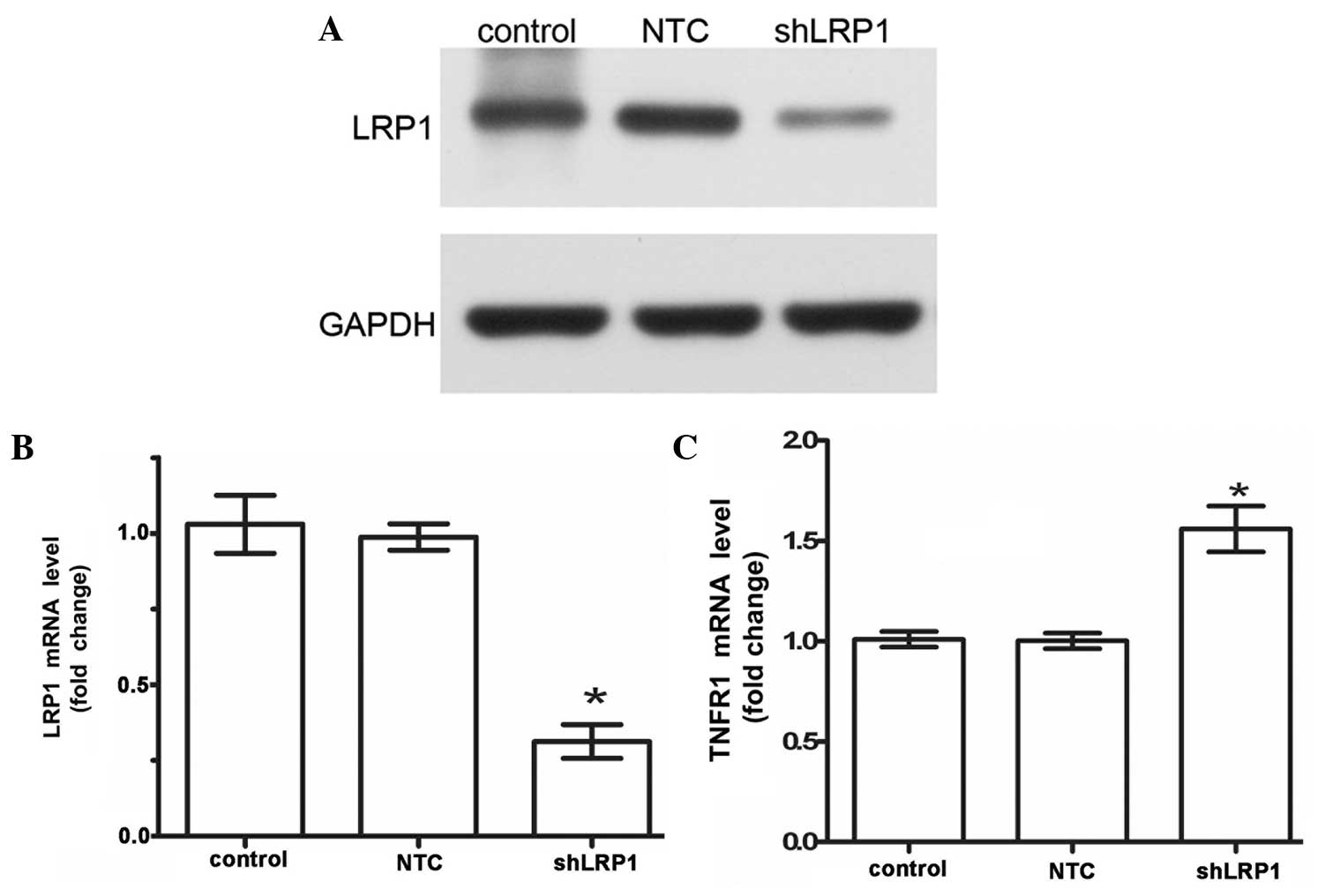
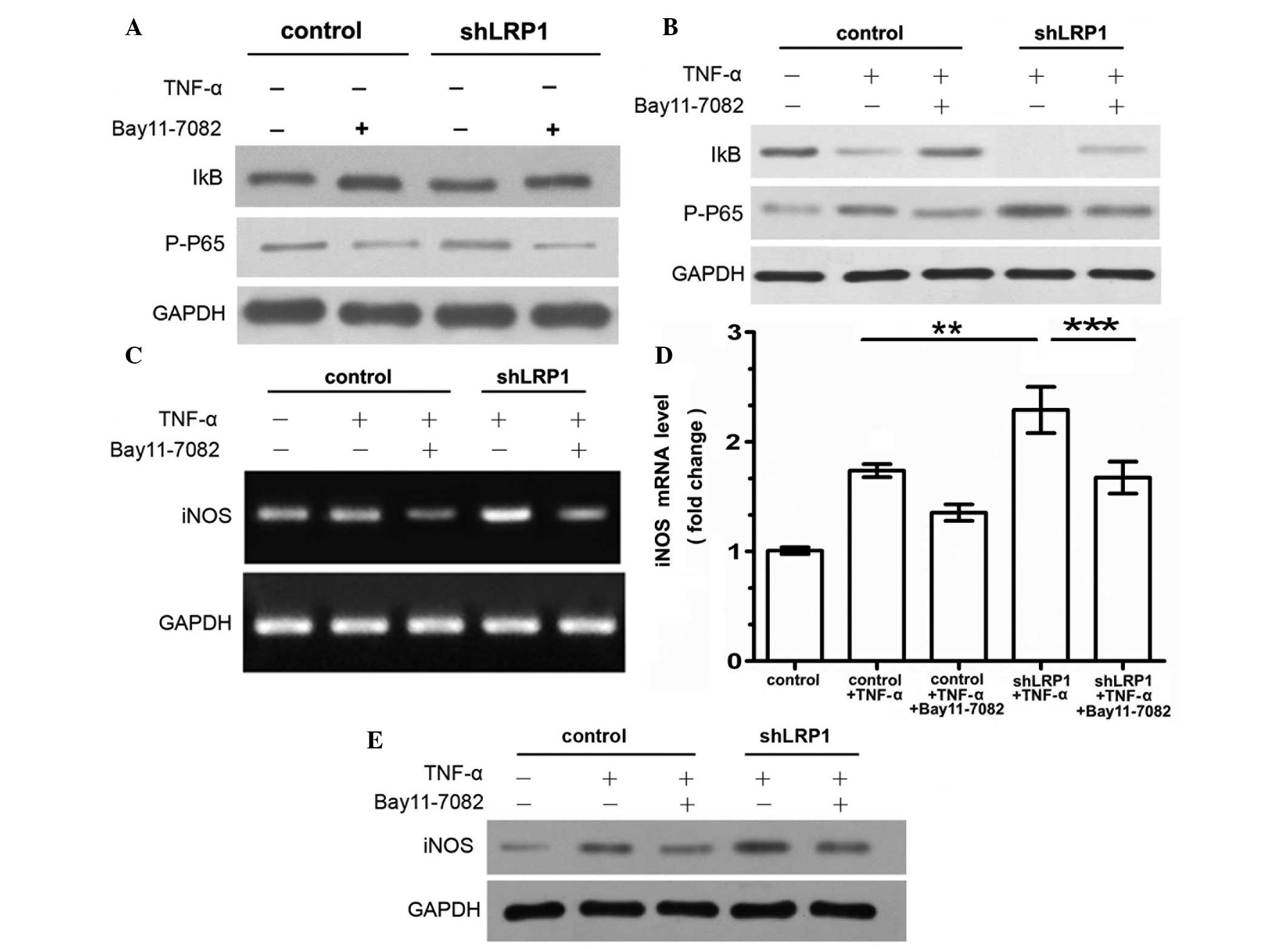
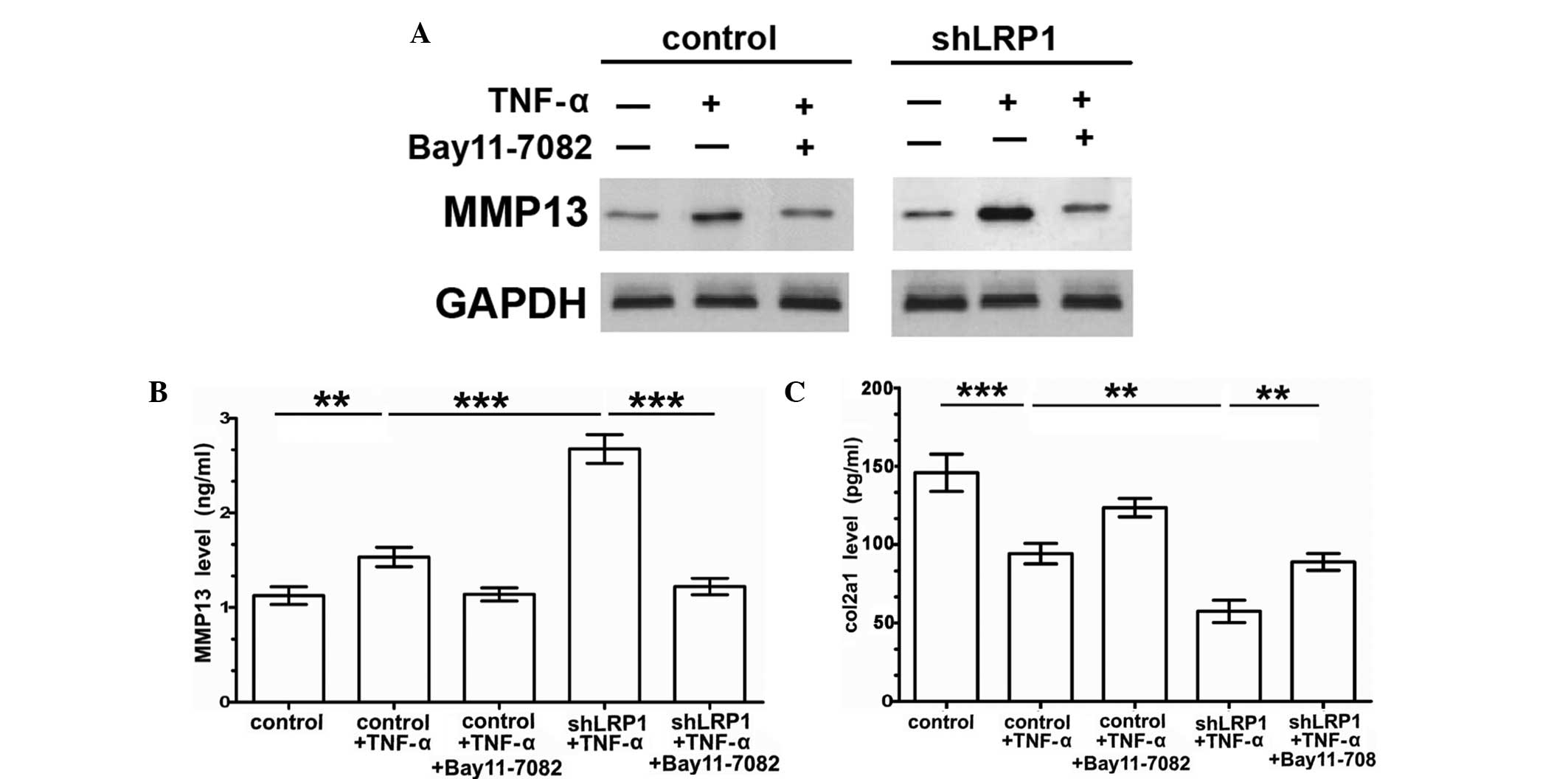
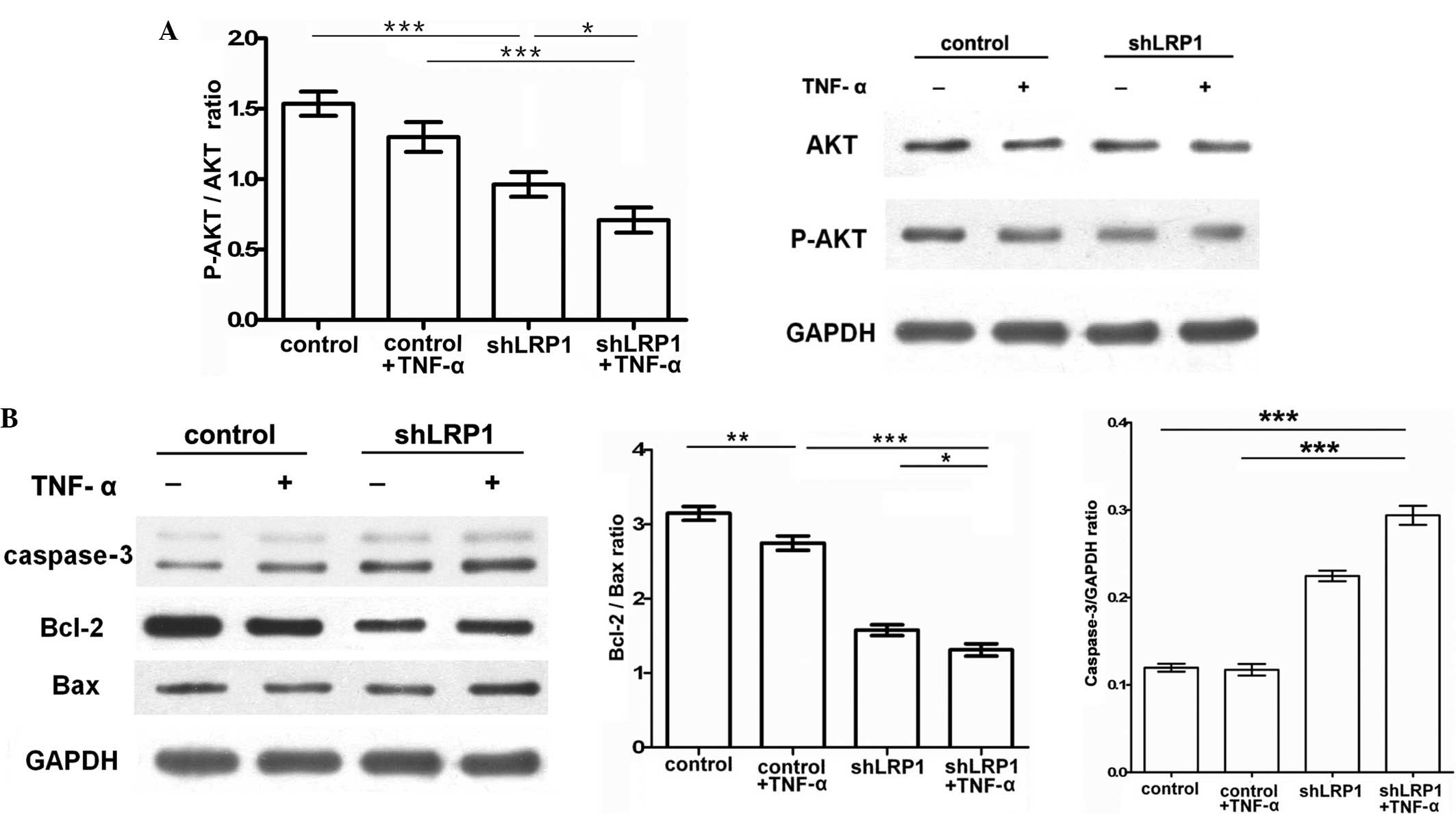
|
1
|
Mengshol JA, Vincenti MP, Coon CI,
Barchowsky A and Brinckerhoff CE: Interleukin-1 induction of
collagenase3 (matrix metalloproteinase 13) gene expression in
chondrocytes requires p38, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and nuclear
factor kappaB: Differential regulation of collagenase 1 and
