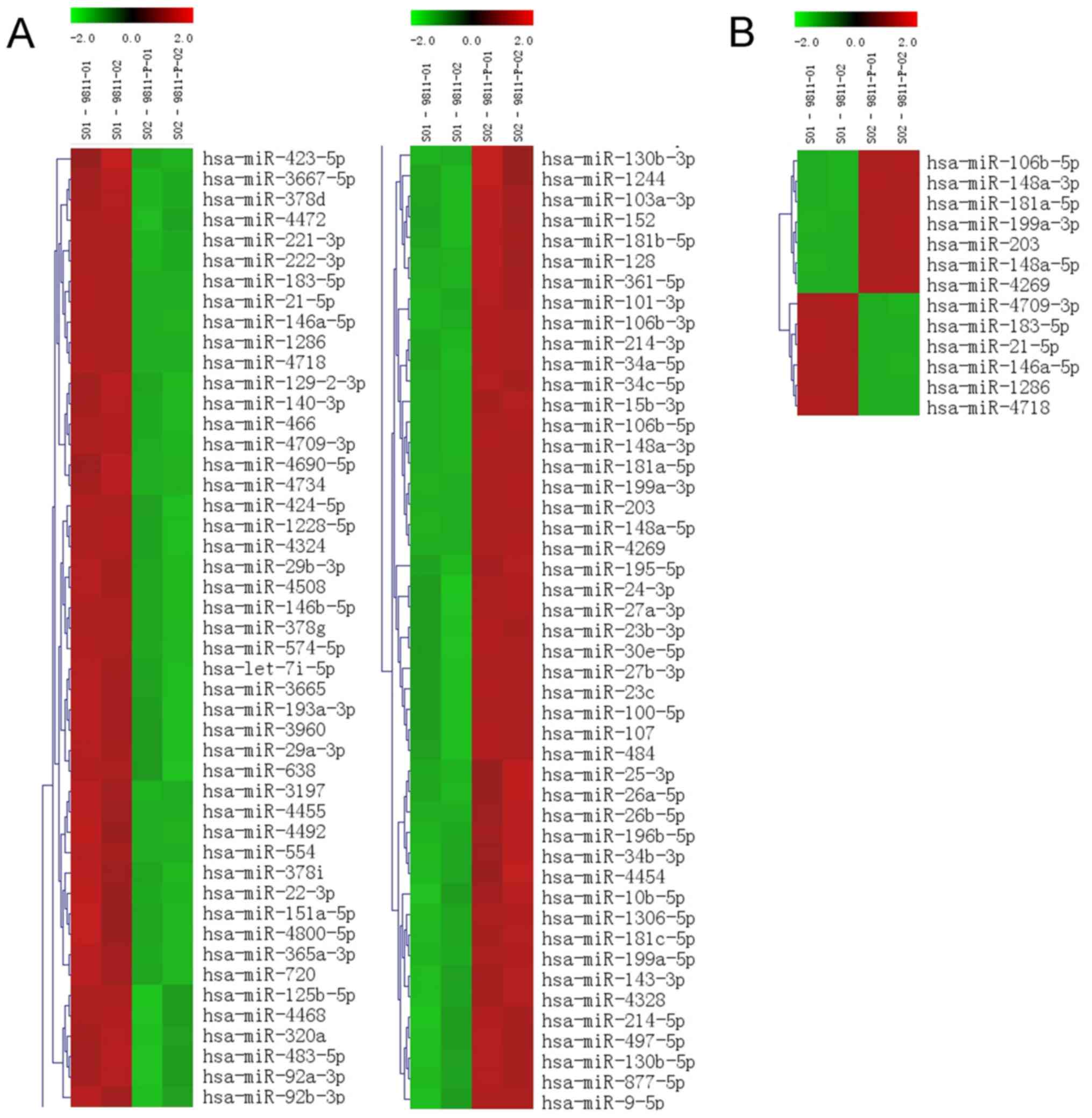
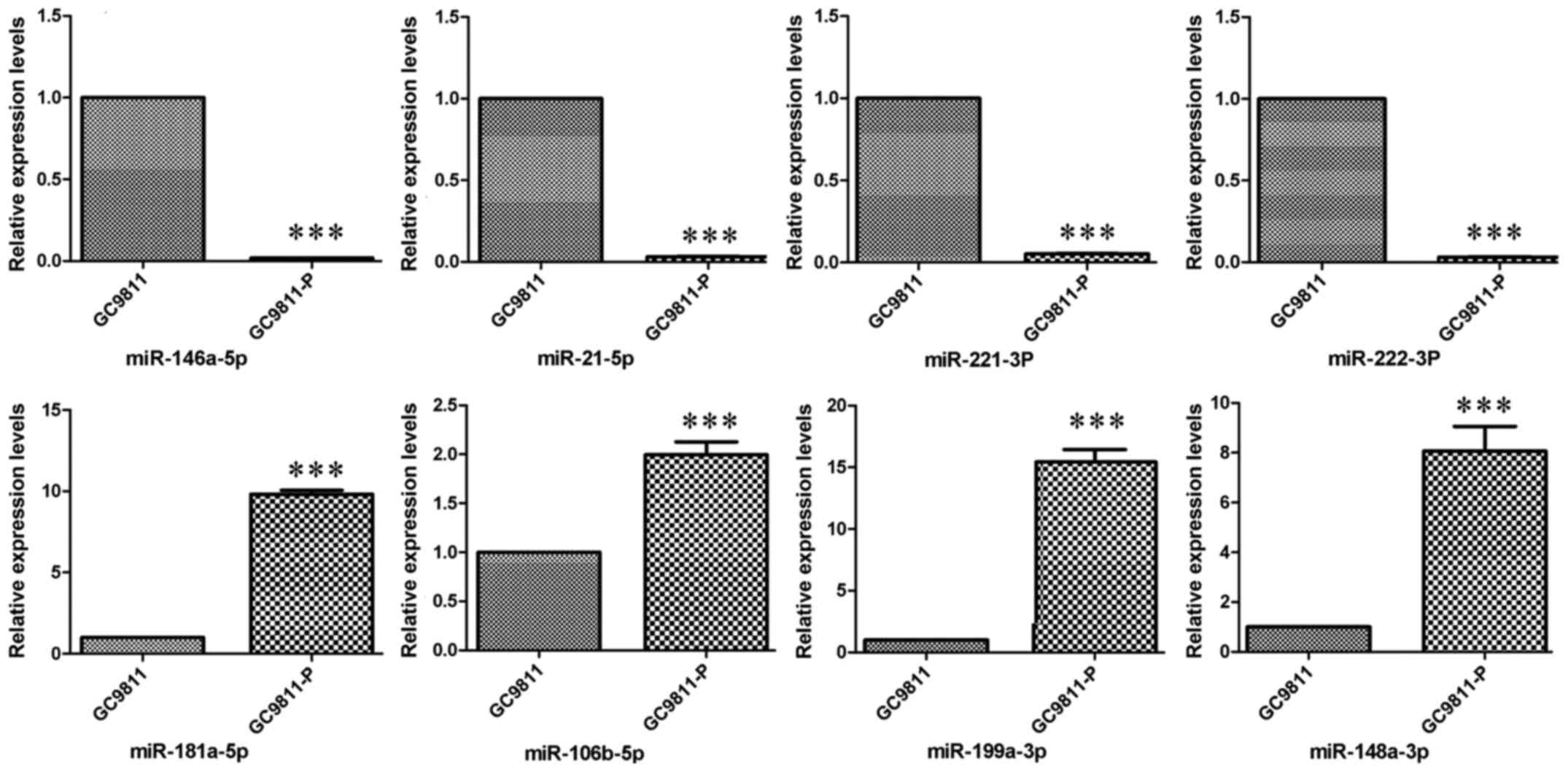
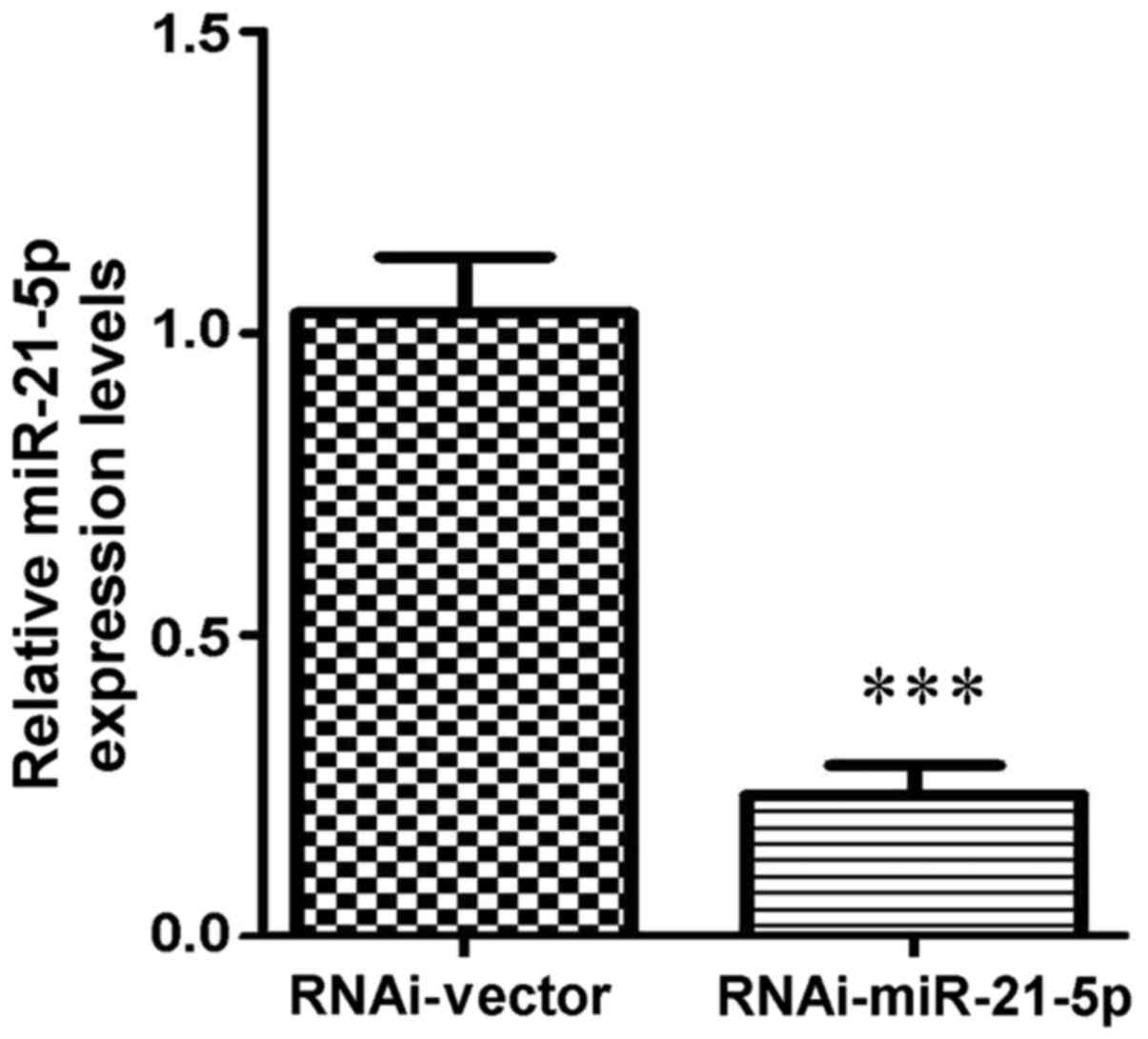
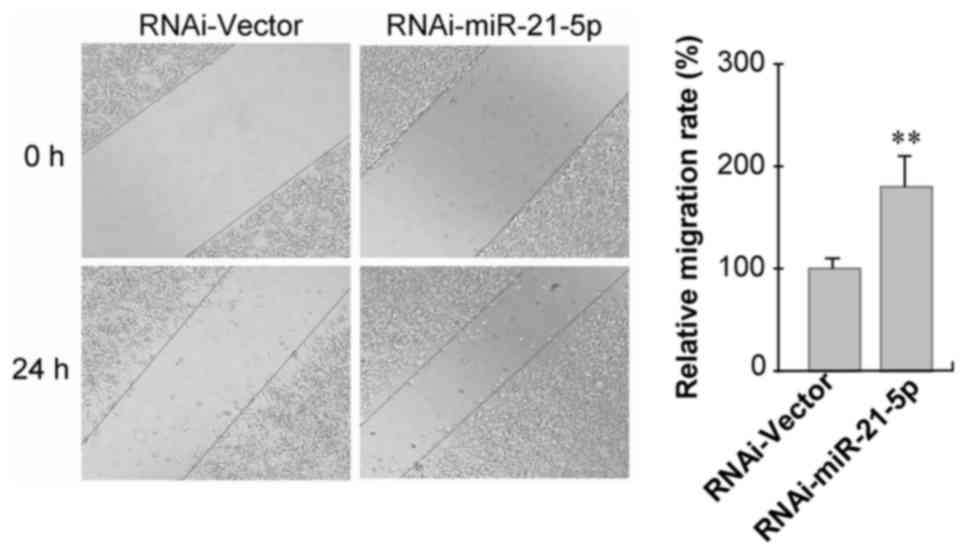
|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yonemura Y, Endou Y, Sasaki T, Hirano M,
Mizumoto A, Matsuda T, Takao N, Ichinose M, Miura M and Li Y:
Surgical treatment for peritoneal carcinomatosis from gastric
cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 36:1131–1138. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bozzetti F, Yu W, Baratti D, Kusamura S
and Deraco M: Locoregional treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis
from gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 98:273–276. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wightman B, Ha I and Ruvkun G:
Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by
lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell.
75:855–862. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Takei Y, Takigahira M, Mihara K, Tarumi Y
and Yanagihara K: The metastasis-associated microRNA miR-516a-3p is
a novel therapeutic target for inhibiting peritoneal dissemination
of human scirrhous gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 71:1442–1453. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nishida N, Mimori K, Fabbri M, Yokobori T,
Sudo T, Tanaka F, Shibata K, Ishii H, Doki Y and Mori M:
MicroRNA-125a-5p is an independent prognostic factor in gastric
cancer and inhibits the proliferation of human gastric cancer cells
in combination with trastuzumab. Clin Cancer Res. 17:2725–2733.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liang S, He L, Zhao X, Miao Y, Gu Y, Guo
C, Xue Z, Dou W, Hu F, Wu K, et al: MicroRNA let-7f inhibits tumor
invasion and metastasis by targeting MYH9 in human gastric cancer.
PLoS One. 6:e184092011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bai F, Guo X, Yang L, Wang J, Shi Y, Zhang
F, Zhai H, Lu Y, Xie H, Wu K and Fan D: Establishment and
characterization of a high metastatic potential in the peritoneum
for human gastric cancer by orthotopic tumor cell implantation. Dig
Dis Sci. 52:1571–1578. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
You Y, Liu J, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Ran Y, Guo
X, Liu H and Wang H: The enhancement of radiosensitivity in human
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells by zoledronic acid and its
potential mechanism. Cytotechnology. 66:17–25. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
You Y, Yang W, Qin X, Wang F, Li H, Lin C,
Li W, Gu C, Zhang Y and Ran Y: ECRG4 acts as a tumor suppressor and
as a determinant of chemotherapy resistance in human nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Cell Oncol(Dordr). 38:205–214. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tseng CW, Lin CC, Chen CN, Huang HC and
Juan HF: Integrative network analysis reveals active microRNAs and
their functions in gastric cancer. BMC Syst Biol. 5:992011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu K, LI G, Fan C, Diao Y, Wu B and LI J:
Increased expression of microRNA-221 in gastric cancer and its
clinical significance. J Int Med Res. 40:467–474. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kogo R, Mimori K, Tanaka F, Komune S and
Mori M: Clinical significance of miR-146a in gastric cancer cases.
