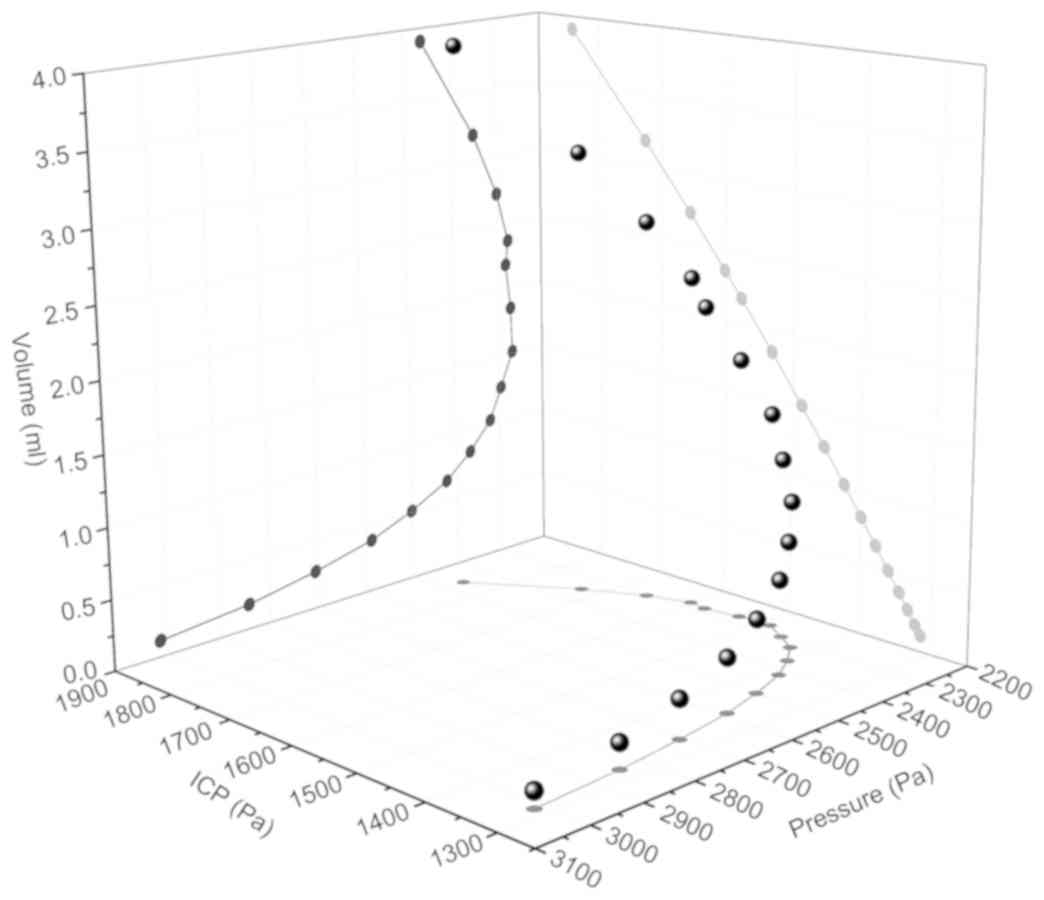
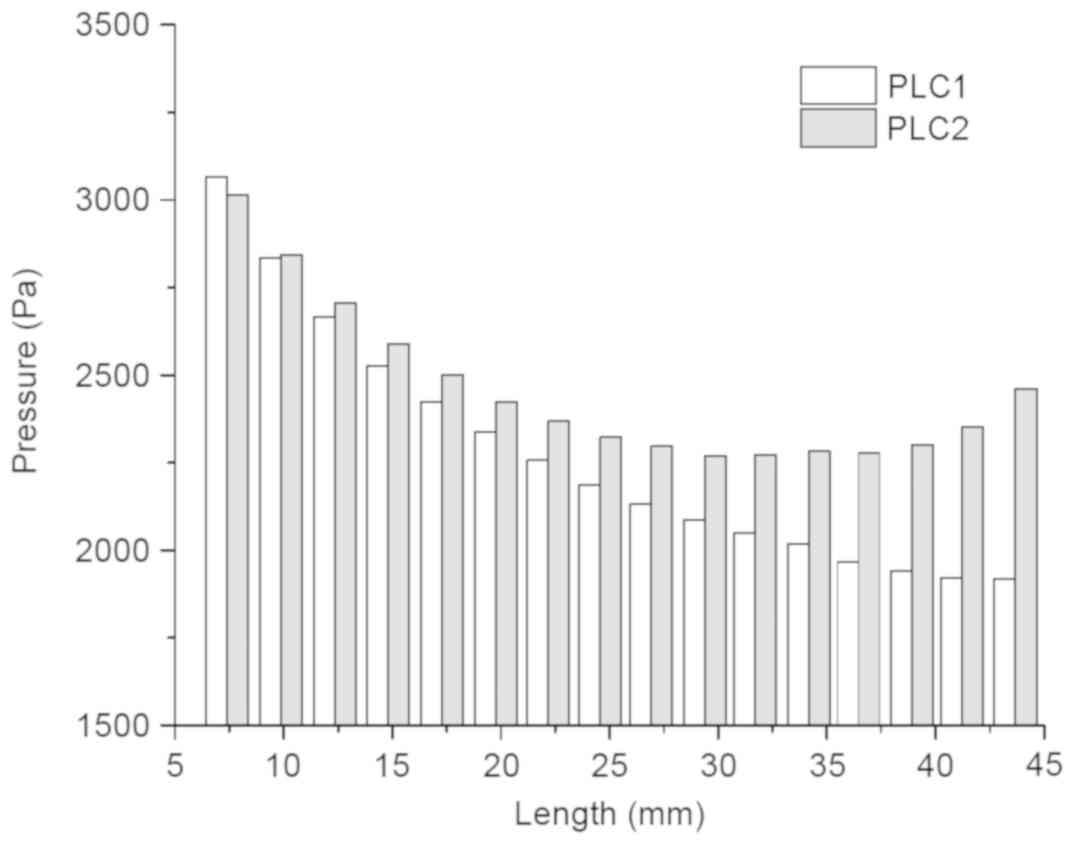
|
1
|
Xi G, Strahle J, Hua Y and Keep RF:
Progress in translational research on intracerebral hemorrhage: Is
there an end in sight? Prog Neurobiol. 115:45–63. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wu G, Xi G and Huang F: Spontaneous
intracerebral hemorrhage in humans: Hematoma enlargement, clot
lysis, and brain edema. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 96:78–80. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Steiner T, Al-Shahi Salman R, Beer R,
Christensen H, Cordonnier C, Csiba L, Forsting M, Harnof S, Klijn
CJ, Krieger D, et al: European stroke organisation (ESO) guidelines
for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Int J
Stroke. 9:840–855. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kalita J, Misra UK, Vajpeyee A, Phadke RV,
Handique A and Salwani V: Brain herniations in patients with
intracerebral hemorrhage. Acta Neurol Scand. 119:254–260. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hiploylee C and Colbourne F: Intracranial
pressure measured in freely moving rats for days after
intracerebral hemorrhage. Exp Neurol. 255:49–55. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fung YCB: Elasticity of soft tissues in
simple elongation. Am J Physiol. 213:1532–1544. 1967. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zebian B and Critchley G: Spontaneous
intracranial haemorrhage. Surgery (Oxford). 30:136–141. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Estes MS and McElhane JH: Response of
brain tissue to compressive loading. New York ASME. 1970.
|
|
9
|
Miller K and Chinzei K: Constitutive
modelling of brain tissue: Experiment and theory. J Biomech.
30:1115–1121. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Goriely A, Geers MA, Holzapfel GA,
Jayamohan J, Jérusalem A, Sivaloganathan S, Squier W, van Dommelen
JA, Waters S and Kuhl E: Mechanics of the brain: Perspectives,
challenges, and opportunities. Biomech Model Mechanobiol.
