:
Inhibition of MER proto-oncogene tyrosine kinase by an antisense
oligonucleotide enhances treatment efficacy of immunoradiotherapy.
J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 43:702024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Prakash TP, Graham MJ, Yu J, Carty R, Low
A, Chappell A, Schmidt K, Zhao C, Aghajan M, Murray HF, et al: NAR
breakthrough article targeted delivery of antisense
oligonucleotides to hepatocytes using triantennary N-acetyl
galactosamine improves potency 10-fold in mice. Nucleic Acids Res.
42:8796–8807. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Ojansivu M, Barriga HMG, Holme MN, Morf S,
Doutch JJ, Andaloussi SE, Kjellman T, Johnsson M, Barauskas J and
Stevens MM: Formulation and characterization of novel ionizable and
cationic lipid nanoparticles for the delivery of splice-switching
oligonucleotides. Adv Mater. 37:e24195382025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Alvarez-Erviti L, Seow Y, Yin H, Betts C,
Lakhal S and Wood MJ: Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by
systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat Biotechnol.
29:341–345. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Fei Y, Cao D, Li Y, Wang Z, Dong R, Zhu M,
Gao P, Wang X, Cai J and Zuo X: Circ_0008315 promotes tumorigenesis
and cisplatin resistance and acts as a nanotherapeutic target in
gastric cancer. J Nanobiotechnology. 22:5192024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Li Y, Wang Z, Gao P, Cao D, Dong R, Zhu M,
Fei Y, Zuo X and Cai J: CircRHBDD1 promotes immune escape via
IGF2BP2/PD-L1 signaling and acts as a nanotherapeutic target in
gastric cancer. J Transl Med. 22:7042024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Du A, Li S, Zhou Y, Disoma C, Liao Y,
Zhang Y, Chen Z, Yang Q, Liu P, Liu S, et al: M6A-mediated
upregulation of circMDK promotes tumorigenesis and acts as a
nanotherapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer.
21:1092022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Zhou B, Mo Z, Lai G, Chen X, Li R, Wu R,
Zhu J and Zheng F: Targeting tumor exosomal circular RNA cSERPINE2
suppresses breast cancer progression by modulating MALT1-NF-κB-IL-6
axis of tumor-associated macrophages. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
42:482023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Xu L, Ma X, Zhang X, Zhang C, Zhang Y,
Gong S, Wu N, Zhang P, Feng X, Guo J, et al: hsa_circ_0007919
induces LIG1 transcription by binding to FOXA1/TET1 to enhance the
DNA damage response and promote gemcitabine resistance in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer. 22:1952023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Yin Y, Wang Y, Yu X, Li Y, Zhao Y, Wang Y
and Liu Z: Spatial isoforms reveal the mechanisms of metastasis.
Adv Sci. 11:24022422024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Yang L, Niu K, Wang J, Shen W, Jiang R,
Liu L, Song W, Wang X, Zhang X, Zhang R, et al: Nucleolin
lactylation contributes to intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
pathogenesis via RNA splicing regulation of MADD. J Hepatol.
81:651–666. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|