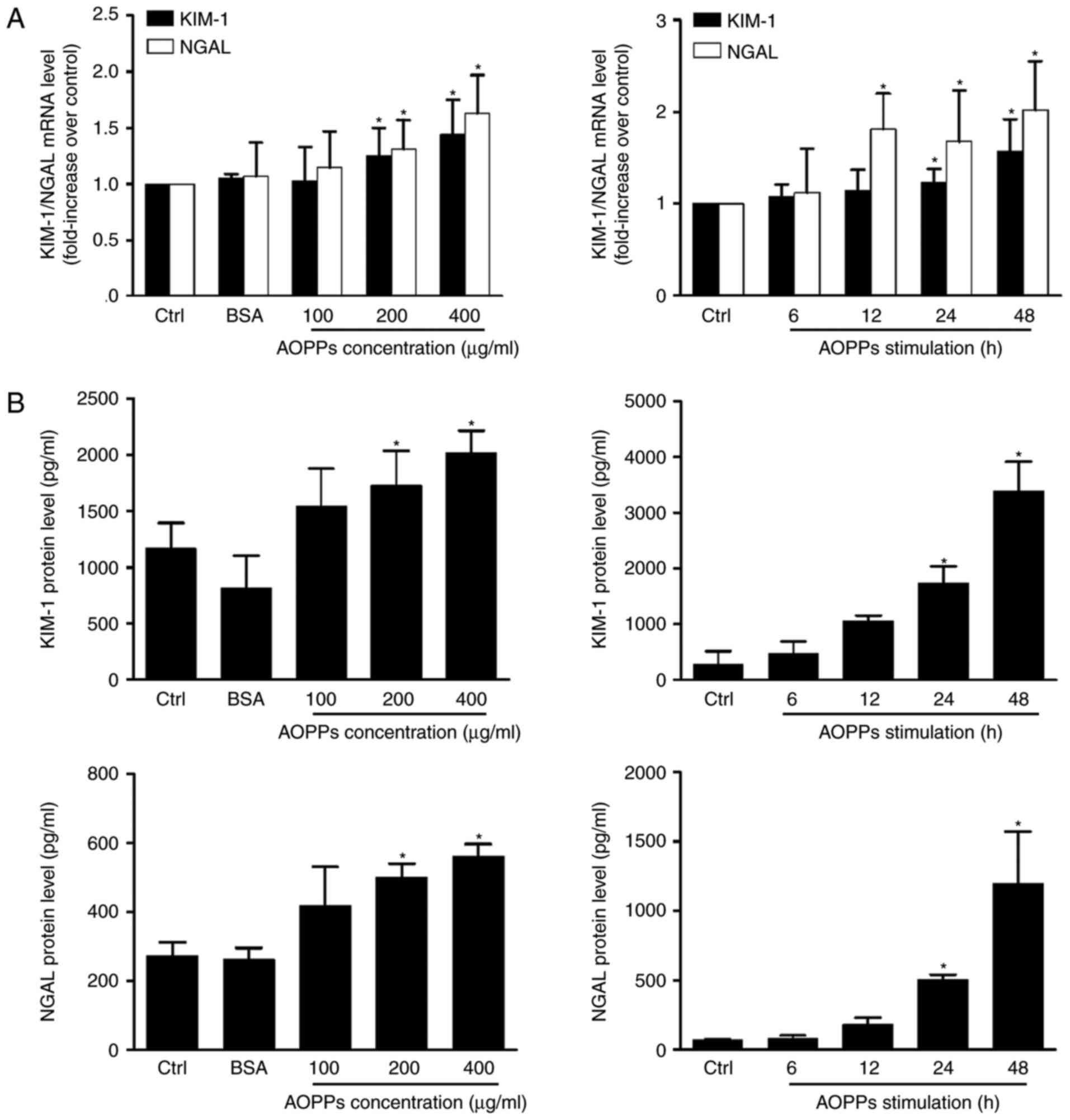
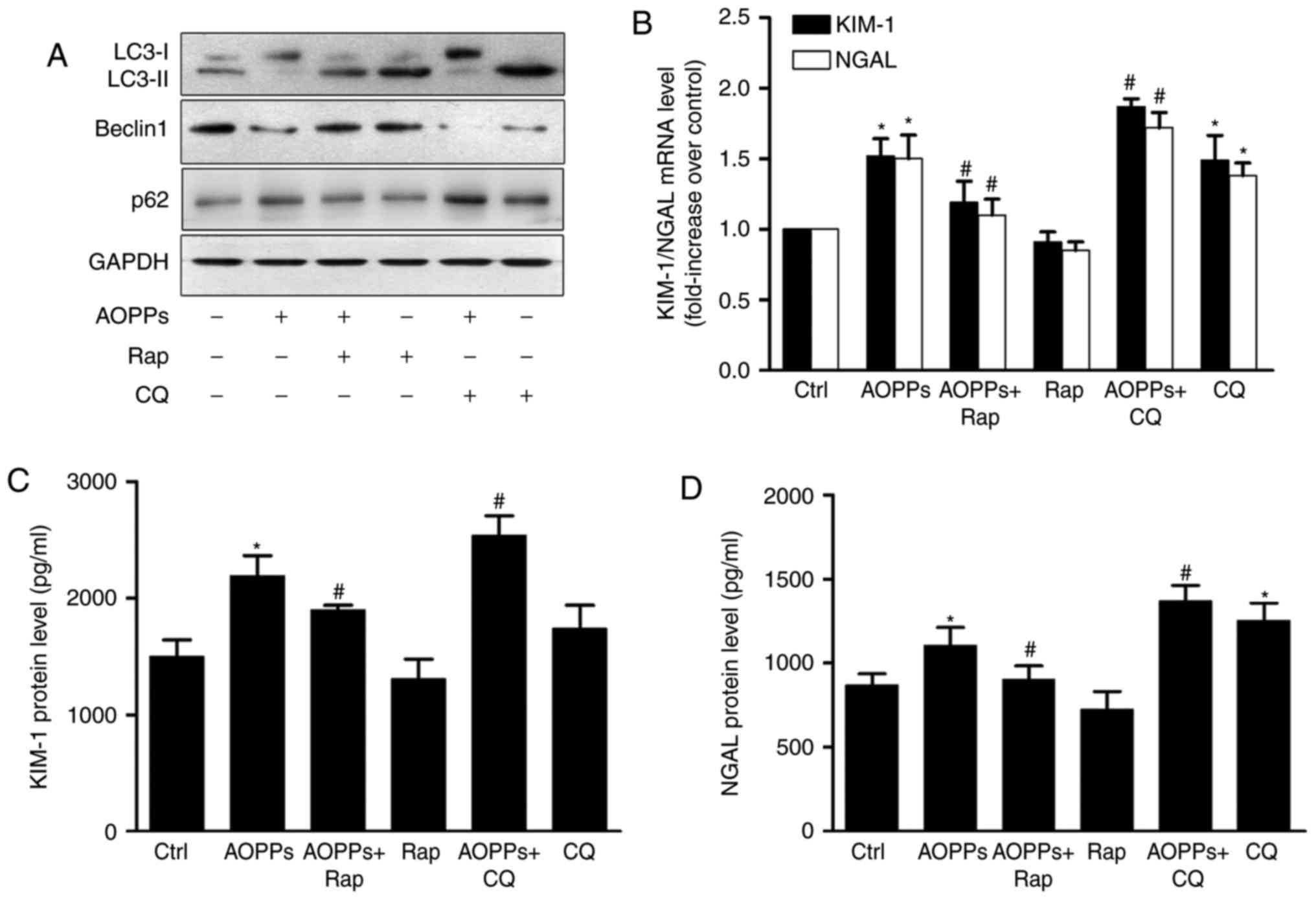
|
1
|
Couser WG, Remuzzi G, Mendis S and Tonelli
M: The contribution of chronic kidney disease to the global burden
of major noncommunicable diseases. Kidney Int. 80:1258–1270. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Eddy AA: Progression in chronic kidney
disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 12:353–365. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Grgic I, Campanholle G, Bijol V, Wang C,
Sabbisetti VS, Ichimura T, Humphreys BD and Bonventre JV: Targeted
proximal tubule injury triggers interstitial fibrosis and
glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int. 82:172–183. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huber TB, Edelstein CL, Hartleben B, Inoki
K, Jiang M, Koya D, Kume S, Lieberthal W, Pallet N, Quiroga A, et
al: Emerging role of autophagy in kidney function, diseases and
aging. Autophagy. 8:1009–1031. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Levine B and Klionsky DJ: Development by
self-digestion: Molecular mechanisms and biological functions of
autophagy. Dev Cell. 6:463–477. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A,
Kirisako T, Noda T, Kominami E, Ohsumi Y and Yoshimori T: LC3, a
mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome
membranes after processing. EMBO J. 19:5720–5728. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shimizu S, Kanaseki T, Mizushima N, Mizuta
T, Arakawa-Kobayashi S, Thompson CB and Tsujimoto Y: Role of Bcl-2
family proteins in a non-apoptotic programmed cell death dependent