14:931–965. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Prevost TP, Balakrishnan A, Suresh S and
Socrate S: Biomechanics of brain tissue. Acta Biomater. 7:83–95.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bilston LE, Liu Z and Phan-Thien N: Large
strain behaviour of brain tissue in shear: Some experimental data
and differential constitutive model. Biorheology. 38:335–345.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bayly PV, Black EE, Pedersen RC, Leister
EP and Genin GM: In vivo imaging of rapid deformation and strain in
an animal model of traumatic brain injury. J Biomech. 39:1086–1095.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rashid B, Destrade M and Gilchrist MD:
Mechanical characterization of brain tissue in compression at
dynamic strain rates. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 10:23–38. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
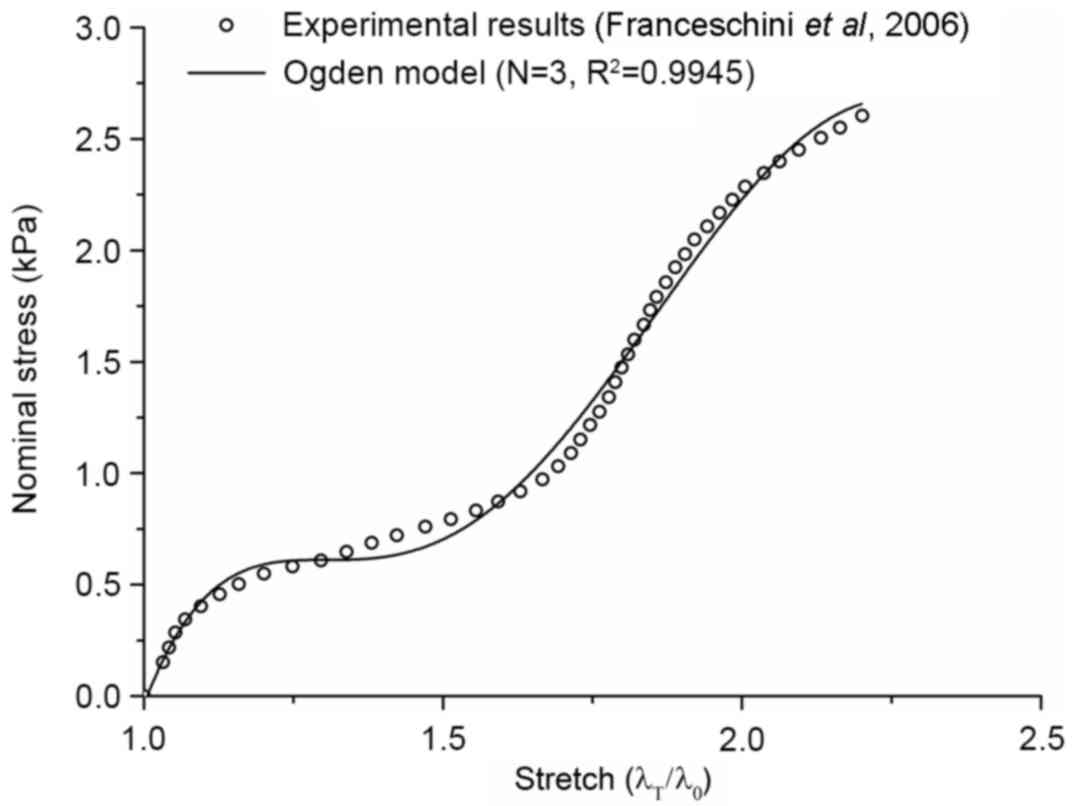
Franceschini G, Bigoni D, Regitnig P and
Holzapfel GA: Brain tissue deforms similarly to filled elastomers
and follows consolidation theory. J Mech Phys Solids. 54:2592–2620.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jin X, Zhu F, Mao H, Shen M and Yang KH: A
comprehensive experimental study on material properties of human
brain tissue. J Biomech. 46:2795–2801. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Linninger AA, Tangen K, Hsu CY and Frim D:
Cerebrospinal fluid mechanics and its coupling to cerebrovascular
dynamics. Ann Rev Fluid Mech. 48:219–257. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Taylor Z and Miller K: Reassessment of
brain elasticity for analysis of biomechanisms of hydrocephalus. J
Biomech. 37:1263–1269. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wittek A, Miller K, Kikinis R and Warfield
SK: Patient-specific model of brain deformation: Application to
medical image registration. J Biomech. 40:919–929. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ren P, Wang BC, Wang YZ, Hao SL, Guo TW
and Li XF: Evaluating tensile damage of brain tissue in
