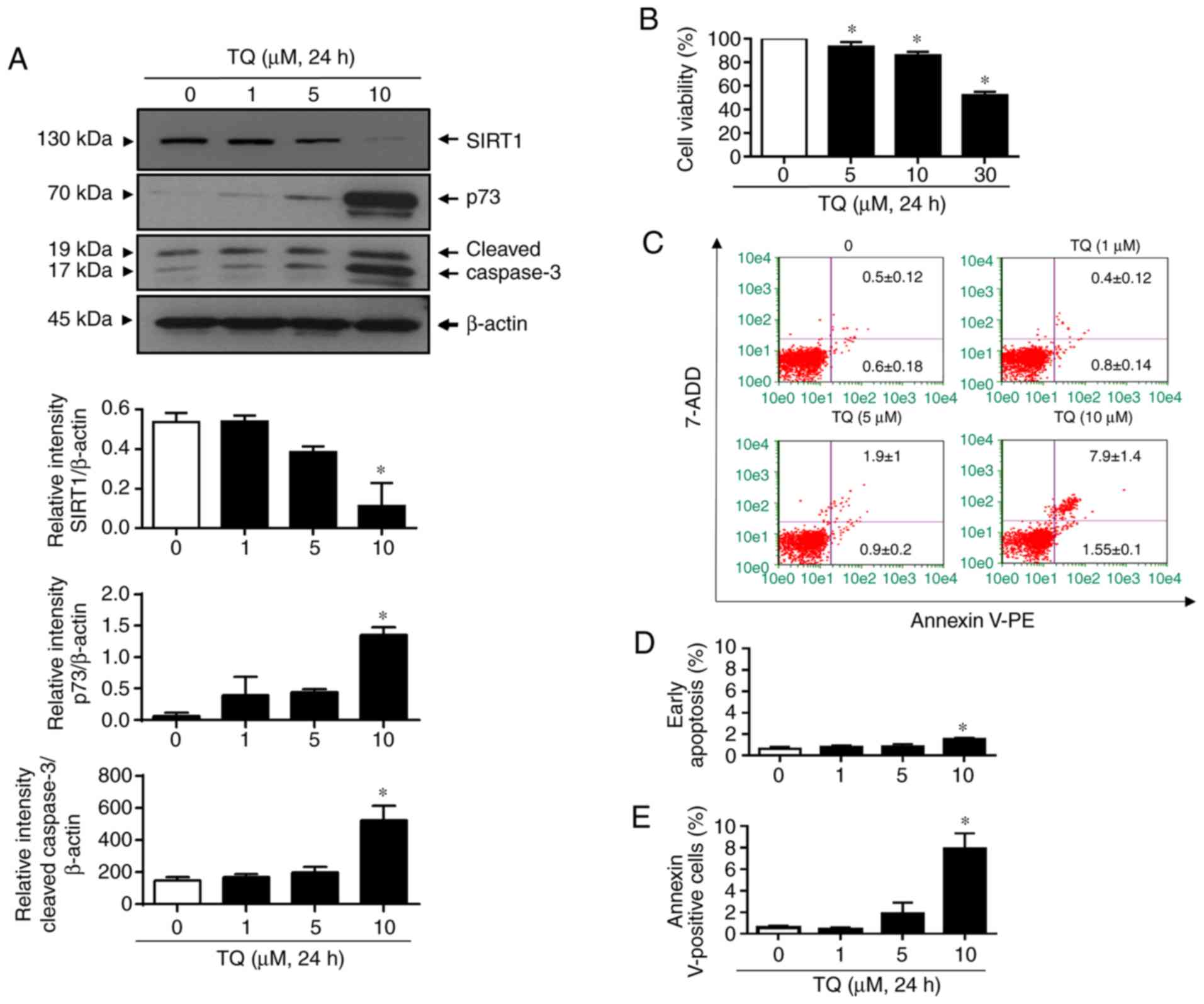
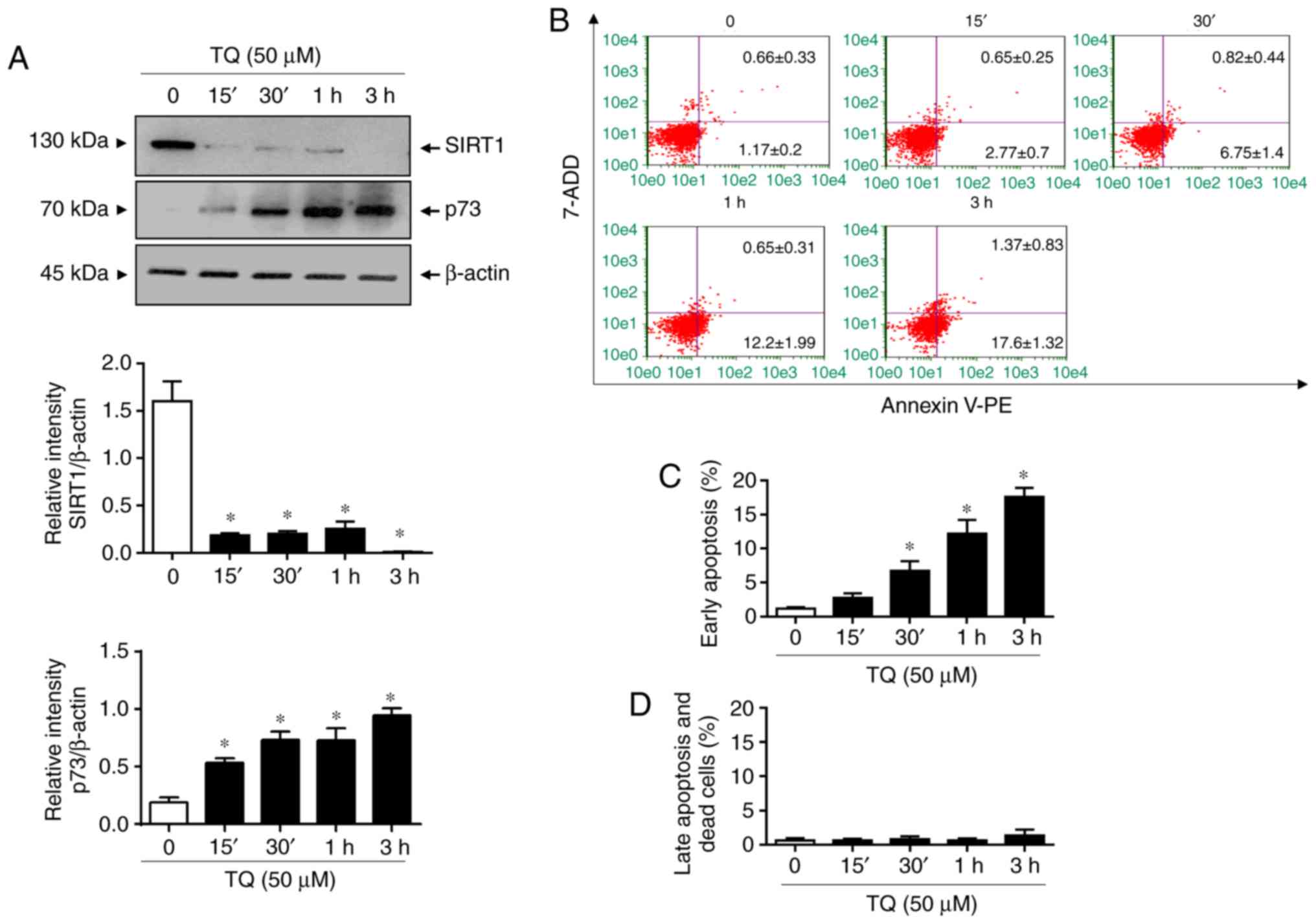
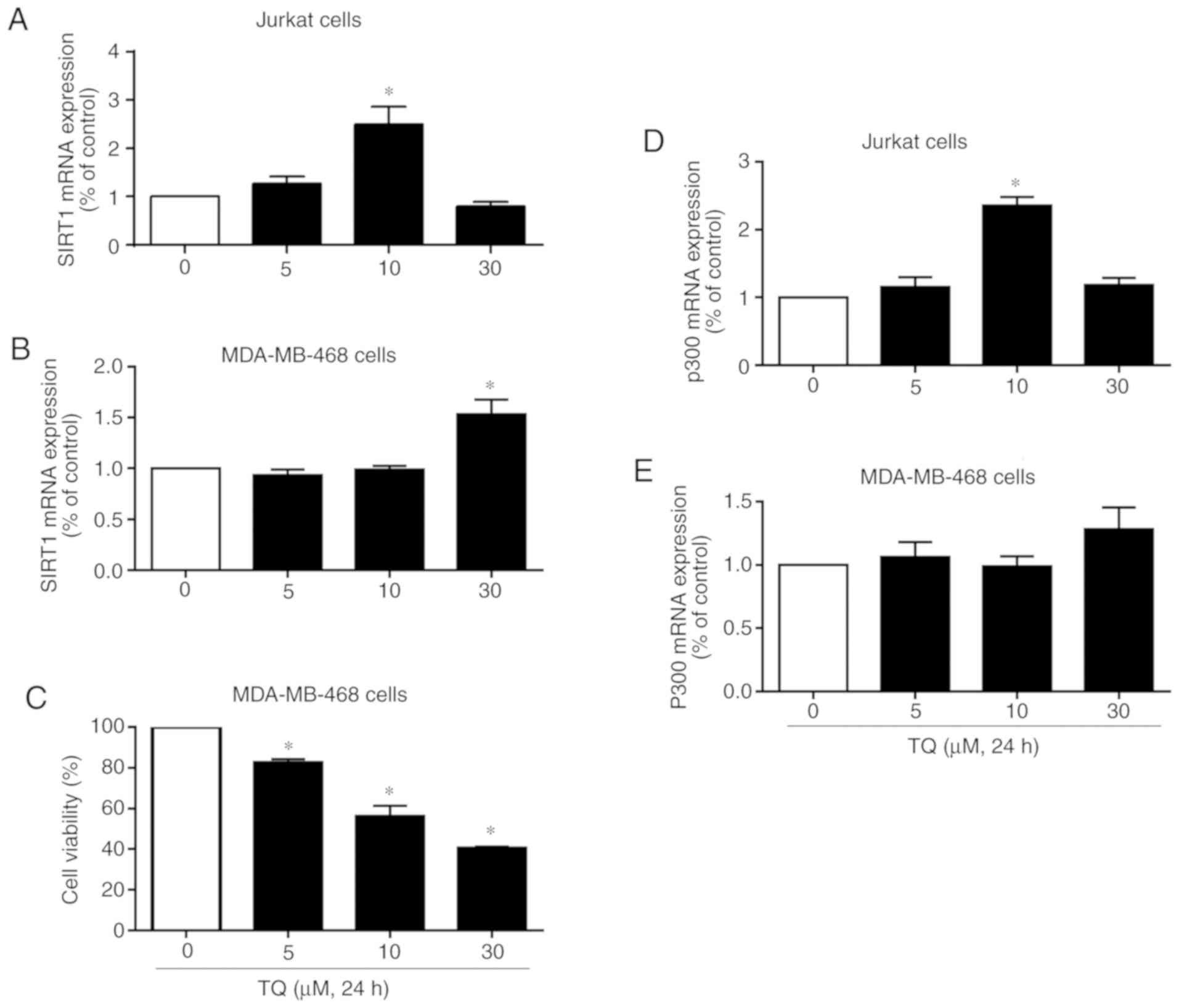
|
1
|
Jin Y, Cao Q, Chen C, Du X, Jin B and Pan
J: Tenovin-6-mediated inhibition of SIRT1/2 induces apoptosis in
acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cells and eliminates ALL
stem/progenitor cells. BMC Cancer. 15(226)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Yu W, Li L, Wang G, Zhang W, Xu J and
Liang A: KU70 inhibition impairs both non-homologous end joining
and homologous recombination DNA damage repair through SHP-1
induced dephosphorylation of SIRT1 in T-cell acute lymphoblastic
leukemia (T-ALL) [corrected]. Cell Physiol Biochem. 49:2111–2123.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Chung SY, Jung YY, Park IA, Kim H, Chung
YR, Kim JY, Park SY, Im SA, Lee KH, Moon HG, et al: Oncogenic role
of SIRT1 associated with tumor invasion, lymph node metastasis, and
poor disease-free survival in triple negative breast cancer. Clin
Exp Metastasis. 33:179–185. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sinha S, Patel S, Athar M, Vora J,
Chhabria MT, Jha PC and Shrivastava N: Structure-based
identification of novel sirtuin inhibitors against triple negative
breast cancer: An in silico and in vitro study. Int J Biol
Macromol. 140:454–468. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Cheng J and Haas M: Frequent mutations in
the p53 tumor suppressor gene in human leukemia T-cell lines. Mol
Cell Biol. 10:5502–5509. 1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Shan X, Czar MJ, Bunnell SC, Liu P, Liu Y,
Schwartzberg PL and Wange RL: Deficiency of PTEN in Jurkat T cells
causes constitutive localization of Itk to the plasma membrane and
hyperresponsiveness to CD3 stimulation. Mol Cell Biol.