on autophagy genes. Nat Cell Biol. 6:1221–1228. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mizushima N: Autophagy: Process and
function. Genes Dev. 21:2861–2873. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bjorkoy G, Lamark T, Pankiv S, Øvervatn A,
Brech A and Johansen T: Monitoring autophagic degradation of
p62/SQSTM1. Methods Enzymol. 452:181–197. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang C, Kaushal V, Shah SV and Kaushal GP:
Autophagy is associated with apoptosis in cisplatin injury to renal
tubular epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
294:F777–F787. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Suzuki C, Isaka Y, Takabatake Y, Tanaka H,
Koike M, Shibata M, Uchiyama Y, Takahara S and Imai E:
Participation of autophagy in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 368:100–106. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu WJ, Luo MN, Tan J, Chen W, Huang LZ,
Yang C, Pan Q, Li B and Liu HF: Autophagy activation reduces renal
tubular injury induced by urinary proteins. Autophagy. 10:243–256.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang C, Lin MZ, Cheng D, Braet F, Pollock
CA and Chen XM: Thioredoxin-interacting protein mediates
dysfunction of tubular autophagy in diabetic kidneys through
inhibiting autophagic flux. Lab Invest. 94:309–320. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Witko-Sarsat V, Friedlander M,
Capeillère-Blandin C, Nguyen-Khoa T, Nguyen AT, Zingraff J, Jungers
P and Descamps-Latscha B: Advanced oxidation protein products as a
novel marker of oxidative stress in uremia. Kidney Int.
