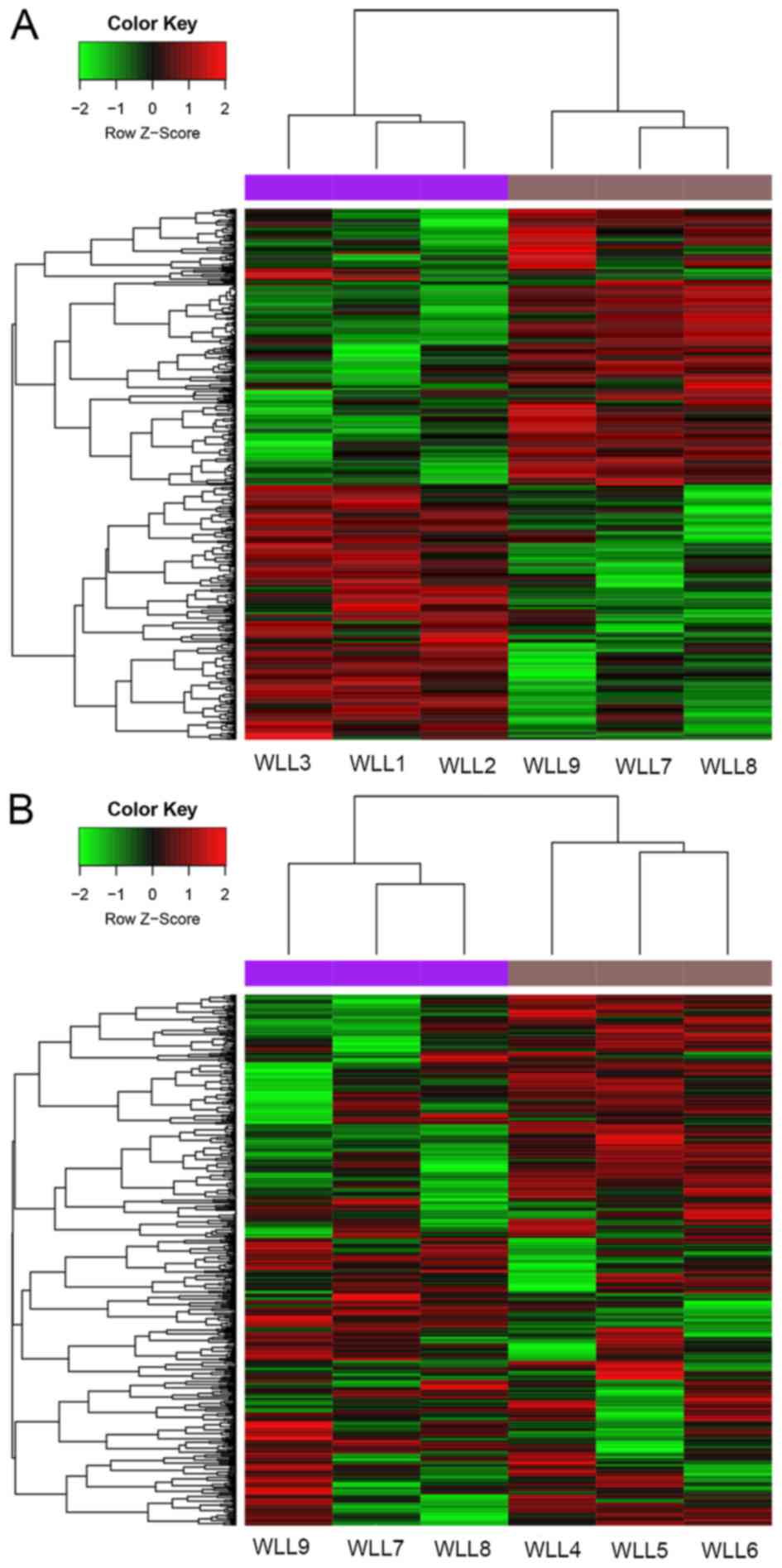
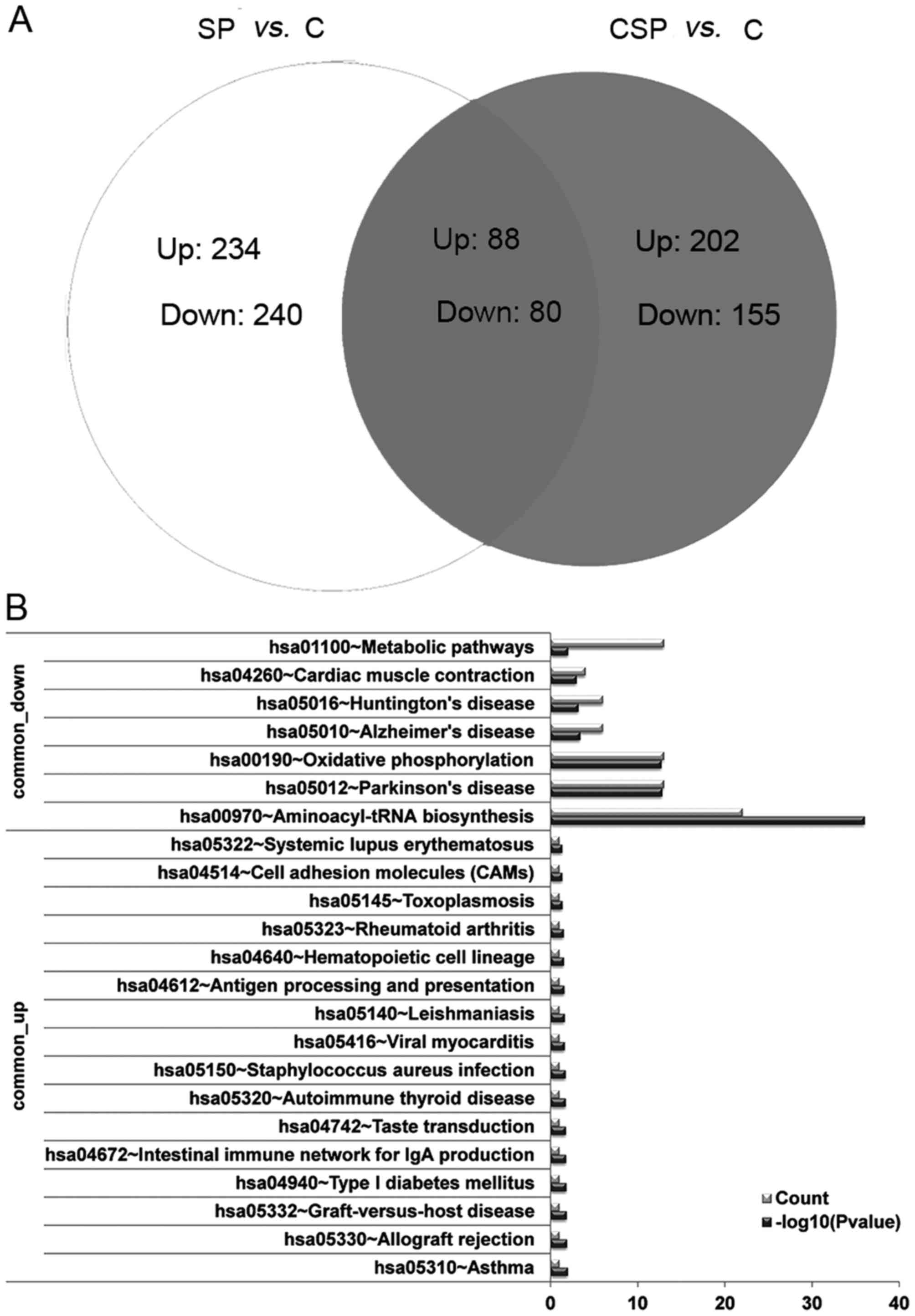
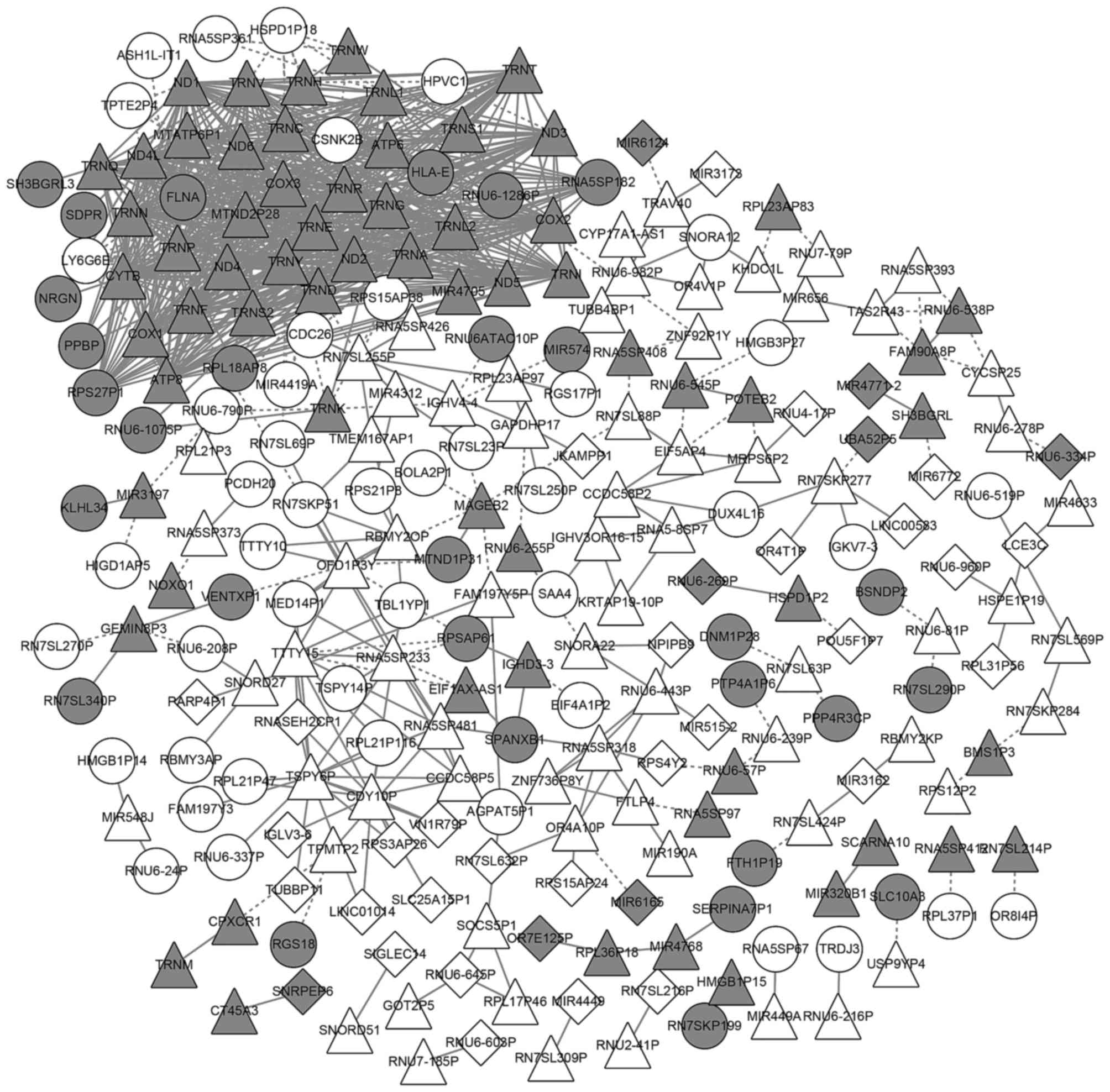
|
1
|
Marrie TJ: Community-acquired pneumonia.
Clin Infect Dis. 18:501–515. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thomas CP, Ryan M, Chapman JD, Stason WB,
Tompkins CP, Suaya JA, Polsky D, Mannino DM and Shepard DS:
Incidence and cost of pneumonia in Medicare beneficiaries. Chest.
142:973–981. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ewig S, Ruiz M, Mensa J, Marcos MA,
Martinez JA, Arancibia F, Niederman MS and Torres A: Severe
community-acquired pneumonia: Assessment of severity criteria. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 158:1102–1108. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nazir SA and Erbland ML: Chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Drugs Aging. 26:813–831. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Iyer Parameswaran G and Murphy TF: Chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease: Role of bacteria and updated guide
to antibacterial selection in the older patient. Drugs Aging.
26:985–995. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Calverley PM, Anderson JA, Celli B,
Ferguson GT, Jenkins C, Jones PW, Yates JC and Vestbo J: TORCH
investigators: Salmeterol and fluticasone propionate and survival
in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med.
356:775–789. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Singh S, Amin AV and Loke YK: Long-term
use of inhaled corticosteroids and the risk of pneumonia in chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease: A meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med.
169:219–229. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eom JS, Song WJ, Yoo H, Jeong BH, Lee HY,
Koh WJ, Jeon K and Park HY: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
severity is associated with severe pneumonia. Ann Thorac Med.