Clin Cancer Res. 17:4277–4284. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Y, Vandenboom TG II, Wang Z, Kong D,
Ali S, Philip PA and Sarkar FH: miR-146a suppresses invasion of
pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 70:1486–1495. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bhaumik D, Scott GK, Schokrpur S, Patil
CK, Campisi J and Benz CC: Expression of microRNA-146 suppresses
NF-kappaB activity with reduction of metastatic potential in breast
cancer cells. Oncogene. 27:5643–5647. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hurst DR, Edmonds MD, Scott GK, Benz CC,
Vaidya KS and Welch DR: Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1
up-regulates miR-146, which suppresses breast cancer metastasis.
Cancer Res. 69:1279–1283. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lin SL, Chiang A, Chang D and Ying SY:
Loss of mir-146a function in hormone-refractory prostate cancer.
RNA. 14:417–424. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Magrelli A, Azzalin G, Salvatore M,
Viganotti M, Tosto F, Colombo T, Devito R, Di Masi A, Antoccia A,
Lorenzetti S, et al: Altered microRNA expression patterns in
hepato-blastoma patients. Transl Oncol. 2:157–163. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Song G, Zeng H, LI J, Xiao L, He Y, Tang Y
and Li Y: miR-199a regulates the tumor suppressor mitogen-activated
protein kinase 11 in gastric cancer. Biol Pharm Bull. 33:1822–1827.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang H, Kong W, He L, Zhao JJ, O'Donnell
JD, Wang J, Wenham RM, Coppola D, Kruk PA, Nicosia SV and Cheng JQ:
MicroRNA expression profling in human ovarian cancer: miR-214
induces cell survival and cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN.
Cancer Res. 68:425–433. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ichimi T, Enokida H, Okuno Y, Kunimoto R,
Chiyomaru T, Kawamoto K, Kawahara K, Toki K, Kawakami K, Nishiyama
K, et al: Identifcation of novel microRNA targets based on microRNA
signatures in bladder cancer. Int J Cancer. 125:345–352. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Feng YH and Tsao CJ: Emerging role of
microRNA-21 in cancer. Biomed Rep. 5:395–402. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Motoyama K, Inoue H, Mimori K, Tanaka F,
Kojima K, Uetake H, Sugihara K and Mori M: Clinicopathological and
prognostic significance of PDCD4 and microRNA-21 in human gastric
cancer. Int J Oncol. 36:1089–1095. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ou H, Li Y and Kang M: Activation of
miR-21 by STAT3 induces proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting PTEN gene. PLoS One.
9:e1099292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal
K, Jacob ST and Patel T: MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the
PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer.
Gastroenterology. 133:647–658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wei X, Wang W, Wang L, Zhang Y, Zhang X,
Chen M, Wang F, Yu J, Ma Y and Sun G: MicroRNA-21 induces
5-fluorouracil resistance in human pancreatic cancer cells by
regulating PTEN and PDCD4. Cancer Med. 5:693–702. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Song Y, Zuo Y, Qian XL, Chen ZP, Wang SK,
Song L and Peng LP: Inhibition of microRNA-21-5p promotes the
radiation sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer through HMSH2.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 43:1258–1272. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cai L, Wang W, Li X, Dong T, Zhang Q, Zhu
B, Zhao H and Wu S: MicroRNA-21-5p induces the metastatic phenotype
of human cervical carcinoma cells in vitro by targeting the von
Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor. Oncol Lett. 15:5213–5219.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|