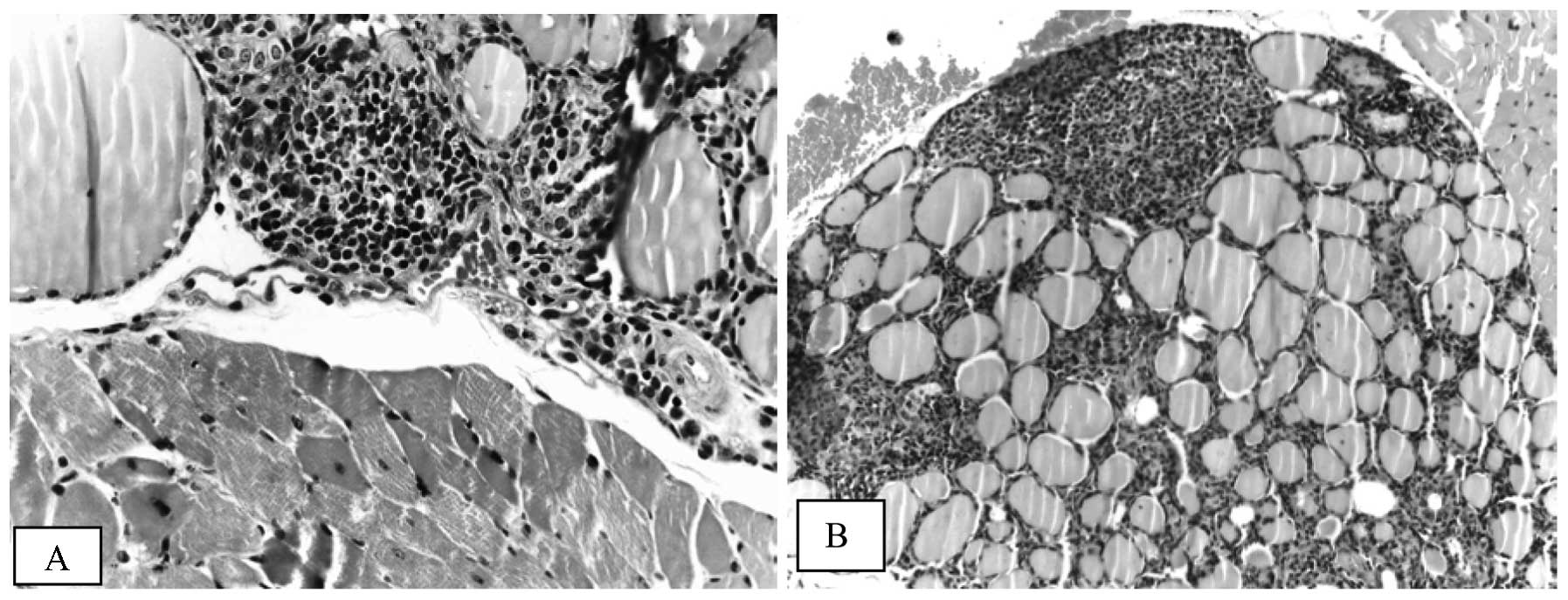
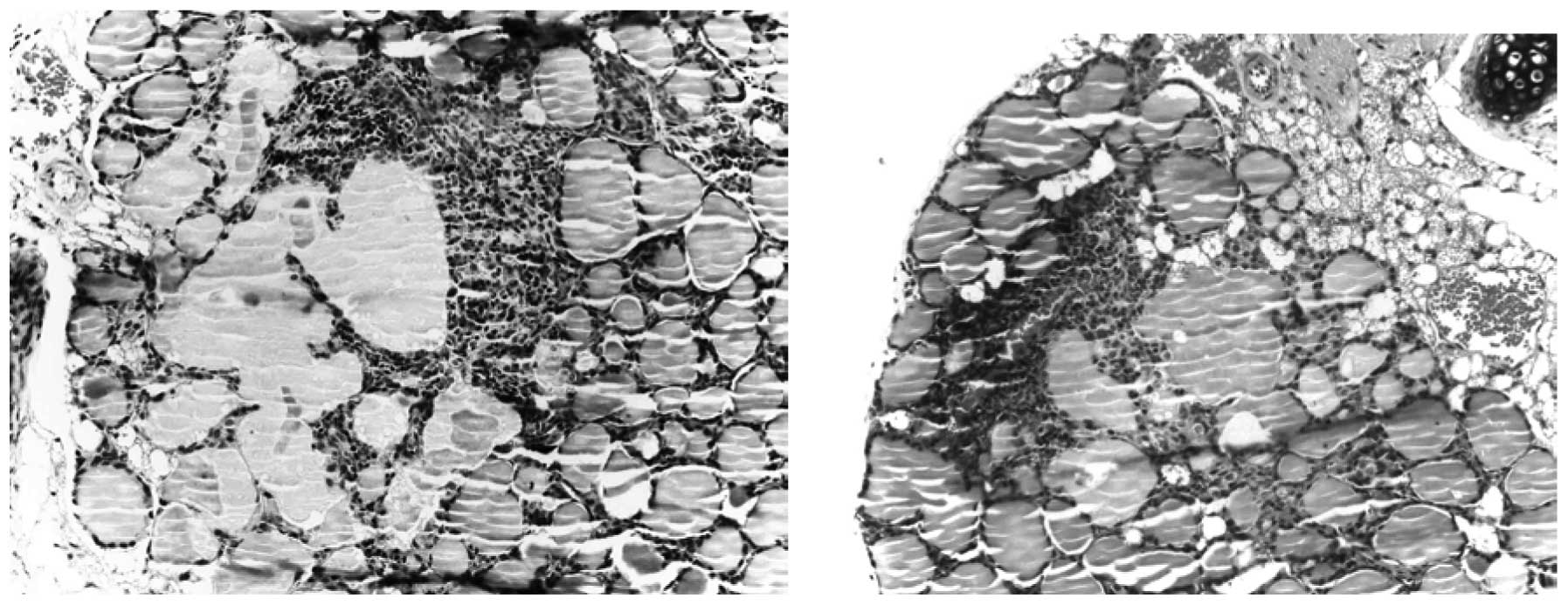
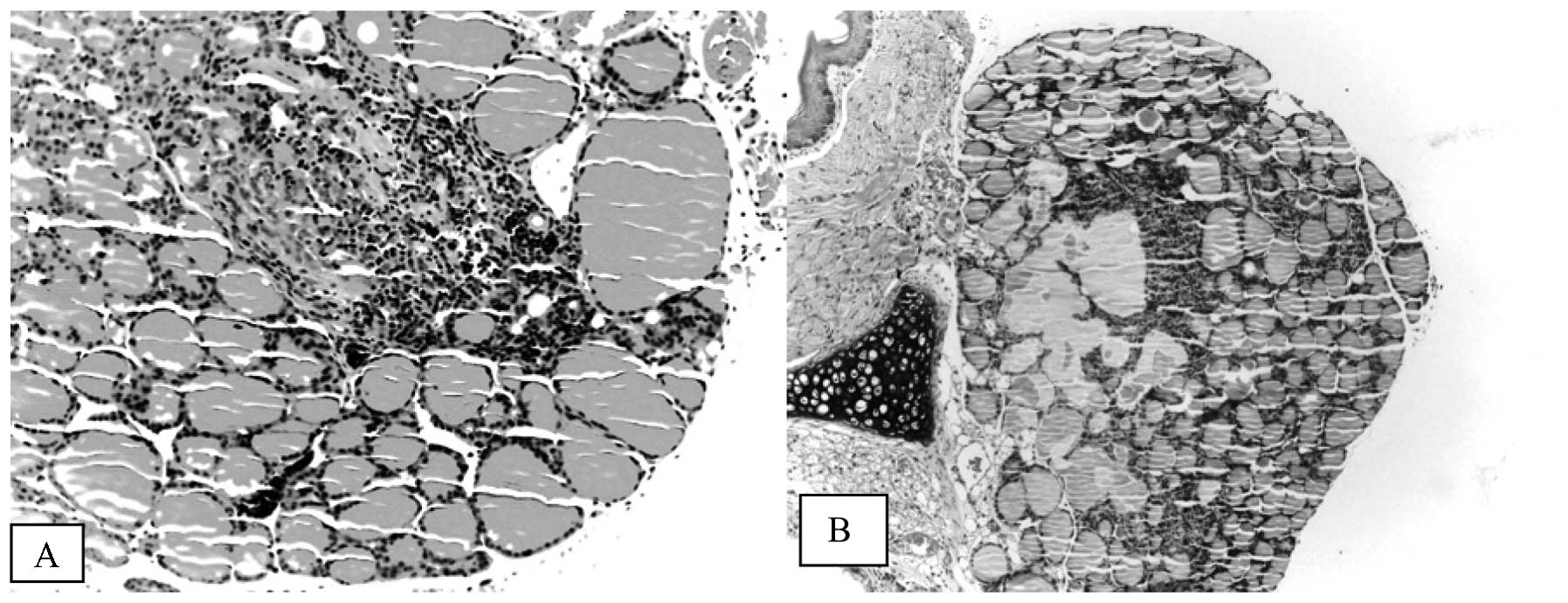
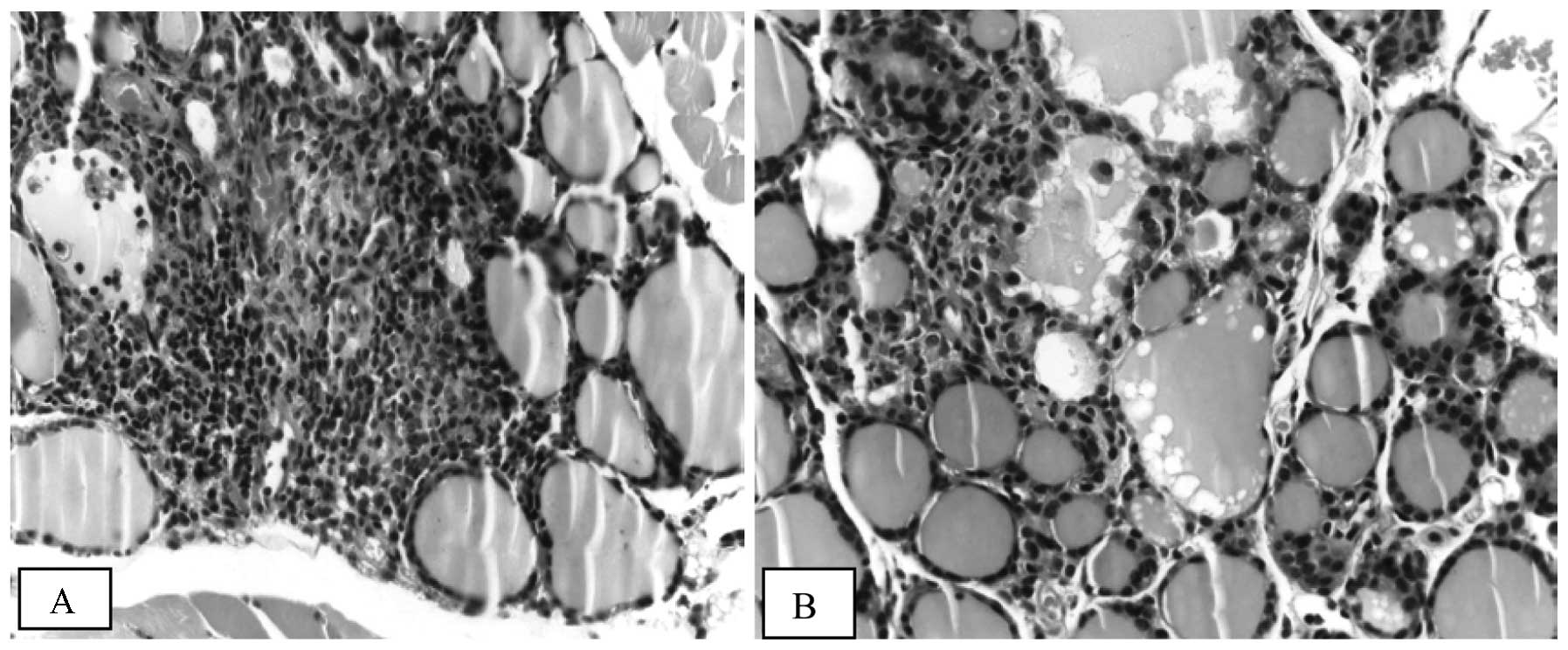
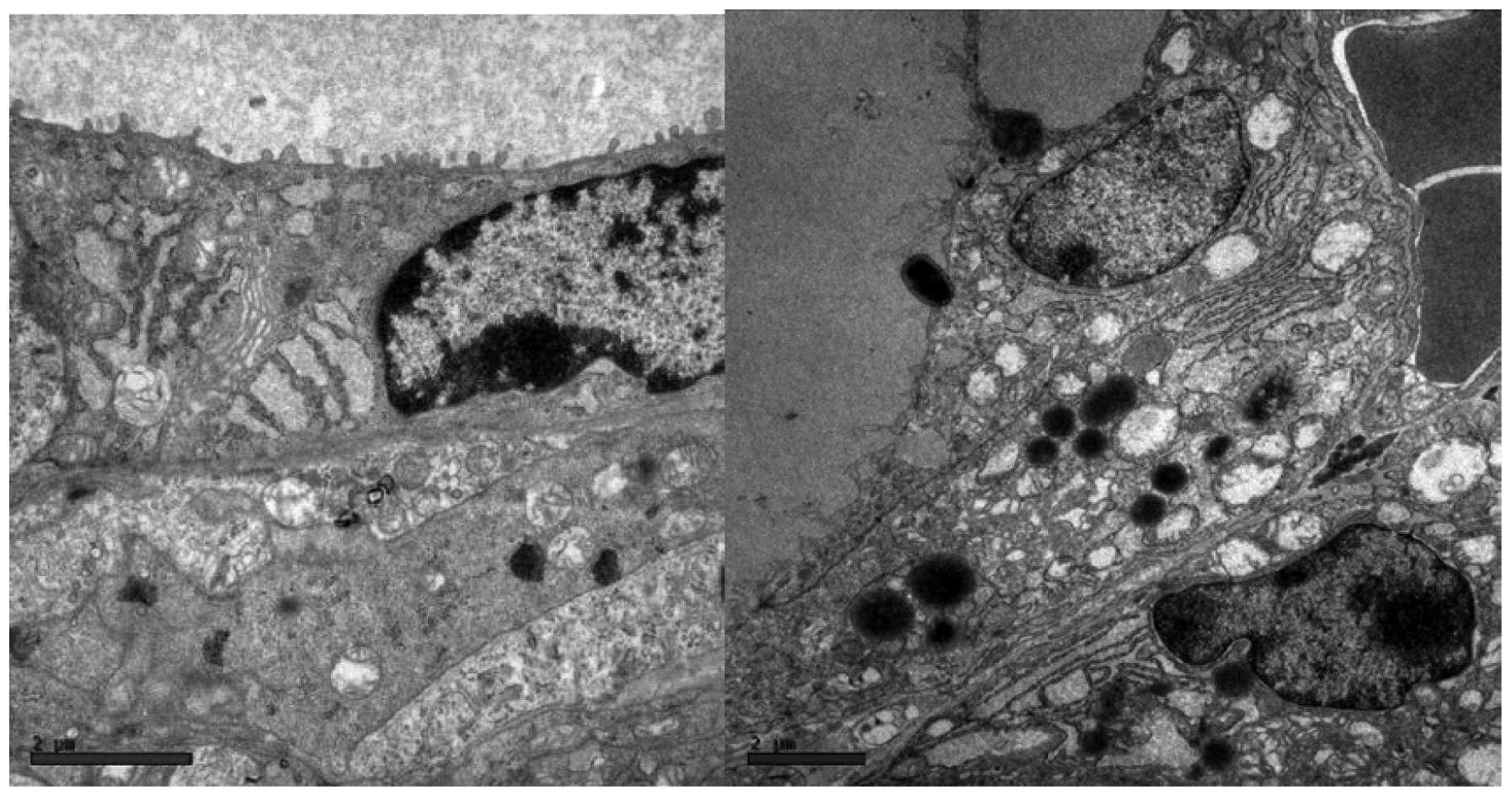
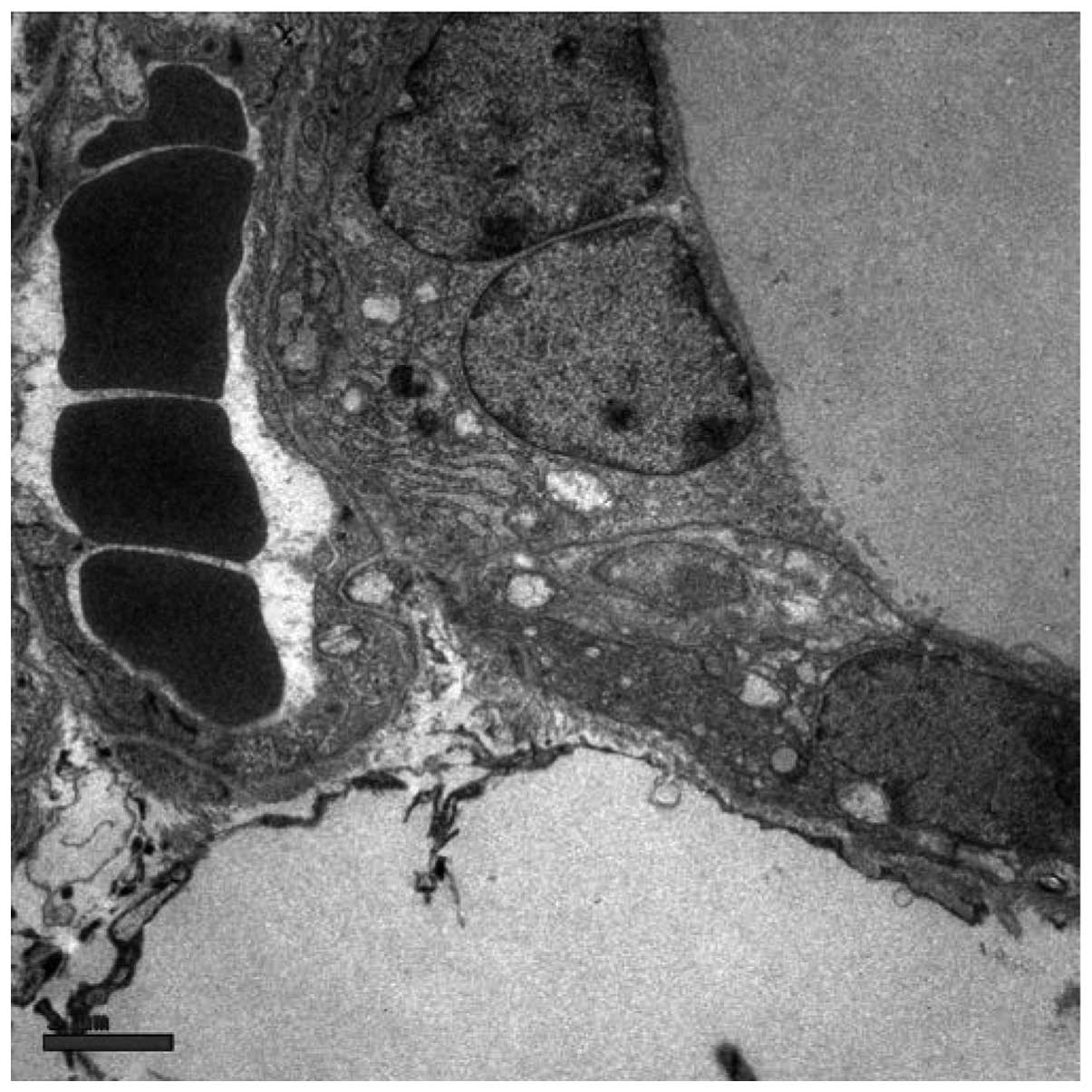
