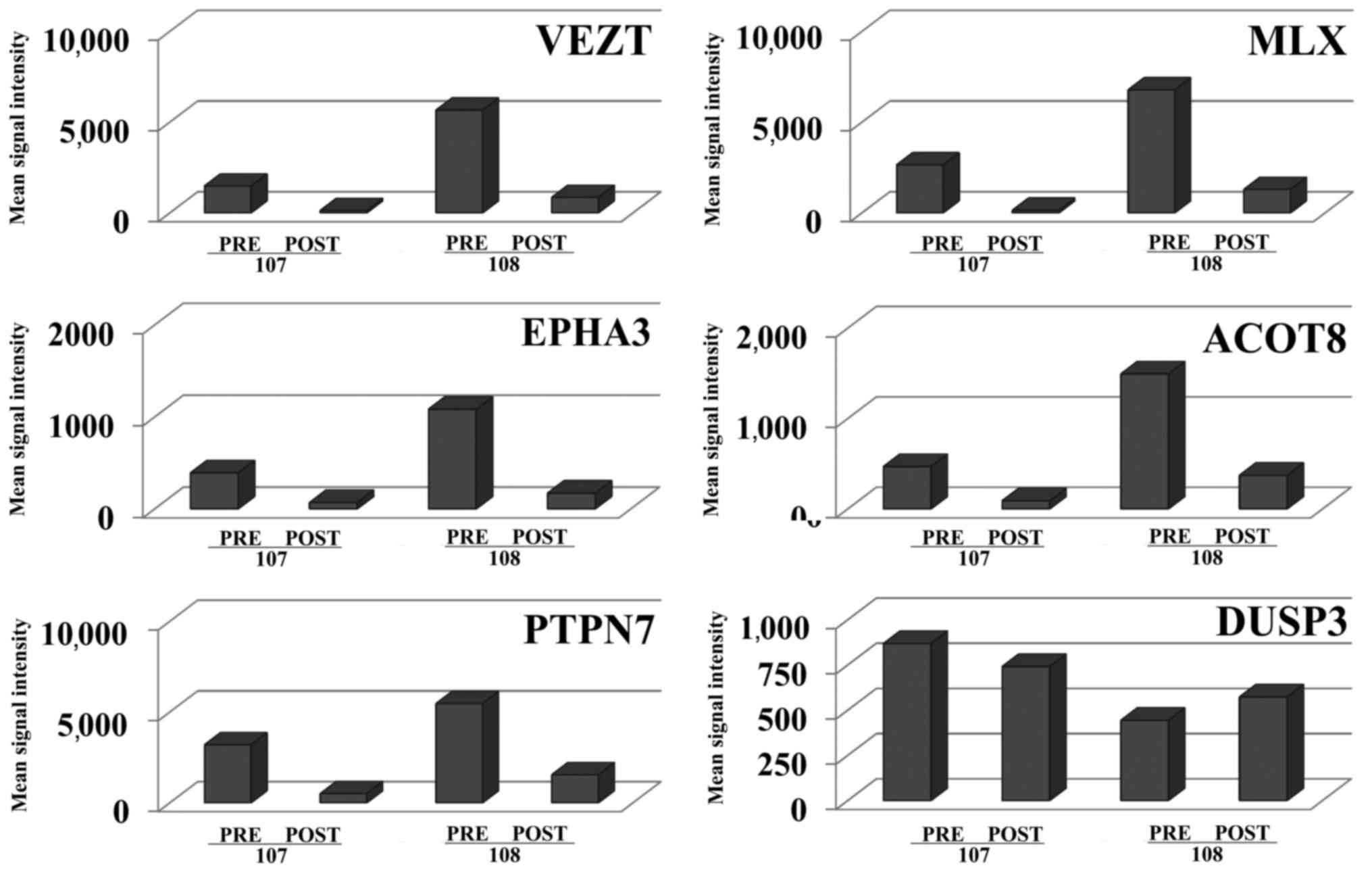
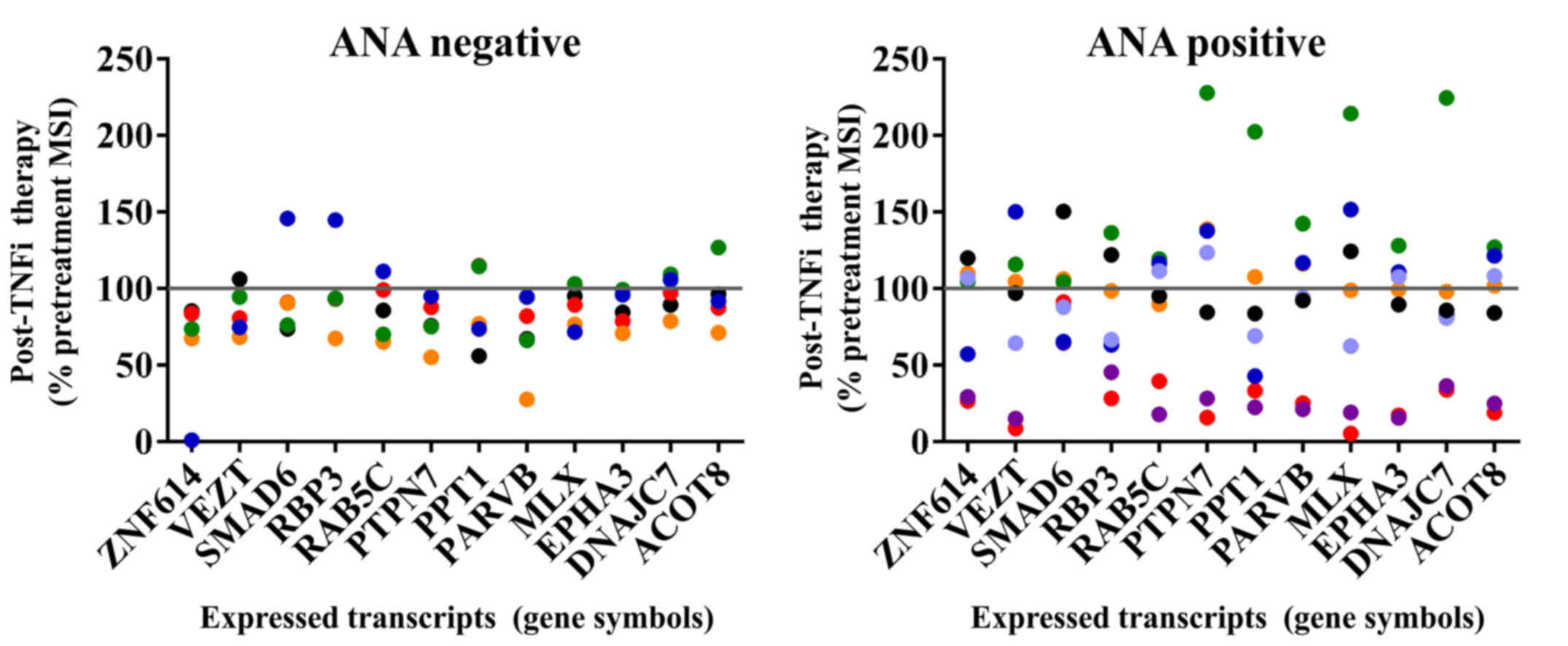
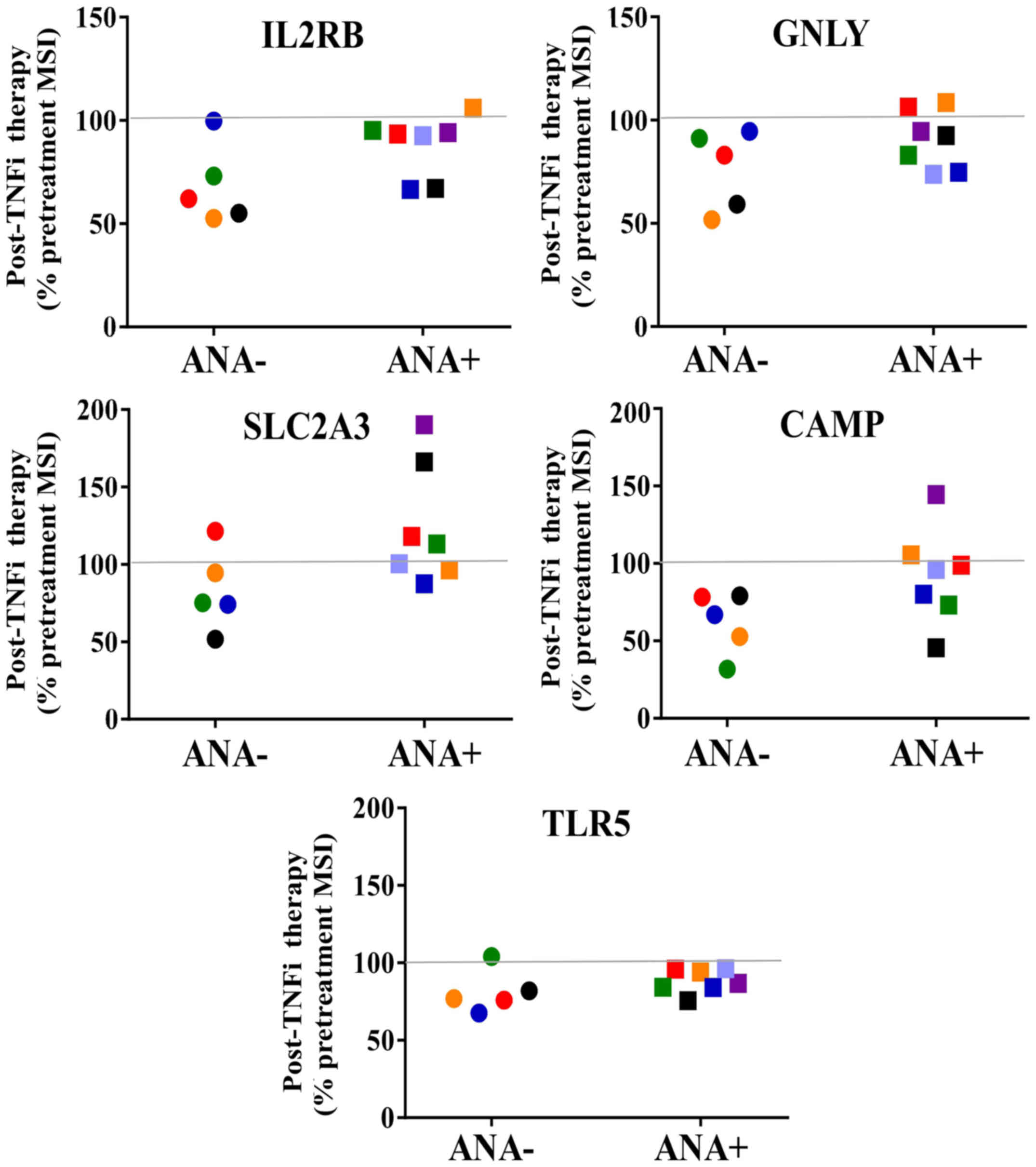
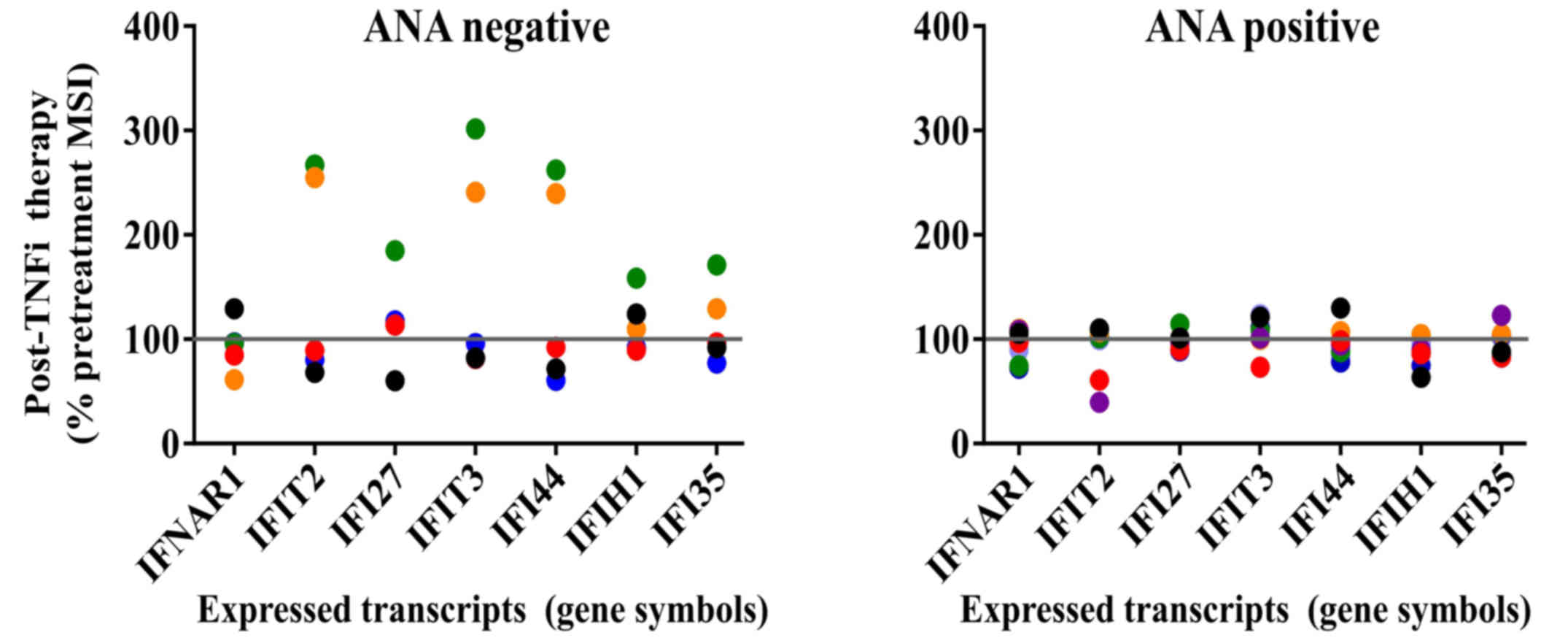
|
1
|
Scott DL and Kingsley GH: Tumor necrosis
factor inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med.
355:704–712. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sciré CA, Caporali R, Sarzi-Puttini P,
Frediani B, Di Franco M, Tincani A, Sinigaglia L, Sfriso P, Tirri
R, Bellis E, et al: Drug survival of the first course of anti-TNF
agents in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and seronegative
spondyloarthritis: Analysis from the MonitorNet database. Clin Exp
Rheumatol. 31:857–863. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lipsky PE, van der Heijde DM, St Clair EW,
Furst DE, Breedveld FC, Kalden JR, Smolen JS, Weisman M, Emery P,
