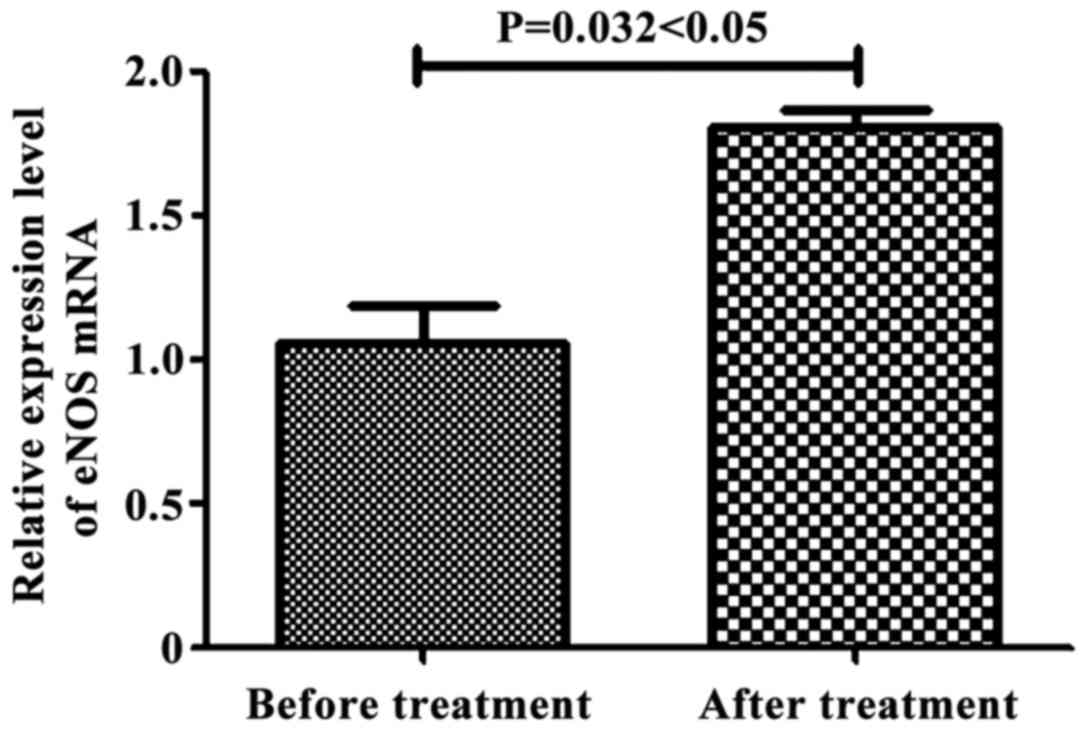
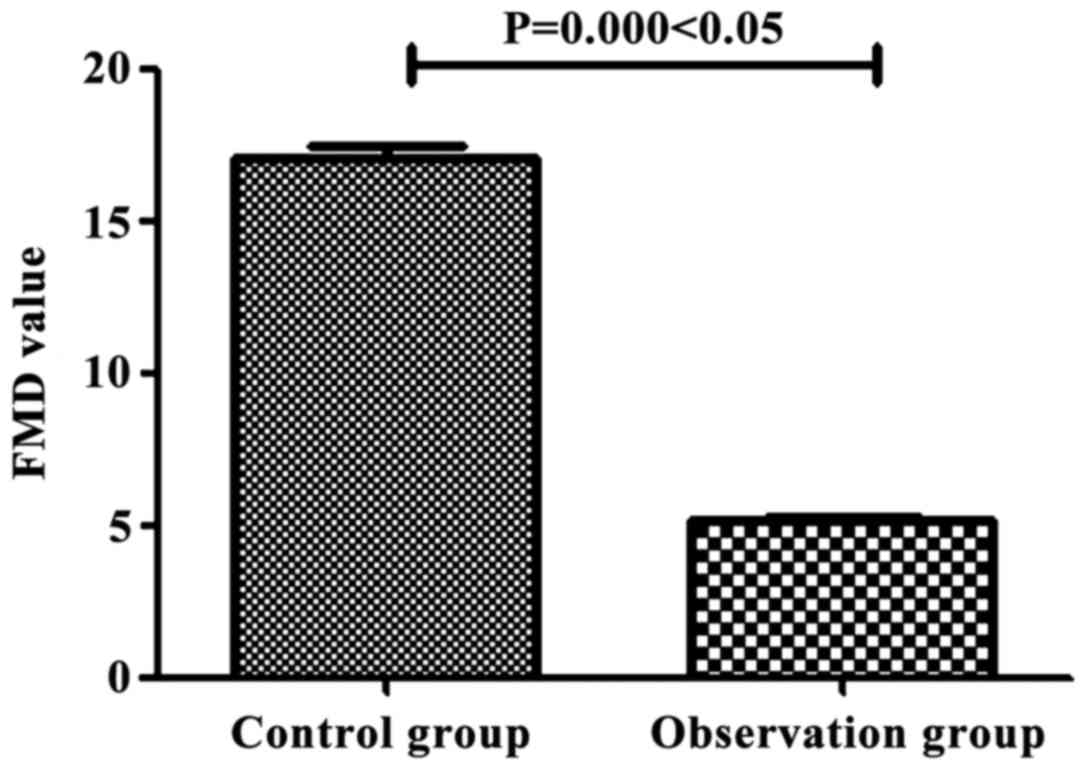
|
1
|
Ma X, Liu H, Foyil SR, Godar RJ,
Weinheimer CJ, Hill JA and Diwan A: Impaired autophagosome
clearance contributes to cardiomyocyte death in
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circulation. 125:3170–3181. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Peng L, Zhuang X, Liao L, He X, Li J, Chen
X, Lu G, Ma H and Gao X: Changes in cell autophagy and apoptosis
during age-related left ventricular remodeling in mice and their
potential mechanisms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 430:822–826.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee G, Ramirez CN, Kim H, Zeltner N, Liu
B, Radu C, Bhinder B, Kim YJ, Choi IY, Mukherjee-Clavin B, et al:
Large-scale screening using familial dysautonomia induced
pluripotent stem cells identifies compounds that rescue IKBKAP
expression. Nat Biotechnol. 30:1244–1248. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
L'vova NV, Tupitsyna IuIu, Badalov NGL,
Krasnikov VE and Lebedeva OD: The influence of carbon dioxide baths
differing in the total mineralization levels on the functional
state of the cardiovascular system of the patients presenting with
hypertensive disease associated with coronary heart disease. Vopr
Kurortol Fizioter Lech Fiz Kult. 6:14–17. 2013.(In Russian).