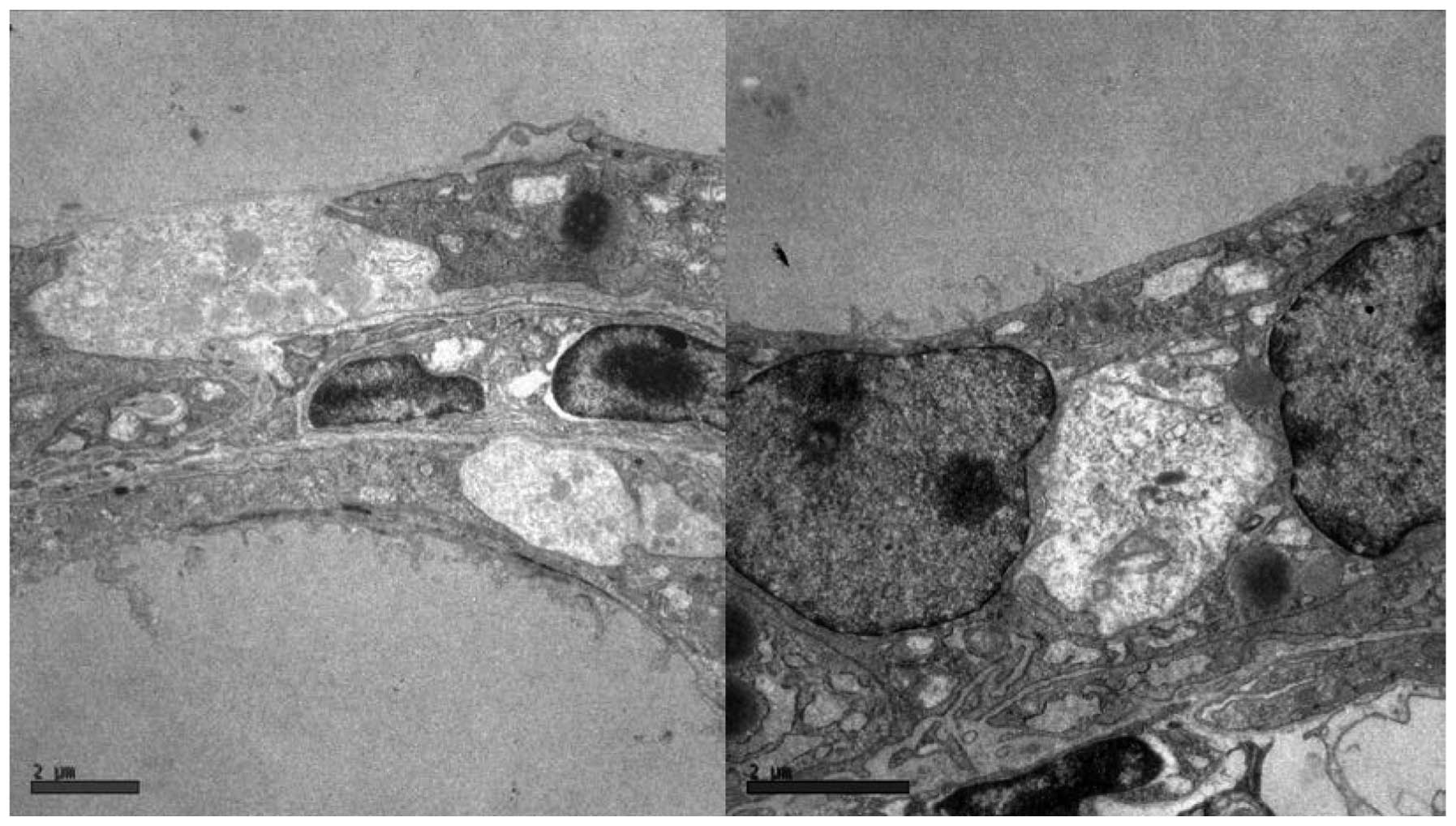
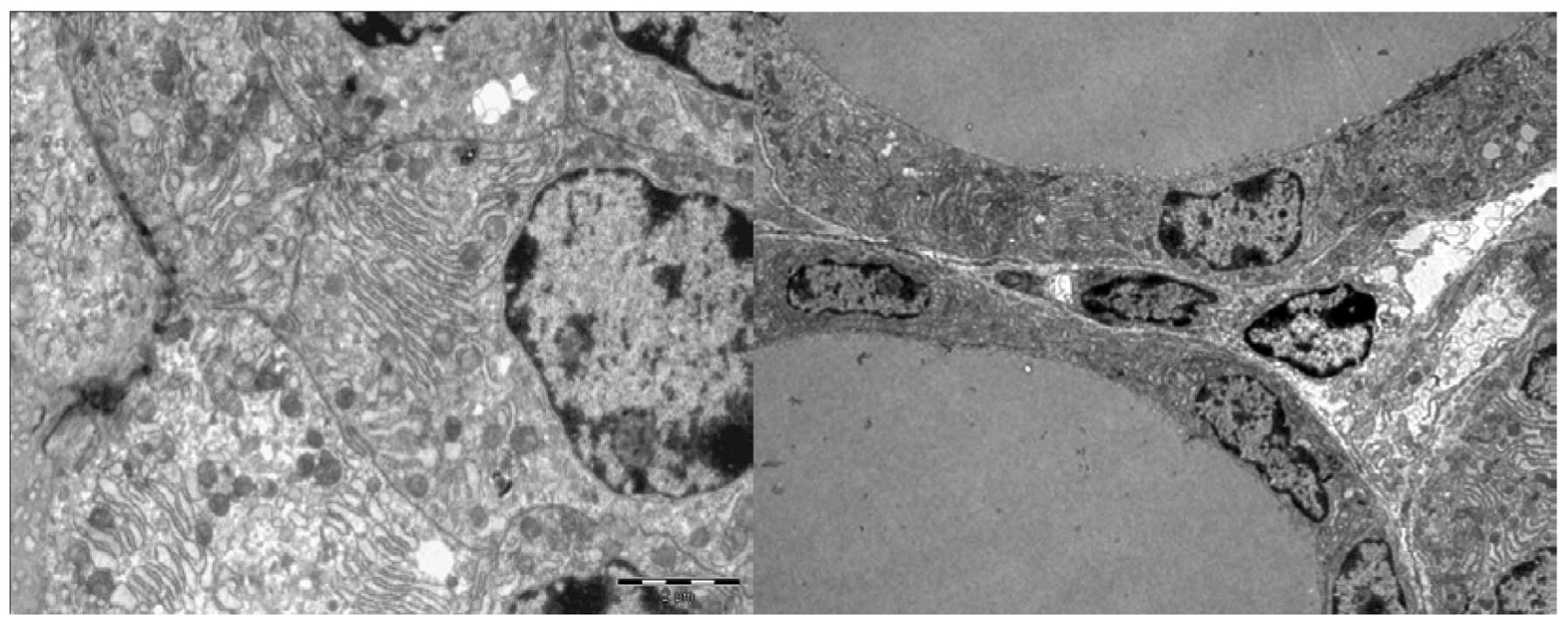
|
1.
|
Bülow Pedersen I, Knudsen N, Jørgensen T,
Perrild H, Ovesen L and Laurberg P: Large differences in incidences
of overt hyper-and hypothyroidism associated with a small
difference in iodine intake: a prospective comparative
register-based population survey. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
87:4462–4469. 2002.
|
|
2.
|
Teng W, Shan Z, Teng X, Guan H, Li Y, Teng
D, et al: Effect of iodine intake on thyroid diseases in China. N
Engl J Med. 354:2783–2793. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Fountoulakis S, Philippou G and Tsatsoulis
A: The role of iodine in the evolution of thyroid disease in
Greece: from endemic goiter to autoimmunity. Hormones (Athens).
6:25–35. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Camargo RY, Tomimori EK, Neves SC, G S
Rubio I, Galrão AL, Knobel M and Medeiros-Neto G: Thyroid and the
enviromment: exposure to excessive nutritional iodine increases the
prevalence of thyroid disorders in São Paulo, Brazil. Eur J
Endocrinol. 159:293–299. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Harach HR and Ceballos GA: Thyroid cancer,
thyroiditis and dietary iodine: A review based on the Salta,
Argentina model. Endocr Pathol. 19:209–220. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Li HS and Carayanniotis G: Induction of
goitrous hypothyroidism by dietary iodide in SJL mice.
