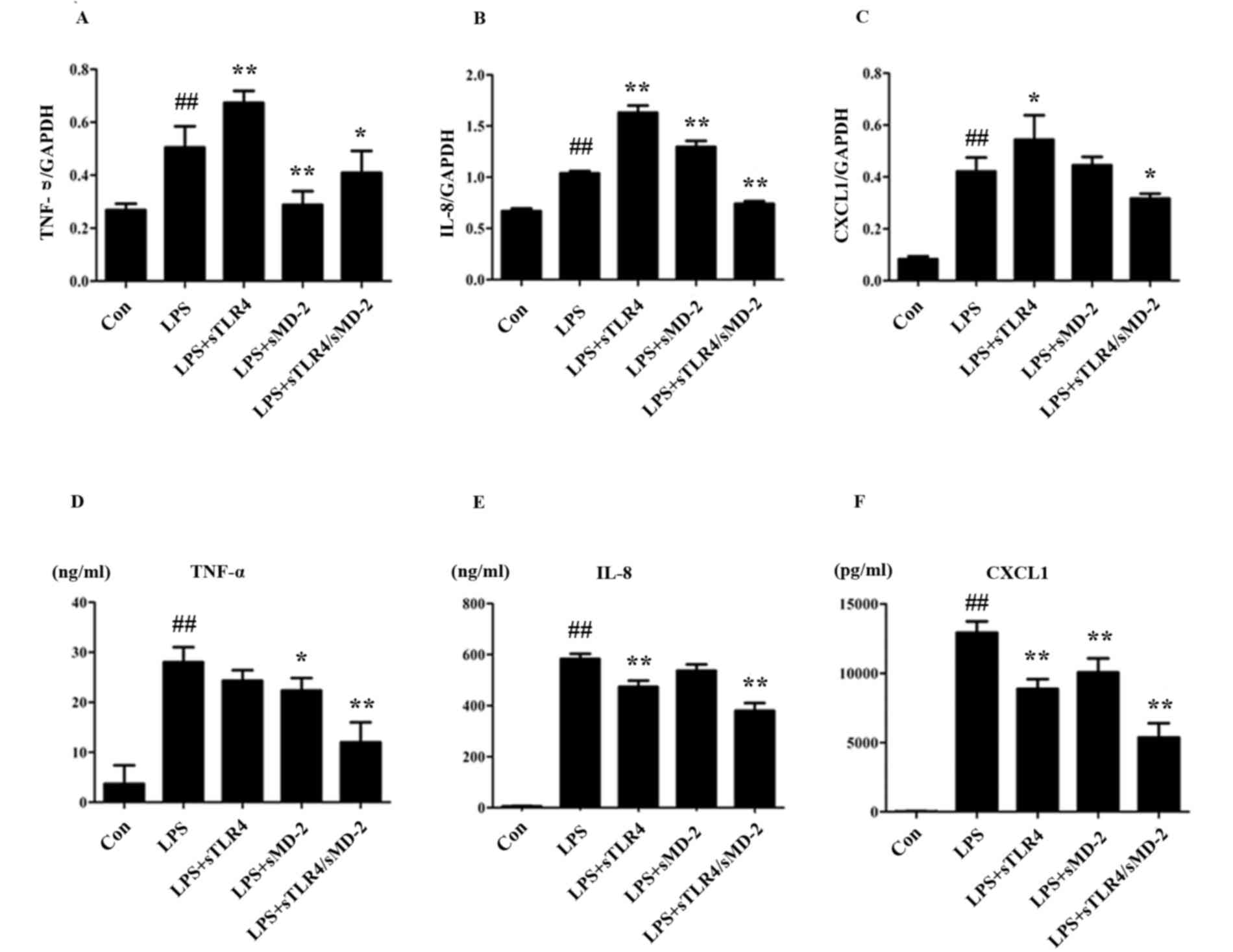
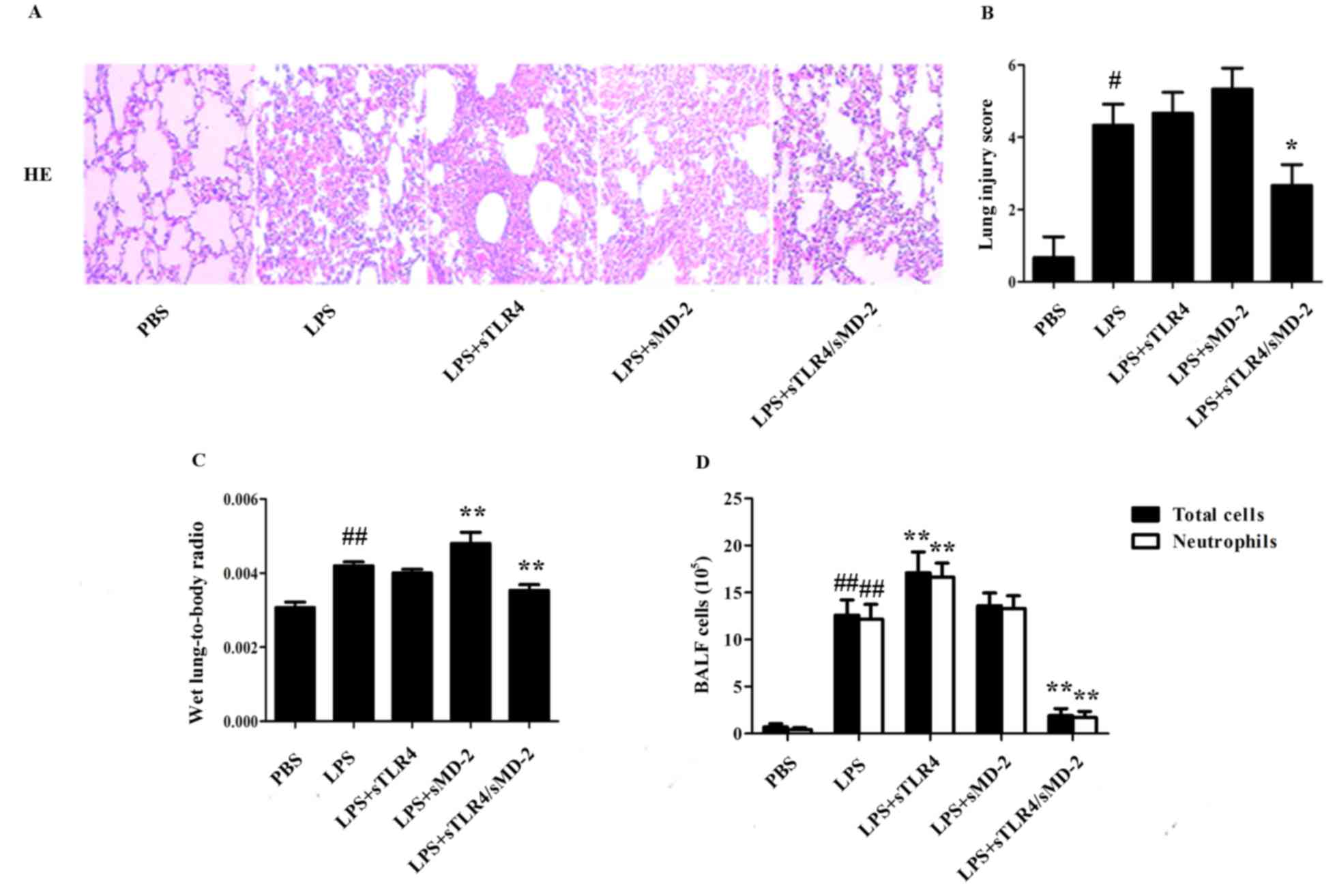
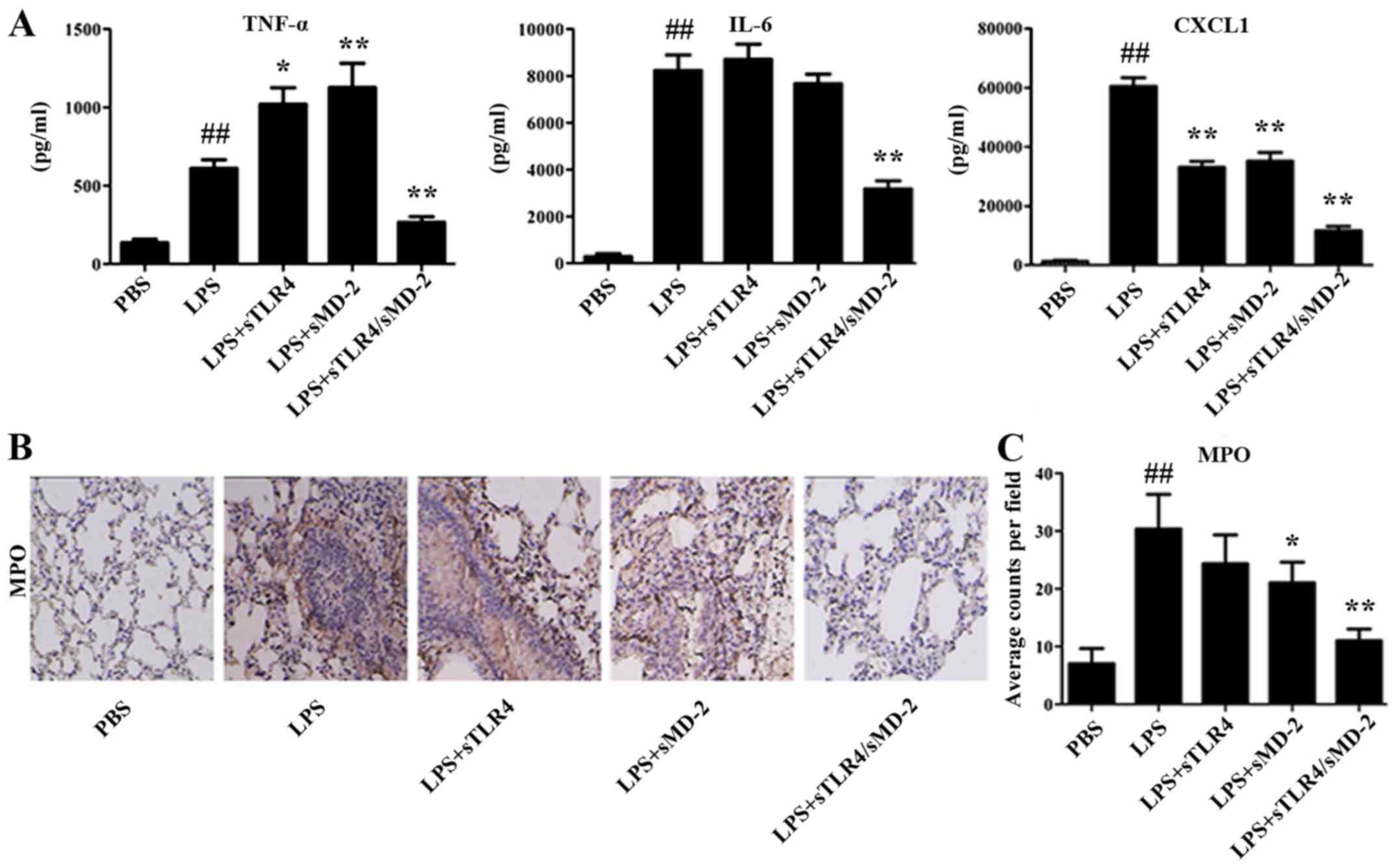
|
1
|
Ulich TR, Fann MJ, Patterson PH, Williams
JH, Samal B, Del Castillo J, Yin S, Guo K and Remick DG:
Intratracheal injection of LPS and cytokines. V. LPS induces
expression of LIF and LIF inhibits acute inflammation. Am J
Physiol. 267:L442–L446. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Beutler B and Rietschel ET: Innate immune
sensing and its roots: The story of endotoxin. Nat Rev Immunol.
3:169–176. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Means TK, Golenbock DT and Fenton MJ: The
biology of Toll-like receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
11:219–232. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ulevitch RJ and Tobias PS: Recognition of
