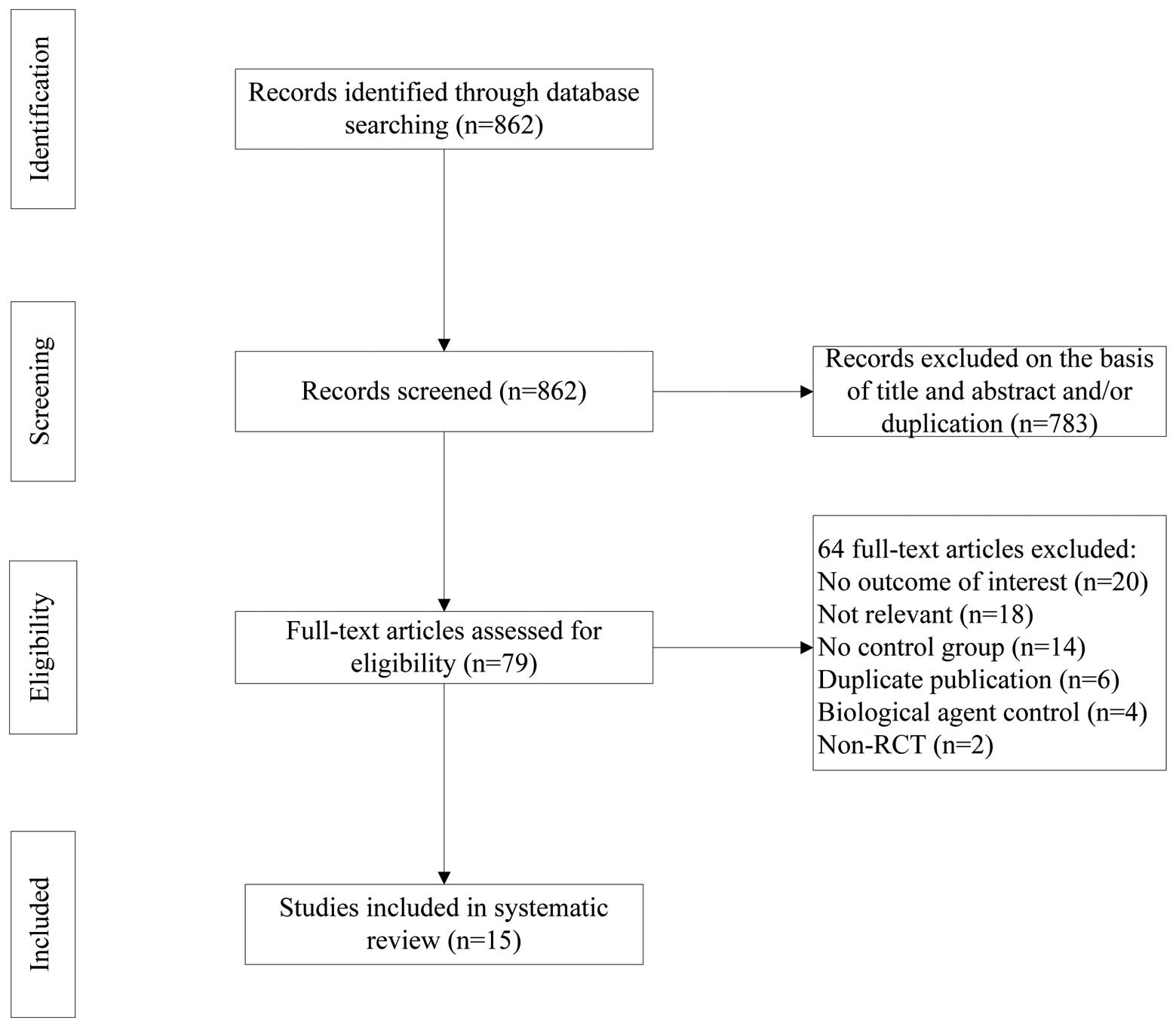
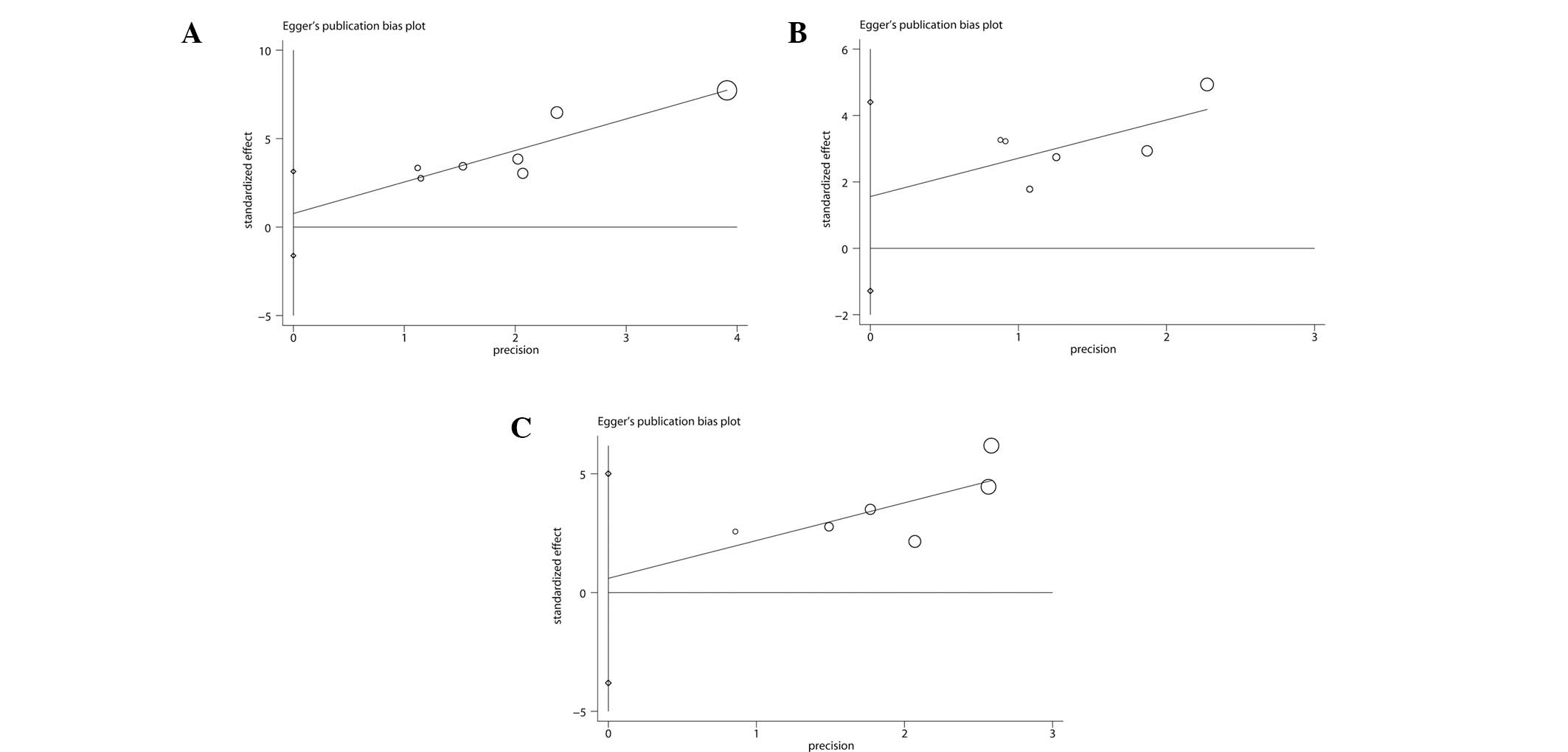
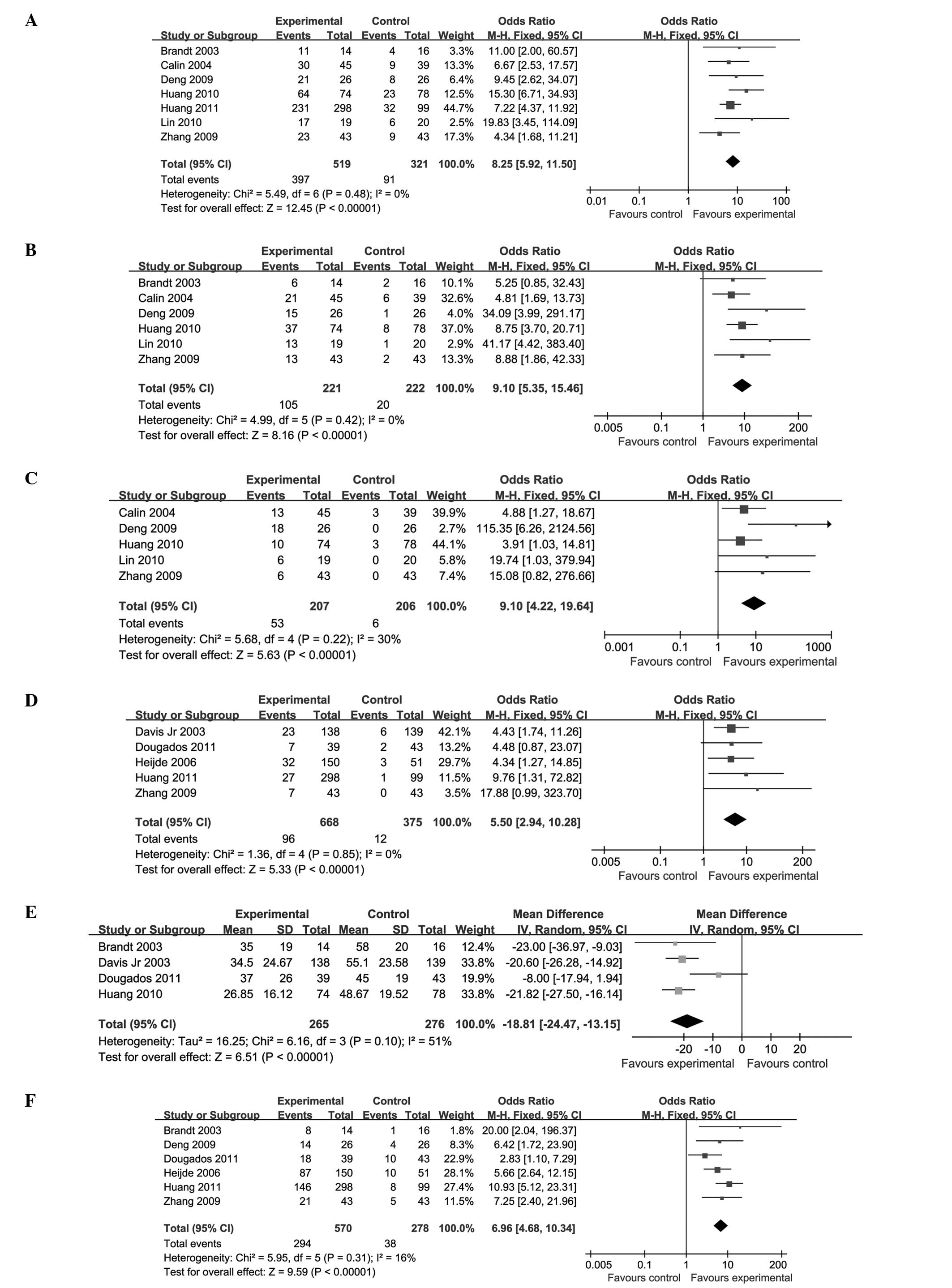
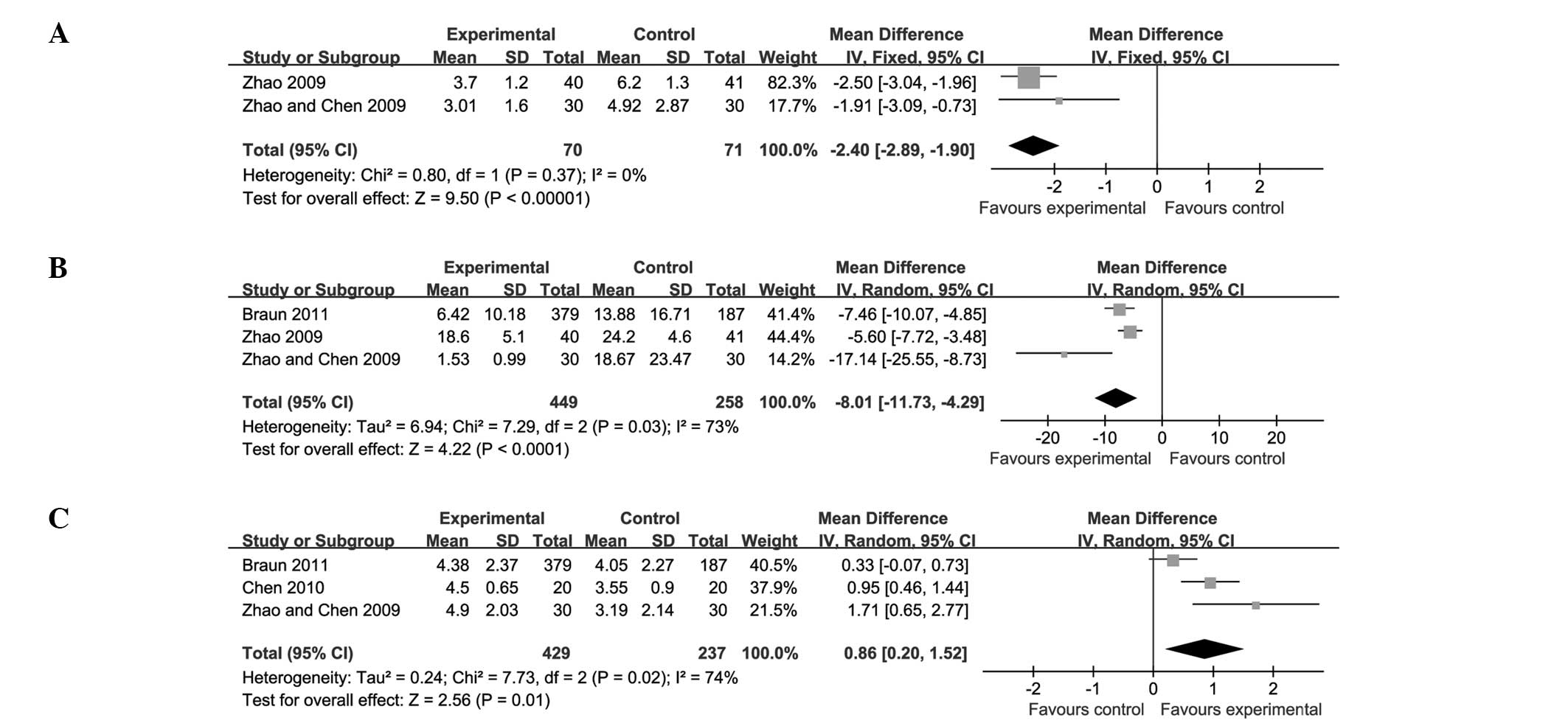
|
1
|
Braun J and Sieper J: Ankylosing
spondylitis. Lancet. 369:1379–1390. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Feldtkeller E, Khan M, van der Heijde D,
et al: Age at disease onset and diagnosis delay in HLA-B27 negative
vs. positive patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol Int.
23:61–66. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sieper J and Braun J: Anti-TNF agents for
the treatment of spondyloarthropathies. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs.
7:235–246. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gratacos J, Collado A, Filella X, et al:
Serum cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β and IFN-γ) in ankylosing
spondylitis: a close correlation between serum IL-6 and disease
activity and severity. Rheumatology. 33:927–931. 1994.
|
|
5
|
Braun J, Bollow M, Neure L, et al: Use of
immunohistologic and in situ hybridization techniques in the
examination of sacroiliac joint biopsy specimens from patients with
ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 38:499–505. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Culy CR and Keating GM: Etanercept: an
updated review of its use in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic
arthritis and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Drugs. 62:2493–2537.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mease PJ, Goffe BS, Metz J, et al:
Etanercept in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis: a
randomised trial. Lancet. 356:385–390. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lovell DJ, Giannini EH, Reiff A, et al:
Etanercept in children with polyarticular juvenile rheumatoid
arthritis. N Engl J Med. 342:763–769. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Braun J, Van den Berg R, Baraliakos X, et
al: 2010 update of the ASAS/EULAR recommendations for the
management of ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 70:896–904.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen J and Liu C: Sulfasalazine for
ankylosing spondylitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
18:CD0048002005.
|
|
11
|
Ferraz MB, Tugwell P, Goldsmith CH, et al:
Meta-analysis of sulfasalazine in ankylosing spondylitis. J
Rheumatol. 17:1482–1486. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li SH, Ma B, Tan JY, et al: Efficacy and
safety of etanercept for patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a
systematic review. Chinese Journal of Evidence-Based Medicine.
9:423–429. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
13
|
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J and Altman
DG; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews
and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med.
