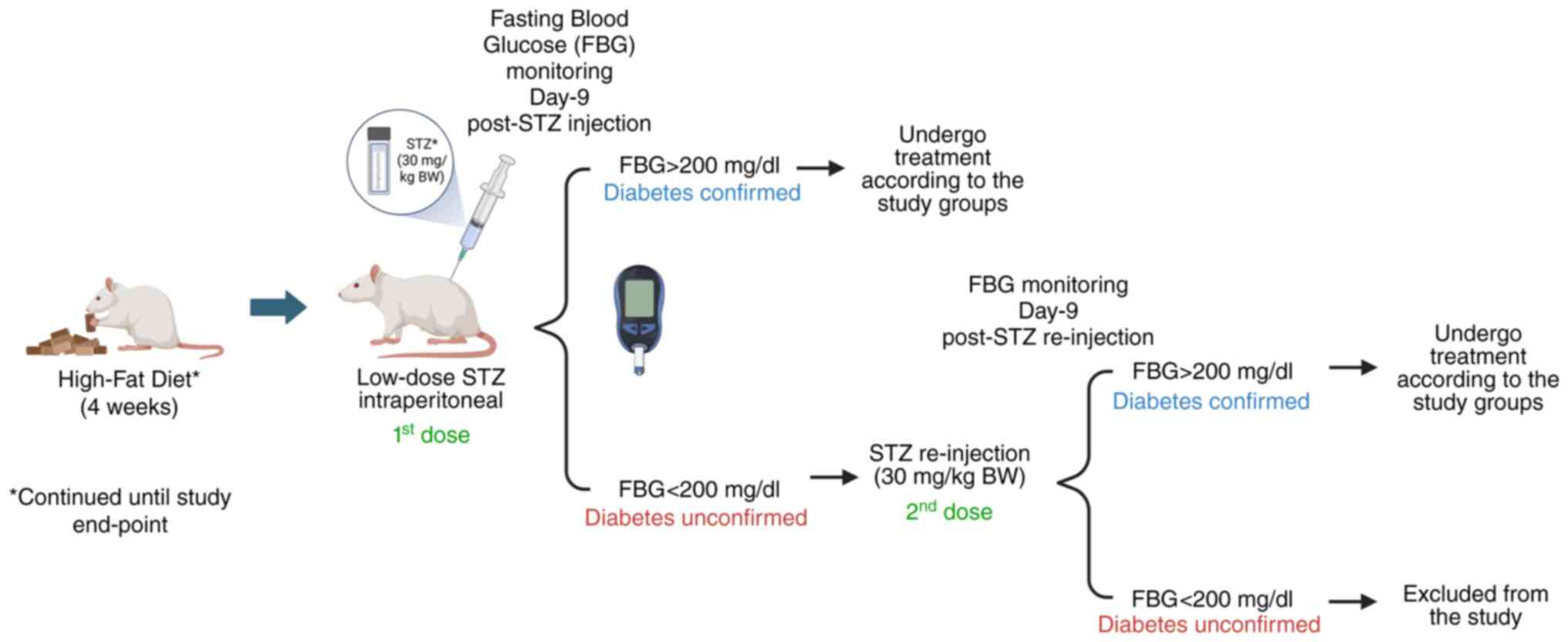
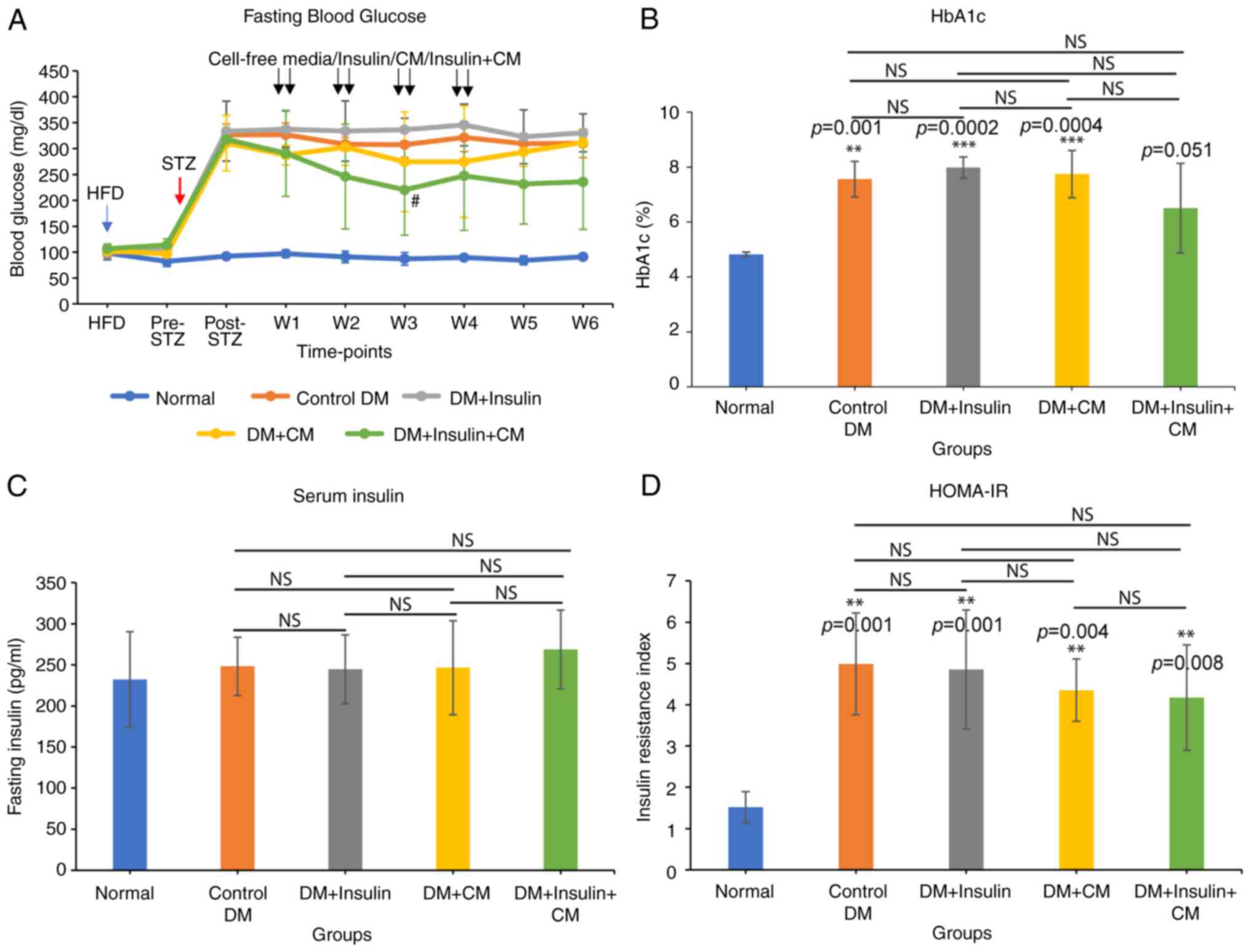
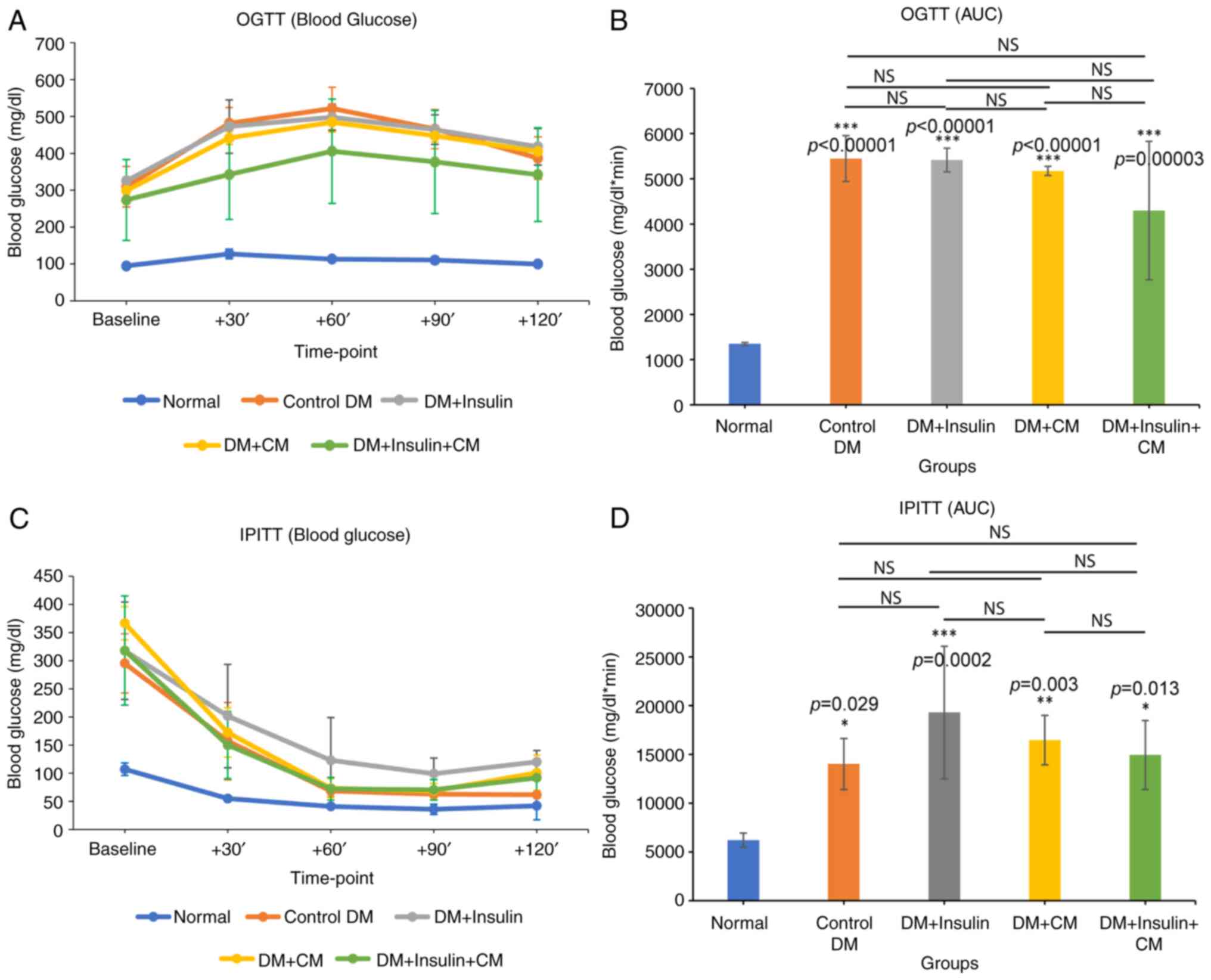
|
1
|
Lin X, Xu Y, Pan X, Xu J, Ding Y, Sun X,
Song X, Ren Y and Shan PF: Global, regional, and national burden
and trend of diabetes in 195 countries and territories: An analysis
from 1990 to 2025. Sci Rep. 10:1–11. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Magliano DJ and Boyko EJ: IDF diabetes
atlas. 10th ed. International Diabetes Federation, Brussels,
2021.
|
|
3
|
Ohiagu FO, Chikezie PC and Chikezie CM:
Pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus complications: Metabolic
events and control. Biomed Res Ther. 8:4243–4257. 2021.
|
|
4
|
Galicia-Garcia U, Benito-Vicente A, Jebari
S, Larrea-Sebal A, Siddiqi H, Uribe KB, Ostolaza H and Martín C:
Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Mol Sci.
