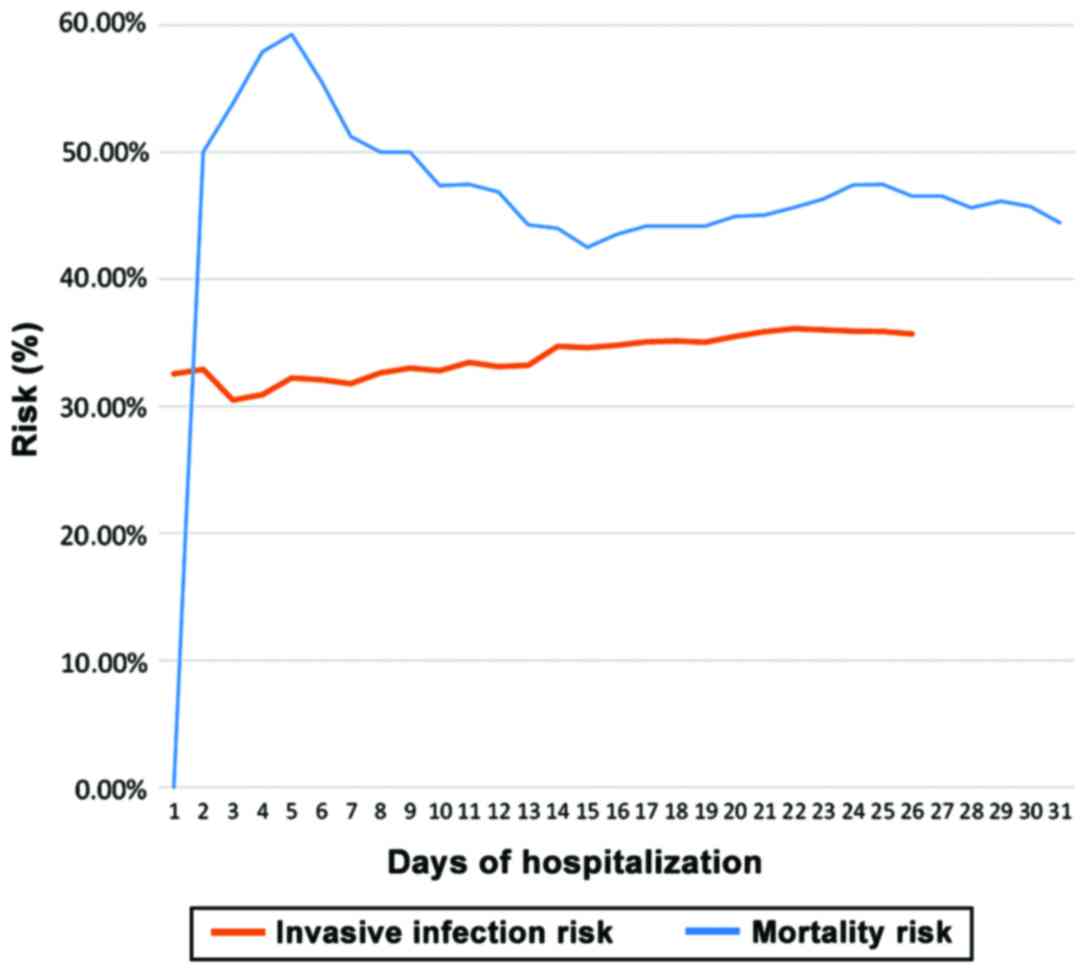
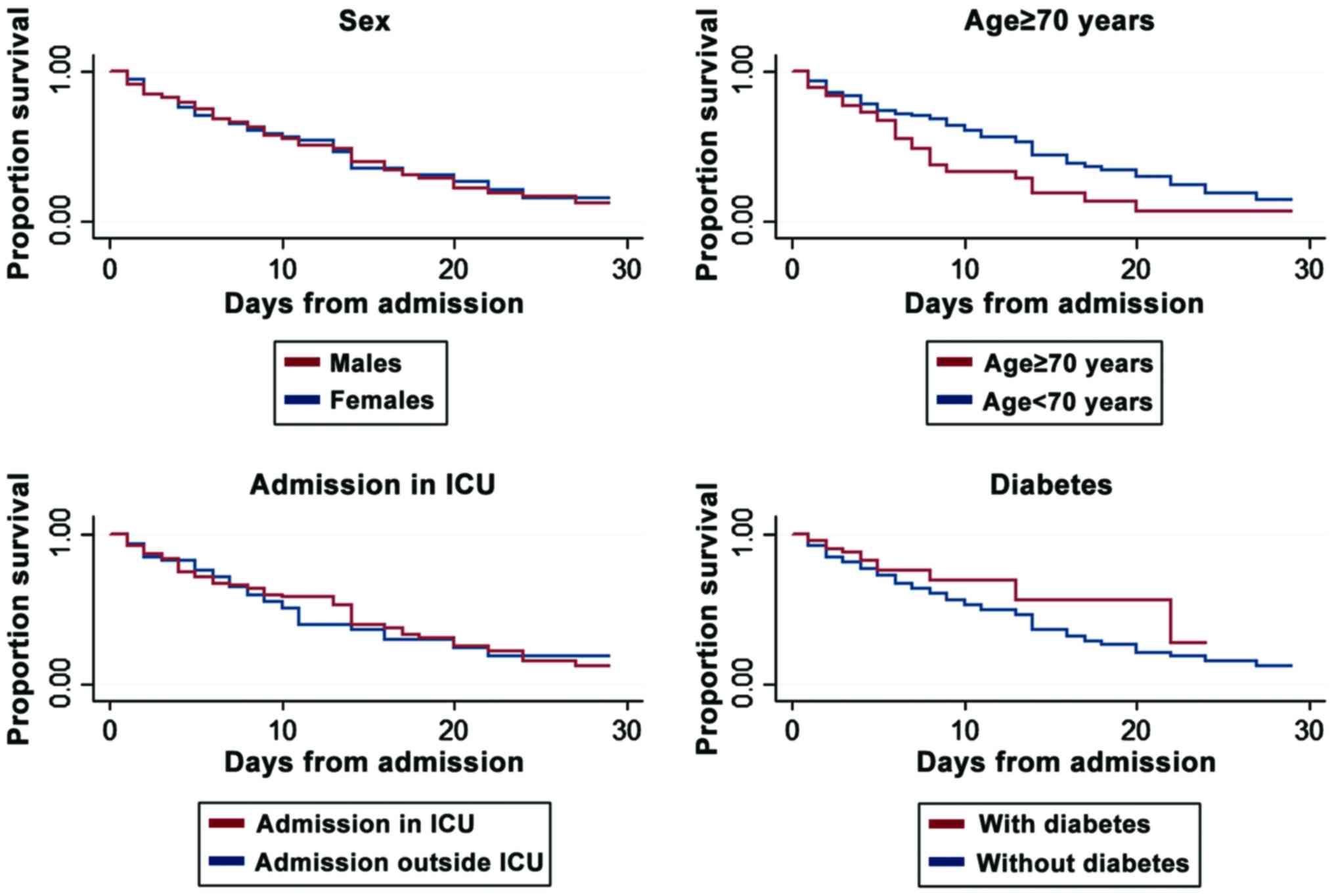
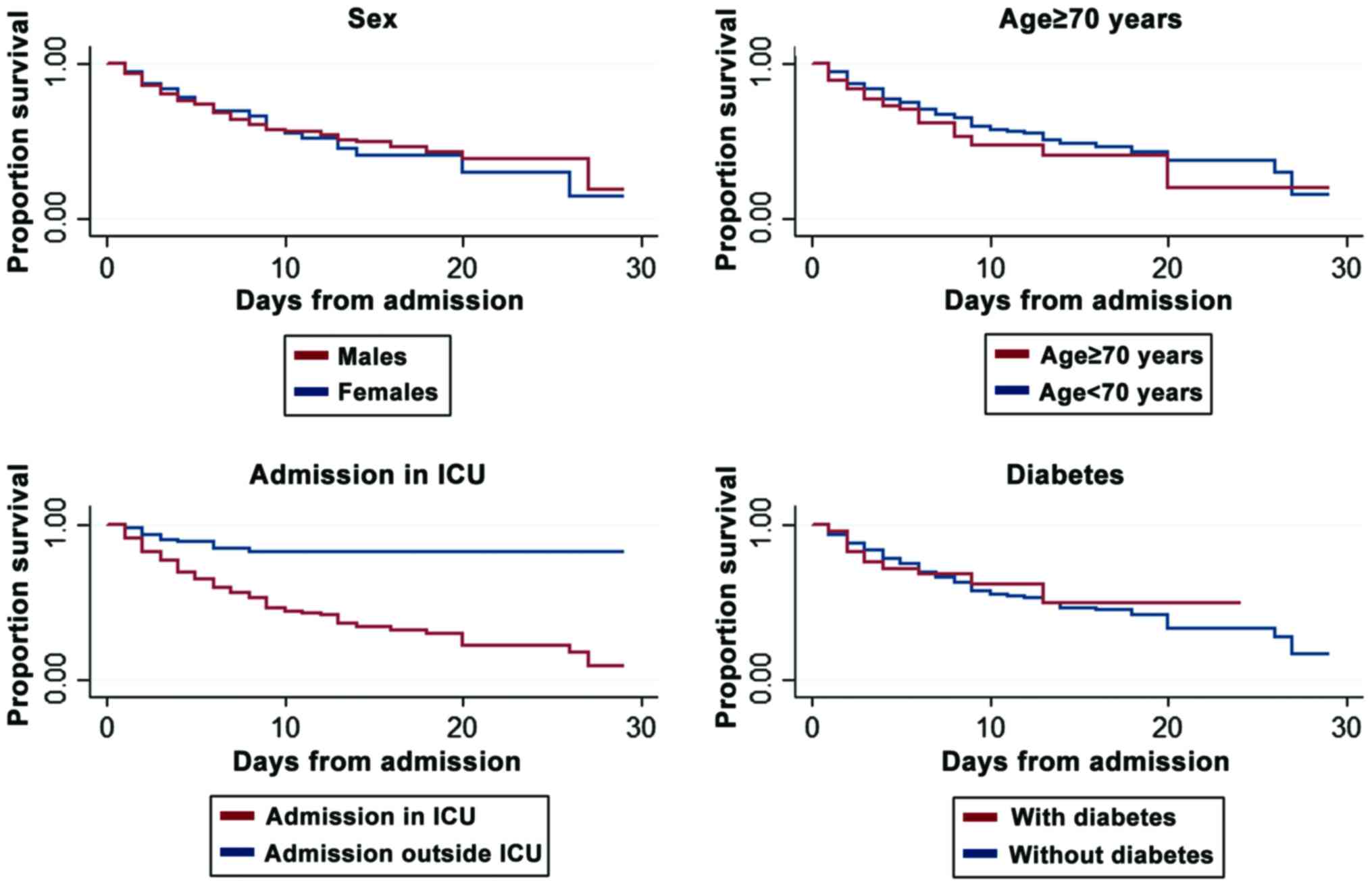
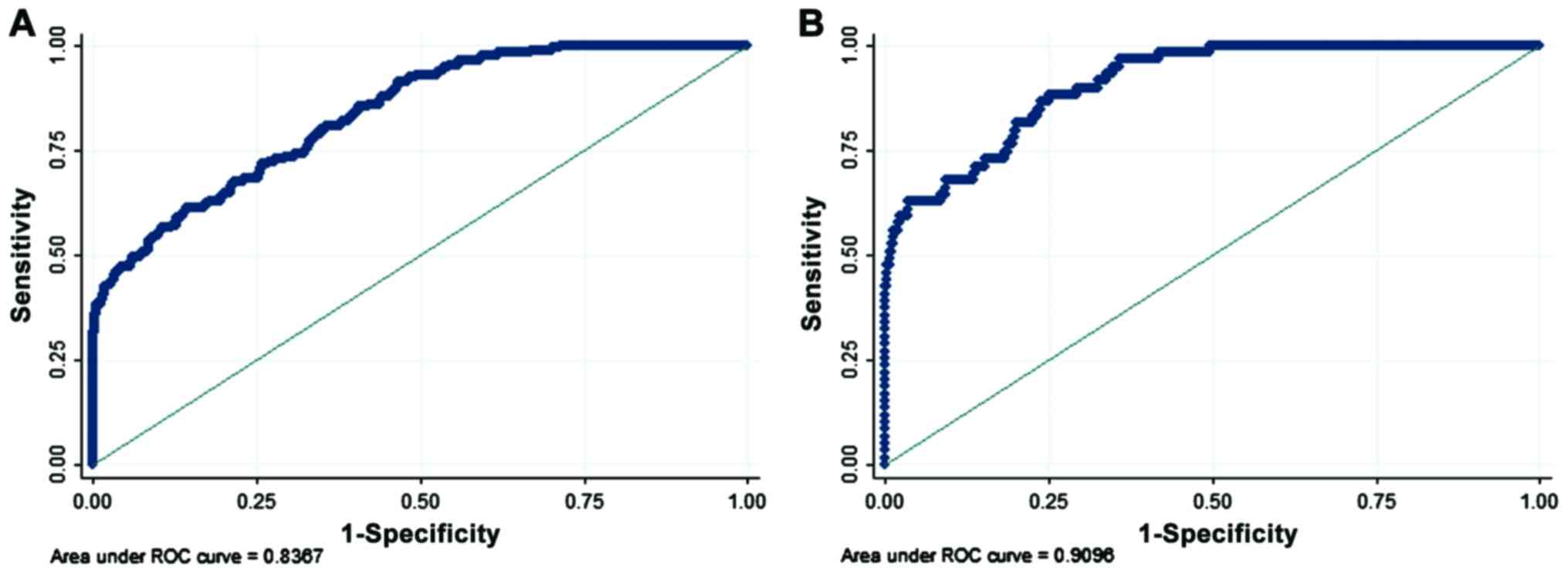
|
1
|
Kaspersen ER, Ræder J and Dahl V:
Guidelines for treatment of sepsis. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen.
138:2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wenzel RP and Edmond MB: The impact of
hospital-acquired bloodstream infections. Emerg Infect Dis.
7:174–177. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nielsen SL, Lassen AT, Kolmos HJ, Jensen
TG, Gradel KO and Pedersen C: The daily risk of bacteremia during
hospitalization and associated 30-day mortality evaluated in
relation to the traditional classification of bacteremia. Am J
Infect Control. 44:167–172. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Anderson DJ, Moehring RW, Sloane R,
