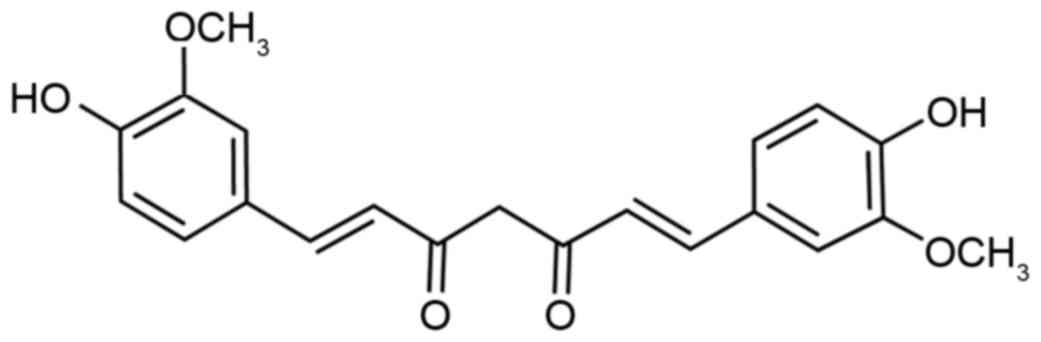
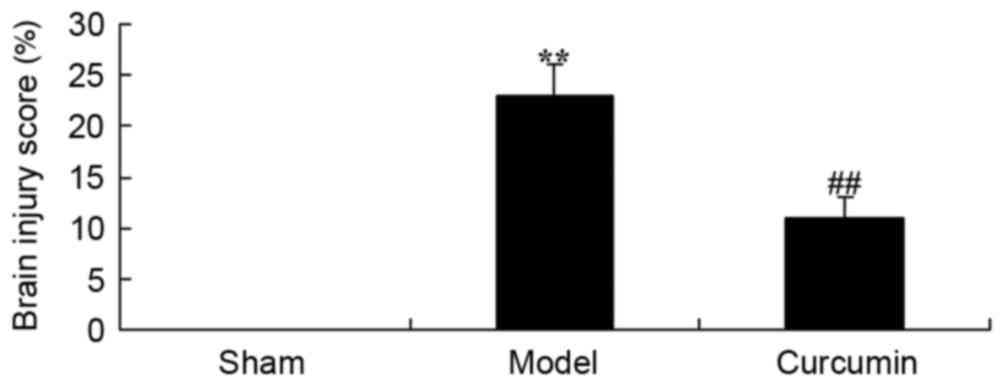
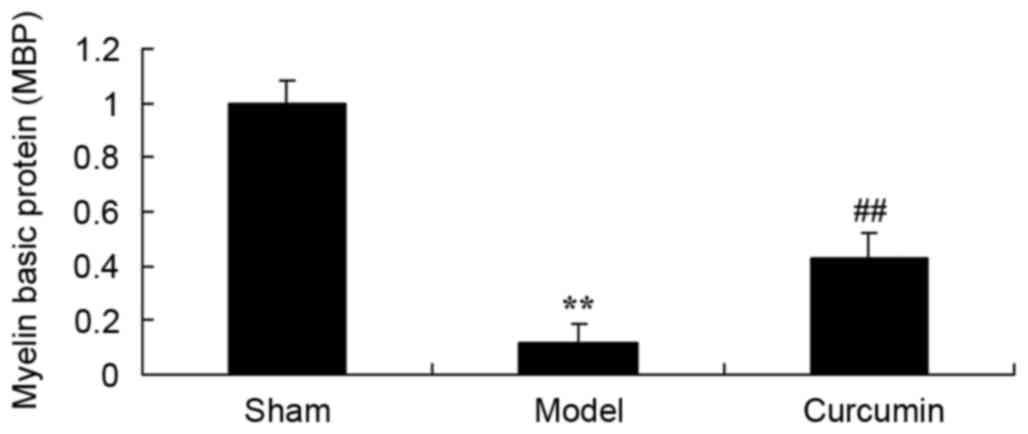
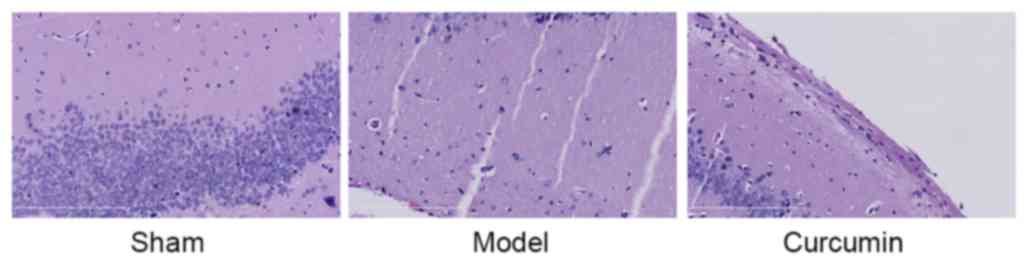
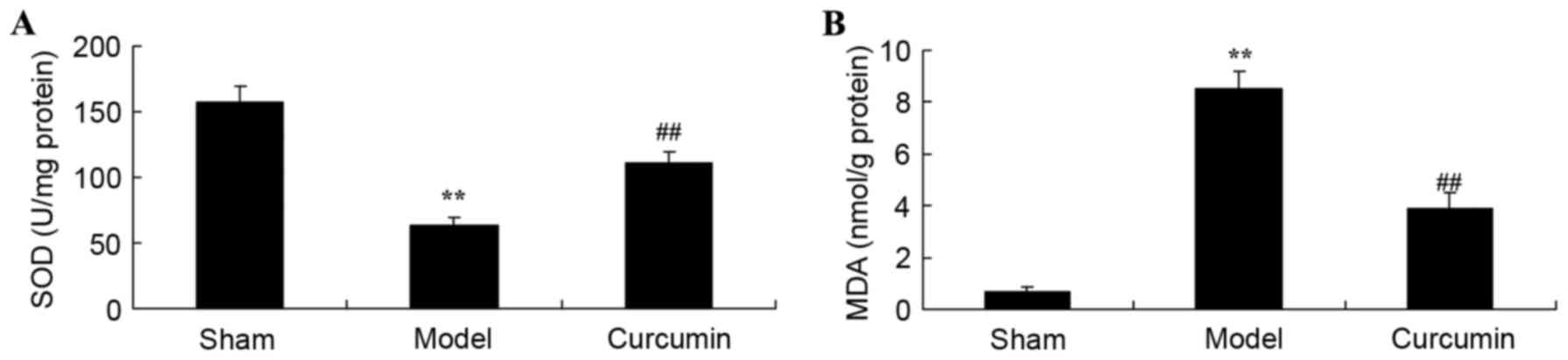
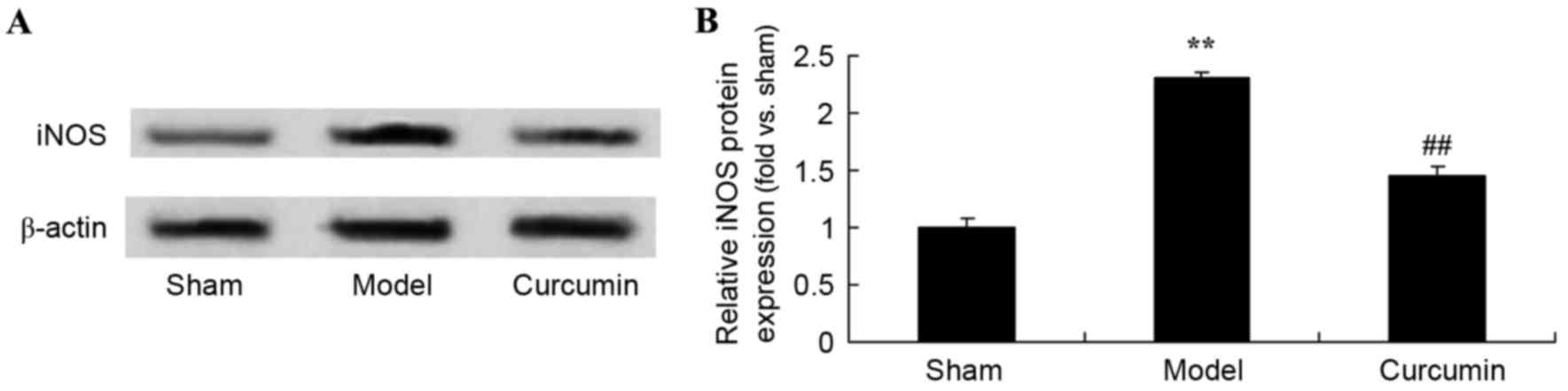
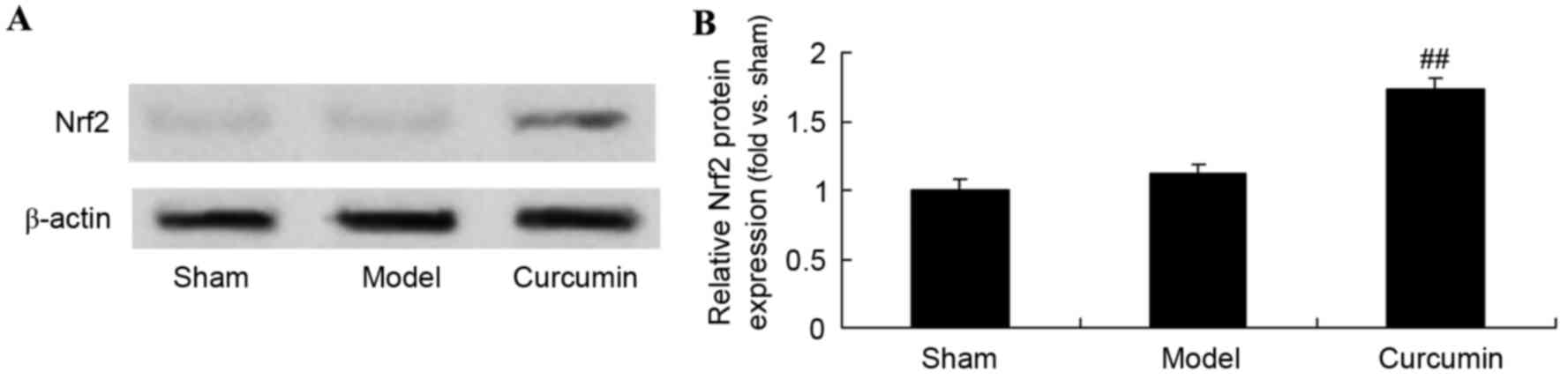
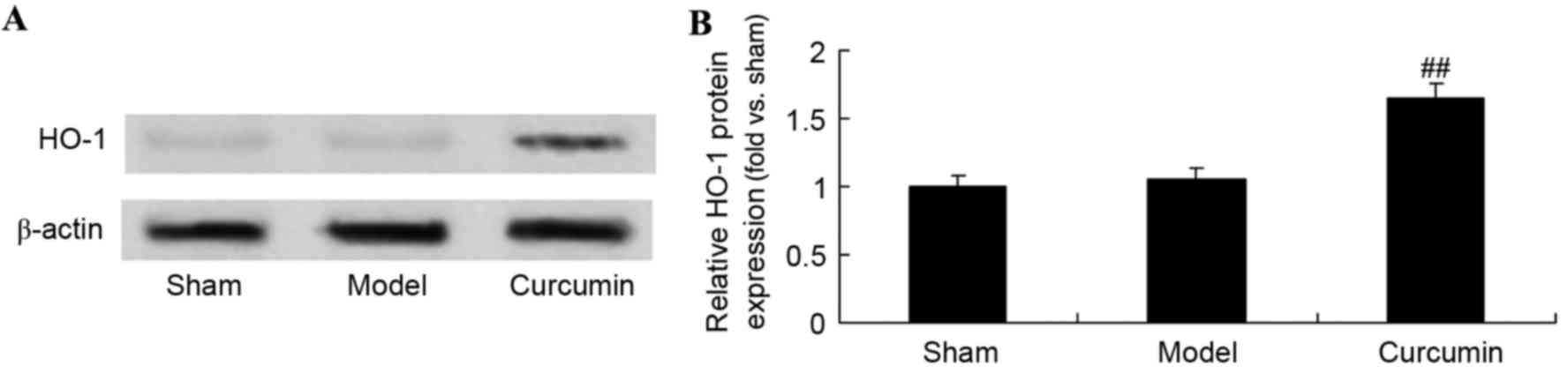
|
1
|
Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Pappas A,
McDonald SA, Das A, Tyson JE, Poindexter BB, Schibler K, Bell EF,
Heyne RJ, et al: Effect of depth and duration of cooling on deaths
in the NICU among neonates with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: A
randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 312:2629–2639. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kracer B, Hintz SR, Van Meurs KP and Lee
HC: Hypothermia therapy for neonatal hypoxic ischemic
encephalopathy in the state of California. J Pediatr. 165:267–273.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Re L, Martinez-Sãnchez G, Bordicchia M,
Malcangi G, Pocognoli A, Morales-Segura MA, Rothchild J and Rojas
A: Is ozone pre-conditioning effect linked to Nrf2/EpRE activation
pathway in vivo? A preliminary result. Eur J Pharmacol.