21:1–34. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Halban PA, Polonsky KS, Bowden DW, Hawkins
MA, Ling C, Mather KJ, Powers AC, Rhodes CJ, Sussel L and Weir GC:
β-Cell failure in type 2 diabetes: Postulated mechanisms and
prospects for prevention and treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
99:1983–1992. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Christensen AA and Gannon M: The beta cell
in type 2 diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 19(81)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Pradhan AD, Manson JE, Rifai N, Buring JE
and Ridker PM: C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and risk of
developing type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Am Med Assoc. 286:327–334.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Esser N, Legrand-Poels S, Piette J, Scheen
AJ and Paquot N: Inflammation as a link between obesity, metabolic
syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 105:141–150.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bunney PE, Zink AN, Holm AA, Billington CJ
and Kotz CM: Orexin activation counteracts decreases in nonexercise
activity thermogenesis (NEAT) caused by high-fat diet. Physiol
Behav. 176:139–148. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Huang B, Cheng X, Wang H, Huang W, la Ga
hu Z, Wang D, Zhang K, Zhang H, Xue Z, Da Y, et al: Mesenchymal
stem cells and their secreted molecules predominantly ameliorate
fulminant hepatic failure and chronic liver fibrosis in mice
respectively. J Transl Med. 14(45)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Fan CG, Zhang QJ and Zhou JR: Therapeutic
potentials of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical
cord. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 7:195–207. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Pawitan JA: Prospect of stem cell
conditioned medium in regenerative medicine. Biomed Res Int.
2014:7–9. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kim HO, Choi SM and Kim HS: Mesenchymal
stem cell-derived secretome and microvesicles as a cell-free
therapeutics for neurodegenerative disorders. Tissue Eng Regen Med.
10:93–101. 2013.
|
|
14
|
Isildar B, Ozkan S and Koyuturk M:
Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived conditioned
medium for diabetes mellitus and related complications. Adv Ther.
6(2300216)2023.
|
|
15
|
Nagaishi K, Ataka K, Echizen E, Arimura Y
and Fujimiya M: Mesenchymal stem cell therapy ameliorates diabetic
hepatocyte damage in mice by inhibiting infiltration of bone
marrow-derived cells. Hepatology. 59:1816–1829. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ormazabal V, Nova-Lampeti E, Rojas D,
Zúñiga FA, Escudero C, Lagos P, Moreno A, Pavez Y, Reyes C, Yáñez
M, et al: Secretome from human mesenchymal stem cells-derived
endothelial cells promotes wound healing in a type-2 diabetes mouse
model. Int J Mol Sci. 23(941)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Sun Y, Shi H, Yin S, Ji C, Zhang X, Zhang
B, Wu P, Shi Y, Mao F, Yan Y, et al: Human mesenchymal stem cell
derived exosomes alleviate type 2 diabetes mellitus by reversing
peripheral insulin resistance and relieving β-cell destruction. ACS
Nano. 12:7613–7628. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hendrawan S, Marcelina O, Tan ST and Baer
HU: Immobilization of hUC-MSCs conditioned medium on 3D PLLA
collagen-coated matrix enhances diabetic wound healing progression.
Eng Regen. 5:421–431. 2024.
|
|
19
|
Charan J and Kantharia N: How to calculate
sample size in animal studies? J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 4:303–306.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Arifin WN and Zahiruddin WM: Sample size
calculation in animal studies using resource equation approach.
Malaysian J Med Sci. 24:101–105. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Gunawan S, Aulia A and Soetikno V:
Development of rat metabolic syndrome models: A review. Vet World.
14:1774–1783. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Gunawan S, Munika E, Wulandari ET,
Ferdinal F, Purwaningsih EH, Wuyung PE, Louisa M and Soetikno V:
6-gingerol ameliorates weight gain and insulin resistance in
metabolic syndrome rats by regulating adipocytokines. Saudi Pharm
J. 31:351–358. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and
Prevalence Collaborators: Global, regional, and national incidence,
prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and
injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: A systematic
analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet.