10:105–111. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liapikou A, Polverino E, Ewig S, Cillóniz
C, Marcos MA, Mensa J, Bello S, Martin-Loeches I, Menéndez R and
Torres A: Severity and outcomes of hospitalised community-acquired
pneumonia in COPD patients. Eur Respir J. 39:855–861. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zuniga J, Buendía-Roldán I, Zhao Y,
Jiménez L, Torres D, Romo J, Ramírez G, Cruz A, Vargas-Alarcon G,
Sheu CC, et al: Genetic variants associated with severe pneumonia
in A/H1N1 influenza infection. Eur Respir J. 39:604–610. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kebaier C, Chamberland RR, Allen IC, Gao
X, Broglie PM, Hall JD, Jania C, Doerschuk CM, Tilley SL and Duncan
JA: Staphylococcus aureus α-hemolysin mediates virulence in a
murine model of severe pneumonia through activation of the NLRP3
inflammasome. J Infect Dis. 205:807–817. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gillet Y, Vanhems P, Lina G, Bes M,
Vandenesch F, Floret D and Etienne J: Factors predicting mortality
in necrotizing community-acquired pneumonia caused by
Staphylococcus aureus containing Panton-Valentine leukocidin. Clin
Infect Dis. 45:315–321. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kilic A, Li H, Stratton CW and Tang YW:
Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns and staphylococcal cassette
chromosome mec types of, as well as Panton-Valentine leukocidin
occurrence among, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
isolates from children and adults in middle Tennessee. J Clin
Microbiol. 44:4436–4440. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Green R, Terclanche A, Becker P, Rheeder
P, Wittenberg DF, Anderson R and Masekela R: Cytokine profile and
clinical correlates in HIV-exposed infants with severe (hypoxic)
pneumonia. South African Respirat J. 22:3–6. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Martín-Loeches I, Solé-Violán J, de Castro
Rodríguez F, García-Laorden MI, Borderías L, Blanquer J, Rajas O,
Briones ML, Aspa J, Herrera-Ramos E, et al: Variants at the
promoter of the interleukin-6 gene are associated with severity and
outcome of pneumococcal community-acquired pneumonia. Intensive
Care Med. 38:256–262. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Association RdbotCm, . The diagnosis and
treatment guideline of community-acquired pneumonia. Chin J Tuberc
Respir Dis. 29:651–655. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Martin M: Cutadapt removes adapter
sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J.
17:10–12. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Robinson MD and Oshlack A: A scaling
normalization method for differential expression analysis of
RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 11:R252010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Law CW, Chen Y, Shi W and Smyth GK: Voom:
Precision weights unlock linear model analysis tools for RNA-seq
read counts. Genome Biol. 15:R292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Routledge R: Fisher's Exact Test.
Encyclopedia of Biostatistics. 3:2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Cai H, Chen H, Yi T, Daimon CM, Boyle JP,
Peers C, Maudsley S and Martin B: VennPlex-a novel Venn diagram
program for comparing and visualizing datasets with differentially
regulated datapoints. PLoS One. 8:e533882013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Davis AP, Grondin CJ, Lennon-Hopkins K,
Saraceni-Richards C, Sciaky D, King BL, Wiegers TC and Mattingly
CJ: The comparative toxicogenomics database's 10th year
anniversary: Update 2015. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:D914–D920. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sparks LM, Xie H, Koza RA, Mynatt R,
Hulver MW, Bray GA and Smith SR: A high-fat diet coordinately
downregulates genes required for mitochondrial oxidative
phosphorylation in skeletal muscle. Diabetes. 54:1926–1933. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Miller JL, Velmurugan K, Cowan MJ and
Briken V: The type I NADH dehydrogenase of Mycobacterium
tuberculosis counters phagosomal NOX2 activity to inhibit
TNF-α-mediated host cell apoptosis. PLoS Pathog. 6:e10008642010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Martín-Gómez L, Villalba A and Abollo E:
Identification and expression of immune genes in the flat oyster
Ostrea edulis in response to bonamiosis. Gene. 492:81–93. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Khan KN, Stanfield K, Trajkovic D and
Harris RK: Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in inflammatory lung lesions
of nonhuman primates. Vet Pathol. 37:512–516. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zaiss AK, Zuber J, Chu C, Machado HB, Jiao
J, Catapang AB, Ishikawa TO, Gil JS, Lowe SW and Herschman HR:
Reversible suppression of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) expression in
vivo by inducible RNA interference. PLoS One. 9:e1012632014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sadikot RT, Zeng H, Azim AC, Joo M, Dey
SK, Breyer RM, Peebles RS, Blackwell TS and Christman JW: Bacterial
clearance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is enhanced by the inhibition
of COX-2. Eur J Immunol. 37:1001–1009. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Giacominelli-Stuffler R, Marruchella G,
Storelli M, Sabatucci A, Angelucci CB and Maccarrone M:
5-Lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase-2 in the lungs of pigs naturally
affected by enzootic pneumonia and porcine pleuropneumonia. Res Vet
Sci. 93:898–903. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Poliseno L, Salmena L, Zhang J, Carver B,
Haveman WJ and Pandolfi PP: A coding-independent function of gene
and pseudogene mRNAs regulates tumour biology. Nature.
465:1033–1038. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sarma NJ, Tiriveedhi V, Subramanian V,
Shenoy S, Crippin JS, Chapman WC and Mohanakumar T: Hepatitis C
virus mediated changes in miRNA-449a modulates inflammatory
biomarker YKL40 through components of the NOTCH signaling pathway.
PLoS One. 7:e508262012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wölfle U, Haarhaus B and Schempp CM:
Amarogentin displays immunomodulatory effects in human mast cells
and keratinocytes. Mediators inflamm. 2015:6301282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|