Schmader KE, Weber DJ, Fowler VG Jr, Smathers E and Sexton DJ:
Bloodstream infections in community hospitals in the 21st century:
A multicenter cohort study. PLoS One. 9:e917132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thaden JT, Park LP, Maskarinec SA, Ruffin
F, Fowler VG Jr and van Duin D: Results from a 13-year prospective
cohort study showincreased mortality associated with bloodstream
infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa compared to other
bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 61:e02671–e16. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gradel KO, Nielsen SL, Pedersen C, Knudsen
JD, Østergaard C, Arpi M, Jensen TG, Kolmos HJ, Schønheyder HC,
Søgaard M, et al: Danish Collaborative Bacteraemia Network; Danish
Observational Registry of Infectious Syndromes: No specific time
window distinguishes between community-, healthcare-, and
hospital-acquired bacteremia, but they are prognostically robust.
Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 35:1474–1482. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Leibovici L, Schønheyder H, Pitlik SD,
Samra Z and Møller JK: Bacteraemia caused by hospital-type
micro-organisms during hospital stay. J Hosp Infect. 44:31–36.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Buetti N, Marschall J, Atkinson A and
Kronenberg A; Swiss Centre for Antibiotic Resistance (ANRESIS), :
National Bloodstream Infection Surveillance in Switzerland
2008–2014: Different Patterns and Trends for University and
Community Hospitals. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 37:1060–1067.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NK,
Hartog CS, Tsaganos T, Schlattmann P, Angus DC and Reinhart K:
International forum of acute care trialists: Assessment of global
incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis. Current
Estimates and Limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 193:259–272.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Călina D, Docea AO, Roşu L, Zlatian O,
Roşu AF, Anghelina F, Rogoveanu O, Arsene AL, Nicolae AC, Drăgoi
CM, et al: Antimicrobial resistance development following surgical
site infections. Mol Med Rep. 15:681–688. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Călina D, Roșu L, Roșu AF, Ianoşi G,
Ianoşi S, Zlatian O, Mitruț R, Docea AO, Rogoveanu O, Mitruț P, et
al: Etiological diagnosis and pharmacotherapeutic management of
parapneumonic pleurisy. Farmacia. 64:946–952. 2016.