collagenase 3. Arthritis Rheum. 43:801–811. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhong Y, Yu W, Feng J, Fan Z and Li J:
Curcumin suppresses tumor necrosis factor-α-induced matrix
metalloproteinase-2 expression and activity in rat vascular smooth
muscle cells via the NF-κB pathway. Exp Ther Med. 7:1653–1658.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ling H and Recklies AD: The chitinase
3-like protein human cartilage glycoprotein 39 inhibits cellular
responses to the inflammatory cytokines interleukin-1 and tumour
necrosis factor-alpha. Biochem J. 380:651–659. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liacini A, Sylvester J, Li WQ, Huang W,
Dehnade F, Ahmad M and Zafarullah M: Induction of matrix
metalloproteinase-13 gene expression by TNF-α is mediated by MAP
kinases, AP-1 and NF-κB transcription factors in articular
chondrocytes. Exp Cell Res. 288:208–217. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Campana WM, Li X, Dragojlovic N, Janes J,
Gaultier A and Gonias SL: The low-density lipoprotein
receptor-related protein is a pro-survival receptor in Schwann
cells: Possible implications in peripheral nerve injury. J
Neurosci. 26:11197–11207. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zurhove K, Nakajima C, Herz J, Bock HH and
May P: Gamma-secretase limits the inflammatory response through the
processing of LRP-1. Sci Signal. 1:ra152008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Herz J and Strickland DK: LRP: A
multifunctional scavenger and signaling receptor. J Clin Invest.