20:6945–6957. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Shtraizent N, Matsui H, Polotskaia A and
Bargonetti J: Hot spot mutation in TP53 (R248Q) causes oncogenic
gain-of-function phenotypes in a breast cancer cell line derived
from an african american patient. Int J Environ Res Public Health.
13(ijerph13010022)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hollestelle A, Nagel JH, Smid M, Lam S,
Elstrodt F, Wasielewski M, Ng SS, French PJ, Peeters JK, Rozendaal
MJ, et al: Distinct gene mutation profiles among luminal-type and
basal-type breast cancer cell lines. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
121:53–64. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Imai S, Armstrong CM, Kaeberlein M and
Guarente L: Transcriptional silencing and longevity protein Sir2 is
an NAD-dependent histone deacetylase. Nature. 403:795–800.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Vaquero A, Scher M, Lee D,
Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P and Reinberg D: Human SirT1 interacts
with histone H1 and promotes formation of facultative
heterochromatin. Mol Cell. 16:93–105. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Vaziri H, Dessain SK, Ng Eaton E, Imai SI,
Frye RA, Pandita TK, Guarente L and Weinberg RA: hSIR2(SIRT1)
functions as an NAD-dependent p53 deacetylase. Cell. 107:149–159.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Dai JM, Wang ZY, Sun DC, Lin RX and Wang
SQ: SIRT1 interacts with p73 and suppresses p73-dependent
transcriptional activity. J Cell Physiol. 210:161–166.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Dotsch V, Bernassola F, Coutandin D, Candi
E and Melino G: p63 and p73, the ancestors of p53. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 2(a004887)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Marin MC, Jost CA, Irwin MS, DeCaprio JA,
Caput D and Kaelin WG Jr: Viral oncoproteins discriminate between
p53 and the p53 homolog p73. Mol Cell Biol. 18:6316–6324.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ahmadianpour MR, Abdolmaleki P, Mowla SJ
and Hosseinkhani S: Gamma radiation alters cell cycle and induces
apoptosis in p53 mutant E6.1 Jurkat cells. Appl Radiat Isot.
71:29–33. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ahmadianpour MR, Abdolmaleki P, Mowla SJ
and Hosseinkhani S: Static magnetic field of 6 mT induces apoptosis
and alters cell cycle in p53 mutant Jurkat cells. Electromagn Biol
Med. 32:9–19. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Laumann R, Jucker M and Tesch H: Point
mutations in the conserved regions of the p53 tumour suppressor
gene do not account for the transforming process in the Jurkat
acute lymphoblastic leukemia T-cells. Leukemia. 6:227–228.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lim LY, Vidnovic N, Ellisen LW and Leong
CO: Mutant p53 mediates survival of breast cancer cells. Br J
Cancer. 101:1606–1612. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Qiu WG, Polotskaia A, Xiao G, Di L, Zhao
Y, Hu W, Philip J, Hendrickson RC and Bargonetti J: Identification,
validation, and targeting of the mutant p53-PARP-MCM chromatin axis
in triple negative breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer.
3:2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bouras T, Fu M, Sauve AA, Wang F, Quong
AA, Perkins ND, Hay RT, Gu W and Pestell RG: SIRT1 deacetylation
and repression of p300 involves lysine residues 1020/1024 within
the cell cycle regulatory domain 1. J Biol Chem. 280:10264–10276.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zeng X, Chen L, Jost CA, Maya R, Keller D,
Wang X, Kaelin WG Jr, Oren M, Chen J and Lu H: MDM2 suppresses p73
function without promoting p73 degradation. Mol Cell Biol.
19:3257–3266. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zeng X, Li X, Miller A, Yuan Z, Yuan W,
Kwok RP, Goodman R and Lu H: The N-terminal domain of p73 interacts
with the CH1 domain of p300/CREB binding protein and mediates
transcriptional activation and apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol.
20:1299–1310. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Costanzo A, Merlo P, Pediconi N, Fulco M,
Sartorelli V, Cole PA, Fontemaggi G, Fanciulli M, Schiltz L,
Blandino G, et al: DNA damage-dependent acetylation of p73 dictates
the selective activation of apoptotic target genes. Mol Cell.