|
|
12
|
Tong SY, Davis JS, Eichenberger E, Holland
TL and Fowler VG Jr: Staphylococcus aureus infections:
Epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
management. Clin Microbiol Rev. 28:603–661. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cahill TJ and Prendergast BD: Infective
endocarditis. Lancet. 387:882–893. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tănase A, Coliță A, Ianoşi G, Neagoe D,
Brănişteanu DE, Călina D, Docea AO, Tsatsakis A and Ianoşi SL: Rare
case of disseminated fusariosis in a young patient with graft vs.
host disease following an allogeneic transplant. Exp Ther Med.
12:2078–2082. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kamal AM, Mitrut P, Docea AO, Soşoi S,
Kamal KC, Mitrut R, Mărgăritescu D, Calina D, Banciu C, Tica OS, et
al: Double therapy with pegylated Interferon and Ribavirin for
chronic hepatitis C. A pharmacogenenetic guide for predicting
adverde events. Farmacia. 65:877–884. 2017.
|
|
16
|
Sader HS, Jones RN, Gales AC, Silva JB,
Pignatari AC and Group SP; SENTRY Participants Group (Latin
America), : SENTRY antimicrobial surveillance program report: Latin
American and Brazilian results for 1997 through 2001. Braz J Infect
Dis. 8:25–79. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sahoo KC, Tamhankar AJ, Sahoo S, Sahu PS,
Klintz SR and Lundborg CS: Geographical variation in
antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli isolates from stool, cow-dung
and drinking water. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 9:746–759.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Central Laboratory Standards Institute, .
Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing;
eighteenth informational supplement. CLSI document M100-18. Wayne,
PA: 2008
|
|
19
|
Bonferroni CE: Teoria statistica delle
classi e calcolo delle probabilità. Pubblicazioni del R Istituto
Superiore di Scienze Economiche e Commerciali di Firenze. 8:3–62.
1936.
|
|
20
|
Ungureanu A, Zlatian O, Mitroi G, Drocaş
A, Ţîrcă T, Călina D, Dehelean C, Docea AO, Izotov BN, Rakitskii
VN, et al: Staphylococcus aureus colonisation in patients from a
primary regional hospital. Mol Med Rep. 16:8771–8780. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Weisman LE: Coagulase-negative
staphylococcal disease: Emerging therapies for the neonatal and
pediatric patient. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 17:237–241. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
da Silva AR, Simões ML, Werneck LS and
Teixeira CH: Healthcare associated infections caused by
coagulase-negative Staphylococci in a neonatal intensive care unit.
Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 25:239–244. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Macharashvili N, Kourbatova E, Butsashvili
M, Tsertsvadze T, McNutt LA and Leonard MK: Etiology of neonatal
blood stream infections in Tbilisi, Republic of Georgia. Int J
Infect Dis. 13:499–505. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Frimodt-Møller N, Espersen F, Skinhøj P
and Rosdahl VT: Epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in
Denmark from 1957 to 1990. Clin Microbiol Infect. 3:297–305. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Uhlemann AC, Otto M, Lowy FD and DeLeo FR:
Evolution of community - and healthcare-associated
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Genet Evol.
21:563–574. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee JH and Kim YH: Predictive factors of
true bacteremia and the clinical utility of blood cultures as a
prognostic tool in patients with community-onset pneumonia.
Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e50582016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
McCulloh RJ, Koster MP, Yin DE, Milner TL,
Ralston SL, Hill VL, Alverson BK and Biondi EA: Evaluating the use
of blood cultures in the management of children hospitalized for
community-acquired pneumonia. PLoS One. 10:e01174622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|