Feldmann M, et al: Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of
rheumatoid arthritis. Anti-tumor necrosis factor trial in
rheumatoid arthritis with concomitant therapy study group. N Engl J
Med. 343:1594–1602. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Genovese MC, Bathon JM, Fleischmann RM,
Moreland LW, Martin RW, Whitmore JB, Tsuji WH and Leff JA: Longterm
safety, efficacy, and radiographic outcome with etanercept
treatment in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol.
32:1232–1242. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Klareskog L, van der Heijde D, de Jager
JP, Gough A, Kalden J, Malaise M, Martín Mola E, Pavelka K, Sany J,
Settas L, et al: Therapeutic effect of the combination of
etanercept and methotrexate compared with each treatment alone in
patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Double-blind randomised
controlled trial. Lancet. 363:675–681. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
van de Putte LB, Atkins C, Malaise M, Sany
J, Russell AS, van Riel PL, Settas L, Bijlsma JW, Todesco S,
Dougados M, et al: Efficacy and safety of adalimumab as monotherapy
in patients with rheumatoid arthritis for whom previous disease
modifying antirheumatic drug treatment has failed. Ann Rheum Dis.
63:508–516. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Atzeni F, Sarzi-Puttini P, Dell'Acqua D,
de Portu S, Cecchini G, Cruini C, Carrabba M and Meroni PL:
Adalimumab clinical efficacy is associated with rheumatoid factor
and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody titer reduction: A
one-year prospective study. Arthritis Res Ther. 8:R32006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Alessandri C, Bombardieri M, Papa N,
Cinquini M, Magrini L, Tincani A and Valesini G: Decrease of
anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and rheumatoid factor
following anti-TNFalpha therapy (infliximab) in rheumatoid
arthritis is associated with clinical improvement. Ann Rheum Dis.
63:1218–1221. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen HA, Lin KC, Chen CH, Liao HT, Wang
HP, Chang HN, Tsai CY and Chou CT: The effect of etanercept on
anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and rheumatoid factor
in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 65:35–39.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pittoni V, Bombardieri M, Spinelli FR,
Scrivo R, Alessandri C, Conti F, Spadaro A and Valesini G:
Anti-tumour necrosis factor (TNF) alpha treatment of rheumatoid
arthritis (infliximab) selectively down regulates the production of
interleukin (IL) 18 but not of IL12 and IL13. Ann Rheum Dis.
