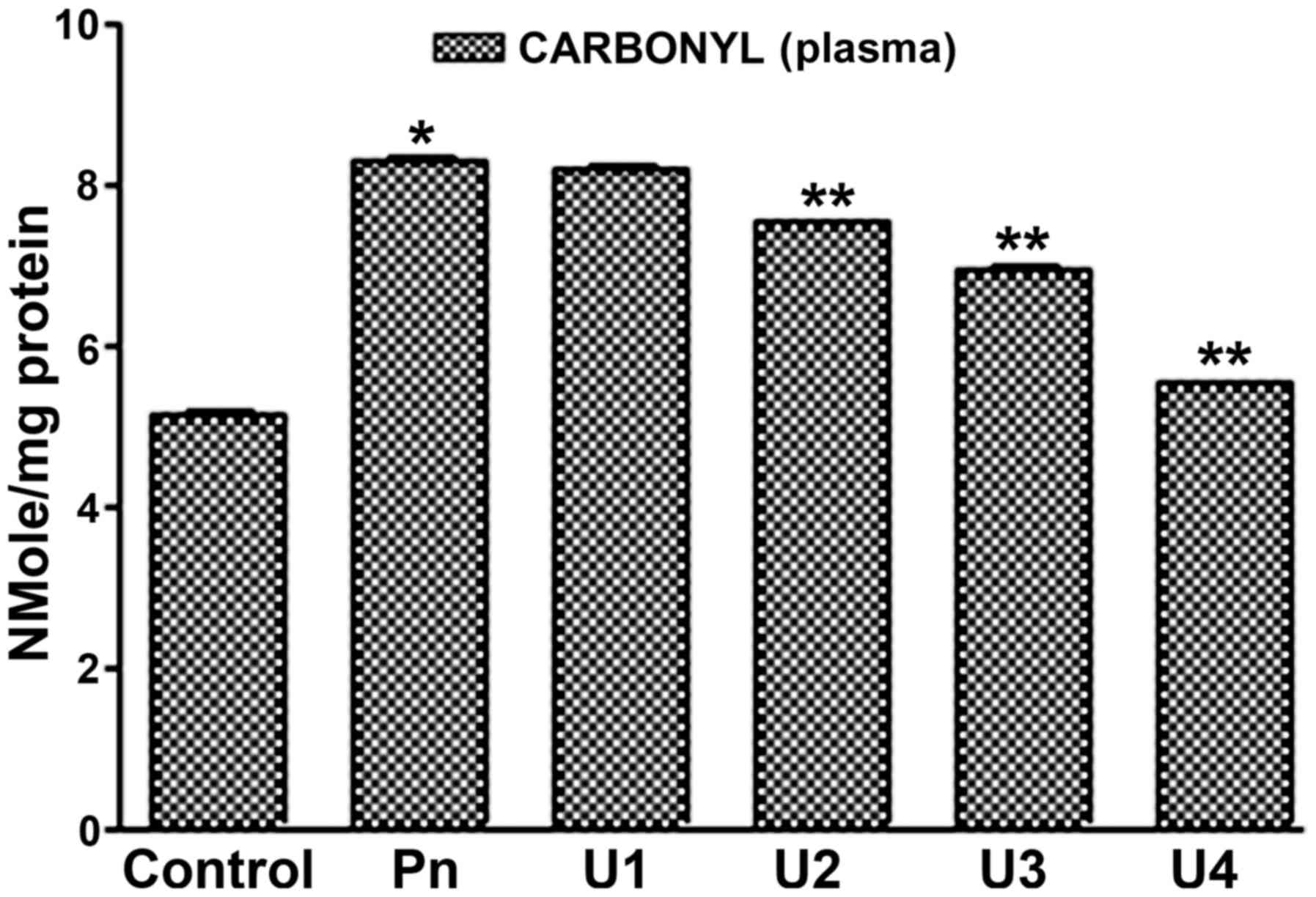
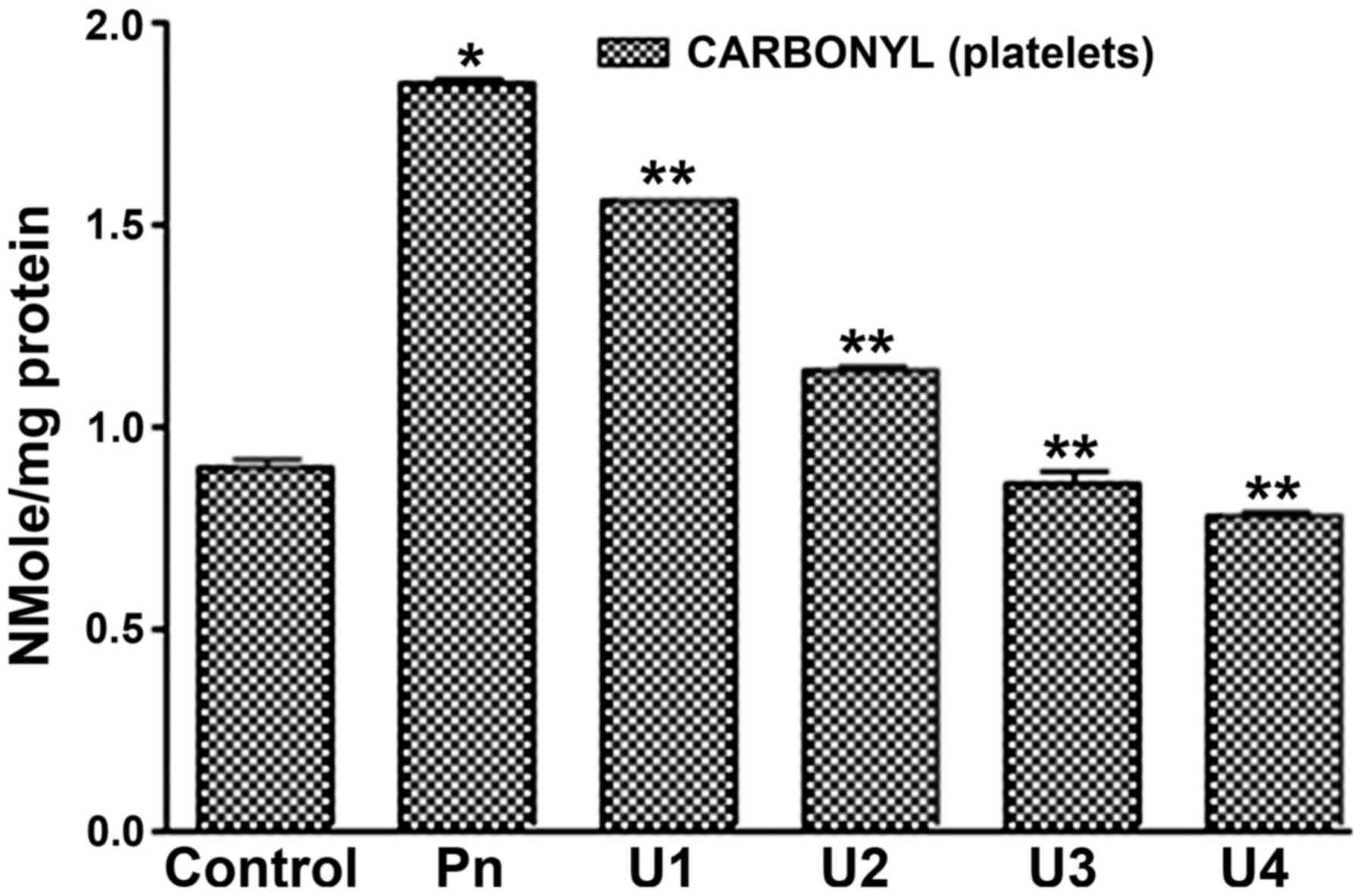
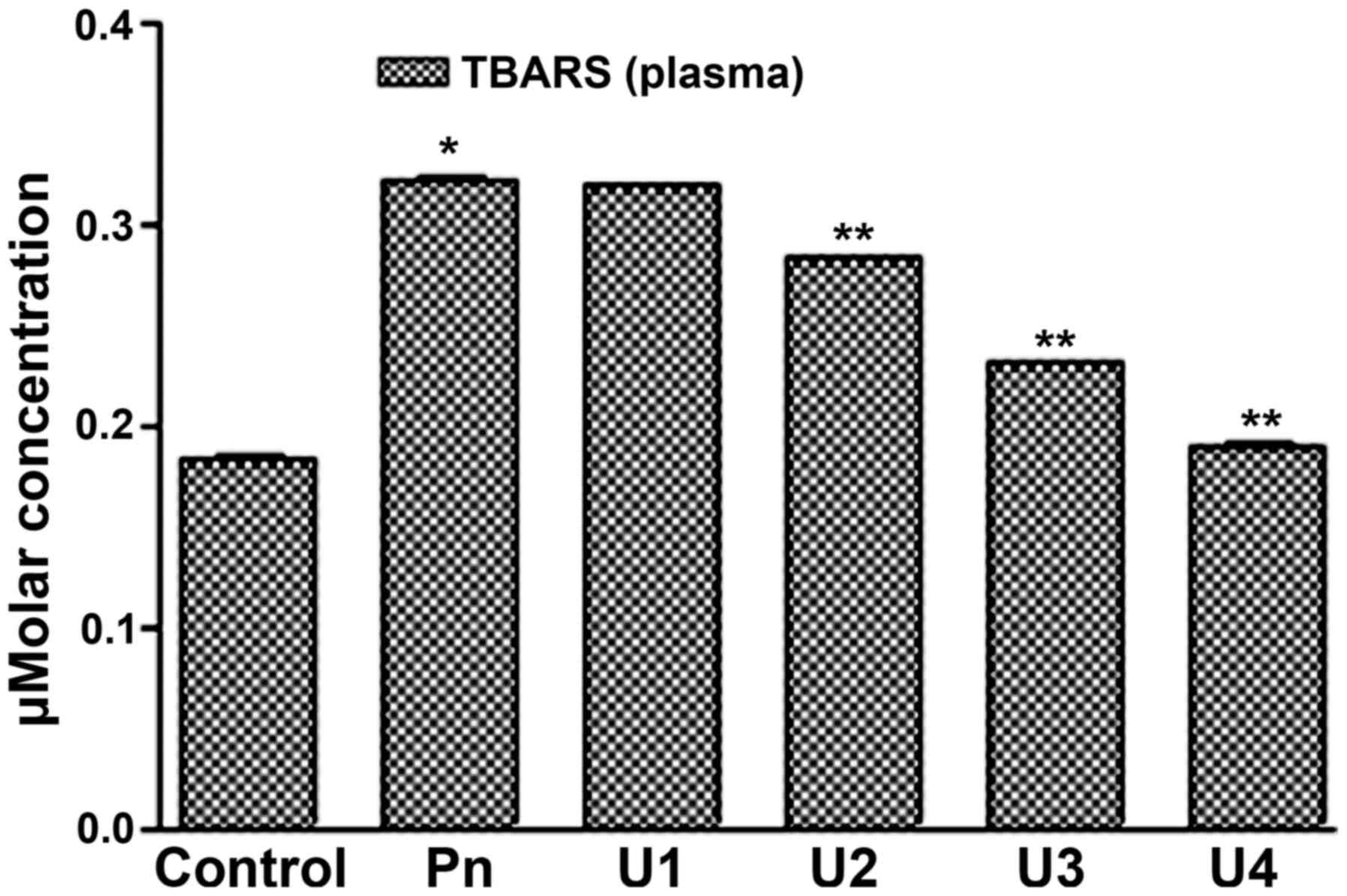
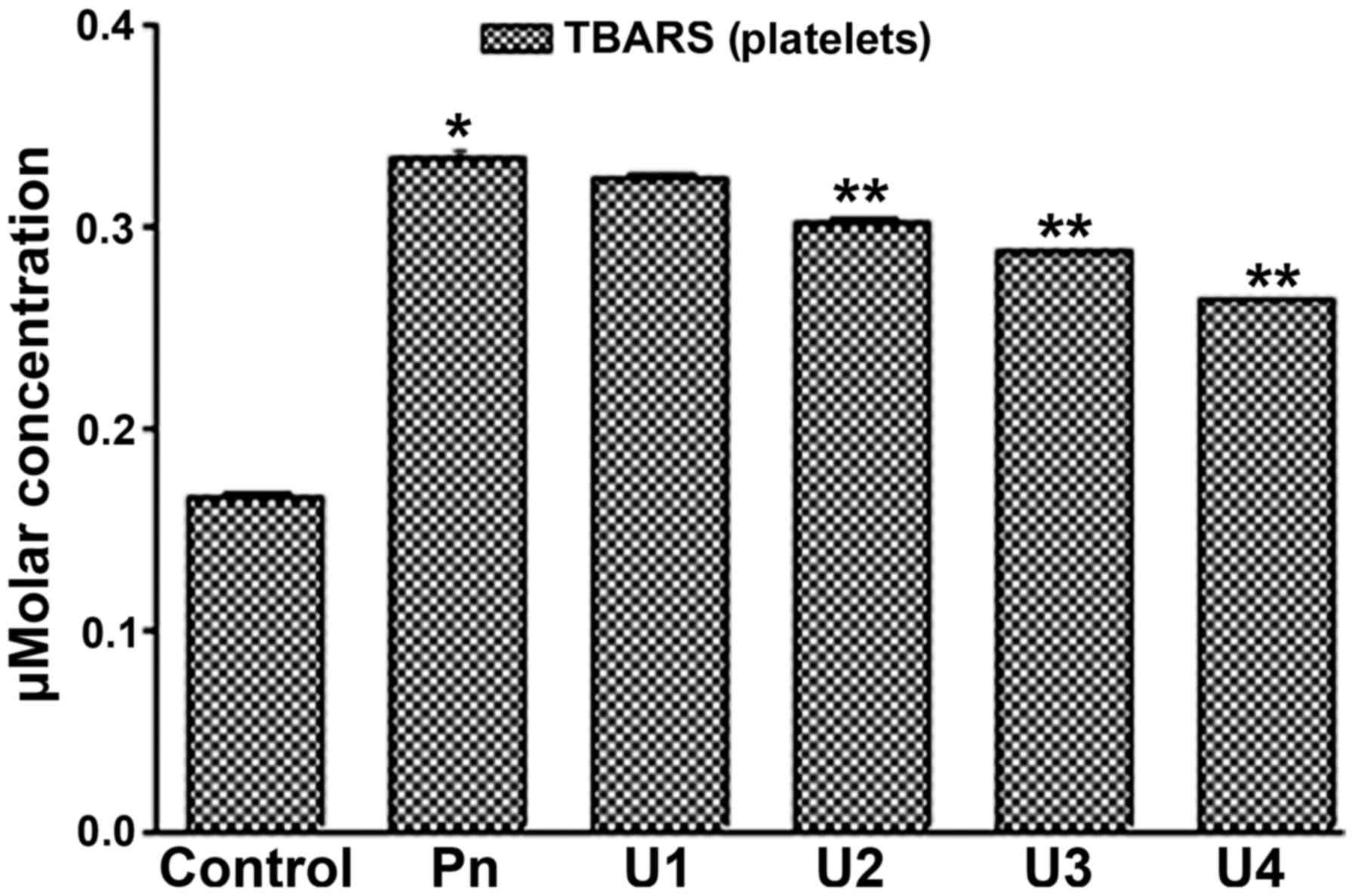
|
1
|
Turrens JF: Mitochondrial formation of
reactive oxygen species. J Physiol. 552:335–344. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hakim J: Reactive oxygen species and
inflammation. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 187:286–295. 1993.(In
French). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bergamini CM, Gambetti S, Dondi A and
Cervellati C: Oxygen, reactive oxygen species and tissue damage.
