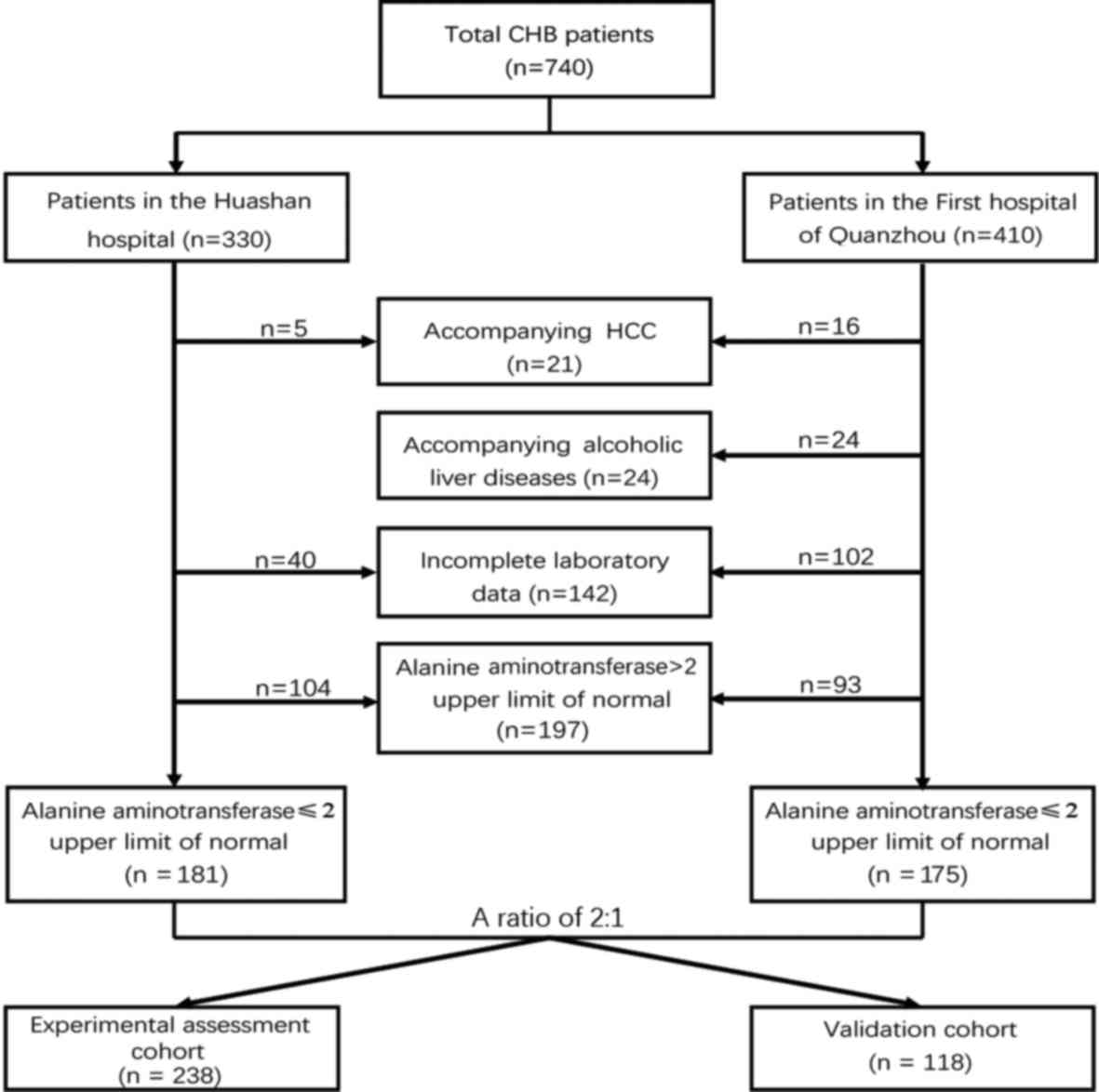
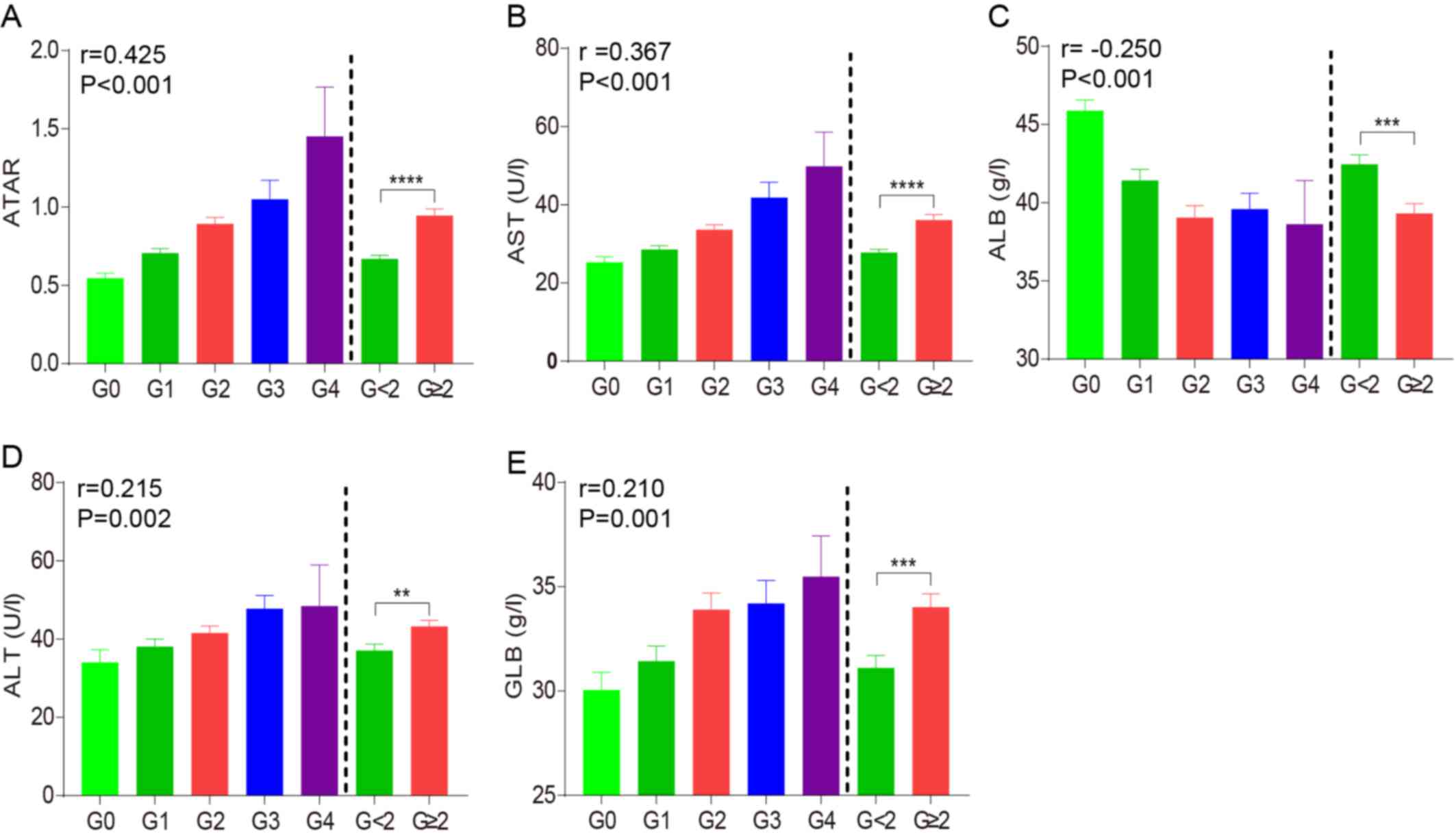
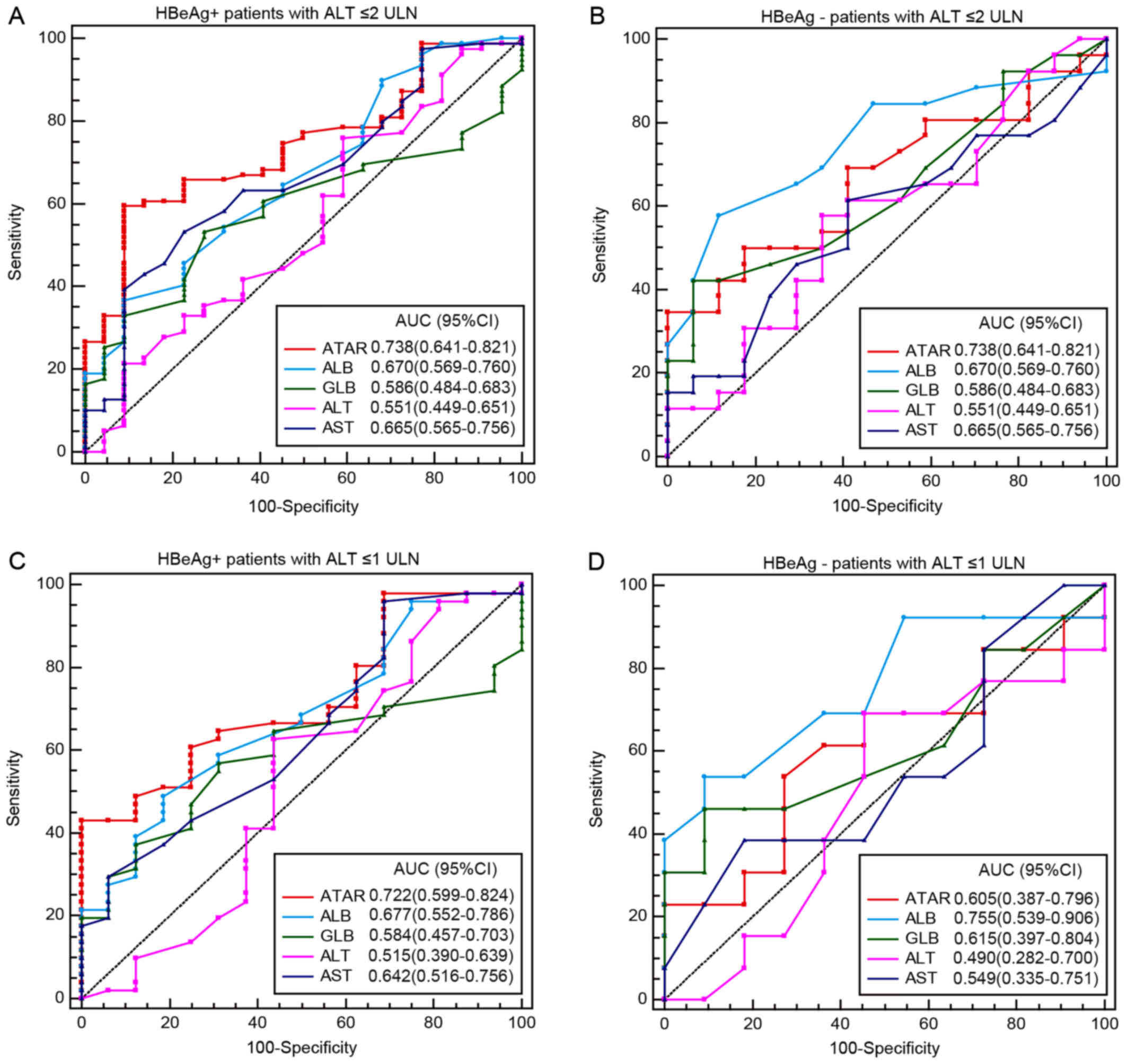
|
1
|
Wong GL, Wong VW, Choi PC, Chan AW, Chim
AM, Yiu KK, Chan HY, Chan FK, Sung JJ and Chan HL: Metabolic
syndrome increases the risk of liver cirrhosis in chronic hepatitis
B. Gut. 58:111–117. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Terrault NA, Lok ASF, McMahon BJ, Chang
KM, Hwang JP, Jonas MM, Brown RS Jr, Bzowej NH and Wong JB: Update
on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B:
AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology. 67:1560–1599. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
European Association for the Study of the
Liver. Electronic address, . simpleeasloffice@easloffice.eu;
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical
Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus
infection. J Hepatol. 67:370–398. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sarin SK, Kumar M, Lau GK, Abbas Z, Chan
HL, Chen CJ, Chen DS, Chen HL, Chen PJ, Chien RN, et al:
Asian-pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of
hepatitis B: A 2015 update. Hepatol Int. 10:1–98. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Castera L: Noninvasive methods to assess
liver disease in patients with hepatitis B or C. Gastroenterology.