61:723–725. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shakoor N, Michalska M, Harris CA and
Block JA: Drug-induced systemic lupus erythematosus associated with
etanercept therapy. Lancet. 359:579–580. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Furst DE, Schiff MH, Fleischmann RM,
Strand V, Birbara CA, Compagnone D, Fischkoff SA and Chartash EK:
Adalimumab, a fully human anti tumor necrosis factor-alpha
monoclonal antibody and concomitant standard antirheumatic therapy
for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: Results of STAR (Safety
Trial of Adalimumab in Rheumatoid Arthritis). J Rheumatol.
30:2563–2571. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Caramaschi P, Biasi D, Colombatti M,
Pieropan S, Martinelli N, Carletto A, Volpe A, Pacor LM and Bambara
LM: Anti-TNFalpha therapy in rheumatoid arthritis and autoimmunity.
Rheumatol Int. 26:209–214. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
De Rycke L, Baeten D, Kruithof E, Van den
Bosch F, Veys EM and De Keyser F: Infliximab, but not etanercept,
induces IgM anti-double-stranded DNA autoantibodies as main
antinuclear reactivity: Biologic and clinical implications in
autoimmune arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 52:2192–2201. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
De Rycke L, Baeten D, Kruithof E, Van den
Bosch F, Veys EM and De Keyser F: The effect of TNFalpha blockade
on the antinuclear antibody profile in patients with chronic
arthritis: Biological and clinical implications. Lupus. 14:931–937.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Toonen EJ, Gilissen C, Franke B, Kievit W,
Eijsbouts AM, den Broeder AA, van Reijmersdal SV, Veltman JA,
Scheffer H, Radstake TR, et al: Validation study of existing gene
expression signatures for anti-TNF treatment in patients with
rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One. 7:e331992012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim TH, Choi SJ, Lee YH, Song GG and Ji
JD: Gene expression profile predicting the response to anti-TNF
treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis; analysis of GEO
datasets. Joint Bone Spine. 81:325–330. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Oswald M, Curran ME, Lamberth SL, Townsend
RM, Hamilton JD, Chernoff DN, Carulli J, Townsend MJ, Weinblatt ME,
Kern M, et al: Modular analysis of peripheral blood gene expression
in rheumatoid arthritis captures reproducible gene expression
changes in tumor necrosis factor responders. Arthritis Rheumatol.
67:344–351. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rosenberg A, Fan H, Chiu YG, Bolce R,
Tabechian D, Barrett R, Moorehead S, Baribaud F, Liu H, Peffer N,
et al: Divergent gene activation in peripheral blood and tissues of
patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and
psoriasis following infliximab therapy. PLoS One. 9:e1106572014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wright HL, Thomas HB, Moots RJ and Edwards
SW: Interferon gene expression signature in rheumatoid arthritis
neutrophils correlates with a good response to TNFi therapy.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 54:188–193. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Julia A, Erra A, Palacio C, Tomas C, Sans
X, Barceló P and Marsal S: An eight-gene blood expression profile
predicts the response to infliximab in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS
One. 4:e75562009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Oliveira RD, Fontana V, Junta CM, Marques
MM, Macedo C, Rassi DM, Passos GA, Donadi EA and Louzada-Junior P:
Differential gene expression profiles may differentiate responder
and nonresponder patients with rheumatoid arthritis for
methotrexate (MTX) monotherapy and MTX plus tumor necrosis factor
inhibitor combined therapy. J Rheumatol. 39:1524–1532. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane
DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH and Luthra
HS: The American rheumatism association 1987 revised criteria for
the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum.
31:315–324. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Prevoo ML, van't Hof MA, Kuper HH, van
Leeuwen MA, van de Putte LB and van Riel PL: Modified disease
activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts. Development
and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with
rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 38:44–48. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Winchester RJ: Characterization of IgG
complexes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
256:73–81. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Roberts-Thomson PJ, McEvoy R, Langhans T
and Bradley J: Routine quantification of rheumatoid factor by rate
nephelometry. Ann Rheum Dis. 44:379–383. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Banal F, Dougados M, Combescure C and
Gossec L: Sensitivity and specificity of the American College of
Rheumatology 1987 criteria for the diagnosis of rheumatoid
arthritis according to disease duration: A systematic literature
review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 68:1184–1191. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schellekens GA, Visser H, de Jong BA, van
den Hoogen FH, Hazes JM, Breedveld FC and van Venrooij WJ: The
diagnostic properties of rheumatoid arthritis antibodies
recognizing a cyclic citrullinated peptide. Arthritis Rheum.