392:1789–1858. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kume E, Fujimura H, Matsuki N, Ito M,
Aruga C, Toriumi W, Kitamura K and Doi K: Hepatic changes in the
acute phase of streptozotocin (SZ)-induced diabetes in mice. Exp
Toxicol Pathol. 55:467–480. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Karimi Z, Daryabor G and Masjedi F:
Effects of conditioned media derived from human Wharton's jelly
mesenchymal stem cells on diabetic nephropathy and hepatopathy via
modulating TGF-β and apelin signaling pathways in male rats. BMC
Endocr Disord. 24:1–15. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Utami A, Putra A, Wibowo JW, Amalina ND
and Irawan RCS: Hypoxic secretome mesenchymal stem cells inhibiting
interleukin-6 expression prevent oxidative stress in type 1
diabetes mellitus. Med Glas. 20:148–155. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Leng YP, Qiu N, Fang WJ, Zhang M, He ZM
and Xiong Y: Involvement of increased endogenous asymmetric
dimethylarginine in the hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress of
type 2 diabetic rats. PLoS One. 9(e97125)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wallace TM, Levy JC and Matthews DR: Use
and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care. 27:1487–1495.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Biadgo B, Tamir W and Ambachew S:
Insulin-like growth factor and its therapeutic potential for
diabetes complications mechanisms and metabolic links: A review.
Rev Diabet Stud. 16:24–34. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liu TY, Shi CX, Gao R, Sun HJ, Xiong XQ,
Ding L, Chen Q, Li YH, Wang JJ, Kang YM and Zhu GQ: Irisin inhibits
hepatic gluconeogenesis and increases glycogen synthesis via the
PI3K/Akt pathway in type 2 diabetic mice and hepatocytes. Clin Sci
(Lond). 129:839–850. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lee SH, Park SY and Choi CS: Insulin
resistance: From mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. Diabetes
Metab J. 46:15–37. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Campbell JE and Newgard CB: Mechanisms
controlling pancreatic islet cell function in insulin secretion.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 22:142–158. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
De la Cruz Concepción B, Flores-Cortez YA,
Barragán-Bonilla MI, Mendoza-Bello JM and Espinoza-Rojo M: Insulin:
A connection between pancreatic β cells and the hypothalamus. World
J Diabetes. 14:76–91. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Tangvarasittichai S: Oxidative stress,
insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
World J Diabetes. 6:456–480. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Mauricio D, Alonso N and Gratacòs M:
Chronic diabetes complications: The need to move beyond classical
concepts. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 31:287–295. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Mendez CE, Walker RJ, Eiler CR, Mishriky
BM and Egede LE: Insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes
and high insulin resistance is associated with increased risk of
complications and mortality. Postgrad Med. 131:376–382.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Mitrousis N, Fokina A and Shoichet MS:
Biomaterials for cell transplantation. Nat Rev Mater. 3:441–456.
2018.
|
|
38
|
Sortwell CE, Pitzer MR and Collier TJ:
Time course of apoptotic cell death within mesencephalic cell
suspension grafts: Implications for improving grafted dopamine
neuron survival. Exp Neurol. 165:268–277. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Hsiao STF, Asgari A, Lokmic Z, Sinclair R,
Dusting GJ, Lim SY and Dilley RJ: Comparative analysis of paracrine
factor expression in human adult mesenchymal stem cells derived
from bone marrow, adipose, and dermal tissue. Stem Cells Dev.
21:2189–2203. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Li S, Liu J, Liu S, Jiao W and Wang X:
Chitosan oligosaccharides packaged into rat adipose mesenchymal
stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles facilitating cartilage
injury repair and alleviating osteoarthritis. J Nanobiotechnology.
