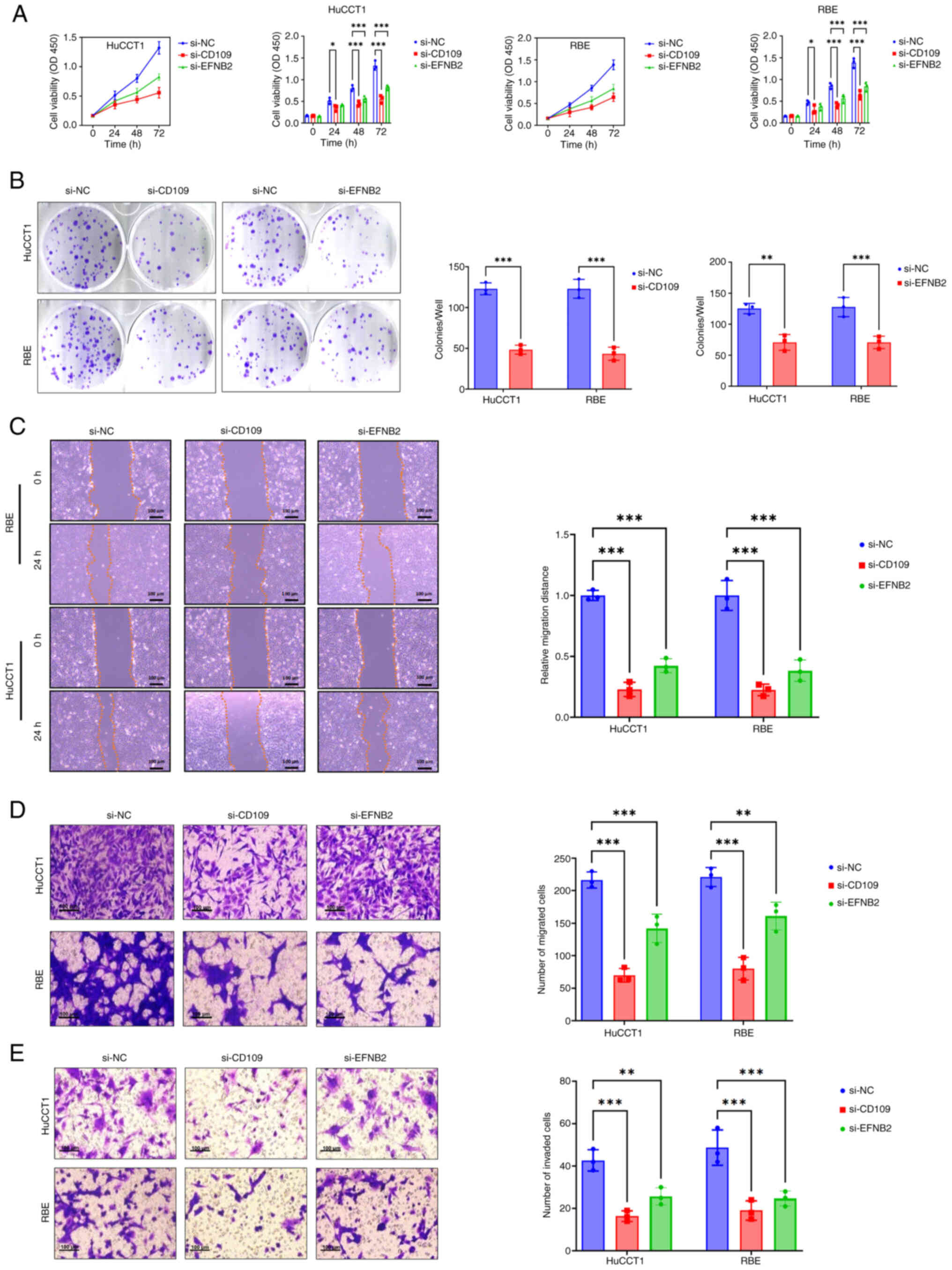
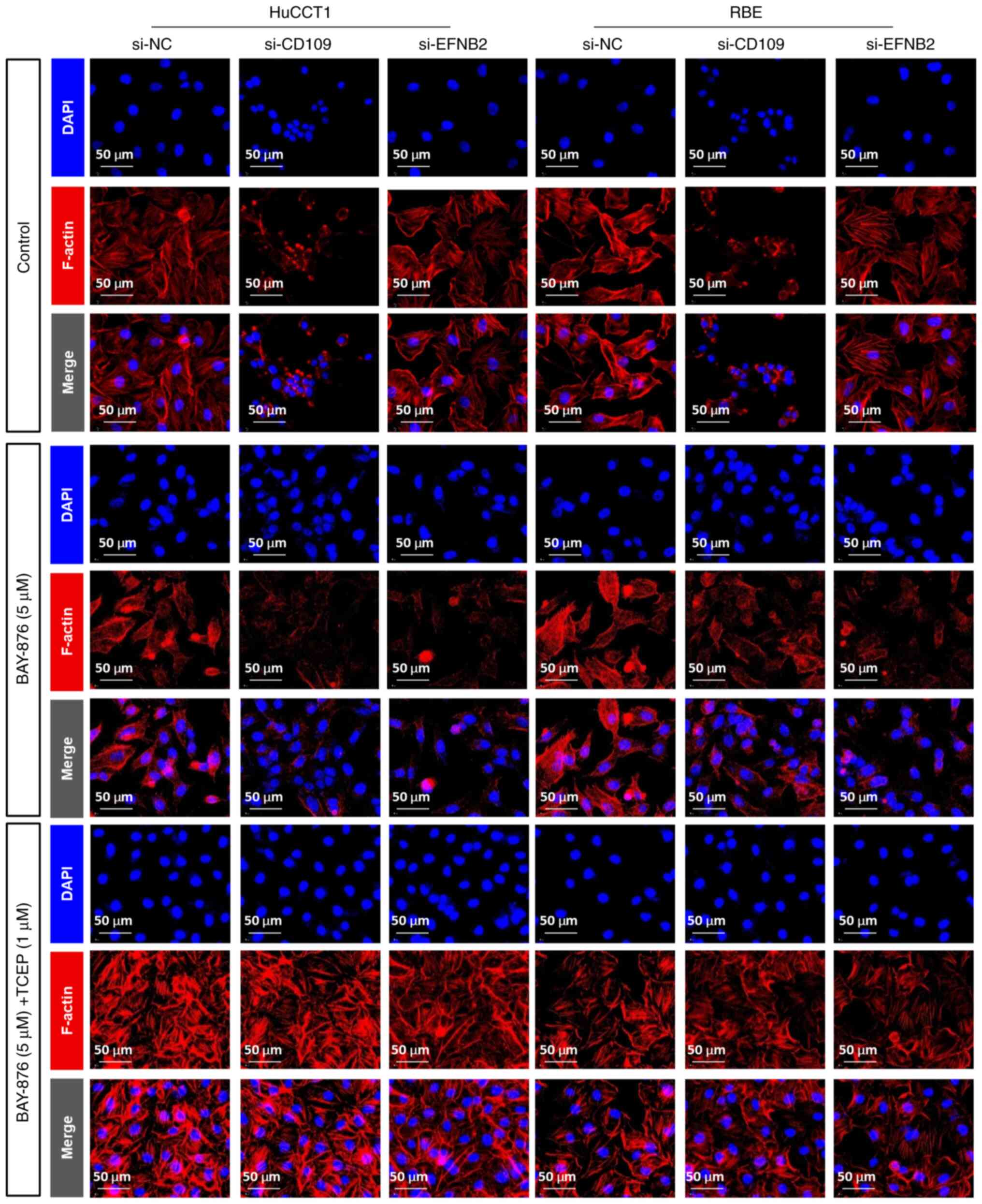
|
1
|
Brindley PJ, Bachini M, Ilyas SI, Khan SA,
Loukas A, Sirica AE, Teh BT, Wongkham S and Gores GJ:
Cholangiocarcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 7:652021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cardinale V: Classifications and
misclassification in cholangiocarcinoma. Liver Int. 39:260–212.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Banales JM, Cardinale V, Carpino G,
Marzioni M, Andersen JB, Invernizzi P, Lind GE, Folseraas T, Forbes
SJ, Fouassier L, et al: Expert consensus document:
Cholangiocarcinoma: Current knowledge and future perspectives
consensus statement from the European network for the study of
cholangiocarcinoma (ENS-CCA). Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
13:261–280. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Clements O, Eliahoo J, Kim JU,
Taylor-Robinson SD and Khan SA: Risk factors for intrahepatic and
extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. J Hepatol. 72:95–103. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sirica AE, Gores GJ, Groopman JD, Selaru
FM, Strazzabosco M, Wei Wang X and Zhu AX: Intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma: Continuing challenges and translational
advances. Hepatology. 69:1803–1815. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fabris L, Perugorria MJ, Mertens J,
Björkström NK, Cramer T, Lleo A, Solinas A, Sänger H, Lukacs-Kornek
V, Moncsek A, et al: The tumour microenvironment and immune milieu
of cholangiocarcinoma. Liver Int. 39 (Suppl 1):S63–S78. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Arrivé L and Djelouah M: Refining
prognosis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: The expanding role of
imaging. Radiol Imaging Cancer. 7:e2503832025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
PDQ Adult Treatment Editorial Board. Bile
duct cancer (cholangiocarcinoma) treatment (PDQ®), . Health
Professional Version. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries. National
Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD: 2002
|
|
9
|
Lockie EB, Sylivris A, Pandanaboyana S,