43:155–163. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Visser H, le Cessie S, Vos K, Breedveld FC
and Hazes JM: How to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis early: A
prediction model for persistent (erosive) arthritis. Arthritis
Rheum. 46:357–365. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Becker AM, Dao KH, Han BK, Kornu R,
Lakhanpal S, Mobley AB, Li QZ, Lian Y, Wu T, Reimold AM, et al: SLE
peripheral blood B cell, T cell and myeloid cell transcriptomes
display unique profiles and each subset contributes to the
interferon signature. PLoS One. 8:e670032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Blanco P, Palucka AK, Pascual V and
Banchereau J: Dendritic cells and cytokines in human inflammatory
and autoimmune diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 19:41–52.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bahloul A, Simmler MC, Michel V, Leibovici
M, Perfettini I, Roux I, Weil D, Nouaille S, Zuo J, Zadro C, et al:
Vezatin, an integral membrane protein of adherens junctions, is
required for the sound resilience of cochlear hair cells. EMBO Mol
Med. 1:125–138. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hyenne V, Harf JC, Latz M, Maro B, Wolfrum
U and Simmler MC: Vezatin, a ubiquitous protein of adherens
cell-cell junctions, is exclusively expressed in germ cells in
mouse testis. Reproduction. 133:563–574. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Akagi T, Shimizu K, Takahama S, Iwasaki T,
Sakamaki K, Endo Y and Sawasaki T: Caspase-8 cleavage of the
interleukin-21 (IL-21) receptor is a negative feedback regulator of
IL-21 signaling. FEBS Lett. 585:1835–1840. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ivanov AI and Romanovsky AA: Putative dual
role of ephrin-Eph receptor interactions in inflammation. IUBMB
Life. 58:389–394. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ivanov AI, Steiner AA, Scheck AC and
Romanovsky AA: Expression of Eph receptors and their ligands,
ephrins, during lipopolysaccharide fever in rats. Physiol Genomics.
21:152–160. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chim SM, Tickner J, Chow ST, Kuek V, Guo
B, Zhang G, Rosen V, Erber W and Xu J: Angiogenic factors in bone
local environment. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 24:297–310. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Verschuren JJ, Trompet S, Sampietro ML,
Heijmans BT, Koch W, Kastrati A, Houwing-Duistermaat JJ, Slagboom
PE, Quax PH and Jukema JW: Pathway analysis using genome-wide
association study data for coronary restenosis-a potential role for
the PARVB gene. PLoS One. 8:e706762013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Eslami A, Miyaguchi K, Mogushi K, Watanabe
H, Okada N, Shibuya H, Mizushima H, Miura M and Tanaka H: PARVB
overexpression increases cell migration capability and defines high
risk for endophytic growth and metastasis in tongue squamous cell
carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 112:338–344. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Flinn RJ, Yan Y, Goswami S, Parker PJ and
Backer JM: The late endosome is essential for mTORC1 signaling. Mol
Biol Cell. 21:833–841. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen PI, Schauer K, Kong C, Harding AR,
Goud B and Stahl PD: Rab5 isoforms orchestrate a ‘division of
labor’ in the endocytic network; Rab5C modulates Rac-mediated cell
motility. PLoS One. 9:e903842014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Alvarez-Dominguez C and Stahl PD:
Interferon-gamma selectively induces Rab5a synthesis and processing
in mononuclear cells. J Biol Chem. 273:33901–33904. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Westin MA, Alexson SE and Hunt MC:
Molecular cloning and characterization of two mouse peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha)-regulated
peroxisomal acyl-CoA thioesterases. J Biol Chem. 279:21841–21848.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Watanabe H, Shiratori T, Shoji H, Miyatake
S, Okazaki Y, Ikuta K, Sato T and Saito T: A novel acyl-CoA
thioesterase enhances its enzymatic activity by direct binding with
HIV Nef. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 238:234–239. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu LX, Margottin F, Le Gall S, Schwartz
O, Selig L, Benarous R and Benichou S: Binding of HIV-1 Nef to a
novel thioesterase enzyme correlates with Nef-mediated CD4
down-regulation. J Biol Chem. 272:13779–13785. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hunt MC, Solaas K, Kase BF and Alexson SE:
Characterization of an acyl-coA thioesterase that functions as a
major regulator of peroxisomal lipid metabolism. J Biol Chem.