9:175–186. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Alhosin M, Abusnina A, Achour M, Sharif T,
Muller C, Peluso J, Chataigneau T, Lugnier C, Schini-Kerth VB,
Bronner C and Fuhrmann G: Induction of apoptosis by thymoquinone in
lymphoblastic leukemia Jurkat cells is mediated by a p73-dependent
pathway which targets the epigenetic integrator UHRF1. Biochem
Pharmacol. 79:1251–1260. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Alhosin M, Ibrahim A, Boukhari A, Sharif
T, Gies JP, Auger C and Schini-Kerth VB: Anti-neoplastic agent
thymoquinone induces degradation of α and β tubulin proteins in
human cancer cells without affecting their level in normal human
fibroblasts. Invest New Drugs. 30:1813–1819. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ibrahim A, Alhosin M, Papin C, Ouararhni
K, Omran Z, Zamzami MA, Al-Malki AL, Choudhry H, Mély Y, Hamiche A,
et al: Thymoquinone challenges UHRF1 to commit auto-ubiquitination:
A key event for apoptosis induction in cancer cells. Oncotarget.
9:28599–28611. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Qadi SA, Hassan MA, Sheikh RA, Baothman
OA, Zamzami MA, Choudhry H, Al-Malki AL, Albukhari A and Alhosin M:
Thymoquinone-induced reactivation of tumor suppressor genes in
cancer cells involves epigenetic mechanisms. Epigenet Insights.
12(2516865719839011)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Helmy SA, El-Mesery M, El-Karef A, Eissa
LA and El Gayar AM: Thymoquinone upregulates TRAIL/TRAILR2
expression and attenuates hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo model.
Life Sci. 233(116673)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhu WQ, Wang J, Guo XF, Liu Z and Dong WG:
Thymoquinone inhibits proliferation in gastric cancer via the STAT3
pathway in vivo and in vitro. World J Gastroenterol. 22:4149–4159.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gali-Muhtasib HU, Abou Kheir WG, Kheir LA,
Darwiche N and Crooks PA: Molecular pathway for
thymoquinone-induced cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in neoplastic
keratinocytes. Anticancer Drugs. 15:389–399. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ivankovic S, Stojkovic R, Jukic M, Milos
M, Milos M and Jurin M: The antitumor activity of thymoquinone and
thymohydroquinone in vitro and in vivo. Exp Oncol. 28:220–224.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Langley E, Pearson M, Faretta M, Bauer UM,
Frye RA, Minucci S, Pelicci PG and Kouzarides T: Human SIR2
deacetylates p53 and antagonizes PML/p53-induced cellular
senescence. EMBO J. 21:2383–2396. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lin Z and Fang D: The roles of SIRT1 in
cancer. Genes Cancer. 4:97–104. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ban J, Aryee DN, Fourtouna A, van der Ent
W, Kauer M, Niedan S, Machado I, Rodriguez-Galindo C, Tirado OM,
Schwentner R, et al: Suppression of deacetylase SIRT1 mediates
tumor-suppressive NOTCH response and offers a novel treatment
option in metastatic Ewing sarcoma. Cancer Res. 74:6578–6588.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ming M, Soltani K, Shea CR, Li X and He
YY: Dual role of SIRT1 in UVB-induced skin tumorigenesis. Oncogene.
34:357–363. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Liarte S, Alonso-Romero JL and Nicolas FJ:
SIRT1 and estrogen signaling cooperation for breast cancer onset
and progression. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9(552)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Sharif T, Ahn DG, Liu RZ, Pringle E,
Martell E, Dai C, Nunokawa A, Kwak M, Clements D, Murphy JP, et al:
The NAD(+) salvage pathway modulates cancer cell viability via p73.
Cell Death Differ. 23:669–680. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Momeny M, Zakidizaji M, Ghasemi R, Dehpour
AR, Rahimi-Balaei M, Abdolazimi Y, Ghavamzadeh A, Alimoghaddam K
and Ghaffari SH: Arsenic trioxide induces apoptosis in NB-4, an
acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line, through up-regulation of
p73 via suppression of nuclear factor kappa B-mediated inhibition
of p73 transcription and prevention of NF-kappaB-mediated induction
of XIAP, cIAP2, BCL-XL and survivin. Med Oncol. 27:833–842.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|