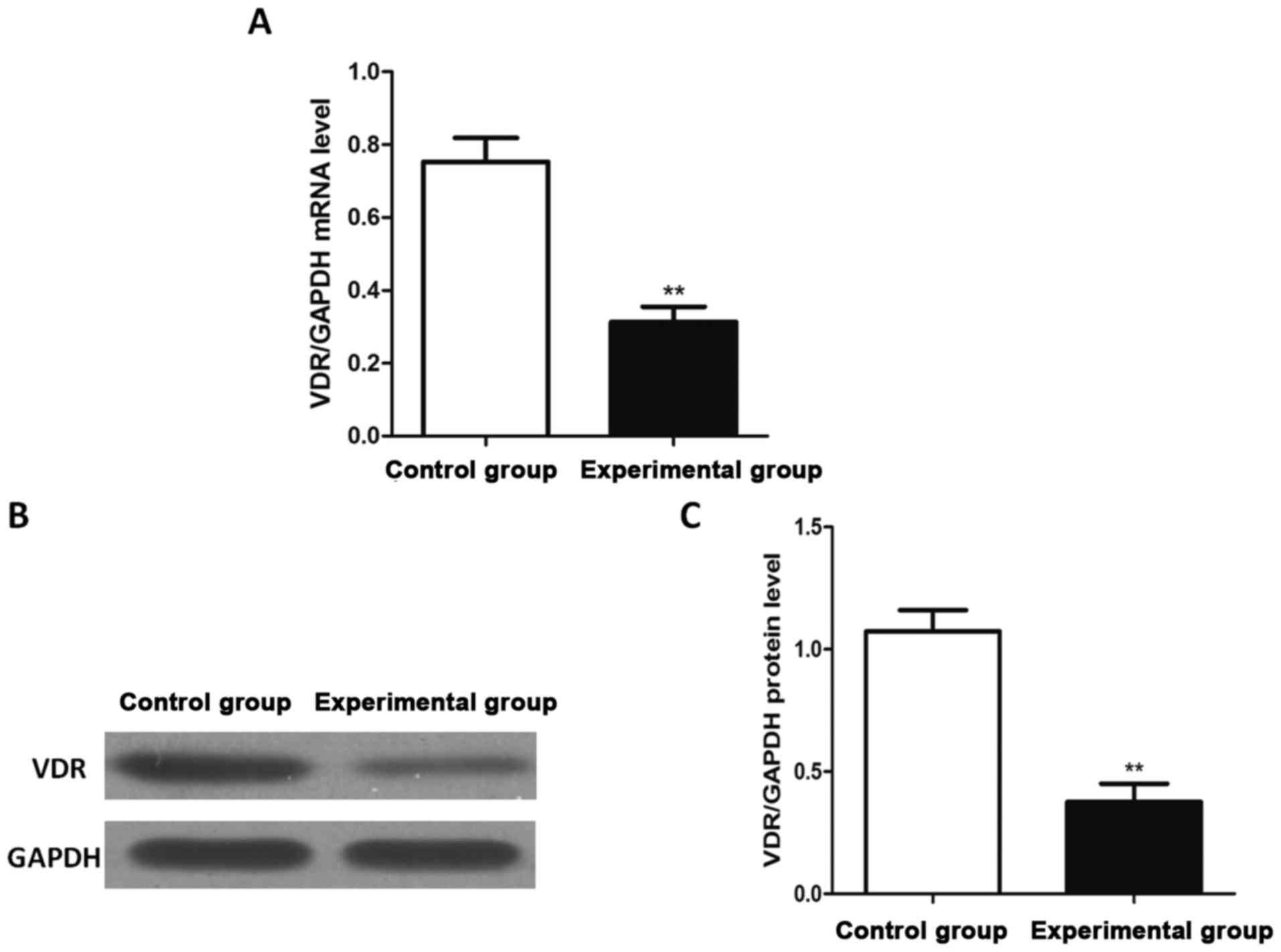
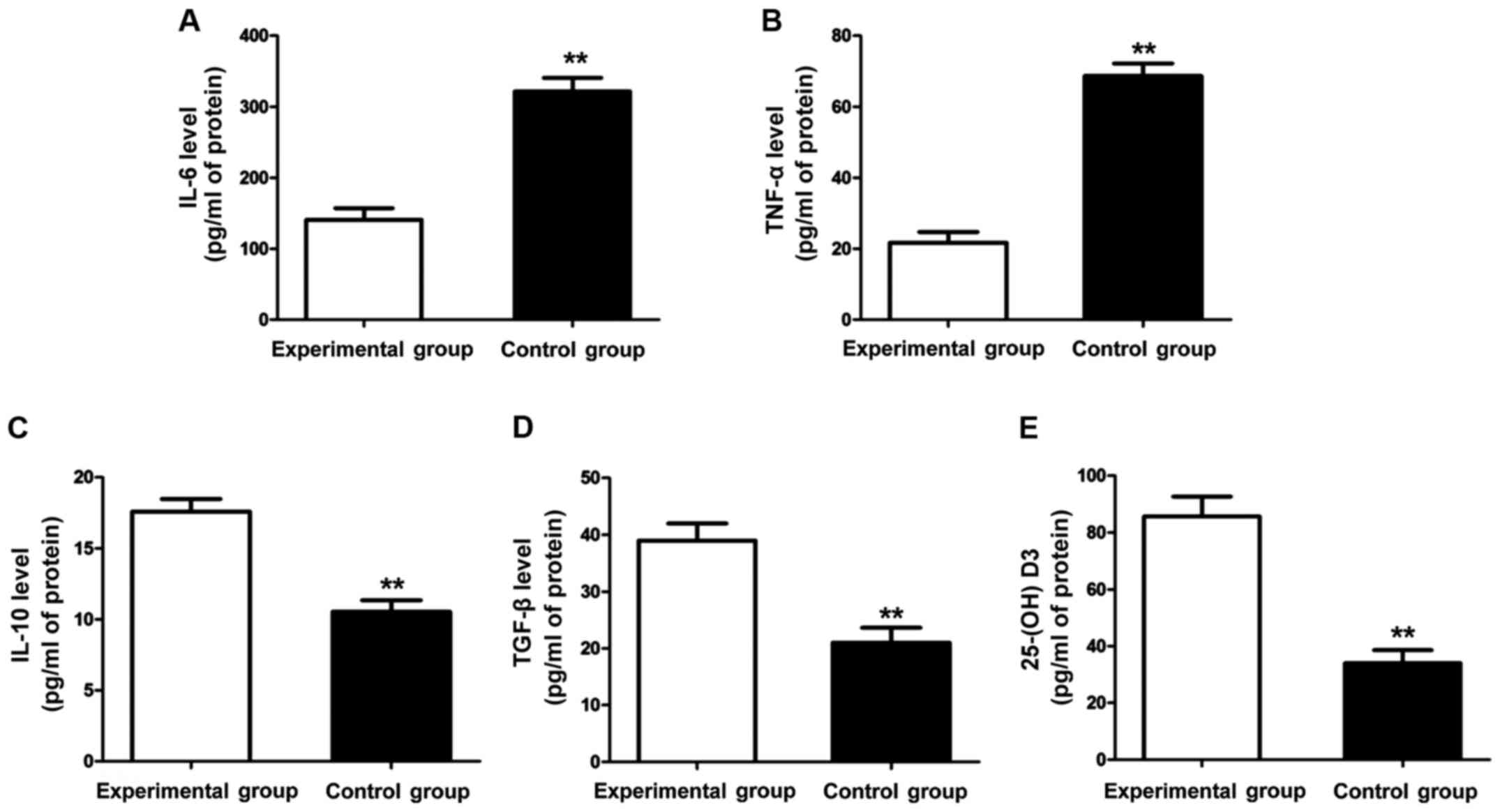
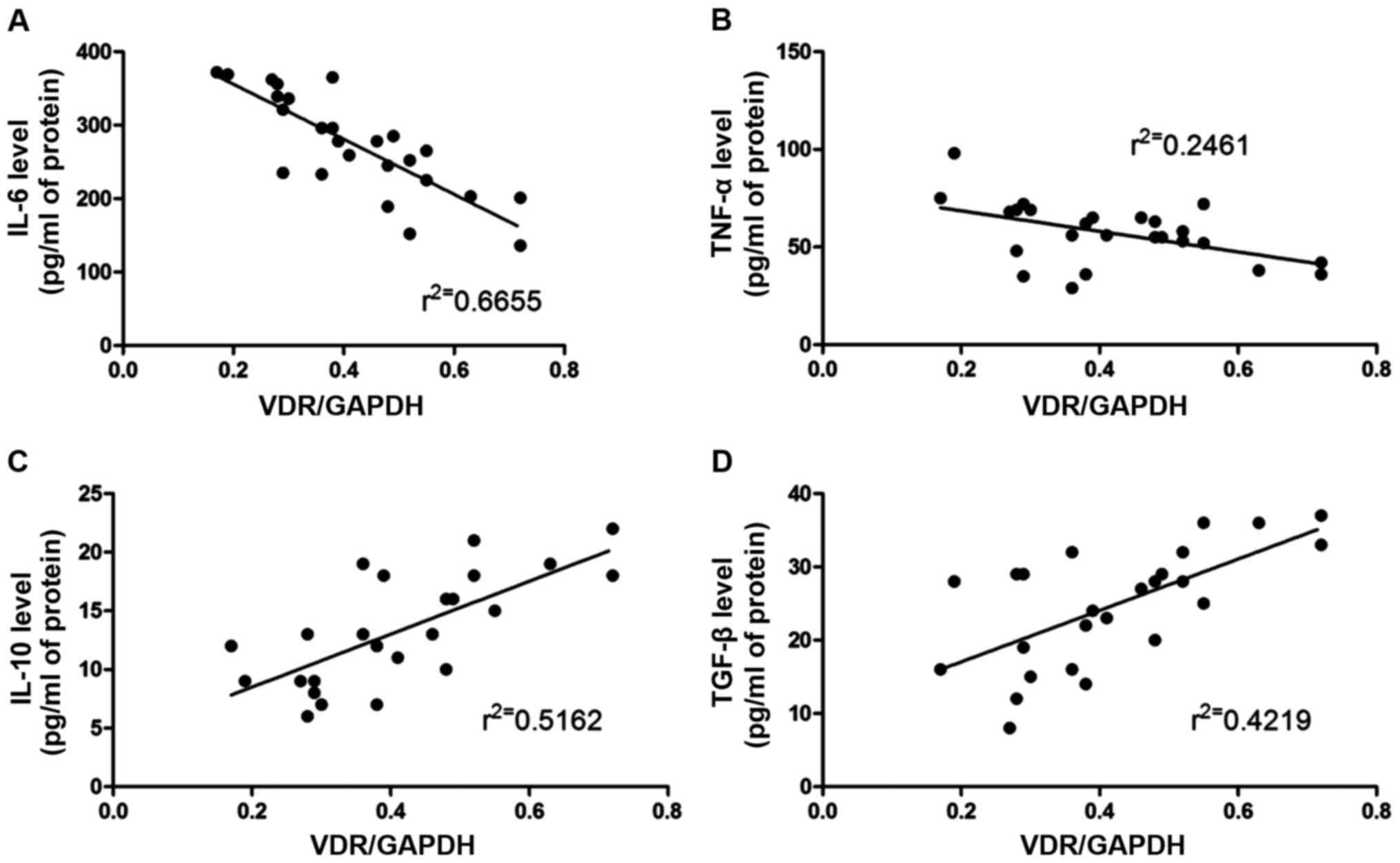
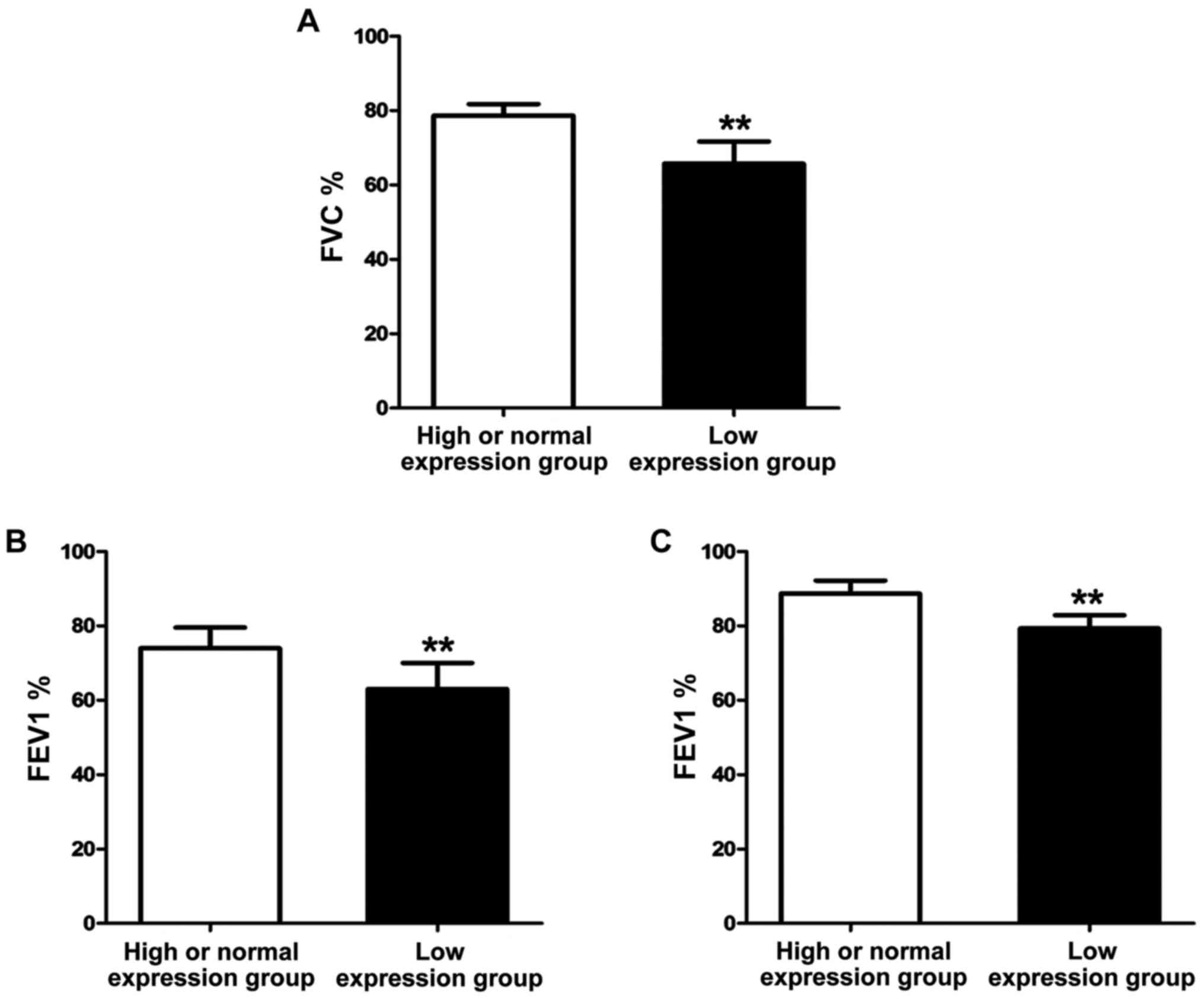
|
1
|
Roxbury CR and Lin SY: Efficacy and safety
of subcutaneous and sublingual immunotherapy for allergic
rhinoconjunctivitis and asthma. Otolaryngol Clin North Am.
50:1111–1119. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li Y, Yu Q, Zhao W, Zhang J, Liu W, Huang
M and Zeng X: Oligomeric proanthocyanidins attenuate airway
inflammation in asthma by inhibiting dendritic cells maturation.
Mol Immunol. 13:226–232. 2012.
|
|
3
|
Chen G, Chiang WL, Shu BC, Guo YL, Chiou
ST and Chiang TL: Associations of caesarean delivery and the
occurrence of neurodevelopmental disorders, asthma or obesity in
childhood based on Taiwan birth cohort study. BMJ Open. 3:622–635.