Zalcberg J, Skandarajah A and Loveday BP: Relationship between
pancreatic cancer resection rate and survival at population level:
Systematic review. BJS Open. 9:zraf0072025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Valle JW, Lamarca A, Goyal L, Barriuso J
and Zhu AX: New horizons for precision medicine in biliary tract
cancers. Cancer Discov. 7:943–962. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Banales JM, Marin JJG, Lamarca A,
Rodrigues PM, Khan SA, Roberts LR, Cardinale V, Carpino G, Andersen
JB, Braconi C, et al: Cholangiocarcinoma 2020: The next horizon in
mechanisms and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
17:557–588. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH and Currie AR:
Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging
implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 26:239–257. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang D, Kang R, Berghe TV, Vandenabeele P
and Kroemer G: The molecular machinery of regulated cell death.
Cell Res. 29:347–364. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shi Y, Wang Y, Niu K, Zhang W, Lv Q and
Zhang Y: How CLSPN could demystify its prognostic value and
potential molecular mechanism for hepatocellular carcinoma: A
crosstalk study. Comput Biol Med. 172:1082602024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi Y, Wang Y, Niu K and Zhang Y: A
commentary on ‘A bibliometric analysis of gastric cancer liver
metastases: Advances in mechanisms of occurrence and treatment
options’. Int J Surg. 110:5897–5898. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu X, Nie L, Zhang Y, Yan Y, Wang C,
Colic M, Olszewski K, Horbath A, Chen X, Lei G, et al: Actin
cytoskeleton vulnerability to disulfide stress mediates
disulfidptosis. Nat Cell Biol. 25:404–414. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu X, Zhuang L and Gan B: Disulfidptosis:
Disulfide stress-induced cell death. Trends Cell Biol. 34:327–337.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zheng T, Liu Q, Xing F, Zeng C and Wang W:
Disulfidptosis: A new form of programmed cell death. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 42:1372023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tang J, Peng X, Xiao D, Liu S, Tao Y and
