|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
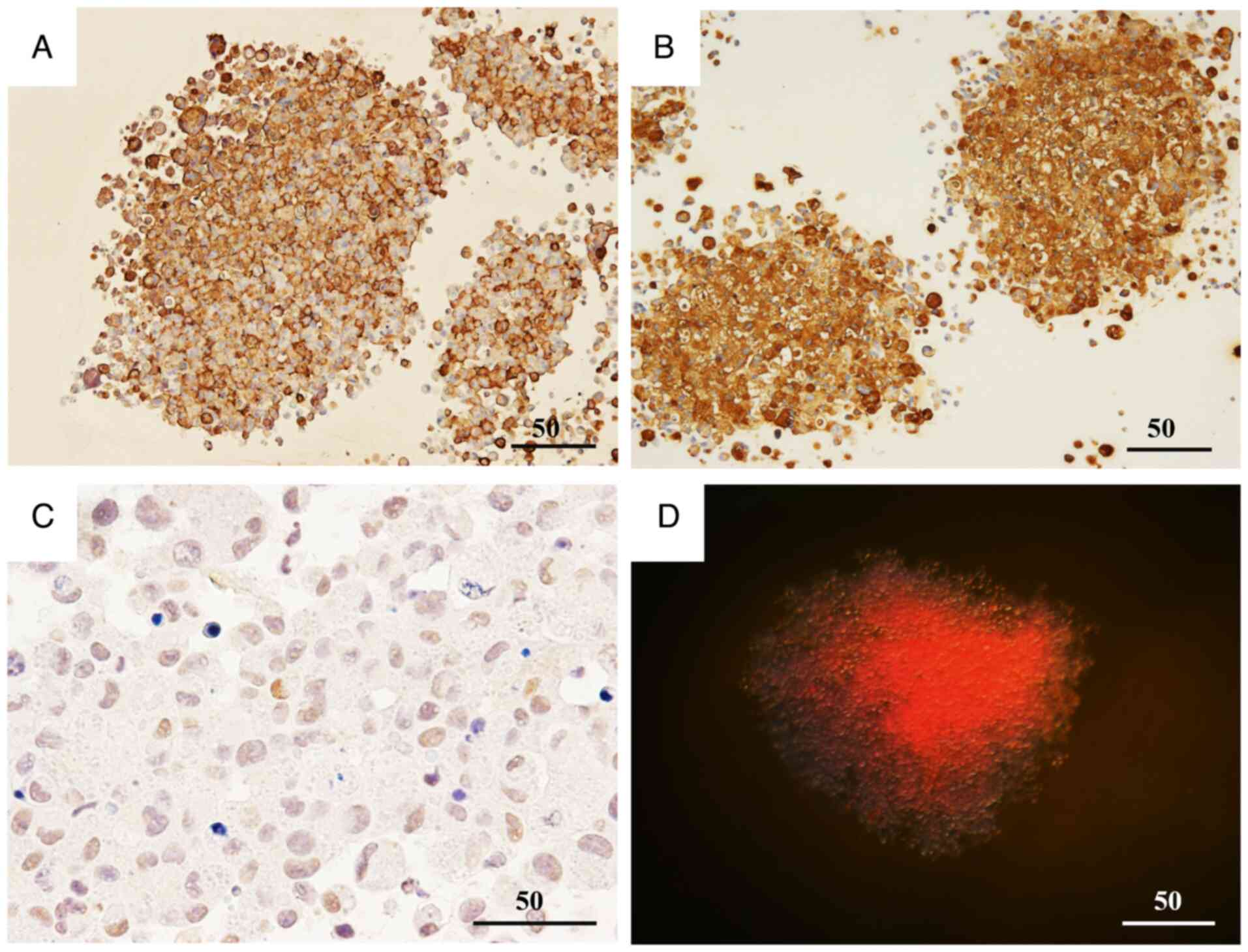
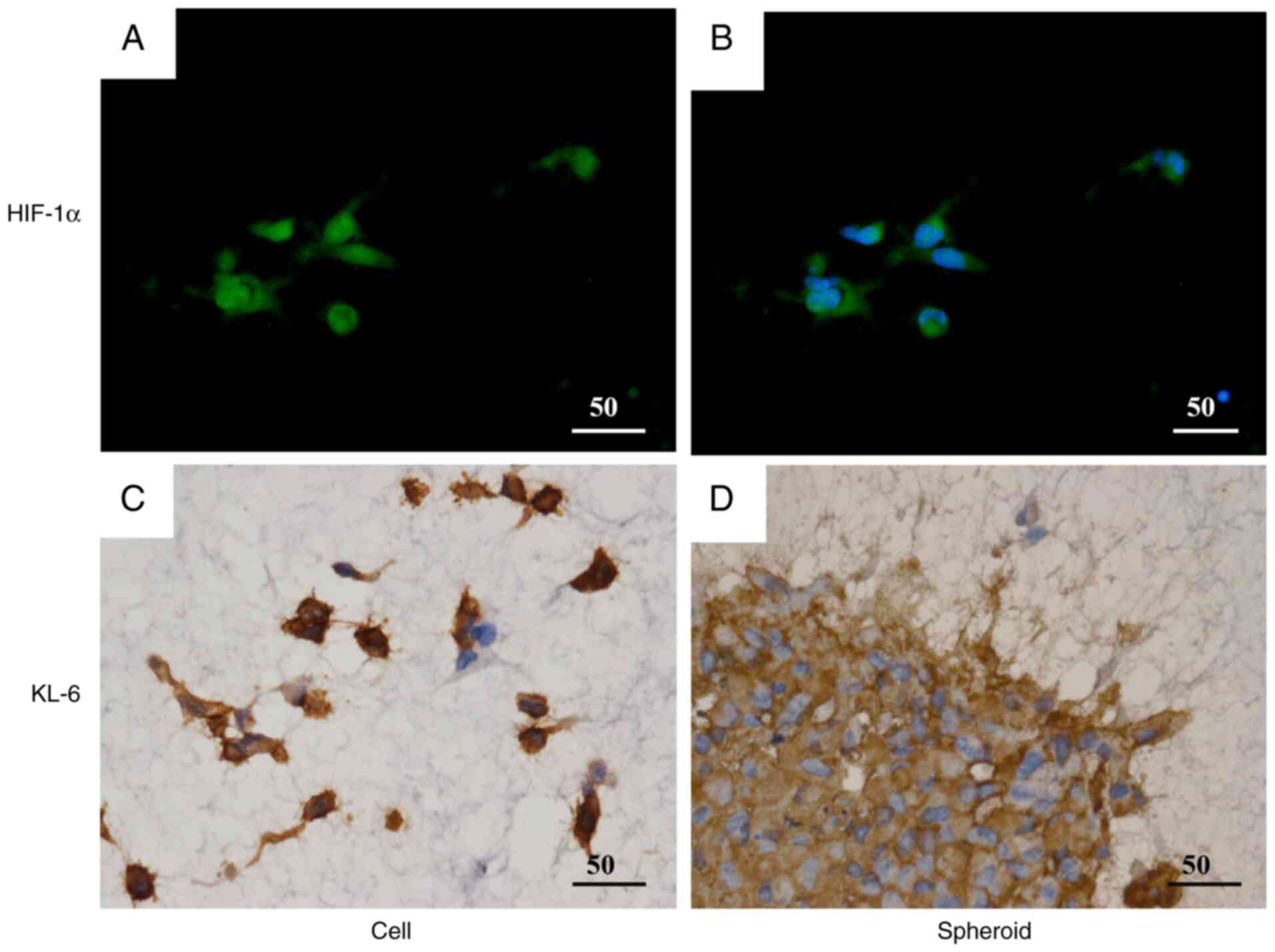
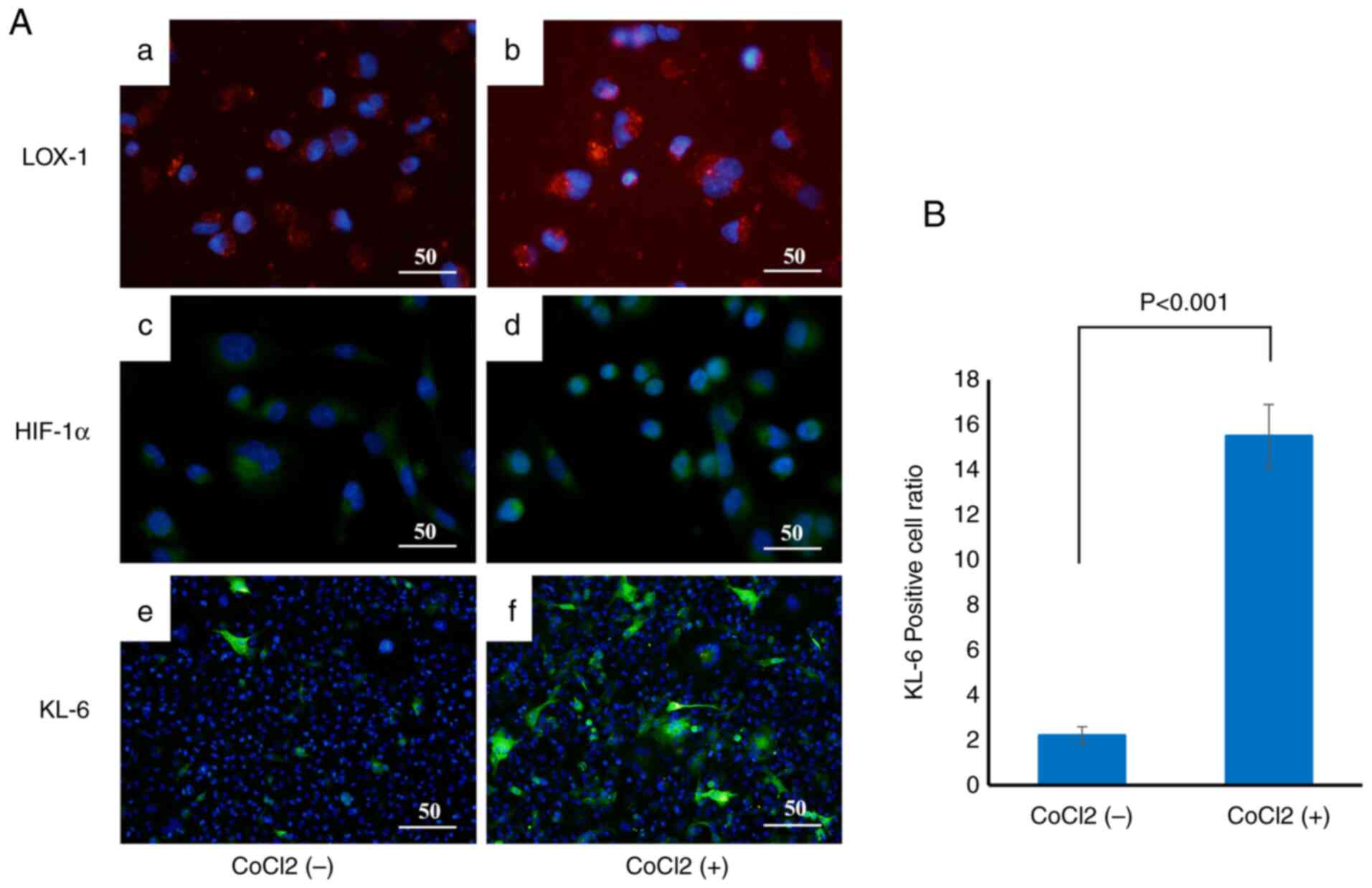
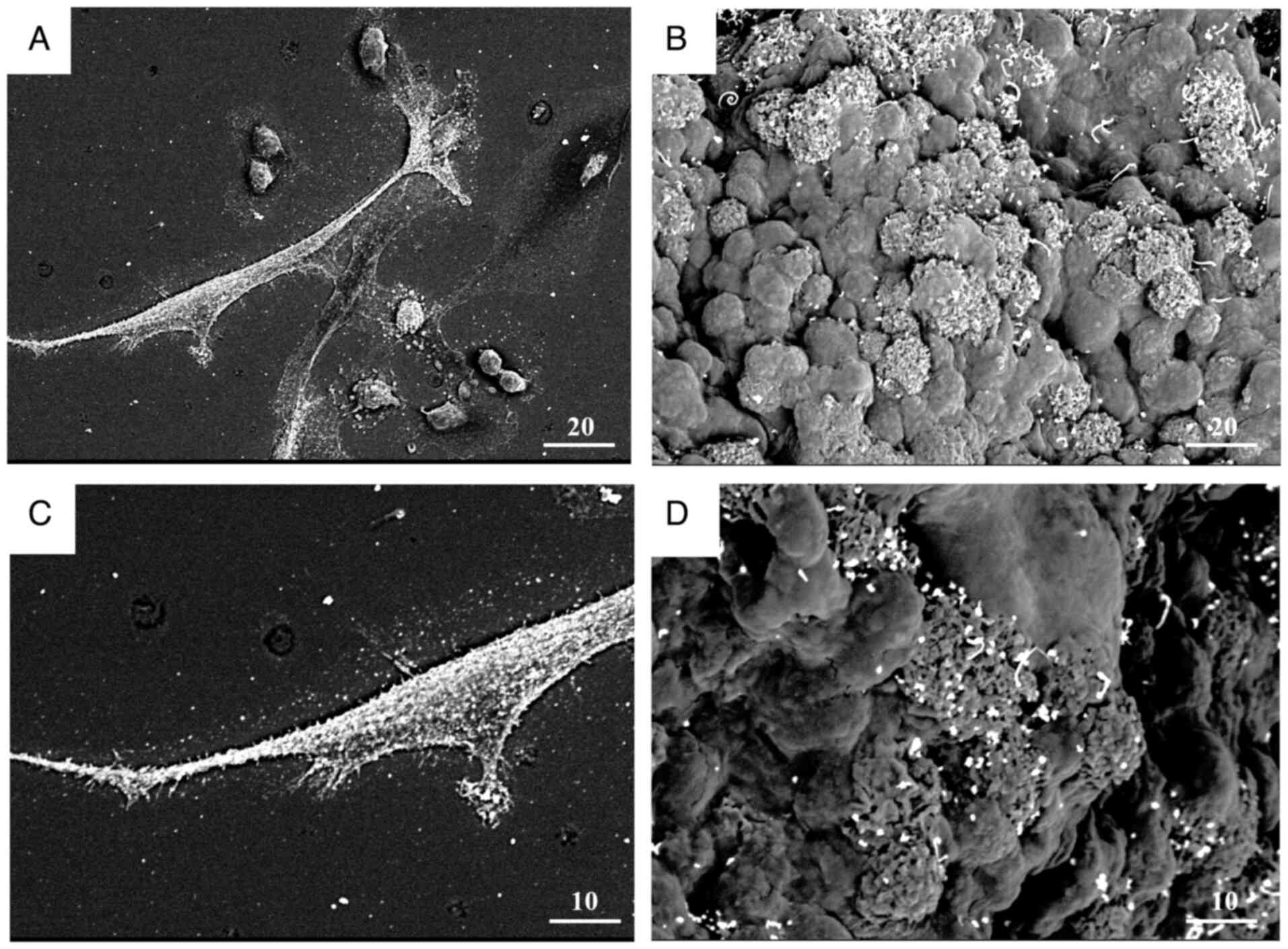
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Salemme V, Centonze G, Avalle L, Natalini
D, Piccolantonio A, Arina P, Morellato A, Ala U, Taverna D, Turco E
and Defilippi P: The role of tumor microenvironment in drug
resistance: Emerging technologies to unravel breast cancer
heterogeneity. Front Oncol. 13:11702642023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network, .
Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature.
490:61–70. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mittal S, Brown NJ and Holen I: The breast