19(343)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Li S, Liu J, Liu S, Jiao W and Wang X:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles prevent the
development of osteoarthritis via the circHIPK3/miR-124-3p/MYH9
axis. J Nanobiotechnology. 19(194)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Cheng H, Chang S, Xu R, Chen L, Song X, Wu
J, Qian J, Zou Y and Ma J: Hypoxia-challenged MSC-derived exosomes
deliver miR-210 to attenuate post-infarction cardiac apoptosis.
Stem Cell Res Ther. 11(224)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhu D, Liu S, Huang K, Wang Z, Hu S, Li J,
Li Z and Cheng K: Intrapericardial exosome therapy dampens cardiac
injury via activating Foxo3. Circ Res. 131:e135–e150.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Kandeel M, Morsy MA, Alkhodair KM and
Alhojaily S: Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles:
An emerging diagnostic and therapeutic biomolecules for
neurodegenerative disabilities. Biomolecules.
13(1250)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Wu B, Feng J, Guo J, Wang J, Xiu G and Xu
J, Ning K, Ling B, Fu Q and Xu J: ADSCs-derived exosomes ameliorate
hepatic fibrosis by suppressing stellate cell activation and
remodeling hepatocellular glutamine synthetase-mediated glutamine
and ammonia homeostasis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 13(494)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Allan D, Tieu A, Lalu M and Burger D:
Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles for
regenerative therapy and immune modulation: Progress and challenges
toward clinical application. Stem Cells Transl Med. 9:39–46.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Li W, Jin L, Cui Y and Xie N: Human
umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal
microRNA-17-3p ameliorates inflammatory reaction and antioxidant
injury of mice with diabetic retinopathy via targeting STAT1. Int
Immunopharmacol. 90(107010)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Yang J, Chen Z, Pan D, Li H and Shen J:
umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes
combined pluronic F127 hydrogel promote chronic diabetic wound
healing and complete skin regeneration. Int J Nanomedicine.
15:5911–5926. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Masithoh DBH, Fibrianto YH, Anggita M,
Nugroho WS and Budipitojo T: Mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned
medium improve the recovery of pancreatic α and β cells in type 1
diabetes mellitus. In: Proceedings of the 20th FAVA Congress and
the 15th KIVNAS PDHI. Bali, Nov 1-3, pp 172–174, 2018. https://journal.ipb.ac.id/hemera/article/view/23814/15670.
|
|
50
|
Liu X, Zheng P, Wang X, Dai G, Cheng H,
Zhang Z, Hua R, Niu X, Shi J and An Y: A preliminary evaluation of
efficacy and safety of Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cell
transplantation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Stem
Cell Res Ther. 5(57)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Zang L, Hao H, Liu J, Li Y, Han W and Mu
Y: Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Diabetol Metab Syndr. 9:1–11. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Kim KS, Choi YK, Kim MJ, Hwang JW, Min K,
Jung SY, Kim SK, Choi YS and Cho YW: Umbilical cord-mesenchymal
stem cell-conditioned medium improves insulin resistance in c2c12
cell. Diabetes Metab J. 44:260–269. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Zhang X, Li Z, Liu D, Xu X, Shen W and Mei
Z: Effects of probucol on hepatic tumor necrosis factor-α,
interleukin-6 and adiponectin receptor-2 expression in diabetic
rats. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 24:1058–1063. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Klover PJ, Zimmers TA, Koniaris LG and
Mooney RA: Chronic exposure to interleukin-6 causes hepatic insulin
resistance in mice. Diabetes. 52:2784–2789. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Shalaby MS, Abdel-Reheim ES, Almanaa TN,
Alhaber LA, Nabil A, Ahmed OM, Elwan M and Abdel-Moneim A:
Therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell conditioned media on
streptozotocin-induced diabetes in Wistar rats. Regen Ther.