Curr Pharm Des. 10:1611–1626. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yu BP: Cellular defenses against damage
from reactive oxygen species. Physiol Rev. 74:139–162. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Foyer CH and Noctor G: Ascorbate and
glutathione: The heart of the redox hub. Plant Physiol. 155:2–18.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pigeolet E, Corbisier P, Houbion A,
Lambert D, Michiels C, Raes M, Zachary MD and Remacle J:
Glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, and catalase
inactivation by peroxides and oxygen derived free radicals. Mech
Ageing Dev. 51:283–297. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Finkel T and Holbrook NJ: Oxidants,
oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature. 408:239–247.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Waris G and Ahsan H: Reactive oxygen
species: Role in the development of cancer and various chronic
conditions. J Carcinog. 5:14. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Benzi G and Moretti A: Are reactive oxygen
species involved in Alzheimer's disease? Neurobiol Aging.
16:661–674. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Werner C and Engelhard K: Pathophysiology
of traumatic brain injury. Br J Anaesth. 99:4–9. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hall ED, Vaishnav RA and Mustafa AG:
Antioxidant therapies for traumatic brain injury.
Neurotherapeutics. 7:51–61. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Houstis N, Rosen ED and Lander ES:
Reactive oxygen species have a causal role in multiple forms of
insulin resistance. Nature. 440:944–948. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Maurya PK, Noto C, Rizzo LB, Rios AC,
Nunes SO, Barbosa DS, Sethi S, Zeni M, Mansur RB, Maes M, et al:
The role of oxidative and nitrosative stress in accelerated aging
and major depressive disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol
Psychiatry. 65:134–144. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gutteridge JM and Halliwell B: The
measurement and mechanism of lipid peroxidation in biological
systems. Trends Biochem Sci. 15:129–135. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hemnani T and Parihar MS: Reactive oxygen
species and oxidative DNA damage. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol.
42:440–452. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bandyopadhyay U, Das D and Banerjee RK:
Reactive oxygen species: Oxidative damage and pathogenesis. Curr
Sci. 77:658–666. 1999.
|
|
17
|
Halliwell B: Reactive oxygen species in
living systems: Source, biochemistry, and role in human disease. Am
J Med. 91(3C): 14S–22S. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Beckman JS, Beckman TW, Chen J, Marshall
PA and Freeman BA: Apparent hydroxyl radical production by
peroxynitrite: Implications for endothelial injury from nitric
oxide and superoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 87:1620–1624. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pacher P, Beckman JS and Liaudet L: Nitric
oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol Rev.
87:315–424. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mustafa AG, Bani-Ahmad MA, Jaradat AQ and
Allouh MZ: Tempol protects blood proteins and lipids against
peroxynitrite-mediated oxidative damage. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
240:109–112. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mustafa AG, Al-Shboul O, Alfaqih MA,
Al-Qudah MA and Al-Dwairi AN: Phenelzine reduces the oxidative
damage induced by peroxynitrite in plasma lipids and proteins. Arch
Physiol Biochem. Dec 19–2017.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Campo GM, Squadrito F, Campo S, Altavilla
D, Avenoso A, Ferlito M, Squadrito G and Caputi AP: Antioxidant
activity of U-83836E, a second generation lazaroid, during
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Free Radic Res. 27:577–590.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Willcox JK, Ash SL and Catignani GL:
Antioxidants and prevention of chronic disease. Crit Rev Food Sci
Nutr. 44:275–295. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hall ED, Detloff MR, Johnson K and Kupina
NC: Peroxynitrite-mediated protein nitration and lipid peroxidation
in a mouse model of traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 21:9–20.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mustafa AG, Singh IN, Wang J, Carrico KM
and Hall ED: Mitochondrial protection after traumatic brain injury
by scavenging lipid peroxyl radicals. J Neurochem. 114:271–280.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Esterbauer H and Cheeseman KH:
Determination of aldehydic lipid peroxidation products:
malonaldehyde and 4-hydroxynonenalMethods in enzymology. 186.
Elsevier; New York, NY: pp. 407–421. 1990, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Buettner GR: The pecking order of free
radicals and antioxidants: Lipid peroxidation, α-tocopherol, and
ascorbate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 300:535–543. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Radi R, Beckman JS, Bush KM and Freeman
BA: Peroxynitrite-induced membrane lipid peroxidation: The
cytotoxic potential of superoxide and nitric oxide. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 288:481–487. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Suzuki YJ, Carini M and Butterfield DA:
Protein carbonylation. Antioxid Redox Signal. 12:323–325. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|