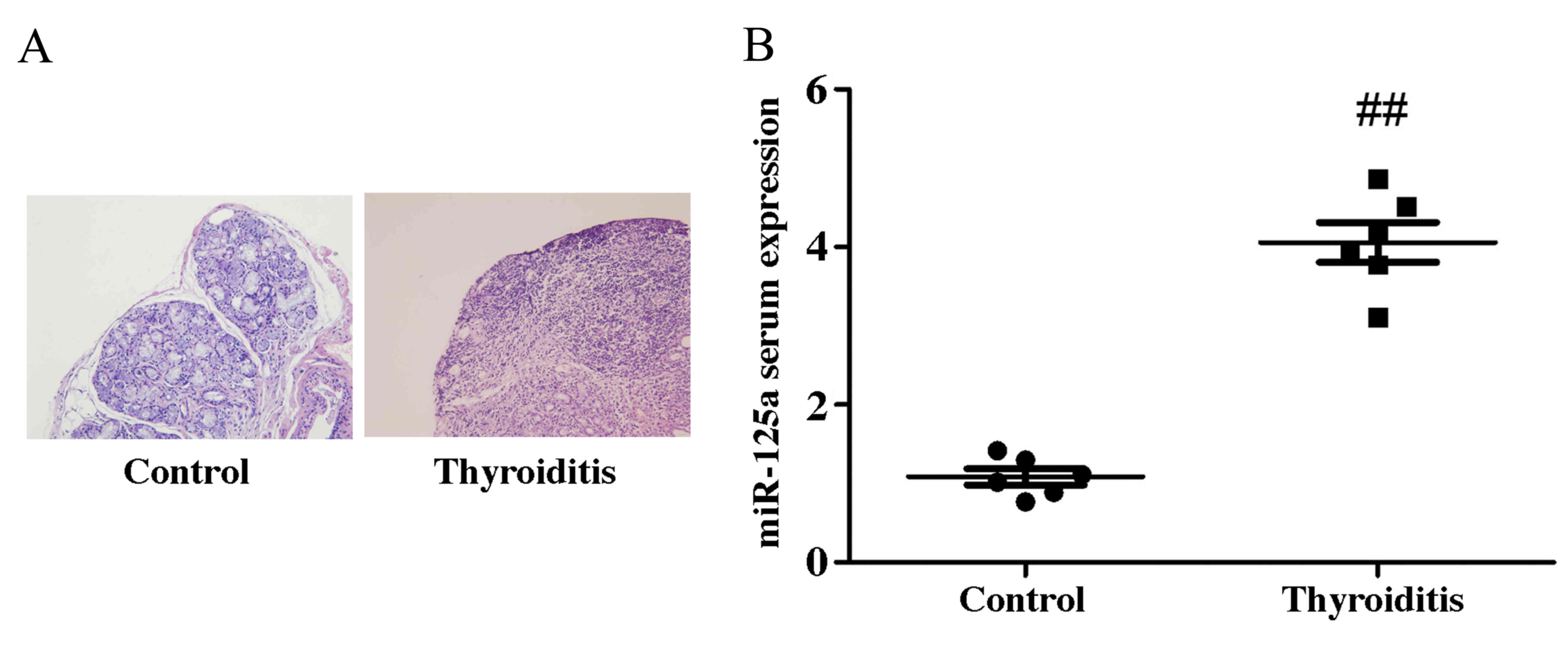
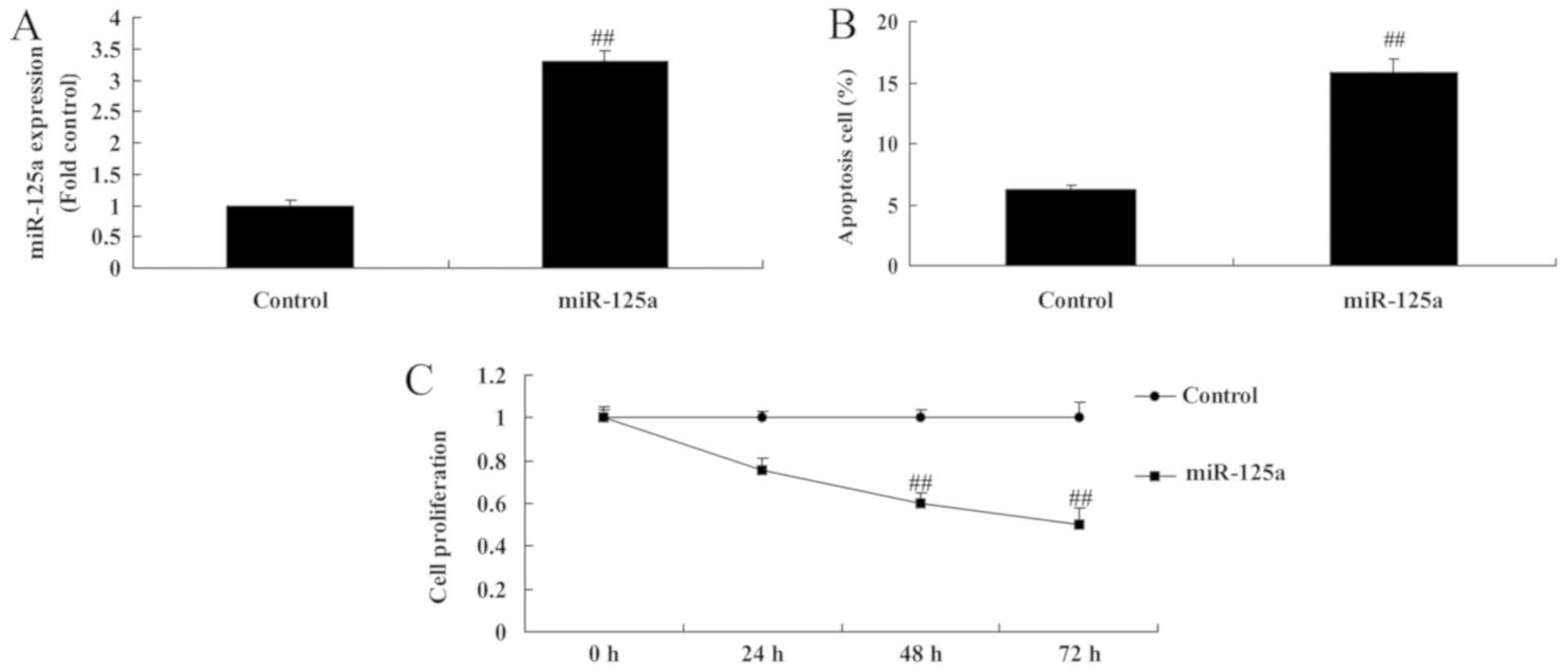
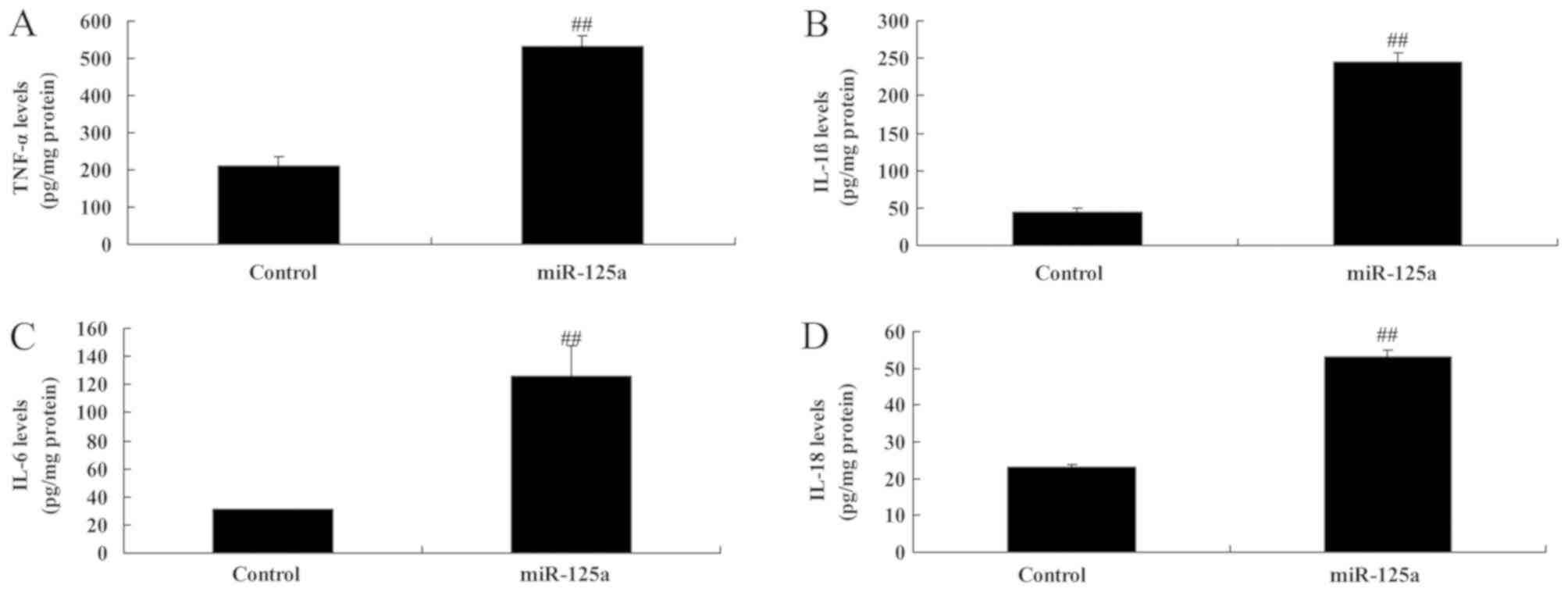
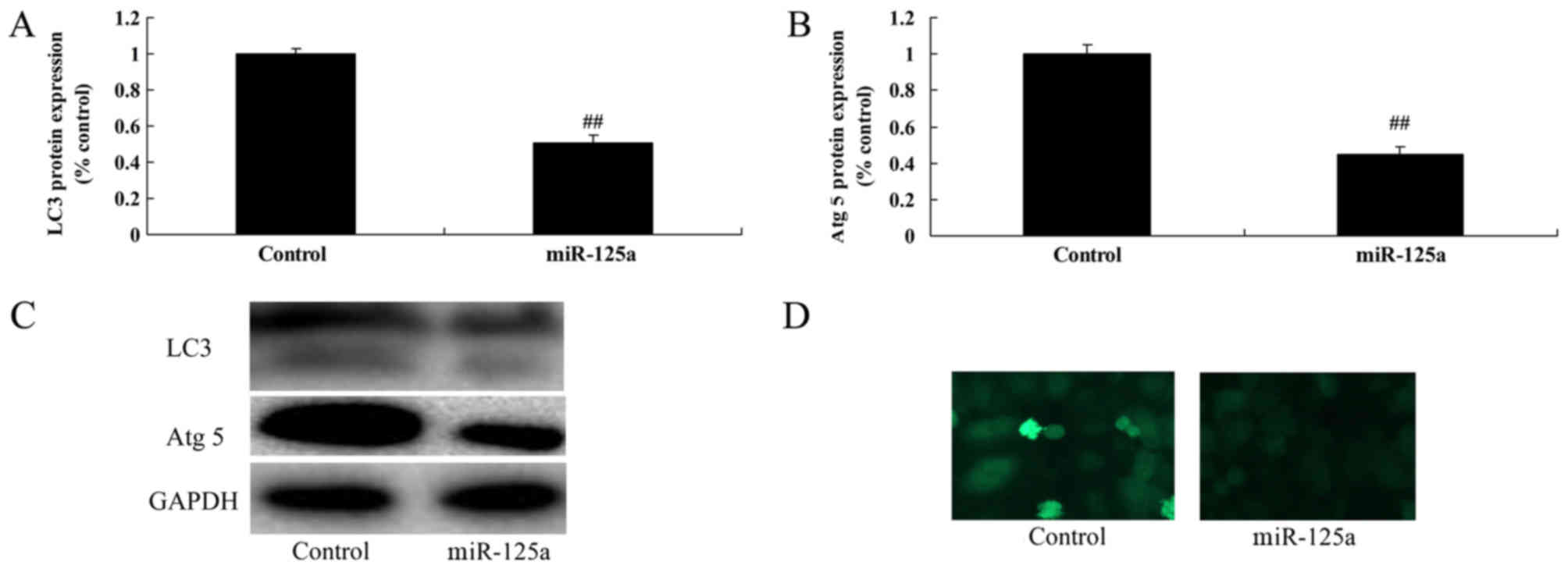
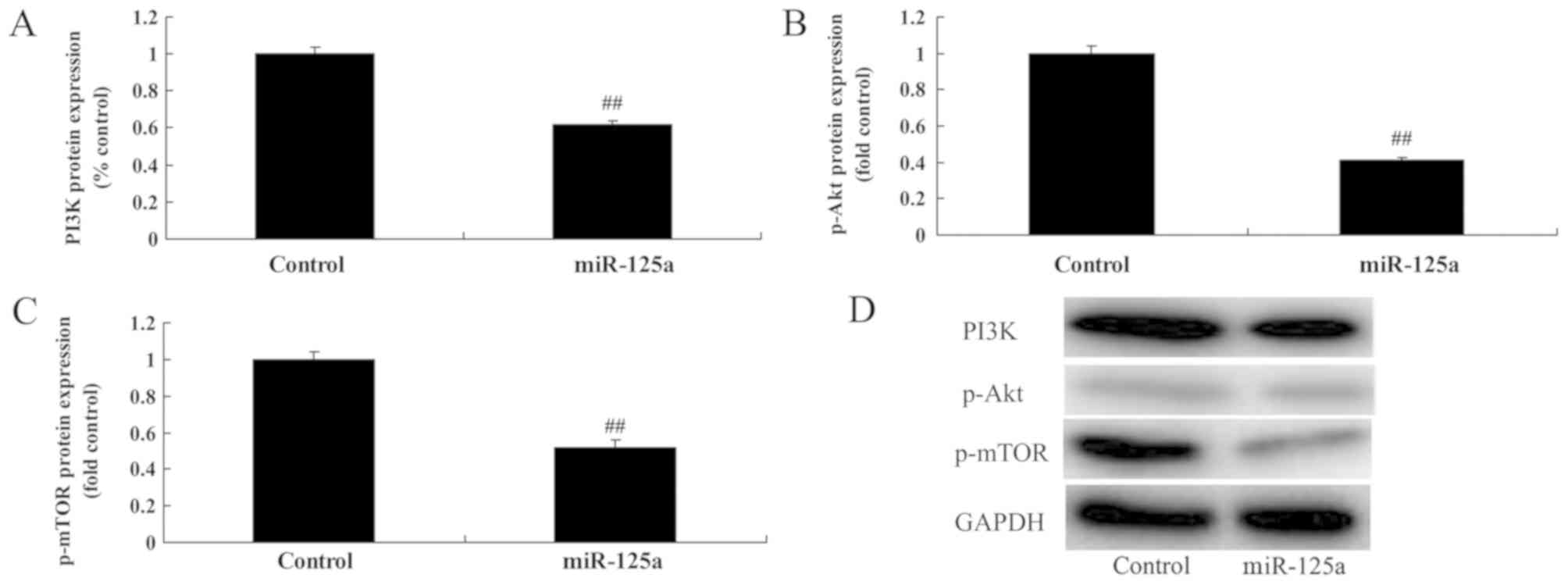
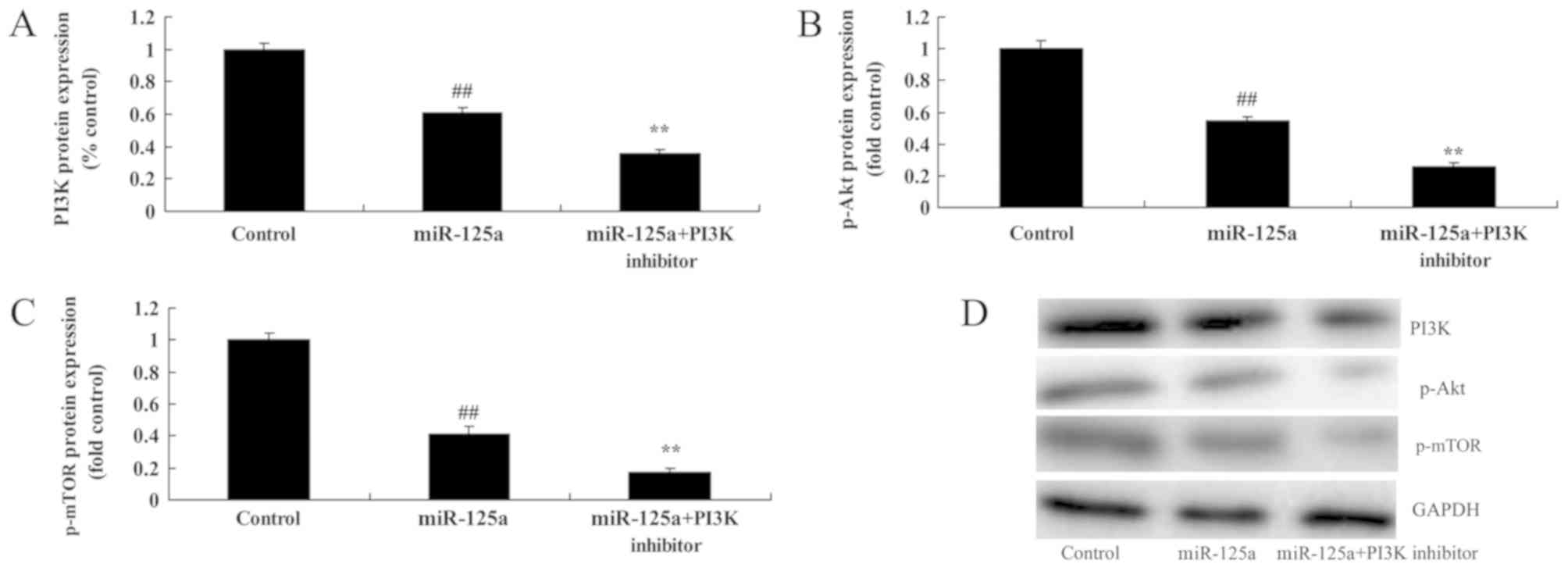
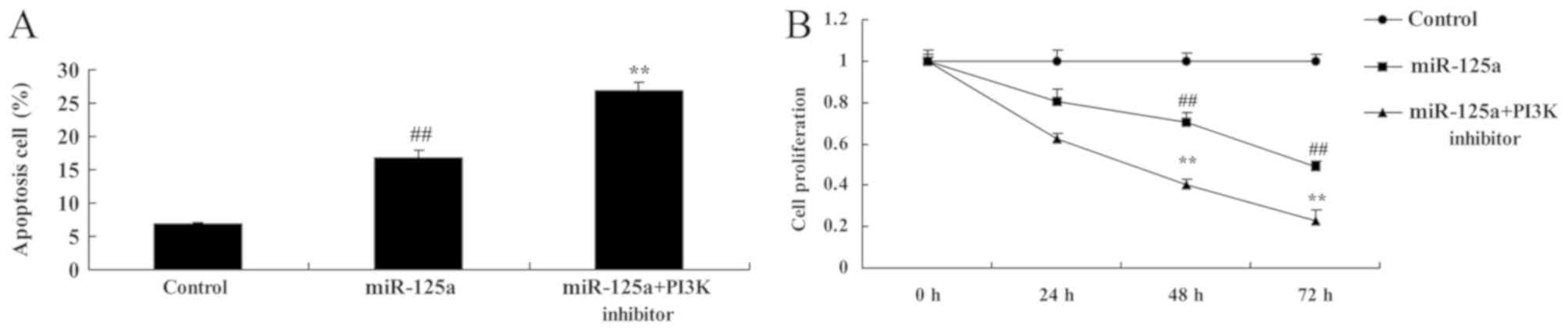
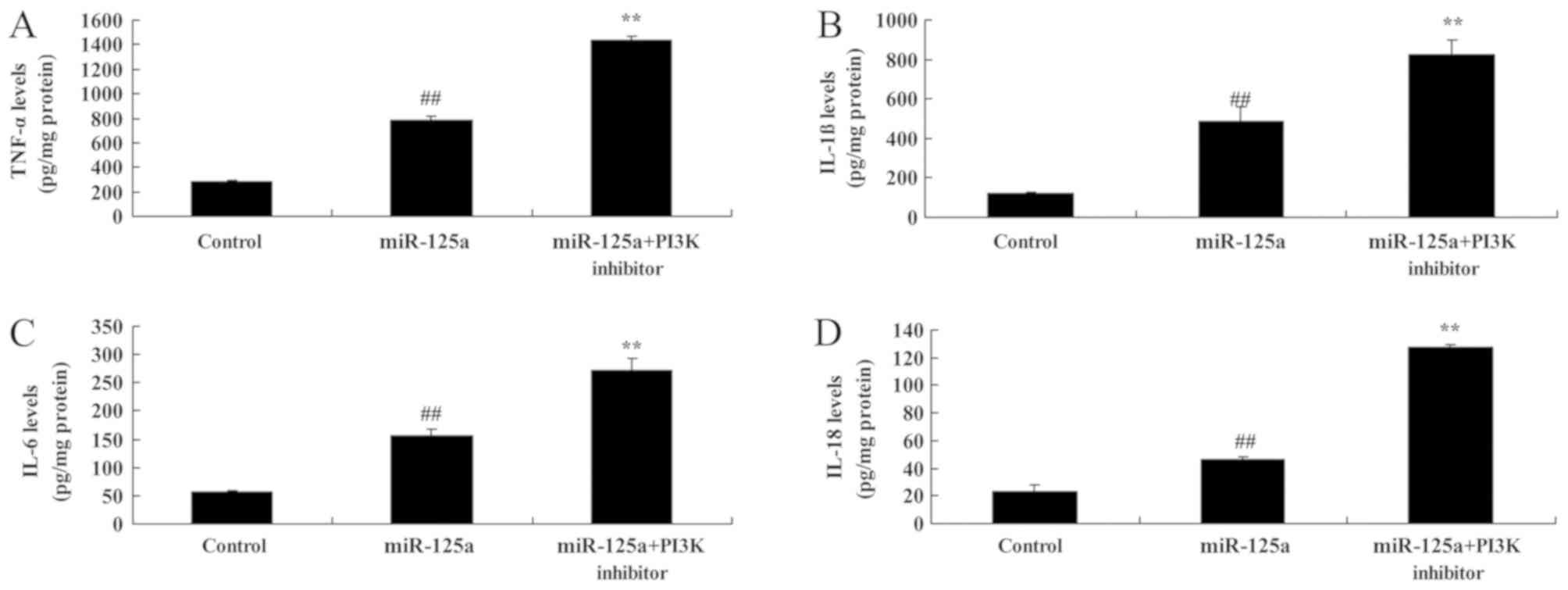
|
1
|
Byun JI, Lee ST, Jung KH, Sunwoo JS, Moon
J, Lim JA, Lee DY, Shin YW, Kim TJ, Lee KJ, et al: Effect of
immunotherapy on seizure outcome in patients with autoimmune
encephalitis: A prospective observational registry study. PLoS One.