Shu L: Disulfidptosis-related signature predicts prognosis and
characterizes the immune microenvironment in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 24:192024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang HB, Pan JY and Zhu T: A
disulfidptosis-related lncRNA prognostic model to predict survival
and response to immunotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma. Front
Pharmacol. 14:12541192023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang J, Zhang J, Zhang F, Lu S, Guo S,
Shi R, Zhai Y, Gao Y, Tao X, Jin Z, et al: Identification of a
disulfidptosis-related genes signature for prognostic implication
in lung adenocarcinoma. Comput Biol Med. 165:107402023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen Y, Xue W, Zhang Y, Gao Y and Wang Y:
A novel disulfidptosis-related immune checkpoint genes signature:
Forecasting the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 149:12843–12854. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dong X, Liao P, Liu X, Yang Z, Wang Y,
Zhong W and Wang B: Construction and validation of a reliable
disulfidptosis-related LncRNAs signature of the subtype,
prognostic, and immune landscape in colon cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
24:129152023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kang K, Li X, Peng Y and Zhou Y:
Comprehensive analysis of disulfidptosis-related LncRNAs in
molecular classification, immune microenvironment characterization
and prognosis of gastric cancer. Biomedicines. 11:31652023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Feng Z, Zhao Q, Ding Y, Xu Y, Sun X, Chen
Q, Zhang Y, Miao J and Zhu J: Identification a unique
disulfidptosis classification regarding prognosis and immune
landscapes in thyroid carcinoma and providing therapeutic
strategies. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 149:11157–11170. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Qi C, Ma J, Sun J, Wu X and Ding J: The
role of molecular subtypes and immune infiltration characteristics
based on disulfidptosis-associated genes in lung adenocarcinoma.