gram-negative bacteria and endotoxin by the innate immune system.
Curr Opin Immunol. 11:19–22. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Beutler B and Poltorak A: Sepsis and
evolution of the innate immune response. Crit Care Med. 29 7
Suppl:S2–S7. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Medzhitov R and Janeway CA Jr: An ancient
system of host defense. Curr Opin Immunol. 10:12–15. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Park BS, Song DH, Kim HM, Choi BS, Lee H
and Lee JO: The structural basis of lipopolysaccharide recognition
by the TLR4-MD-2 complex. Nature. 458:1191–1195. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hoshino K, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Sanjo H,
Ogawa T, Takeda Y, Takeda K and Akira S: Cutting edge: Toll-like
receptor 4 (TLR4)-deficient mice are hyporesponsive to
lipopolysaccharide: Evidence for TLR4 as the Lps gene product. J
Immunol. 162:3749–3752. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Marshall JC: Endotoxin in the pathogenesis
of sepsis. Contrib Nephrol. 167:1–13. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Opal SM: Endotoxins and other sepsis
triggers. Contrib Nephrol. 167:14–24. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Marshall JC, Foster D, Vincent JL, Cook
DJ, Cohen J, Dellinger RP, Opal S, Abraham E, Brett SJ, Smith T, et
al: Diagnostic and prognostic implications of endotoxemia in
critical illness: Results of the MEDIC study. J Infect Dis.