11:e01464552016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Winther KH, Watt T, Bjørner JB, Cramon P,
Feldt-Rasmussen U, Gluud C, Gram J, Groenvold M, Hegedüs L, Knudsen
N, et al: The chronic autoimmune thyroiditis quality of life
selenium trial (CATALYST): Study protocol for a randomized
controlled trial. Trials. 15:1152014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nazarpour S, Ramezani Tehrani F, Simbar M,
Tohidi M, Alavi Majd H and Azizi F: Effects of levothyroxine
treatment on pregnancy outcomes in pregnant women with autoimmune
thyroid disease. Eur J Endocrinol. 176:253–265. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim HM, Kim ES and Koo JS: Expression of
autophagy-related proteins in different types of thyroid cancer.
Int J Mol Sci. 18:E5402017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Singh BK, Sinha RA, Ohba K and Yen PM:
Role of thyroid hormone in hepatic gene regulation, chromatin
remodeling, and autophagy. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 458:160–168. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lin CI, Whang EE, Donner DB, Du J, Lorch
J, He F, Jiang X, Price BD, Moore FD Jr and Ruan DT: Autophagy
induction with RAD001 enhances chemosensitivity and
radiosensitivity through Met inhibition in papillary thyroid
cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 8:1217–1226. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim SH, Kang JG, Kim CS, Ihm SH, Choi MG,
Yoo HJ and Lee SJ: Synergistic cytotoxicity of BIIB021 with
triptolide through suppression of PI3K/Akt/mTOR and NF-κB signal
pathways in thyroid carcinoma cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 83:22–32.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pringle DR, Vasko VV, Yu L, Manchanda PK,
Lee AA, Zhang X, Kirschner JM, Parlow AF, Saji M, Jarjoura D, et
al: Follicular thyroid cancers demonstrate dual activation of PKA
and mTOR as modeled by thyroid-specific deletion of Prkarla and
Pten in mice. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 99:E804–E812. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Souza EC, Ferreira AC and Carvalho DP: The
mTOR protein as a target in thyroid cancer. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 15:1099–1112. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Petrulea MS, Plantinga TS, Smit JW,
Georgescu CE and Netea-Maier RT: PI3K/Akt/mTOR: A promising
therapeutic target for non-medullary thyroid carcinoma. Cancer
Treat Rev. 41:707–713. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Prabahar A and Natarajan J: MicroRNA
mediated network motifs in autoimmune diseases and its crosstalk
between genes, functions and pathways. J Immunol Methods.