Aging (Albany NY). 15:5075–5095. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Raggi C, Taddei ML, Rae C, Braconi C and
Marra F: Metabolic reprogramming in cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatol.
77:849–864. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Duwe L, Fouassier L, Lafuente-Barquero J
and Andersen JB: Unraveling the actin cytoskeleton in the malignant
transformation of cholangiocyte biology. Transl Oncol.
26:1015312022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao X, Zhang M, He J, Li X and Zhuang X:
Emerging insights into ferroptosis in cholangiocarcinoma (review).
Oncol Lett. 28:6062024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
R Core Team, . R: A language and
environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical
Computing; Vienna: 2024, URL. https://www.R–project.org/
|
|
31
|
Mayakonda A, Lin DC, Assenov Y, Plass C
and Koeffler HP: Maftools: Efficient and comprehensive analysis of
somatic variants in cancer. Genome Res. 28:1747–1756. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wilkerson MD and Hayes DN:
ConsensusClusterPlus: A class discovery tool with confidence
assessments and item tracking. Bioinformatics. 26:1572–1573. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jiang X, Stockwell BR and Conrad M:
Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 22:266–282. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang ZJ, Huang YP, Li XX, Liu ZT, Liu K,
Deng XF, Xiong L, Zou H and Wen Y: A novel ferroptosis-related
4-gene prognostic signature for cholangiocarcinoma and photodynamic
therapy. Front Oncol. 11:7474452021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Amontailak S, Titapun A, Jusakul A, Thanan
R, Kimawaha P, Jamnongkan W, Thanee M, Sirithawat P and Techasen A:
Prognostic values of ferroptosis-related proteins ACSL4, SLC7A11,
and CHAC1 in cholangiocarcinoma. Biomedicines. 12:20912024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wan S, Liang C, Wu C, Wang S, Wang J, Xu
L, Zhang X, Hou Y, Xia Y, Xu L and Huang X: Disulfidptosis in tumor
progression. Cell Death Discov. 11:2052025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hu F and Lito P: Insights into how
adeno-squamous transition drives KRAS inhibitor resistance. Cancer
Cell. 42:330–332. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mi T, Kong X, Chen M, Guo P and He D:
Inducing disulfidptosis in tumors: Potential pathways and
significance. MedComm (2020). 5:e7912024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xiao Y, Li ZZ, Zhong NN, Cao LM, Liu B and
Bu LL: Charting new frontiers: Co-inhibitory immune checkpoint
proteins in therapeutics, biomarkers, and drug delivery systems in
cancer care. Transl Oncol. 38:1017942023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cruz D, Rodríguez-Romanos R,
González-Bartulos M, García-Cadenas I, de la Cámara R, Heras I,
Buño I, Santos N, Lloveras N, Velarde P, et al: LAG3 genotype of
the donor and clinical outcome after allogeneic transplantation
from HLA-identical sibling donors. Front Immunol. 14:10663932023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Perea F, Sánchez-Palencia A, Gómez-Morales
M, Bernal M, Concha Á, García MM, González-Ramírez AR, Kerick M,
Martin J, Garrido F, et al: HLA class I loss and PD-L1 expression
in lung cancer: Impact on T-cell infiltration and immune escape.