190:527–534. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Takeda K and Akira S: Toll-like receptors
in innate immunity. Int Immunol. 17:1–14. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Iwami KI, Matsuguchi T, Masuda A, Kikuchi
T, Musikacharoen T and Yoshikai Y: Cutting edge: Naturally
occurring soluble form of mouse Toll-like receptor 4 inhibits
lipopolysaccharide signaling. J Immunol. 165:6682–6686. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ohta S, Bahrun U, Tanaka M and Kimoto M:
Identification of a novel isoform of MD-2 that downregulates
lipopolysaccharide signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
323:1103–1108. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hardy MP and O'Neill LA: The murine IRAK2
gene encodes four alternatively spliced isoforms, two of which are
inhibitory. J Biol Chem. 279:27699–27708. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Leeman JR and Gilmore TD: Alternative
splicing in the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Gene. 423:97–107.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lynch KW: Consequences of regulated
pre-mRNA splicing in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 4:931–940.
2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gray P, Michelsen KS, Sirois CM, Lowe E,
Shimada K, Crother TR, Chen S, Brikos C, Bulut Y, Latz E, et al:
Identification of a novel human MD-2 splice variant that negatively
regulates Lipopolysaccharide-induced TLR4 signaling. J Immunol.
184:6359–6366. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kondo Y, Ikeda K, Tokuda N, Nishitani C,
Ohto U, Akashi-Takamura S, Ito Y, Uchikawa M, Kuroki Y, Taguchi R,
et al: TLR4-MD-2 complex is negatively regulated by an endogenous
ligand, globotetraosylceramide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:4714–4719. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mitsuzawa H, Nishitani C, Hyakushima N,
Shimizu T, Sano H, Matsushima N, Fukase K and Kuroki Y: Recombinant
soluble forms of extracellular TLR4 domain and MD-2 inhibit
lipopolysaccharide binding on cell surface and dampen
lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary inflammation in mice. J
Immunol. 177:8133–8139. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zou Y, Qin F, Chen J, Meng J, Wei L, Wu C,
Zhang Q, Wei D, Chen X, Wu H, et al: sTLR4/MD-2 complex inhibits
colorectal cancer in vitro and in vivo by targeting LPS.
Oncotarget. 7:52032–52044. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Guo Z, Li Q, Han Y, Liang Y, Xu Z and Ren
T: Prevention of LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by
progranulin. Mediators Inflamm. 2012:5407942012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Harrison LM, van den Hoogen C, van Haaften
WC and Tesh VL: Chemokine expression in the monocytic cell line
THP-1 in response to purified shiga toxin 1 and/or
lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 73:403–412. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ware LB and Matthay MA: The acute
respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 342:1334–1349. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shimazu R, Akashi S, Ogata H, Nagai Y,
Fukudome K, Miyake K and Kimoto M: MD-2, a molecule that confers
lipopolysaccharide responsiveness on Toll-like receptor 4. J Exp
Med. 189:1777–1782. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nagai Y, Akashi S, Nagafuku M, Ogata M,
Iwakura Y, Akira S, Kitamura T, Kosugi A, Kimoto M and Miyake K:
Essential role of MD-2 in LPS responsiveness and TLR4 distribution.
Nat Immunol. 3:667–672. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Akashi S, Saitoh S, Wakabayashi Y, Kikuchi
T, Takamura N, Nagai Y, Kusumoto Y, Fukase K, Kusumoto S, Adachi Y,
et al: Lipopolysaccharide interaction with cell surface Toll-like
receptor 4-MD-2: Higher affinity than that with MD-2 or CD14. J Exp
Med. 198:1035–1042. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Akira S and Takeda K: Toll-like receptor
signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 4:499–511. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee JK, Sayers BC, Chun KS, Lao HC,
Shipley-Phillips JK, Bonner JC and Langenbach R: Multi-walled
carbon nanotubes induce COX-2 and iNOS expression via MAP
kinase-dependent and -independent mechanisms in mouse RAW264.7
macrophages. Part Fibre Toxicol. 9:142012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Butt Y, Kurdowska A and Allen TC: Acute
lung injury: A clinical and molecular review. Arch Pathol Lab Med.
140:345–350. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Reutershan J, Morris MA, Burcin TL, Smith
DF, Chang D, Saprito MS and Ley K: Critical role of endothelial
CXCR2 in LPS-induced neutrophil migration into the lung. J Clin
Invest. 116:695–702. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
De Filippo K, Dudeck A, Hasenberg M, Nye
E, van Rooijen N, Hartmann K, Gunzer M, Roers A and Hogg N: Mast
cell and macrophage chemokines CXCL1/CXCL2 control the early stage
of neutrophil recruitment during tissue inflammation. Blood.
121:4930–4937. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dooley JL, Abdel-Latif D, St Laurent CD,
Puttagunta L, Befus D and Lacy P: Regulation of inflammation by
Rac2 in immune complex-mediated acute lung injury. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 297:L1091–L1102. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|