277:1128–1138. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ishizuka M, Toyama Y, Watanabe H, Fujiki
Y, Takeuchi A, Yamasaki S, Yuasa S, Miyazaki M, Nakajima N, Taki S
and Saito T: Overexpression of human acyl-CoA thioesterase
upregulates peroxisome biogenesis. Exp Cell Res. 297:127–141. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kollmann K, Uusi-Rauva K, Scifo E, Tyynelä
J, Jalanko A and Braulke T: Cell biology and function of neuronal
ceroid lipofuscinosis-related proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1832:1866–1881. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang R, Borazjani A, Matthews AT, Mangum
LC, Edelmann MJ and Ross MK: Identification of palmitoyl protein
thioesterase 1 in human THP1 monocytes and macrophages and
characterization of unique biochemical activities for this enzyme.
Biochemistry. 52:7559–7574. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Seo H, Lee IS, Park JE, Park SG, Lee DH,
Park BC and Cho S: Role of protein tyrosine phosphatase
non-receptor type 7 in the regulation of TNF-α production in RAW
264.7 macrophages. PLoS One. 8:e787762013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lang R, Hammer M and Mages J: DUSP meet
immunology: Dual specificity MAPK phosphatases in control of the
inflammatory response. J Immunol. 177:7497–7504. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Diolaiti D, McFerrin L, Carroll PA and
Eisenman RN: Functional interactions among members of the MAX and
MLX transcriptional network during oncogenesis. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1849:484–500. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Mitchell SM and Frayling TM: The role of
transcription factors in maturity-onset diabetes of the young. Mol
Genet Metab. 77:35–43. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Terao C, Yoshifuji H and Mimori T: Recent
advances in Takayasu arteritis. Int J Rheu Dis. 17:238–247. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Timsit YE and Negishi M: Coordinated
regulation of nuclear receptor CAR by CCRP/DNAJC7, HSP70 and the
ubiquitin-proteasome system. PLoS One. 9:e960922014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kubo N, Wu D, Yoshihara Y, Sang M,
Nakagawara A and Ozaki T: Co-chaperon DnaJC7/TPR2 enhances p53
stability and activity through blocking the complex formation
between p53 and MDM2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 430:1034–1039.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ohno M, Kanayama T, Moore R, Ray M and
Negishi M: The Roles of Co-Chaperone CCRP/DNAJC7 in Cyp2b10 gene
activation and steatosis development in mouse livers. PLoS One.
9:e1156632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Menendez D, Shatz M and Resnick MA:
Interactions between the tumor suppressor p53 and immune responses.
Curr Opin Oncol. 25:85–92. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kim YC, Kim KK and Shevach EM: Simvastatin
induces Foxp3+ T regulatory cells by modulation of transforming
growth factor-beta signal transduction. Immunology. 130:484–493.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yan X and Chen YG: Smad7: Not only a
regulator, but also a cross-talk mediator of TGF-beta signalling.
Biochem J. 434:1–10. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yan X, Liu Z and Chen Y: Regulation of
TGF-beta signaling by Smad7. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
41:263–272. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Chen D, Zhao M and Mundy GR: Bone
morphogenetic proteins. Growth Factors. 22:233–241. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Bai S, Shi X, Yang X and Cao X: Smad6 as a
transcriptional corepressor. J Biol Chem. 275:8267–8270. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Ichijo T, Voutetakis A, Cotrim AP,
Bhattachryya N, Fujii M, Chrousos GP and Kino T: The Smad6-histone
deacetylase 3 complex silences the transcriptional activity of the
glucocorticoid receptor: Potential clinical implications. J Biol
Chem. 280:42067–42077. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhu L, Shen W, Zhu M, Coorey NJ, Nguyen
AP, Barthelmes D and Gillies MC: Anti-retinal antibodies in
patients with macular telangiectasia type 2. Invest Ophthalmol Vis
Sci. 54:5675–5683. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Edwards CJ, Feldman JL, Beech J, Shields
KM, Stover JA, Trepicchio WL, Larsen G, Foxwell BM, Brennan FM,
Feldmann M and Pittman DD: Molecular profile of peripheral blood
mononuclear cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Med.
13:40–58. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Dozmorov I, Dominguez N, Sestak AL,
Robertson JM, Harley JB, James JA and Guthridge JM: Evidence of
dynamically dysregulated gene expression pathways in
hyperresponsive B cells from African American lupus patients. PLoS
One. 8:e713972013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|