2015.
|
|
4
|
Shin E, Lee YC, Kim SR, Kim SH and Park J:
Drug signature-based finding of additional clinical use of
LC28-0126 for neutrophilic bronchial asthma. Sci Rep. 5:177842015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kaur S, Gupta VK, Shah A, Thiel S, Sarma
PU and Madan T: Elevated levels of mannan-binding lectin
[corrected] (MBL) and eosinophilia in patients of bronchial asthma
with allergic rhinitis and allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
associate with a novel intronic polymorphism in MBL. Clin Exp
Immunol. 143:414–419. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen L, Zhong N and Lai K: Re-challenge
with ovalbumin failed to induce bronchial asthma in mice with
eosinophilic bronchitis. PLoS One. 8:e751952013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Checkley W, Robinson CL, Baumann LM,
Hansel NN, Romero KM, Pollard SL, Wise RA, Gilman RH, Mougey E and
Lima JJ; PURA Study Investigators, . 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels
are associated with childhood asthma in a population-based study in
Peru. Clin Exp Allergy. 45:226–232. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ali NS and Nanji K: A Review on the role
of vitamin D in asthma. Cureus. 9:e12882017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Staticescu S, Chereches-Panta P, Ichim G,
Valeanu M and Nanulescu MV: The value of induced sputum in the
diagnosis and management of children with bronchial asthma. Clujul
Med. 87:171–176. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Berenguer AG, Fernandes AT, Oliveira S,
Rodrigues M, Ornelas P, Romeira D, Serrão T, Rosa A and Câmara R:
Genetic polymorphisms and asthma: Findings from a case-control
study in the Madeira island population. Biol Res. 47:402014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pásztor D, Kolozsvári BL, Csutak A, Berta
A, Hassan Z, Kettesy BA, Gogolák P and Fodor M: Scheimpflug imaging
parameters associated with tear mediators and bronchial asthma in
keratoconus. J Ophthalmol. 2016:93926402016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lim SY, Jo YJ and Chun EM: The correlation
between the bronchial hyperresponsiveness to methacholine and
asthma like symptoms by GINA questionnaires for the diagnosis of
asthma. BMC Pulm Med. 14:1612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Luo J, Liu D and Liu CT: Can vitamin D
supplementation in addition to asthma controllers improve clinical
outcomes in patients with asthma? A Meta-Analysis. Medicine
(Baltimore). 94:e21852015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Somashekar AR, Prithvi AB and Gowda MN:
Vitamin D levels in children with bronchial asthma. J Clin Diagn
Res. 8:4–7. 2014.
|
|
15
|
Augusto A: Vitamin D deficiency as a risk
factor for childhood allergic disease and asthma. Curr Opin Allergy
Clin Immunol. 12:86–91. 2012.
|
|
16
|
Jat KR and Khairwa A: Vitamin D and asthma
in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational
studies. Lung India. 34:1787–1799. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jensen ME, Mailhot G, Alos N, Rousseau E,
White JH, Khamessan A and Ducharme FM: Vitamin D intervention in
preschoolers with viral-induced asthma (DIVA): A pilot randomised
controlled trial. Trials. 17:3532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brehm JM, Schuemann B, Fuhlbrigge AL,
Hollis BW, Strunk RC, Zeiger RS, Weiss ST and Litonjua AA;
Childhood Asthma Management Program Research Group, . Serum vitamin
D levels and severe asthma exacerbations in the Childhood Asthma
Management Program study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 126:52–8.e5.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Boonpiyathad T, Chantveerawong T,
Pradubpongsa P and Sangasapaviliya A: Serum vitamin D levels and
vitamin D supplement in adult patients with asthma exacerbation. J
Allergy (Cairo). 2016:40706352016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cantorna MT, Zhao J and Yang L: Vitamin D,
invariant natural killer T-cells and experimental autoimmune
disease. Proc Nutr Soc. 71:62–66. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jain SK, Micinski D, Huning L, Kahlon G,
Bass PF and Levine SN: Vitamin D and L-cysteine levels correlate
positively with GSH and negatively with insulin resistance levels
in the blood of type 2 diabetic patients. Eur J Clin Nutr.
68:1148–1153. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|