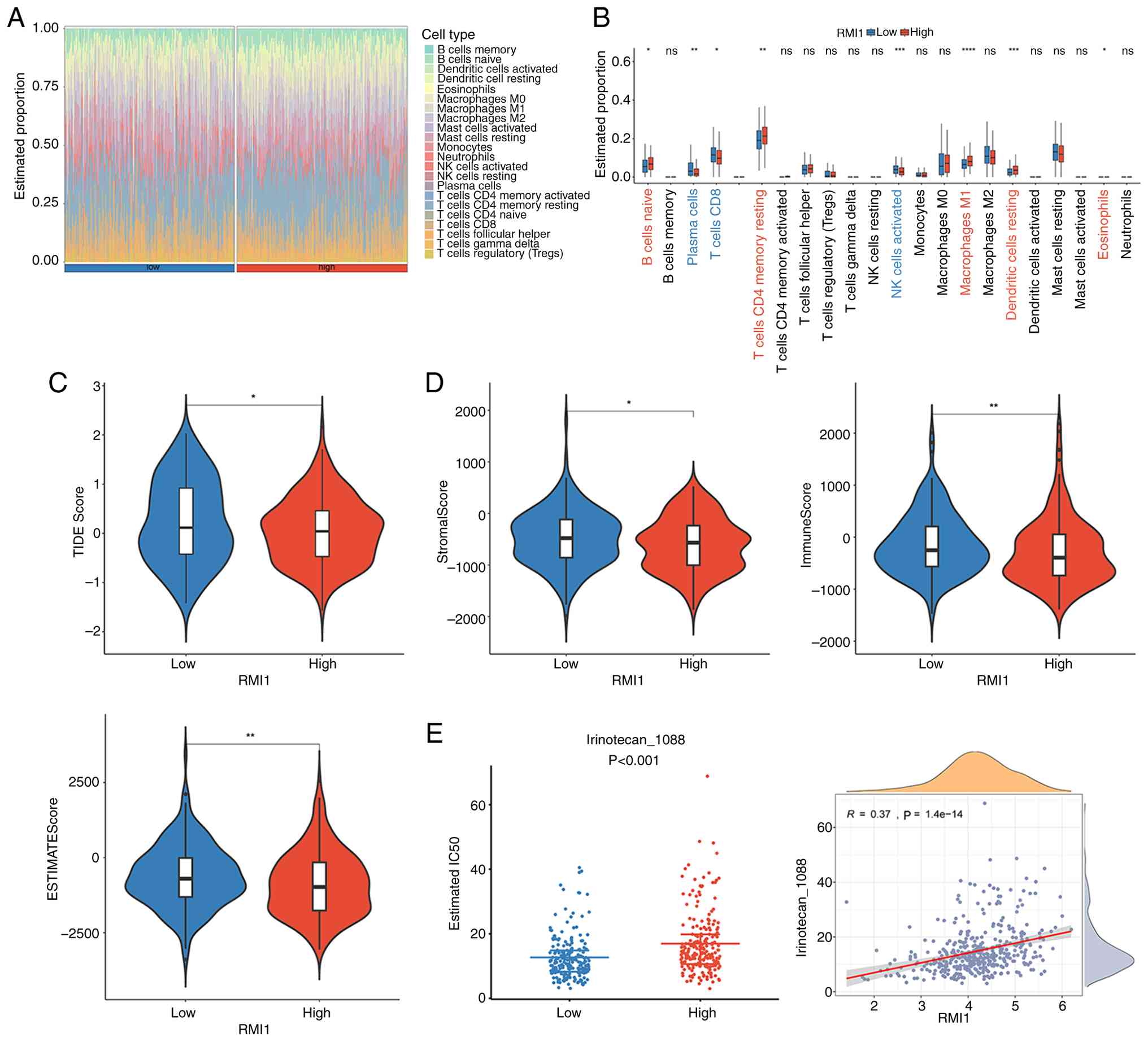
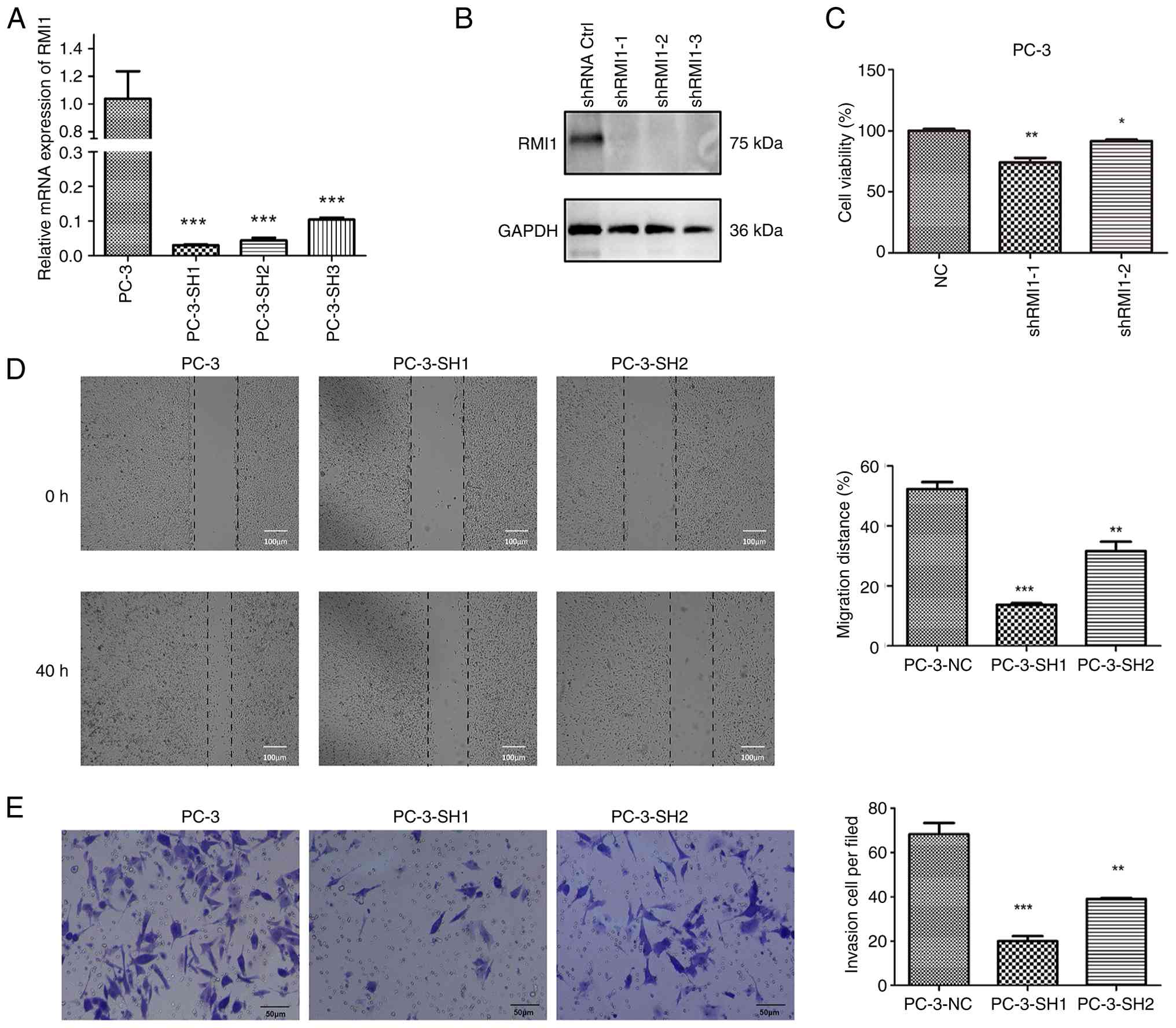
|
1
|
Rawla P: Epidemiology of prostate cancer.
World J Oncol. 10:63–89. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Graham LS, Lin JK, Lage DE, Kessler ER,
Parikh RB and Morgans AK: Management of prostate cancer in older
adults. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 43:e3903962023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sekhoacha M, Riet K, Motloung P, Gumenku
L, Adegoke A and Mashele S: Prostate cancer review: Genetics,
diagnosis, treatment options, and alternative approaches.
Molecules. 27:57302022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shen P, Sun J, Xu G, Zhang L, Yang Z, Xia
S, Wang Y, Liu Y and Shi G: KLF9, a transcription factor induced in
flutamide-caused cell apoptosis, inhibits AKT activation and
suppresses tumor growth of prostate cancer cells: KLF9 inhibits
tumor growth of prostate cancer cells. Prostate. 74:946–958. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yao K, Zhang R, Li L, Liu M, Feng S, Yan
H, Zhang Z and Xie D: The signature of cuproptosis-related immune
genes predicts the tumor microenvironment and prognosis of prostate
adenocarcinoma. Front Immunol. 14:11813702023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Altwaijry N, Somani S and Dufès C:
Targeted nonviral gene therapy in prostate cancer. Int J
Nanomedicine. 13:5753–5767. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ziaran S, Varchulova Novakova Z, Bohmer D
and Danisovic L: Biomarkers for determination prostate cancer:
Implication for diagnosis and prognosis. Neoplasma. 62:683–691.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Saxena S and Zou L: Hallmarks of DNA
replication stress. Mol Cell. 82:2298–2314. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bowry A, Kelly RDW and Petermann E:
Hypertranscription and replication stress in cancer. Trends Cancer.