|
|
5
|
Şentürk T, Çavun S, Avcı B, Yermezler A,
Serdar Z and Savcı V: Effective inhibition of cardiomyocyte
apoptosis through the combination of trimetazidine and
N-acetylcysteine in a rat model of myocardial ischemia and
reperfusion injury. Atherosclerosis. 237:760–766. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yamashita K, Kondo T, Muramatsu T,
Matsushita K, Nagahiro T, Maeda K, Shintani S and Murohara T:
Effects of valsartan versus amlodipine in diabetic hypertensive
patients with or without previous cardiovascular disease. Am J
Cardiol. 112:1750–1756. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ussher JR, Jaswal JS and Lopaschuk GD:
Pyridine nucleotide regulation of cardiac intermediary metabolism.
Circ Res. 111:628–641. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Egan BM, Zhao Y, Li J, Brzezinski WA,
Todoran TM, Brook RD and Calhoun DA and Calhoun DA: Prevalence of
optimal treatment regimens in patients with apparent
treatment-resistant hypertension based on office blood pressure in
a community-based practice network. Hypertension. 62:691–697. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dedkova EN, Seidlmayer LK and Blatter LA:
Mitochondria-mediated cardioprotection by trimetazidine in rabbit
heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 59:41–54. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lopez-Jaramillo P, Lopez-Lopez J,
Lopez-Lopez C and Rodriguez-Alvarez MI: The goal of blood pressure
in the hypertensive patient with diabetes is defined: Now the
challenge is go from recommendations to practice. Diabetol Metab
Syndr. 6:312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Al-Shabanah OA, Aleisa AM, Hafez MM,
Al-Rejaie SS, Al-Yahya AA, Bakheet SA, Al-Harbi MM and Sayed-Ahmed
MM: Desferrioxamine attenuates doxorubicin-induced acute
cardiotoxicity through TFG-β/Smad p53 pathway in rat model. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2012:6191852012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Roĭtberg GE, Artamonova EA and Ushakova
TI: State of the brachial artery wall in patients with and without
metabolic syndrome. Angiol Sosud Khir. 12:23–27. 2006.(In Russian).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zemljic G, Bunc M and Vrtovec B:
Trimetazidine shortens QTc interval in patients with ischemic heart
failure. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 15:31–36. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu J, Chai Y, Wang Y, Kheir MM, Li H, Yuan
Z, Wan H, Xing D, Lei F and Du L: PI3K p55γ promoter activity
enhancement is involved in the anti-apoptotic effect of berberine
against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Eur J Pharmacol.
674:132–142. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou X, Li C, Xu W and Chen J:
Trimetazidine protects against smoking-induced left ventricular
remodeling via attenuating oxidative stress, apoptosis, and
inflammation. PLoS One. 7:e404242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Soliman EZ, Lopez F, O'Neal WT, Chen LY,
Bengtson L, Zhang ZM, Loehr L, Cushman M and Alonso A: Atrial
fibrillation and risk of ST-segment-elevation versus
non-ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction: The Atherosclerosis
Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Circulation. 131:1843–1850. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vitale C, Spoletini I, Malorni W,
Perrone-Filardi P, Volterrani M and Rosano GM: Efficacy of
trimetazidine on functional capacity in symptomatic patients with
stable exertional angina - the VASCO-angina study. Int J Cardiol.
168:1078–1081. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jones LW, Hornsby WE, Goetzinger A, Forbes
LM, Sherrard EL, Quist M, Lane AT, West M, Eves ND, Gradison M, et
al: Prognostic significance of functional capacity and exercise
behavior in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer.
Lung Cancer. 76:248–252. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pathak RK, Middeldorp ME, Lau DH, Mehta
AB, Mahajan R, Twomey D, Alasady M, Hanley L, Antic NA, McEvoy RD,
et al: Aggressive risk factor reduction study for atrial
fibrillation and implications for the outcome of ablation: The
ARREST-AF cohort study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 64:2222–2231. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Montalescot G, Sechtem U, Achenbach S,
Andreotti F, Arden C, Budaj A, Bugiardini R, Crea F, Cuisset T, Di
Mario C, et al: Document Reviewers: 2013 ESC guidelines on the
management of stable coronary artery disease: The Task Force on the
management of stable coronary artery disease of the European
Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 34:2949–3003. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|