intracerebral hemorrhage based on strain energy. Exp Ther Med.
16:4843–4852. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Marmarou A and Beaumont A: Physiology of
the cerebrospinal fluid and intracranial pressure. Youmans
neurological surgery. Winn HR: 6th. Springer; Philadelphia, PA: pp.
169–182. 2011, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Maset AL, Marmarou A, Ward JD, Choi S,
Lutz HA, Brooks D, Moulton RJ, DeSalles A, Muizelaar JP, Turner H,
et al: Pressure-volume index in head-injury. J Neurosurg.
67:832–840. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tsai MS, Chou YL, Chang GL and Shen CL:
The effect of magnitudes and duration of pressure on cerebral
cortex in a rat model. J Clin Neurosci. 8:157–163. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Agar A, Li S, Agarwal N, Coroneo MT and
Hill MA: Retinal ganglion cell line apoptosis induced by
hydrostatic pressure. Brain Res. 1086:191–200. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tök L, Nazıroğlu M, Uğuz AC and Tök O:
Elevated hydrostatic pressures induce apoptosis and oxidative
stress through mitochondrial membrane depolarization in PC12
neuronal cells: A cell culture model of glaucoma. J Recept Signal
Transduct Res. 34:410–416. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xi G, Keep RF and Hoff JT: Mechanisms of
brain injury after intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol.
5:53–63. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gore RW: Pressures in cat mesenteric
arterioles and capillaries during changes in systemic arterial
blood pressure. Circ Res. 34:581–591. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lipowsky HH: Microvascular rheology and
hemodynamics. Microcirculation. 12:5–15. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Boas DA, Jones SR, Devor A, Huppert TJ and
Dale AM: A vascular anatomical network model of the spatio-temporal
response to brain activation. Neuroimage. 40:1116–1129. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|