742:158–162. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu Z, Uchi H, Morino-Koga S, Shi W and
Furue M: Z-ligustilide ameliorated ultraviolet B-induced oxidative
stress and inflammatory cytokine production in human keratinocytes
through upregulation of Nrf2/HO-1 and suppression of NF-κB pathway.
Exp Dermatol. 24:703–708. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sasaki H, Suzuki A, Shitara M, Hikosaka Y,
Okuda K, Moriyama S, Yano M and Fujii Y: Polymorphisms of NRF2 gene
correlated with decreased FEV1 in lung cancers of smokers. Biomed
Rep. 1:484–488. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Barnett M, Hall S, Dixit M and Arany I:
Simvastatin attenuates oleic acid-induced oxidative stress through
CREB-dependent induction of heme oxygenase-1 in renal proximal
tubule cells. Pediatr Res. 79:243–250. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lin SH, Song W, Cressatti M, Zukor H, Wang
E and Schipper HM: Heme oxygenase-1 modulates microRNA expression
in cultured astroglia: Implications for chronic brain disorders.
Glia. 63:1270–1284. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Morita K, Itoh M, Nishibori N, Her S and
Lee MS: Spirulina non-protein components induce BDNF gene
transcription via HO-1 activity in C6 glioma cells. Appl Biochem
Biotechnol. 175:892–901. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qian Y, Zhong P, Liang D, Xu Z, Skibba M,
Zeng C, Li X, Wei T, Wu L and Liang G: A newly designed curcumin
analog Y20 mitigates cardiac injury via anti-inflammatory and
anti-oxidant actions in obese rats. PLoS One. 10:e01202152015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Patel PB, Thakkar VR and Patel JS:
Cellular effect of curcumin and citral combination on breast cancer
cells: Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. J Breast
Cancer. 18:225–234. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jang EM, Choi MS, Jung UJ, Kim MJ, Kim HJ,
Jeon SM, Shin SK, Seong CN and Lee MK: Beneficial effects of
curcumin on hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance in high-fat-fed
hamsters. Metabolism. 57:1576–1583. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yeh CH, Chen TP, Wu YC, Lin YM and Lin P
Jing: Inhibition of NFkappaB activation with curcumin attenuates
plasma inflammatory cytokines surge and cardiomyocytic apoptosis
following cardiac ischemia/reperfusion. J Surg Res. 125:109–116.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu L, Liu C, Lu Y, Liu L and Jiang Y: ER
stress related factor ATF6 and caspase-12 trigger apoptosis in
neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:6960–6966. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kaandorp JJ, Benders MJ, Rademaker CM,
Torrance HL, Oudijk MA, de Haan TR, Bloemenkamp KW, Rijken M, van
Pampus MG, Bos AF, et al: Antenatal allopurinol for reduction of
birth asphyxia induced brain damage (ALLO-Trial); a randomized
double blind placebo controlled multicenter study. BMC Pregnancy
Childbirth. 10:82010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bell MJ, Adelson PD, Hutchison JS,
Kochanek PM, Tasker RC, Vavilala MS, Beers SR, Fabio A, Kelsey SF
and Wisniewski SR: Multiple Medical Therapies for Pediatric
Traumatic Brain Injury Workgroup: Differences in medical therapy
goals for children with severe traumatic brain injury-an
international study. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 14:811–818. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Agut T, Leon M, Rebollo M, Muchart J, Arca
G and Garcia-Alix A: Early identification of brain injury in
infants with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy at high risk for
severe impairments: Accuracy of MRI performed in the first days of
life. BMC Pediatr. 14:1772014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao M, Zhu P, Fujino M, Zhuang J, Guo H,
Sheikh I, Zhao L and Li XK: Oxidative stress in hypoxic-ischemic
encephalopathy: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies.