28:1–11. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Kuo FY, Cheng KC, Li Y and Cheng JT: Oral
glucose tolerance test in diabetes, the old method revisited. World
J Diabetes. 12:786–793. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Liu KF, Niu CS, Tsai JC, Yang CL, Peng WH
and Niu HS: Comparison of area under the curve in various models of
diabetic rats receiving chronic medication. Arch Med Sci.
18:1078–1087. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Kasprzak A: Insulin-like growth factor 1
(IGF-1) signaling in glucose metabolism in colorectal cancer. Int J
Mol Sci. 22(6434)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Kim SH and Park MJ: Effects of growth
hormone on glucose metabolism and insulin resistance in human. Ann
Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 22:145–152. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Clemmons DR: Role of insulin-like growth
factor iin maintaining normal glucose homeostasis. Horm Res
Paediatr. 62:77–82. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Van Dijk PR, Logtenberg SJJ, Chisalita SI,
Hedman CA, Groenier KH, Gans ROB, Kleefstra N, Arnqvist HJ and Bilo
HJG: Different effects of intraperitoneal and subcutaneous insulin
administration on the GH-IGF-1 axis in type 1 diabetes. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 101:2493–2501. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Nijenhuis-Noort EC, Berk KA, Neggers SJCMM
and van der Lely AJ: The fascinating interplay between growth
hormone, insulin-like growth factor-1, and insulin. Endocrinol
Metab (Seoul). 39:83–89. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Li N, Guenancia C, Rigal E, Hachet O,
Chollet P, Desmoulins L, Leloup C, Rochette L and Vergely C:
Short-term moderate diet restriction in adulthood can reverse
oxidative, cardiovascular and metabolic alterations induced by
postnatal overfeeding in mice. Sci Rep. 6(30817)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Su W, Yu S, Yin Y, Li B, Xue J, Wang J, Gu
Y, Zhang H, Lyu Z, Mu Y and Cheng Y: Diabetic microenvironment
preconditioning of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells
enhances their anti-diabetic, anti-long-term complications, and
anti-inflammatory effects in type 2 diabetic rats. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 13:1–14. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Zeinhom A, Fadallah SA and Mahmoud M:
Human mesenchymal stem/stromal cell based-therapy in diabetes
mellitus: Experimental and clinical perspectives. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 15(384)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Kono TM, Sims EK, Moss DR, Yamamoto W, Ahn
G, Diamond J, Tong X, Day KH, Territo PR, Hanenberg H, et al: Human
adipose-derived stromal/stem cells protect against STZ-induced
hyperglycemia: Analysis of hASC-derived paracrine effectors. Stem
Cells. 32:1831–1842. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
El-Kersh AOFO, El-Akabawy G and Al-Serwi
RH: Transplantation of human dental pulp stem cells in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Anat Sci Int. 95:523–539.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Yang M, Chen J and Chen L: The roles of
mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in diabetes mellitus and its
related complications. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:1–16.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Yap SK, Tan KL, Rahaman NY, Hamid NF, Ooi
DJ, Tor YS, Looi QH, Tan LK, How CW and Foo JB: Human umbilical
cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles
ameliorated insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats.
Pharmaceutics. 14(649)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Kim JE, Lee JW, Cha GD and Yoon JK: The
potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes to treat
diabetes mellitus. Biomimetics (Basel). 10(49)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Keshtkar S, Azarpira N and Ghahremani MH:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: Novel
frontiers in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Res Ther.
9(63)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Abu-Rmeileh NME, Husseini A, Capewell S
and O'Flaherty M: MEDCHAMPS project. Preventing type 2 diabetes
among Palestinians: Comparing five future policy scenarios. BMJ
Open. 3(e003558)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Laggner M, Gugerell A, Bachmann C,
Hofbauer H, Vorstandlechner V, Seibold M, Lechner GG, Peterbauer A,
Madlener S, Demyanets S, et al: Reproducibility of GMP-compliant
production of therapeutic stressed peripheral blood mononuclear
cell-derived secretomes, a novel class of biological medicinal
products. Stem Cell Res Ther. 11:1–16. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|