108:779–784. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
van Kerkhof P, Lee J, McCormick L,
Tetrault E, Lu W, Schoenfish M, Oorschot V, Strous GJ, Klumperman J
and Bu G: Sorting nexin 17 facilitates LRP recycling in the early
endosome. EMBO J. 24:2851–2861. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Herz J: The LDL receptor gene family:
(un)expected signal transducers in the brain. Neuron. 29:571–581.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Overton CD, Yancey PG, Major AS, Linton MF
and Fazio S: Deletion of macrophage LDL receptor-related protein
increases atherogenesis in the mouse. Circ Res. 100:670–677. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gaultier A, Arandjelovic S, Niessen S,
Overton CD, Linton MF, Fazio S, Campana WM, Cravatt BF III and
Gonias SL: Regulation of tumor necrosis factor receptor-1 and the
IKK-NF-κB pathway by LDL receptor-related protein explains the
antiinflammatory activity of this receptor. Blood. 111:5316–5325.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gaultier A, Arandjelovic S, Li X, et al: A
shed form of LDL receptor-related protein-1 regulates peripheral
nerve injury and neuropathic pain in rodents. J Clin Invest.
118:161–172. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hu DN, Yang PY, Ku MC, Chu CH, Lim AY and
Hwang MH: Isolation and cultivation of human articular
chondrocytes. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 18:113–120. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hermann C, Assmus B, Urbich C, Zeiher AM
and Dimmeler S: Insulin-mediated stimulation of protein kinase Akt:
A potent survival signaling cascade for endothelial cells.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 20:402–409. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gaultier A, Simon G, Niessen S, Dix M,
Takimoto S, Cravatt BF III and Gonias SL: LDL receptor-related
protein 1 regulates the abundance of diverse cell-signaling
proteins in the plasma membrane proteome. J Proteome Res.
9:6689–6695. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Barmina OY, Walling HW, Fiacco GJ, Freije
JM, López-Otín C, Jeffrey JJ and Partridge NC: Collagenase-3 binds
to a specific receptor and requires the low density lipoprotein
receptor-related protein for internalization. J Biol Chem.
274:30087–30093. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Raggatt LJ, Jefcoat SC Jr, Choudhury I,
Williams S, Tiku M and Partridge NC: Matrix metalloproteinase-13
influences ERK signalling in articular rabbit chondrocytes.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 14:680–689. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Manicourt DH, Poilvache P, Van Egeren A,
Devogelaer JP, Lenz ME and Thonar EJ: Synovial fluid levels of
tumor necrosis factor alpha and oncostatin M correlate with levels
of markers of the degradation of crosslinked collagen and cartilage
aggrecan in rheumatoid arthritis but not in osteoarthritis.
Arthritis Rheum. 43:281–288. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Henrotin Y, Kurz B and Aigner T: Oxygen
and reactive oxygen species in cartilage degradation: Friends or
foes? Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 13:643–654. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Henrotin Y and Kurz B: Antioxidant to
treat osteoarthritis: Dream or reality? Curr Drug Targets.