Oncotarget. 9:4120–4133. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Saigí M, Mate JL, Carcereny E,
Martínez-Cardús A, Esteve A, Andreo F, Centeno C, Cucurull M, Mesia
R, Pros E and Sanchez-Cespedes M: HLA-I levels correlate with
survival outcomes in response to immune checkpoint inhibitors in
non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 189:1075022024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Itatani Y, Kawada K and Sakai Y:
Transforming growth Factor-β signaling pathway in colorectal cancer
and its tumor microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. 20:58222019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hao Y, Baker D and Ten Dijke P:
TGF-β-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer
metastasis. Int J Mol Sci. 20:27672019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Naoi H, Suzuki Y, Miyagi A, Horiguchi R,
Aono Y, Inoue Y, Yasui H, Hozumi H, Karayama M, Furuhashi K, et al:
CD109 attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting
TGF-β signaling. J Immunol. 212:1221–1231. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Taki T, Shiraki Y, Enomoto A, Weng L, Chen
C, Asai N, Murakumo Y, Yokoi K, Takahashi M and Mii S: CD109
regulates in vivo tumor invasion in lung adenocarcinoma through
TGF-β signaling. Cancer Sci. 111:4616–4628. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Litvinov IV, Bizet AA, Binamer Y, Jones
DA, Sasseville D and Philip A: CD109 release from the cell surface
in human keratinocytes regulates TGF-β receptor expression, TGF-β
signalling and STAT3 activation: Relevance to psoriasis. Exp
Dermatol. 20:627–632. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zeng X, Hunt A, Jin SC, Duran D, Gaillard
J and Kahle KT: EphrinB2-EphB4-RASA1 signaling in human
cerebrovascular development and disease. Trends Mol Med.
25:265–286. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhu F, Dai SN, Xu DL, Hou CQ, Liu TT, Chen
QY, Wu JL and Miao Y: EFNB2 facilitates cell proliferation,
migration, and invasion in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via the
p53/p21 pathway and EMT. Biomed Pharmacother. 125:1099722020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Xu C, Gu L, Kuerbanjiang M, Jiang C, Hu L,
Liu Y, Xue H, Li J, Zhang Z and Xu Q: Adaptive activation of
EFNB2/EPHB4 axis promotes post-metastatic growth of colorectal
cancer liver metastases by LDLR-mediated cholesterol uptake.
Oncogene. 42:99–112. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Koppula P, Zhang Y, Zhuang L and Gan B:
Amino acid transporter SLC7A11/xCT at the crossroads of regulating
redox homeostasis and nutrient dependency of cancer. Cancer Commun
(Lond). 38:122018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hwang YS, Cho HJ, Park ES, Lim J, Yoon HR,
Kim JT, Yoon SR, Jung H, Choe YK, Kim YH, et al: KLK6/PAR1 axis
promotes tumor growth and metastasis by regulating cross-talk
between tumor cells and macrophages. Cells. 11:41012022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang L, Lovell S, De Vita E, Jagtap PKA,
Lucy D, Goya Grocin A, Kjær S, Borg A, Hennig J, Miller AK and Tate
EW: A KLK6 activity-based probe reveals a role for KLK6 activity in
pancreatic cancer cell invasion. J Am Chem Soc. 144:22493–22504.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
He RZ, Zheng JH, Yao HF, Xu DP, Yang MW,
Liu DJ, Sun YW and Huo YM: ADAMTS12 promotes migration and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and predicts poor prognosis for
pancreatic cancer. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 22:169–178.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Dekky B, Azar F, Bonnier D, Monseur C,
Kalebić C, Arpigny E, Colige A, Legagneux V and Théret N: ADAMTS12
is a stromal modulator in chronic liver disease. FASEB J.
37:e232372023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|