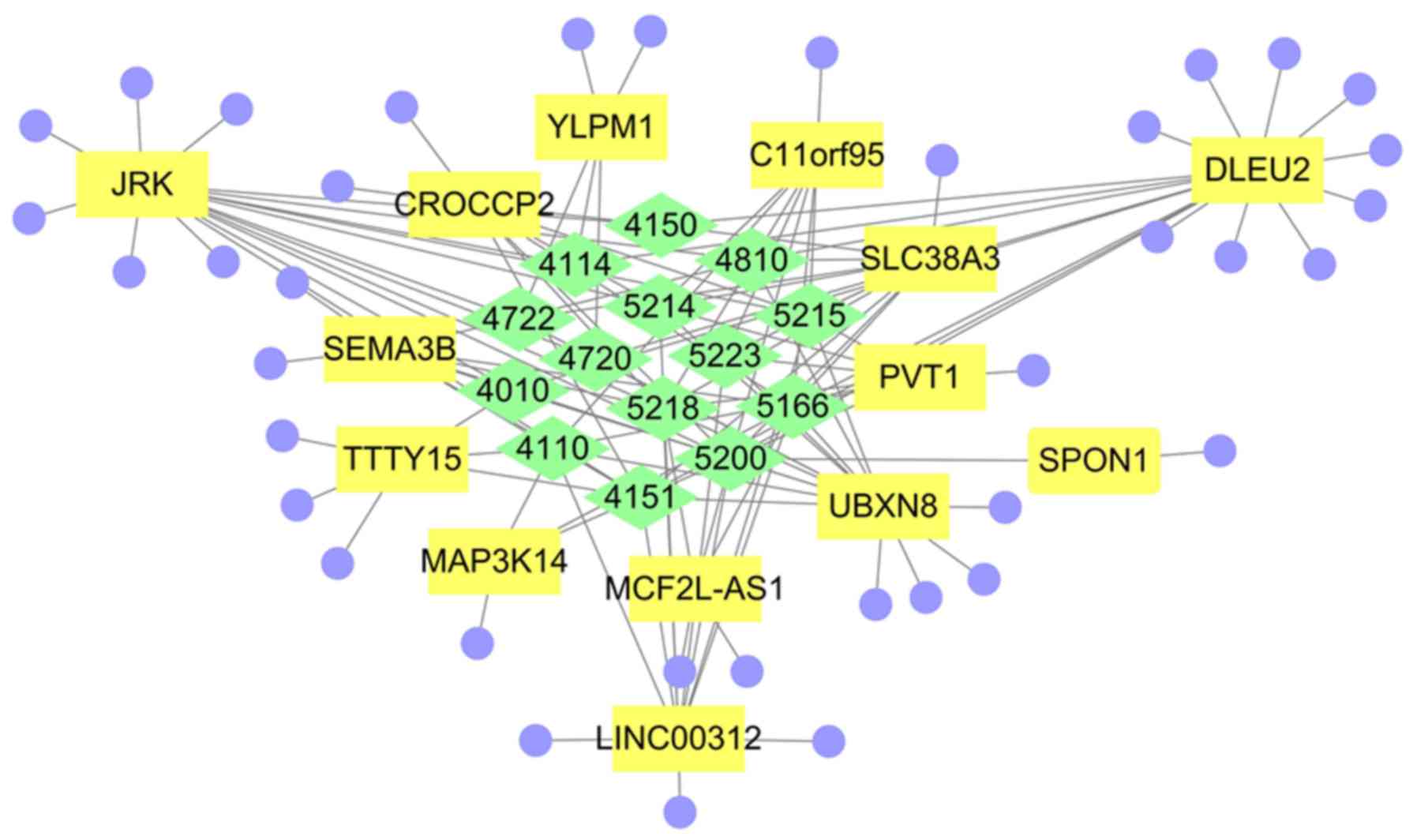
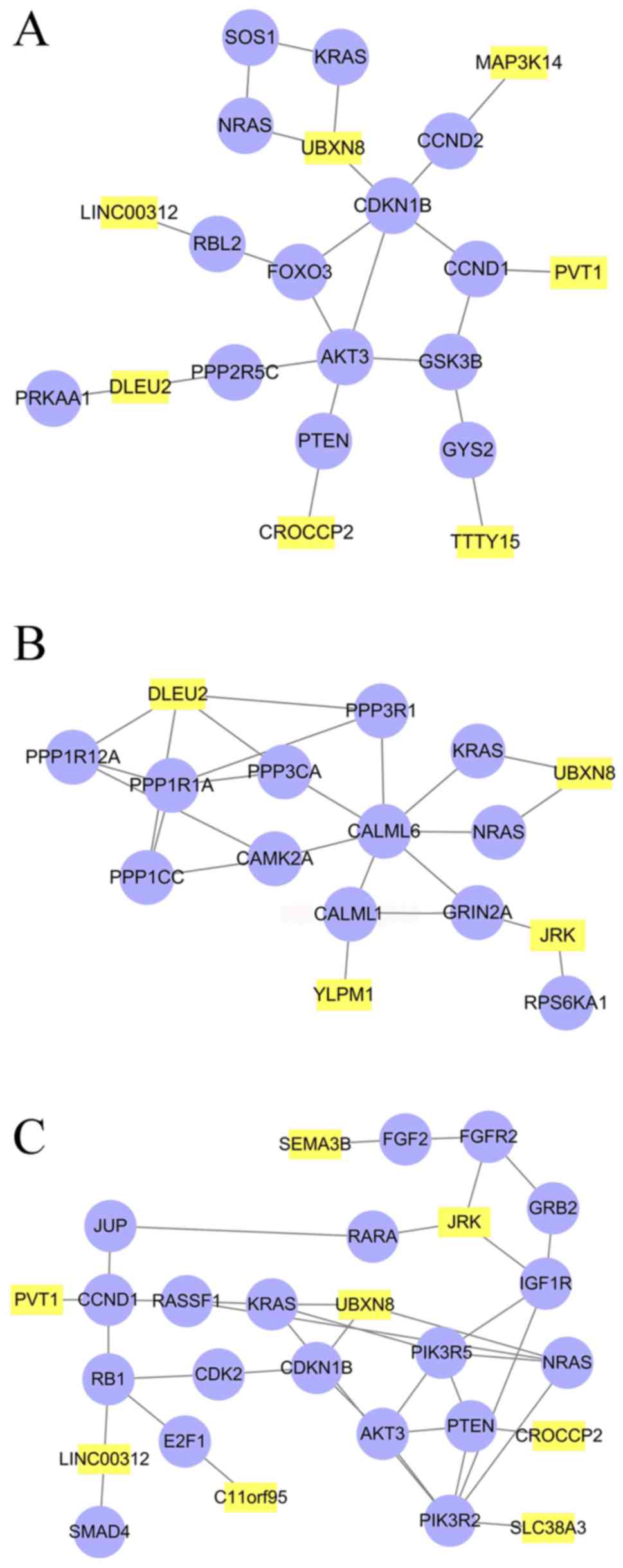
|
1
|
Watts NB, Bilezikian JP, Camacho PM,
Greenspan SL, Harris ST, Hodgson SF, Kleerekoper M, Luckey MM,
McClung MR, Pollack RP, et al: American Association of Clinical
Endocrinologists Medical Guidelines for Clinical Practice for the
diagnosis and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Endocr
Pract. 3:1–37. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Unni S, Yao Y, Milne N, Gunning K, Curtis
JR and LaFleur J: An evaluation of clinical risk factors for
estimating fracture risk in postmenopausal osteoporosis using an
electronic medical record database. Osteoporos Int. 26:581–587.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Reid IR, Bolland MJ and Grey A: Effects of
vitamin D supplements on bone mineral density: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Lancet. 383:146–155. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Neer RM, Arnaud CD, Zanchetta JR, Prince
R, Gaich GA, Reginster JY, Hodsman AB, Eriksen EF, Ish-Shalom S,
Genant HK, et al: Effect of parathyroid hormone (1–34) on fractures
and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis.
N Engl J Med. 344:1434–1441. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lips P: Epidemiology and predictors of
fractures associated with osteoporosis. Am J Med. 103:3S–8S;
discussion 8S-11S. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
McClung MR, Grauer A, Boonen S, Bolognese
MA, Brown JP, Diez-Perez A, Langdahl BL, Reginster JY, Zanchetta
JR, Wasserman SM, et al: Romosozumab in postmenopausal women with
low bone mineral density. N Engl J Med. 370:412–420. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ebert MS and Sharp PA: Emerging roles for
natural microRNA sponges. Curr Biol. 20:R858–R861. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tay Y, Rinn J and Pandolfi PP: The
multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature.