142:1293–1302.e4. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Verveer C, Zondervan PE, Ten Kate FJ,
Hansen BE, Janssen HL and de Knegt RJ: Evaluation of transient
elastography for fibrosis assessment compared with large biopsies
in chronic hepatitis B and C. Liver Int. 32:622–628. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wai CT, Greenson JK, Fontana RJ,
Kalbfleisch JD, Marrero JA, Conjeevaram HS and Lok AS: A simple
noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and
cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology.
38:518–526. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sterling RK, Lissen E, Clumeck N, Sola R,
Correa MC, Montaner J, Sulkowski S M, Torriani FJ, Dieterich DT,
Thomas DL, et al: Development of a simple noninvasive index to
predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection.
Hepatology. 43:1317–1325. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bala S, Petrasek J, Mundkur S, Catalano D,
Levin I, Ward J, Alao H, Kodys K and Szabo G: Circulating microRNAs
in exosomes indicate hepatocyte injury and inflammation in
alcoholic, drug-induced, and inflammatory liver diseases.
Hepatology. 56:1946–1957. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Arataki K, Hayes CN, Akamatsu S, Akiyama
R, Abe H, Tsuge M, Miki D, Ochi H, Hiraga N, Imamura M, et al:
Circulating microRNA-22 correlates with microRNA-122 and represents
viral replication and liver injury in patients with chronic
hepatitis B. J Med Virol. 85:789–798. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang JY, Mao RC, Zhang YM, Zhang YJ, Liu
HY, Qin YL, Lu MJ and Zhang JM: Serum microRNA-124 is a novel
biomarker for liver necroinflammation in patients with chronic
hepatitis B virus infection. J Viral Hepat. 22:128–136. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li F, Zhou P, Deng W, Wang J, Mao R, Zhang
Y, Li J, Yu J, Yang F, Huang Y, et al: Serum microRNA-125b
correlates with hepatitis B viral replication and liver
necroinflammation. Clin Microbiol Infect. 22:384.e1–384.e10. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Liang LB, Zhu X, Yan LB, Du LY, Liu C,
Liao J and Tang H: Quantitative intrahepatic HBV cccDNA correlates
with histological liver inflammation in chronic hepatitis B virus
infection. Int J Infect Dis. 52:77–82. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li J, Zhang TY, Song LW, Qi X, Yu XP, Li
FH, Zhou P, Qin YL, Yang L, Zhao JH, et al: Role of quantitative
hepatitis B core antibody levels in predicting significant liver
inflammation in chronic hepatitis B patients with normal or
near-normal alanine aminotransferase levels. Hepatol Res.
48:E133–E145. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Huang H, Sun Z, Pan H, Chen M, Tong Y,
Zhang J, Chen D, Su X and Li L: Serum metabolomic signatures
discriminate early liver inflammation and fibrosis stages in
patients with chronic hepatitis B. Sci Rep. 6:308532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hong MZ, Ye L, Jin LX, Ren YD, Yu XF, Liu
XB, Zhang RM, Fang K and Pan JS: Noninvasive scoring system for
significant inflammation related to chronic hepatitis B. Sci Rep.
7:437522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Desmet VJ, Gerber M, Hoofnagle JH, Manns M
and Scheuer PJ: Classification of chronic hepatitis: Diagnosis,
grading and staging. Hepatology. 19:1513–1520. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese
Medical Association, ; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases,
Chinese Medical Association, . Hou JL and Lai W: The guideline of
prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B: A 2015 update.
Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 23:888–905. 2015.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
European Association For The Study Of The
Liver, . EASL clinical practice guidelines: Management of chronic
hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 50:227–242. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xiao G, Zhu S, Xiao X, Yan L, Yang J and
Wu G: Comparison of laboratory tests, ultrasound, or magnetic
resonance elastography to detect fibrosis in patients with
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis. Hepatology.
66:1486–1501. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gao S, Li XY, Fan YC, Sun FK, Han LY, Li
F, Ji XF and Wang K: A noninvasive model to predict liver histology
in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B with alanine aminotransferase
≤2 upper limit of normal. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 32:215–220.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li YP, Li CY and Chen YP: Independent
predictive factors for significant liver histological changes in
patients with HBeAg-positive high-viral-load chronic HBV infection
and a normal alanine aminotransferase level. J Clin Hepatol.
32:42016.
|
|
23
|
Chen LY, Wang J, Wang WY, Tang H and Feng
P: Correlation between serological indices and liver histological
pathology in patients with HBV infection. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao.
Yi Xue. 46:641–644. 2015.(In Chinese).
|