7:863–877. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gaillard H, García-Muse T and Aguilera A:
Replication stress and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:276–89. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Maiorano D, El Etri J, Franchet C and
Hoffmann JS: Translesion synthesis or repair by specialized DNA
polymerases limits excessive genomic instability upon replication
stress. Int J Mol Sci. 22:39242021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ubhi T and Brown GW: Exploiting DNA
replication stress for cancer treatment. Cancer Res. 79:1730–1739.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bai G, Smolka MB and Schimenti JC: Chronic
DNA Replication stress reduces replicative lifespan of cells by
TRP53-Dependent, microRNA-Assisted MCM2-7 downregulation. PLoS
Genet. 12:e10057872016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Macheret M and Halazonetis TD: DNA
replication stress as a hallmark of cancer. Annu Rev Pathol.
10:425–448. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang Y, Gao Y, Mutter-Rottmayer L,
Zlatanou A, Durando M, Ding W, Wyatt D, Ramsden D, Tanoue Y,
Tateishi S and Vaziri C: DNA repair factor RAD18 and DNA polymerase
Polκ confer tolerance of oncogenic DNA replication stress. J Cell
Biol. 216:3097–3115. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang RH, Hong YK, Du H, Ke WQ, Lin BB and
Li YL: A machine learning framework develops a DNA replication
stress model for predicting clinical outcomes and therapeutic
vulnerability in primary prostate cancer. J Transl Med. 21:202023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin C, Salzillo TC, Bader DA, Wilkenfeld
SR, Awad D, Pulliam TL, Dutta P, Pudakalakatti S, Titus M, McGuire
SE, et al: Prostate cancer energetics and biosynthesis. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 1210:185–237. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Eidelman E, Twum-Ampofo J, Ansari J and
Siddiqui MM: The metabolic phenotype of prostate cancer. Front
Oncol. 7:1312017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Griffin JE: Androgen resistance-the
clinical and molecular spectrum. N Engl J Med. 326:611–618. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lima AR, Pinto J, Amaro F, Bastos ML,
Carvalho M and Guedes de Pinho P: Advances and perspectives in
prostate cancer biomarker discovery in the last 5 years through
tissue and urine metabolomics. Metabolites. 11:1812021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kwon H, Oh S, Jin X, An YJ and Park S:
Cancer metabolomics in basic science perspective. Arch Pharm Res.
38:372–380. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Green SM, Mostaghel EA and Nelson PS:
Androgen action and metabolism in prostate cancer. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 360:3–13. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cardoso HJ, Carvalho TMA, Fonseca LRS,
Figueira MI, Vaz CV and Socorro S: Revisiting prostate cancer
metabolism: From metabolites to disease and therapy. Med Res Rev.
41:1499–1538. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hardie DG: AMP-activated protein kinase:
An energy sensor that regulates all aspects of cell function. Genes
Dev. 25:1895–1908. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Penfold L, Woods A, Pollard AE, Arizanova
J, Pascual-Navarro E, Muckett PJ, Dore MH, Montoya A, Whilding C,
Fets L, et al: AMPK activation protects against prostate cancer by
inducing a catabolic cellular state. Cell Rep. 42:1123962023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shi S, Wen G, Lei C, Chang J, Yin X, Liu X
and Huang S: A DNA replication Stress-based prognostic model for
lung adenocarcinoma. Acta Naturae. 15:100–110. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
R: The R Project for Statistical
Computing.
|
|
28
|
Xu Q, Ma L, Streuer A, Altrock E, Schmitt
N, Rapp F, Klär A, Nowak V, Obländer J, Weimer N, et al: Machine
learning-based in-silico analysis identifies signatures of lysyl
oxidases for prognostic and therapeutic response prediction in
cancer. Cell Commun Signal. 23:1692025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Siddiqui JA, Seshacharyulu P, Muniyan S,
Pothuraju R, Khan P, Vengoji R, Chaudhary S, Maurya SK, Lele SM,
Jain M, et al: GDF15 promotes prostate cancer bone metastasis and
colonization through osteoblastic CCL2 and RANKL activation. Bone
Res. 10:62022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mahon KL, Sutherland SI, Lin HM, Stockler
MR, Gurney H, Mallesara G, Briscoe K, Marx G, Higano CS, de Bono
JS, et al: Clinical validation of circulating GDF15/MIC-1 as a
marker of response to docetaxel and survival in men with metastatic
castration-resistant prostate cancer. Prostate. 84:747–755. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yamamichi G, Kato T, Arakawa N, Ino Y,
Ujike T, Nakano K, Koh Y, Motoyama Y, Outani H, Myoba S, et al:
GDF15 propeptide promotes bone metastasis of castration-resistant
prostate cancer by augmenting the bone microenvironment. Biomark
Res. 12:1472024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang W, Hu C, Wang X, Bai S, Cao S,
Kobelski M, Lambert JR, Gu J and Zhan Y: Role of GDF15 in
methylseleninic acid-mediated inhibition of cell proliferation and
induction of apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. PLoS One.