Endocrinology. 148:2747–2752. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Poncin S, Gérard AC, Boucquey M, Senou M,
Calderon PB, Knoops B, Lengelé B, Many MC and Colin IM: Oxidative
stress in the thyroid gland: from harmlessness to hazard depending
on the iodine content. Endocrinology. 149:424–433. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Fassbender WJ, Vogel C, Doppl W, Stracke
H, Bretzel RG and Klör HU: Thyroid function, thyroid immunoglobulin
status and urinary iodine excretion after enteral contrast-agent
administration by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
Endoscopy. 33:245–252. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Linder N, Sela B, German B, Davidovitch N,
Kuint J, Hegesh J, Lubin D and Sack J: Iodine and hypothyroidism in
neonates with congenital heart disease. Arch Dis Child Fetal
Neonatal Ed. 77:F239–F240. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Grubeck-Loebenstein B, Kronik G,
Mösslacher H and Waldhäusl W: The effect of iodine containing
contrast medium on thyroid function of patients undergoing coronary
angiography. Exp Clin Endocrinol. 81:59–64. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
del Cerro Marín M, Fernández Ruiz A,
García-Guereta L, Benito Bartolomé F, Burgueros M, Ares Segura S,
Moreno F and Gracia Bouthelier R: Thyroid function alterations in
children with congenital cardiac disease after catheterization with
iodinated contrast agents. Rev Esp Cardiol. 53:517–524. 2000.(In
Spanish).
|
|
12.
|
Gartner W and Weissel M: Do
iodine-containing contrast media induce clinically relevant changes
in thyroid function parameters of euthyroid patients within the
first week? Thyroid. 14:521–524. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13.
|
Nakazawa T, Murata S, Kondo T, Nakamura N,
Yamane T, Iwasa S and Katoh R: Histopathology of the thyroid in
amiodarone-induced hypothyroidism. Pathol Int. 58:55–58. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Many MC, Maniratunga S, Varis I, Dardenne
M, et al: Two-step development of Hashimoto-like thyroiditis in
genetically autoimmune prone non-obese diabetic mice: effects of
iodine-induced cell necrosis. J Endocrinol. 147:311–320. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Many MC, Mestdagh C, van den Hove MF and
Denef JF: In vitro study of acute toxic effects of high iodide
doses in human thyroid follicles. Endocrinology. 131:621–630.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Melo M: Autoimmune thyroiditis. Acta Med
Port. 19:387–394. 2006.(In Portuguese).
|
|
17.
|
Tanimoto C, Hirakawa S, Kaiwasaki H,
Hayakawa N and Ota Z: Apoptosis in thyroid diseases: a
histochemical study. Endocr J. 42:193–201. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Wang SH and Baker JR: The role of
apoptosis in thyroid autoimmunity. Thyroid. 17:975–979. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Arscott PL and Baker JR Jr: Apoptosis and
thyroiditis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 87:207–217. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Kotani T, Aratake Y, Hirai K, Fukazawa Y,
Sato H and Ohtaki S: Apoptosis in thyroid tissue from patients with
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Autoimmunity. 20:231–236. 1995.
|
|
21.
|
Chen X, Liu L, Yao P, Yu D, Hao L and Sun
X: Effect of excessive iodine on immune function of lymphocites and
intervention with selenium. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci.
27:422–425. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Allen EM, Appel MC and Braverman LE:
Iodine-induced thyroiditis and hypothyroidism in
hemithyroidectomized BB/W rat. Endocrinology. 121:481–485. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Bagchi N, Brown TR and Sundick RS: Thyroid
cell injury is an initial event in the induction of autoimmune
thyroiditis by iodine in obese strain chickens. Endocrinology.
136:5054–5060. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Damotte D, Colomb E, Cailleau C, Brousse
N, Charreire J and Carnaud C: Analysis of susceptibility of NOD
mice to spontaneous and experimentally induced thyroiditis. Eur J
Immunol. 27:2854–2862. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Li HS, Verginis P and Carayanniotis G:
Maturation of dendritic cells by necrotic thyrocytes facilitates
induction of experimental autoimmune thyroiditis. Clin Exp Immunol.
144:467–474. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|