49:1304–1313. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kalousová M, Skrha J and Zima T: Advanced
glycation end-products and advanced oxidation protein products in
patients with diabetes mellitus. Physiol Res. 51:597–604.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou LL, Hou FF, Wang GB, Yang F, Xie D,
Wang YP and Tian JW: Accumulation of advanced oxidation protein
products induces podocyte apoptosis and deletion through
NADPH-dependent mechanisms. Kidney Int. 76:1148–1160. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li HY, Hou FF, Zhang X, Chen PY, Liu SX,
Feng JX, Liu ZQ, Shan YX, Wang GB, Zhou ZM, et al: Advanced
oxidation protein products accelerate renal fibrosis in a remnant
kidney model. J Am Soc Nephrol. 18:528–538. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tang X, Rong G, Bu Y, Zhang S, Zhang M,
Zhang J and Liang X: Advanced oxidation protein products induce
hypertrophy and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human
proximal tubular cells through induction of endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:816–828. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang YP, Liang ZQ, Gu ZL and Qin ZH:
Molecular mechanism and regulation of autophagy. Acta Pharmacol
Sin. 26:1421–1434. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lieberthal W and Levine JS: The role of
the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in renal disease. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 20:2493–2502. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Heras-Sandoval D, Pérez-Rojas JM,
Hernández-Damián J and Pedraza-Chaverri J: The role of
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in the modulation of autophagy and the
clearance of protein aggregates in neurodegeneration. Cell Signal.
26:2694–2701. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Satriano J and Sharma K: Autophagy and
metabolic changes in obesity-related chronic kidney disease.
Nephrol Dial Transplant. 28 Suppl 4:S29–S36. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lieberthal W and Levine JS: Mammalian
target of rapamycin and the kidney. II. Pathophysiology and
therapeutic implications. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
303:F180–F191. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Witko-Sarsat V, Friedlander M, Nguyen Khoa
T, Capeillère-Blandin C, Nguyen AT, Canteloup S, Dayer JM, Jungers
P, Drüeke T and Descamps-Latscha B: Advanced oxidation protein
products as novel mediators of inflammation and monocyte activation
in chronic renal failure. J Immunol. 161:2524–2532. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C-T method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Caplin B and Nitsch D: Urinary biomarkers
of tubular injury in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 91:21–23.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H,
Abraham RT, Acevedo-Arozena A, Adeli K, Agholme L, Agnello M,
Agostinis P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA, et al: Guidelines for the use and
interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy.
8:445–544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Boya P, Reggiori F and Codogno P: Emerging
regulation and functions of autophagy. Nat Cell Biol. 15:713–720.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mavroeidi V, Petrakis I, Stylianou K,
Katsarou T, Giannakakis K, Perakis K, Vardaki E, Stratigis S,
Ganotakis E, Papavasiliou S and Daphnis E: Losartan affects
glomerular AKT and mTOR phosphorylation in an experimental model of
type 1 diabetic nephropathy. J Histochem Cytochem. 61:433–443.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang Z and Choi ME: Autophagy in kidney
health and disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 20:519–537. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Takabatake Y, Kimura T, Takahashi A and
Isaka Y: Autophagy and the kidney: Health and disease. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 29:1639–1647. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yamahara K, Kume S, Koya D, Tanaka Y,
Morita Y, Chin-Kanasaki M, Araki H, Isshiki K, Araki S, Haneda M,
et al: Obesity-mediated autophagy insufficiency exacerbates
proteinuria-induced tubulointerstitial lesions. J Am Soc Nephrol.
24:1769–1781. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kitada M, Takeda A, Nagai T, Ito H,
Kanasaki K and Koya D: Dietary restriction ameliorates diabetic
nephropathy through anti-inflammatory effects and regulation of the
autophagy via restoration of Sirt1 in diabetic Wistar fatty (fa/fa)
rats: A model of type 2 diabetes. Exp Diabetes Res.
2011:9081852011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huang JX, Kaeslin G, Ranall MV, Blaskovich
MA, Becker B, Butler MS, Little MH, Lash LH and Cooper MA:
Evaluation of biomarkers for in vitro prediction of drug-induced
nephrotoxicity: Comparison of HK-2, immortalized human proximal
tubule epithelial and primary cultures of human proximal tubular
cells. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 3:e001482015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|