151:264–269. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA and Cats
A: Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A
proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis
Rheum. 27:361–368. 1984.
|
|
15
|
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al:
Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is
blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 17:1–12. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Anderson JJ, Baron G, van der Heijde D, et
al: Ankylosing spondylitis assessment group preliminary definition
of short-term improvement in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis
Rheum. 44:1876–1886. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Garrett S, Jenkinson T, Kennedy LG, et al:
A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing
spondylitis: the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity
Index. J Rheumatol. 21:2286–2291. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Calin A, Garrett S, Whitelock H, et al: A
new approach to defining functional ability in ankylosing
spondylitis: the development of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis
Functional Index. J Rheumatol. 21:2281–2285. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dougados M, Braun J, Szanto S, et al:
Efficacy of etanercept on rheumatic signs and pulmonary function
tests in advanced ankylosing spondylitis: results of a randomised
double-blind placebo-controlled study (SPINE). Ann Rheum Dis.
70:799–804. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lin Q, Lin Z, Gu J, et al: Abnormal
high-expression of CD154 on T lymphocytes of ankylosing spondylitis
patients is down-regulated by etanercept treatment. Rheumatol Int.
30:317–323. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gorman JD, Sack KE and Davis JC Jr:
Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis by inhibition of tumor necrosis
factor α. N Engl J Med. 346:1349–1356. 2002.
|
|
22
|
Davis JC Jr, Van Der Heijde D, Braun J, et
al; Enbrel Ankylosing Spondylitis Study Group. Recombinant human
tumor necrosis factor receptor (etanercept) for treating ankylosing
spondylitis: a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum.
48:3230–3236. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Braun J, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, Huang
F, et al: Clinical efficacy and safety of etanercept versus
sulfasalazine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: A
randomized, double-blind trial. Arthritis Rheum. 63:1543–1551.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Calin A, Dijkmans BAC, Emery P, et al:
Outcomes of a multicentre randomised clinical trial of etanercept
to treat ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 63:1594–1600. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
van der Heijde D, Da Silva JC, Dougados M,
et al; Etanercept Study 314 Investigators. Etanercept 50 mg once
weekly is as effective as 25 mg twice weekly in patients with
ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 65:1572–1577.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Brandt J, Khariouzov A, Listing J, et al:
Six-month results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of
etanercept treatment in patients with active ankylosing
spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 48:1667–1675. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang F, Zhang J, Zheng Y, et al: A
multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical
trial of etanercept in the treatment of Chinese patients with
active ankylosing spondylitis. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi.
50:1043–1047. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
28
|
Huang F, Zhang J, Huang JL, et al: A
multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical
study of etanercept in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis.
Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 49:741–745. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
29
|
Deng XH, Hang F, Zhang YM, et al:
Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis with recombinant human tumor
necrosis factor-Fc fusion protein (etanercept): a multicenter,
randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Jun Yi Jin Xiu
Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 30:21–23. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
30
|
Zhang J, Zhang YM, Zhang JL, et al:
Efficacy of etanercept in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: A
double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled trial. Zhongguo Xin
Yao Za Zhi. 18:1846–1849. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
31
|
Zhao WM, Chen ZW and Wang MJ: Clinical
observation of etanercept in treatment of ankylosing spondylitis.
Suzhou Da Xue Xue Bao. 29:518–523. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
32
|
Zhao FT, Zhao H and Wang YL: Efficacy of
etanercept on ankylosing spondylitis. Shanghai Jiaotong Daxue
Xuebao Yixueban. 29:1506–1508. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
33
|
Sterne JA, Gavaghan D and Egger M:
Publication and related bias in meta-analysis: power of statistical
tests and prevalence in the literature. J Clin Epidemiol.
53:1119–1129. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Davis JC Jr: The role of etanercept in
ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 20(Suppl 28):
S111–S115. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen MZ, Zhao RGT, Wang HY, et al:
Clinical control study of recombinant human tumor necrosis
factor-Fc fusion protein and traditional immunity depressant in
treatment of ankylosing spondylitis (AS). Xinjiang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue
Bao. 33:913–915. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
36
|
Machado MA, Barbosa MM, Almeida AM, et al:
Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis with TNF blockers: a
meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int. 33:2199–2213. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li ZH, Zhang Y, Wang J and Shi ZJ:
Etanercept in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: a
meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled
clinical trials, and the comparison of the Caucasian and Chinese
population. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 23:497–506. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|