tumor microenvironment: role in cancer development, progression and
response to therapy. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 18:227–243. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Quail DF and Joyce JA: Microenvironmental
regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med.
19:1423–1437. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ogawa Y, Ishikawa T, Ikeda K, Nakata B,
Sawada T, Ogisawa K, Kato Y and Hirakawa K: Evaluation of serum
KL-6, a mucin-like glycoprotein, as a tumor marker for breast
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 6:4069–4072. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ohyabu N, Hinou H, Matsushita T, Izumi R,
Shimizu H, Kawamoto K, Numata Y, Togame H, Takemoto H, Kondo H and
Nishimura S: An essential epitope of anti-MUC1 monoclonal antibody
KL-6 revealed by focused glycopeptide library. J Am Chem Soc.
131:17102–17109. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu HL, Zhao X, Zhang KM, Tang W and Kokudo
N: Inhibition of KL-6/MUC1 glycosylation limits aggressive
progression of pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol.
20:1217–12181. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wong CC, Gilkes DM, Zhang H, Chen J, Wei
H, Chaturvedi P, Fraley SI, Wong CM, Khoo US, Ng IO, et al:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a master regulator of breast cancer
metastatic niche formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:16369–16374. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Basheeruddin M and Qausain S:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1alpha) and cancer:
Mechanisms of tumor hypoxia and therapeutic targeting. Cureus.
16:e707002024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rankin EB, Nam JM and Giaccia AJ: Hypoxia:
Signaling the metastatic cascade. Trends Cancer. 2:295–304. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mikami Y, Hisatsune A, Tashiro T, Isohama
Y and Katsuki H: Hypoxia enhances MUC1 expression in a lung
adenocarcinoma cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
379:1060–1065. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Aubert S, Fauquette V, Hémon B, Lepoivre
R, Briez N, Bernard D, Van Seuningen I, Leroy X and Perrais M:
MUC1, a new hypoxia inducible factor target gene, is an actor in
clear renal cell carcinoma tumor progression. Cancer Res.