Int J Mol Sci. 17(pii): E20782016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vasiljević B, Maglajlić-Djukić S, Gojnić M
and Stanković S: The role of oxidative stress in perinatal
hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 140:35–41. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Burchell SR, Dixon BJ, Tang J and Zhang
JH: Isoflurane provides neuroprotection in neonatal hypoxic
ischemic brain injury. J Investig Med. 61:1078–1083. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu C, Xu F, Fukuda A, Wang X, Fukuda H,
Korhonen L, Hagberg H, Lannering B, Nilsson M, Eriksson PS, et al:
X chromosome-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein reduces
oxidative stress after cerebral irradiation or hypoxia-ischemia
through up-regulation of mitochondrial antioxidants. Eur J
Neurosci. 26:3402–3410. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Perrone S, Tataranno LM, Stazzoni G,
Ramenghi L and Buonocore G: Brain susceptibility to oxidative
stress in the perinatal period. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 28
Suppl 1:S2291–S2295. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chang CC, Wang YH, Chern CM, Liou KT, Hou
YC, Peng YT and Shen YC: Prodigiosin inhibits gp91(phox) and iNOS
expression to protect mice against the oxidative/nitrosative brain
injury induced by hypoxia-ischemia. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
257:137–147. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sosunov SA, Ameer X, Niatsetskaya ZV,
Utkina-Sosunova I, Ratner VI and Ten VS: Isoflurane anesthesia
initiated at the onset of reperfusion attenuates oxidative and
hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. PLoS One. 10:e01204562015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Feng Y, Lu S, Wang J, Kumar P, Zhang L and
Bhatt AJ: Dexamethasone-induced neuroprotection in hypoxic-ischemic
brain injury in newborn rats is partly mediated via Akt activation.
Brain Res. 1589:68–77. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gao S, Zhou J, Liu N, Wang L, Gao Q, Wu Y,
Zhao Q, Liu P, Wang S, Liu Y, et al: Curcumin induces M2 macrophage
polarization by secretion IL-4 and/or IL-13. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
85:131–139. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao H, Mitchell S, Ciechanowicz S, Savage
S, Wang T, Ji X and Ma D: Argon protects against hypoxic-ischemic
brain injury in neonatal rats through activation of nuclear factor
(erythroid-derived 2)-like 2. Oncotarget. 7:25640–25651.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhai X, Lin H, Chen Y, Chen X, Shi J, Chen
O, Li J and Sun X: Hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning ameliorates
hypoxia-ischemia brain damage by activating Nrf2 expression in vivo
and in vitro. Free Radic Res. 50:454–466. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li B, Choi HJ, Lee DS, Oh H, Kim YC, Moon
JY, Park WH, Park SD and Kim JE: Amomum tsao-ko suppresses
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in RAW264.7
macrophages via Nrf2-dependent heme oxygenase-1 expression. Am J
Chin Med. 42:1229–1244. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang H, Xu W, Zhou Z, Liu J, Li X, Chen L,
Weng J and Yu Z: Curcumin attenuates urinary excretion of albumin
in type II diabetic patients with enhancing nuclear factor
erythroid-derived 2-like 2 (Nrf2) system and repressing
inflammatory signaling efficacies. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes.
123:360–367. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rzepecka J, Pineda MA, Al-Riyami L,
Rodgers DT, Huggan JK, Lumb FE, Khalaf AI, Meakin PJ, Corbet M,
Ashford ML, et al: Prophylactic and therapeutic treatment with a
synthetic analogue of a parasitic worm product prevents
experimental arthritis and inhibits IL-1β production via
NRF2-mediated counter-regulation of the inflammasome. J Autoimmun.
60:59–73. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang X, Liang D, Guo L, Liang W, Jiang Y,
Li H, Zhao Y, Lu S and Chi ZH: Curcumin protects renal tubular
epithelial cells from high glucose-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through Nrf2-mediated
upregulation of heme oxygenase-1. Mol Med Rep. 12:1347–1355.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zimmermann K, Baldinger J, Mayerhofer B,
Atanasov AG, Dirsch VM and Heiss EH: Activated AMPK boosts the
Nrf2/HO-1 signaling axis-A role for the unfolded protein response.
Free Radic Biol Med. 88:417–426. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Askalan R, Gabarin N, Armstrong EA, Liu Y
Fang, Couchman D and Yager JY: Mechanisms of neurodegeneration
after severe hypoxic-ischemic injury in the neonatal rat brain.
Brain Res. 1629:94–103. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cai J, Kang Z, Liu WW, Luo X, Qiang S,
Zhang JH, Ohta S, Sun X, Xu W, Tao H and Li R: Hydrogen therapy
reduces apoptosis in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia rat model. Neurosci
Lett. 441:167–172. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bucak A, Ozdemir C, Ulu S, Gonul Y,
Aycicek A, Uysal M and Cangal A: Investigation of protective role
of curcumin against paclitaxel-induced inner ear damage in rats.
Laryngoscope. 125:1175–1182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|