505:344–352. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Koyutürk M, Grama A and Szpankowski W: An
efficient algorithm for detecting frequent subgraphs in biological
networks. Bioinformatics. 20 (Suppl 1):i200–i207. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li C, Han J, Yao Q, Zou C, Xu Y, Zhang C,
Shang D, Zhou L, Zou C, Sun Z, et al: Subpathway-GM: Identification
of metabolic subpathways via joint power of interesting genes and
metabolites and their topologies within pathways. Nucleic Acids
Res. 41:e1012013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li C, Li X, Miao Y, Wang Q, Jiang W, Xu C,
Li J, Han J, Zhang F, Gong B, et al: SubpathwayMiner: A software
package for flexible identification of pathways. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:e1312009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shi X, Xu Y, Zhang C, Feng L, Sun Z, Han
J, Su F, Zhang Y, Li C and Li X: Subpathway-LNCE: Identify
dysfunctional subpathways competitively regulated by lncRNAs
through integrating lncRNA-mRNA expression profile and pathway
topologies. Oncotarget. 7:69857–69870. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang JH, Li JH, Shao P, Zhou H, Chen YQ
and Qu LH: starBase: A database for exploring microRNA-mRNA
interaction maps from Argonaute CLIP-Seq and Degradome-Seq data.
Nucleic Acids Res. 39 (Suppl_1):D202–D209. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xiao F, Zuo Z, Cai G, Kang S, Gao X and Li
T: miRecords: An integrated resource for microRNA-target
interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 37 (Database). D105–D110. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Skala M: Hypergeometric tail inequalities:
Ending the insanity. Statistics, eprint arXiv:1311.5939, 2013.
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1311.5939.pdf
|
|
16
|
Niwattanakul S, Singthongchai J, Naenudorn
E and Wanapu S: Using of Jaccard Coefficient for Keywords
Similarity. Lecture Notes in Engineering & Computer Science,
2013. International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer
Scientists 2013. I. Hong Kong: pp. pp380–384. 2013
|
|
17
|
Irizarry RA, Bolstad BM, Collin F, Cope
LM, Hobbs B and Speed TP: Summaries of Affymetrix GeneChip probe
level data. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:e152003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M and
Speed TP: A comparison of normalization methods for high density
oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias.
Bioinformatics. 19:185–193. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nahler G: Pearson correlation coefficient.
Dictionary of Pharmaceutical Medicine. Springer; Vienna: pp.
pp1322009, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Best DJ and Roberts DE: Algorithm AS 89:
The Upper Tail Probabilities of Spearman's Rho. J R Stat Soc [Ser
A]. 24:377–379. 1975.
|
|
21
|
Whitlock MC: Combining probability from
independent tests: The weighted Z-method is superior to Fisher's
approach. J Evol Biol. 18:1368–1373. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Routledge R: Fisher's Exact Test. In:
Encyclopedia of Biostatistics. Armitage P and Colton T (eds). John
Wiley & Sons; Ltd., New York, NY: 2005
|
|
23
|
Benjamini Y, Drai D, Elmer G, Kafkafi N
and Golani I: Controlling the false discovery rate in behavior
genetics research. Behav Brain Res. 125:279–284. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fog A: Calculation methods for Wallenius'
noncentral hypergeometric distribution. Commun Stat Simul Comput.
37:258–273. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Epstein MP, Duncan R, Jiang Y, Conneely
KN, Allen AS and Satten GA: A permutation procedure to correct for
confounders in case-control studies, including tests of rare
variation. Am J Hum Genet. 91:215–223. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Stuss M, Rieske P, Cegłowska A,
Stêpień-Kłos W, Liberski PP, Brzeziańska E and Sewerynek E:
Assessment of OPG/RANK/RANKL gene expression levels in peripheral
blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) after treatment with strontium
ranelate and ibandronate in patients with postmenopausal
osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 98:E1007–E1011. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Martini M, De Santis MC, Braccini L,
Gulluni F and Hirsch E: PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: An
updated review. Ann Med. 46:372–383. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
De Luca A, Maiello MR, D'Alessio A,
Pergameno M and Normanno N: The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and the PI3K/AKT
signalling pathways: Role in cancer pathogenesis and implications
for therapeutic approaches. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 16 (Suppl
2):S17–S27. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sabine VS, Crozier C, Brookes CL, Drake C,
Piper T, van de Velde CJ, Hasenburg A, Kieback DG, Markopoulos C,
Dirix L, et al: Mutational analysis of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
in tamoxifen exemestane adjuvant multinational pathology study. J
Clin Oncol. 32:2951–2958. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|