69:5707–5715. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Godet I, Oza HH, Shi Y, Joe NS, Weinstein
AG, Johnson J, Considine M, Talluri S, Zhang J, Xu R, et al:
Hypoxia induces ROS-resistant memory upon reoxygenation in vivo
promoting metastasis in part via MUC1-C. Nat Commun. 15:84162024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yamamoto Y, Hayashi Y, Sakaki H and
Murakami I: Downregulation of fascin induces collective cell
migration in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 50:1502023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hayashi Y, Yamamoto Y and Murakami I:
Micromorphological observation of HLE cells under knockdown of
fascin using LV-SEM. Med Mol Morphol. 56:257–265. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Isert L, Mehta A, Loiudice G, Oliva A,
Roidl A and Merkel OM: An in vitro approach to model emt in breast
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 24:77572023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu CY, Lin HH, Tang MJ and Wang YK:
Vimentin contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition cancer
cell mechanics by mediating cytoskeletal organization and focal
adhesion maturation. Oncotarget. 6:15966–15983. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gest C, Joimel U, Huang L, Pritchard LL,
Petit A, Dulong C, Buquet C, Hu CQ, Mirshahi P, Laurent M, et al:
Rac3 induces a molecular pathway triggering breast cancer cell
aggressiveness: differences in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 breast cancer
cell lines. BMC Cancer. 13:632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nguyen CH, Senfter D, Basilio J, Holzner
S, Stadler S, Krieger S, Huttary N, Milovanovic D, Viola K,
Simonitsch-Klupp I, et al: NF-κB contributes to MMP1 expression in
breast cancer spheroids causing paracrine PAR1 activation and
disintegrations in the lymph endothelial barrier in vitro.
Oncotarget. 6:39262–39275. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li H, Qiu Z, Li F and Wang C: The
relationship between MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression levels with breast
cancer incidence and prognosis. Oncol Lett. 14:5865–5870.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dobie C and Skropeta D: Insights into the
role of sialylation in cancer progression and metastasis. Br J
Cancer. 124:76–90. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Julien S, Lagadec C, Krzewinski-Recchi MA,
Courtand G, Le Bourhis X and Delannoy P: Stable expression of
sialyl-Tn antigen in T47-D cells induces a decrease of cell
adhesion and an increase of cell migration. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 90:77–84. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou X, Chi K, Zhang C, Liu Q and Yang G:
Sialylation: A cloak for tumors to trick the immune system in the
microenvironment. Biology (Basel). 12:8322023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tian X, Wang W, Zhang Q, Zhao L, Wei J,
Xing H, Song Y, Wang S, Ma D, Meng L and Chen G: Hypoxia-inducible
factor-1α enhances the malignant phenotype of multicellular
spheroid HeLa cells in vitro. Oncol Lett. 1:893–897. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Koike T, Kimura N, Miyazaki K, Yabuta T,
Kumamoto K, Takenoshita S, Chen J, Kobayashi M, Hosokawa M,
Taniguchi A, et al: Hypoxia induces adhesion molecules on cancer
cells: a missing link between Warburg effect and induction of
selectin-ligand carbohydrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:8132–8137. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Arriagada C, Silva P and Torres VA: Role
of glycosylation in hypoxia-driven cell migration and invasion.
Cell Adh Migr. 13:13–22. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Goudarzi H, Iizasa H, Furuhashi M,
Nakazawa S, Nakane R, Liang S, Hida Y, Yanagihara K, Kubo T,
Nakagawa K, et al: Enhancement of in vitro cell motility and
invasiveness of human malignant pleural mesothelioma cells through
the HIF-1α-MUC1 pathway. Cancer Lett. 339:82–92. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Habeeb IF, Alao TE, Delgado D and Buffone
A Jr: When a negative (charge) is not a positive: Sialylation and
its role in cancer mechanics and progression. Front Oncol.
14:14873062024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shen L, Luo Z, Wu J, Qiu L, Luo M, Ke Q
and Dong X: Enhanced expression of α2,3-linked sialic acids
promotes gastric cancer cell metastasis and correlates with poor
prognosis. Int J Oncol. 50:1201–1210. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu X, Zhao J, Ruan Y, Sun L, Xu C and
Jiang H: Sialyltransferase ST3GAL1 promotes cell migration,
invasion, and TGF-β1-induced EMT and confers paclitaxel resistance
in ovarian cancer. Cell Death Dis. 9:11022018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pietrobono S, Anichini G, Sala C, Manetti
F, Almada LL, Pepe S, Carr RM, Paradise BD, Sarkaria JN, Davila JI,
et al: ST3GAL1 is a target of the SOX2-GLI1 transcriptional complex
and promotes melanoma metastasis through AXL. Nat Commun.
11:58652020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|