14:e02228122019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang W, Yang X, Dai J, Lu Y, Zhang J and
Keller ET: Prostate cancer promotes a vicious cycle of bone
metastasis progression through inducing osteocytes to secrete GDF15
that stimulates prostate cancer growth and invasion. Oncogene.
38:4540–4559. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Teo MY, Rathkopf DE and Kantoff P:
Treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Annu Rev Med. 70:479–499.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Linxweiler J, Hajili T, Saar M, Maßmann C,
Junker K and Stöckle M: Influence of local treatment on the biology
of advanced prostate cancer : Treatment of the primary tumor may
delay hormone resistance of metastases. Urologe A. 61:518–525.
2022.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dreyer SB, Upstill-Goddard R, Paulus-Hock
V, Paris C, Lampraki EM, Dray E, Serrels B, Caligiuri G, Rebus S,
Plenker D, et al: Targeting DNA damage response and replication
stress in pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology. 160:362–377.e13.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yu SB and Pekkurnaz G: Mechanisms
orchestrating mitochondrial dynamics for energy homeostasis. J Mol
Biol. 430:3922–3941. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zadra G, Priolo C, Patnaik A and Loda M:
New strategies in prostate cancer: Targeting lipogenic pathways and
the energy sensor AMPK. Clin Cancer Res. 16:3322–3328. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li Y, He X, Zhang X, Xu Y, Chen W, Liu X
and Xu X: RMI2 is a prognostic biomarker and promotes tumor growth
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Exp Med. 22:229–243. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen S, Liu W and Huang Y: Identification
and external validation of a prognostic signature associated with
DNA repair genes in gastric cancer. Sci Rep. 11:71412021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xu C, Wang Y, Wang L, Wang Q, Du LQ, Fan
S, Liu Q and Li L: Accumulation and phosphorylation of
RecQ-mediated genome instability protein 1 (RMI1) at Serine 284 and
Serine 292 during Mitosis. Int J Mol Sci. 16:26395–405. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chen H, You MJ, Jiang Y, Wang W and Li L:
RMI1 attenuates tumor development and is essential for early
embryonic survival: RMI1 and Tumor Development. Mol Carcinog.
50:80–88. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Suwa A, Kurama T and Shimokawa T:
Adipocyte hyperplasia and RMI1 in the treatment of obesity:
Adipocyte hyperplasia and RMI1. FEBS J. 278:565–569. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Qian J, Xu Y, Xu X, Tao Z, Luo Y, Xu Y,
Zhang Y and Qian C: Hsa_circ_0091581 promotes glioma progression by
regulating RMI1 via sponging miR-1243-5p. J Cancer. 12:3249–3256.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Suwa A, Yoshino M, Yamazaki C, Naitou M,
Fujikawa R, Matsumoto S, Kurama T, Shimokawa T and Aramori I: RMI1
deficiency in mice protects from diet and Genetic-induced obesity.
FEBS J. 277:677–686. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Isaacsson Velho P and Antonarakis ES:
PD-1/PD-L1 pathway inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer. Expert
Rev Clin Pharmacol. 11:475–486. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang Q, Helfand BT, Carneiro BA, Qin W,
Yang XJ, Lee C, Zhang W, Giles FJ, Cristofanilli M and Kuzel TM:
Efficacy against human prostate cancer by prostate-specific
membrane antigen-specific, transforming growth Factor-β insensitive
genetically targeted CD8+ T-cells derived from patients with
metastatic Castrate-resistant disease. Eur Urol. 73:648–652. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bian X, Wang W, Abudurexiti M, Zhang X, Ma
W, Shi G, Du L, Xu M, Wang X, Tan C, et al: Integration analysis of
single-cell multi-omics reveals prostate cancer heterogeneity. Adv
Sci (Weinh). 11:e23057242024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang N, Wang S, Wang X, Zheng Y, Yang B,
Zhang J, Pan B, Gao J and Wang Z: Research trends in
pharmacological modulation of tumor-associated macrophages. Clin
Transl Med. 11:e2882021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gu Q, Qi A, Wang N, Zhou Z and Zhou X:
Macrophage dynamics in prostate cancer: Molecular to therapeutic
insights. Biomed Pharmacother. 177:1170022024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|