440:19–26. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Otsu H, Watanabe M, Inoue N, Masutani R
and Iwatani Y: Intraindividual variation of microRNA expression
levels in plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells and the
associations of these levels with the pathogenesis of autoimmune
thyroid diseases. Clin Chem Lab Med. 55:626–635. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li H and Ding G: Elevated serum
inflammatory cytokines in lupus nephritis patients, in association
with promoted hsa-miR-125a. Clin Lab. 62:631–638. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu H, Hu S, Xu S, Gao Y, Zeng F and Shui
H: miR-29b regulates Ang II-induced EMT of rat renal tubular
epithelial cells via targeting PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Int J
Mol Med. 42:453–460. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xia N, Chen G, Liu M, Ye X, Pan Y, Ge J,
Mao Y, Wang H, Wang J and Xie S: Anti-inflammatory effects of
luteolin on experimental autoimmune thyroiditis in mice. Exp Ther
Med. 12:4049–4054. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Buschur E, Sarma AV, Pietropaolo M, Dunn
RL, Braffett BH, Cleary PA, Cowie C, Larkin ME, Wessells H, Nathan
DM, et al: Self-reported autoimmune disease by sex in the diabetes
control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes
interventions and complications (DCCT/EDIC) study. Diabetes Care.
37:e28–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Höfling DB, Chavantes MC, Juliano AG,
Cerri GG, Knobel M, Yoshimura EM and Chammas MC: Low-level laser in
the treatment of patients with hypothyroidism induced by chronic
autoimmune thyroiditis: A randomized, placebo-controlled clinical
trial. Lasers Med Sci. 28:743–753. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee J, Yi S, Kang YE, Chang JY, Kim JT,
Sul HJ, Kim JO, Kim JM, Kim J, Porcelli AM, et al: Defective
ciliogenesis in thyroid hürthle cell tumors is associated with
increased autophagy. Oncotarget. 7:79117–79130. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu C, Wu F, Mao C, Wang X, Zheng T, Bu L,
Mou X, Zhou Y, Yuan G, Wang S and Xiao Y: Excess iodine promotes
apoptosis of thyroid follicular epithelial cells by inducing
autophagy suppression and is associated with Hashimoto thyroiditis
disease. J Autoimmun. 75:50–57. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim JK, Yuk JM, Kim SY, Kim TS, Jin HS,
Yang CS and Jo EK: MicroRNA-125a inhibits autophagy activation and
antimicrobial responses during mycobacterial infection. J Immunol.
194:5355–5365. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Raad H, Eskalli Z, Corvilain B, Miot F and
De Deken X: Thyroid hydrogen peroxide production is enhanced by the
Th2 cytokines, IL-4 and IL-13, through increased expression of the
dual oxidase 2 and its maturation factor DUOXA2. Free Radic Biol
Med. 56:216–225. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Koc A, Batar B, Celik O, Onaran I, Tasan E
and Sultuybek GK: Polymorphism of the NFKB1 affects the serum
inflammatory levels of IL-6 in Hashimoto thyroiditis in a Turkish
population. Immunobiology. 219:531–536. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xian H, Wang F, Teng W, Yang D and Zhang
M: Thyroid hormone induce a p53-dependent DNA damage through
PI3K/Akt activation in sperm. Gene. 615:1–7. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhu P, Liao LY, Zhao TT, Mo XM, Chen GG
and Liu ZM: GPER/ERK&AKT/NF-κB pathway is involved in
cadmium-induced proliferation, invasion and migration of
GPER-positive thyroid cancer cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 442:68–80.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tang H, Li RP, Liang P, Zhou YL and Wang
GW: miR-125a inhibits the migration and invasion of liver cancer
cells via suppression of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Oncol
Lett. 10:681–686. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|