8:347–357. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Séguin CA and Bernier SM: TNFalpha
suppresses link protein and type II collagen expression in
chondrocytes: Role of MEK1/2 and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. J
Cell Physiol. 197:356–369. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Robbins JR, Thomas B, Tan L, Choy B,
Arbiser JL, Berenbaum F and Goldring MB: Immortalized human adult
articular chondrocytes maintain cartilage-specific phenotype and
responses to interleukin-1beta. Arthritis Rheum. 43:2189–2201.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Murakami S, Lefebvre V and de Crombrugghe
B: Potent inhibition of the master chondrogenic factor Sox9 gene by
interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Biol Chem.
275:3687–3692. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sitcheran R, Cogswell PC and Baldwin AS
Jr: NF-kappaB mediates inhibition of mesenchymal cell
differentiation through a posttranscriptional gene silencing
mechanism. Genes Dev. 17:2368–2373. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tetlow LC, Adlam DJ and Woolley DE: Matrix
metalloproteinase and proinflammatory cytokine production by
chondrocytes of human osteoarthritic cartilage: Associations with
degenerative changes. Arthritis Rheum. 44:585–594. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu W, Billinghurst RC, Pidoux I, Antoniou
J, Zukor D, Tanzer M and Poole AR: Sites of collagenase cleavage
and denaturation of type II collagen in aging and osteoarthritic
articular cartilage and their relationship to the distribution of
matrix metalloproteinase 1 and matrix metalloproteinase 13.
Arthritis Rheum. 46:2087–2094. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Neuhold LA, Killar L, Zhao W, Sung ML,
Warner L, Kulik J, et al: Postnatal expression in hyaline cartilage
of constitutively active human collagenase-3 (MMP-13) induces
osteoarthritis in mice. J Clin Invest. 107:35–44. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Aigner T, Vornehm SI, Zeiler G, Dudhia J,
von der Mark K and Bayliss MT: Suppression of cartilage matrix gene
expression in upper zone chondrocytes of osteoarthritic cartilage.
Arthritis Rheum. 40:562–569. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Aigner T, Zien A, Gehrsitz A, Gebhard PM
and McKenna L: Anabolic and catabolic gene expression pattern
analysis in normal versus osteoarthritic cartilage using
complementary DNA-array technology. Arthritis Rheum. 44:2777–2789.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cui N, Li S, Zhao X, Zhang T, Zhang C, Yu
L, Zhu Z and Xie K: Expression of Bcl-2, Bax and Caspase-3 in nerve
tissues of rats chronically exposed to 2,5-hexanedione. Neurochem
Res. 32:1566–1572. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Postolow F, Fediuk J, Nolette N, Hinton M
and Dakshinamurti S: Hypoxia and nitric oxide exposure promote
apoptotic signaling in contractile pulmonary arterial smooth muscle
but not in pulmonary epithelium. Pediatr Pulmonol. 46:1194–1208.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rath PC and Aggarwal BB: TNF-induced
signaling in apoptosis. J Clin Immunol. 19:350–364. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Graham B and Gibson SB: The two faces of
NFkappaB in cell survival responses. Cell Cycle. 4:1342–1345. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Karin M and Lin A: NF-kappaB at the
crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol. 3:221–227. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Luo JJ, Li CY, Liu S, Yu W, Tang SY, Cai
HL and Zhang Y: Overexpression of Helicobacter pylori VacA
N-terminal fragment induces proinflammatory cytokine expression and
apoptosis in human monocytic cell line through activation of NF-κB.
Can J Microbiol. 59:523–533. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu X, Xiao Q, Zhao K and Gao Y: Ghrelin
inhibits high glucose-induced PC12 cell apoptosis by regulating
TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Inflammation. 36:1286–1294. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Swaminathan JK, Khan M, Mohan IK,
Selvendiran K, Niranjali Devaraj S, Rivera BK and Kuppusamy P:
Cardioprotective properties of Crataegus oxycantha extract against
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Phytomedicine. 17:744–752. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|