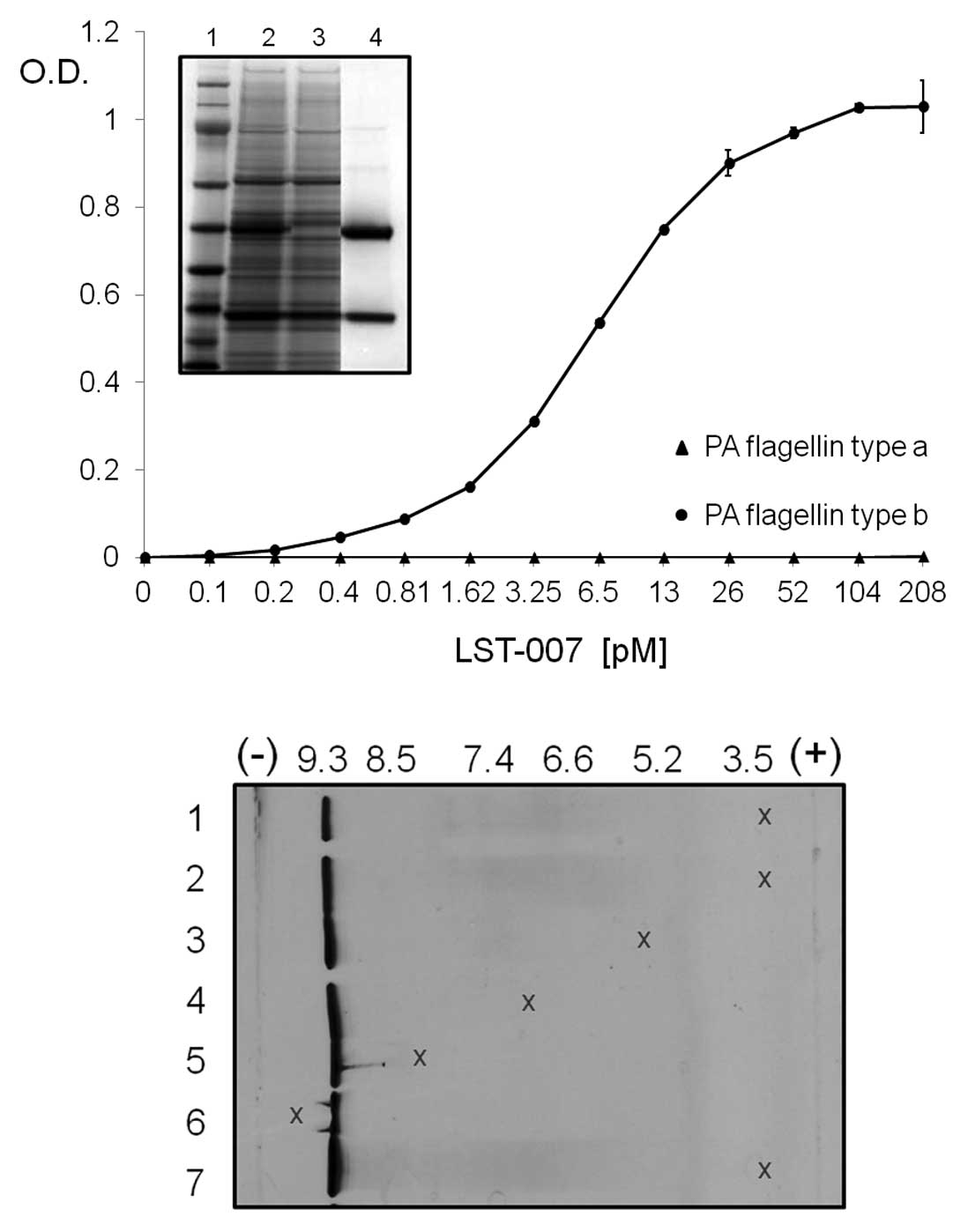
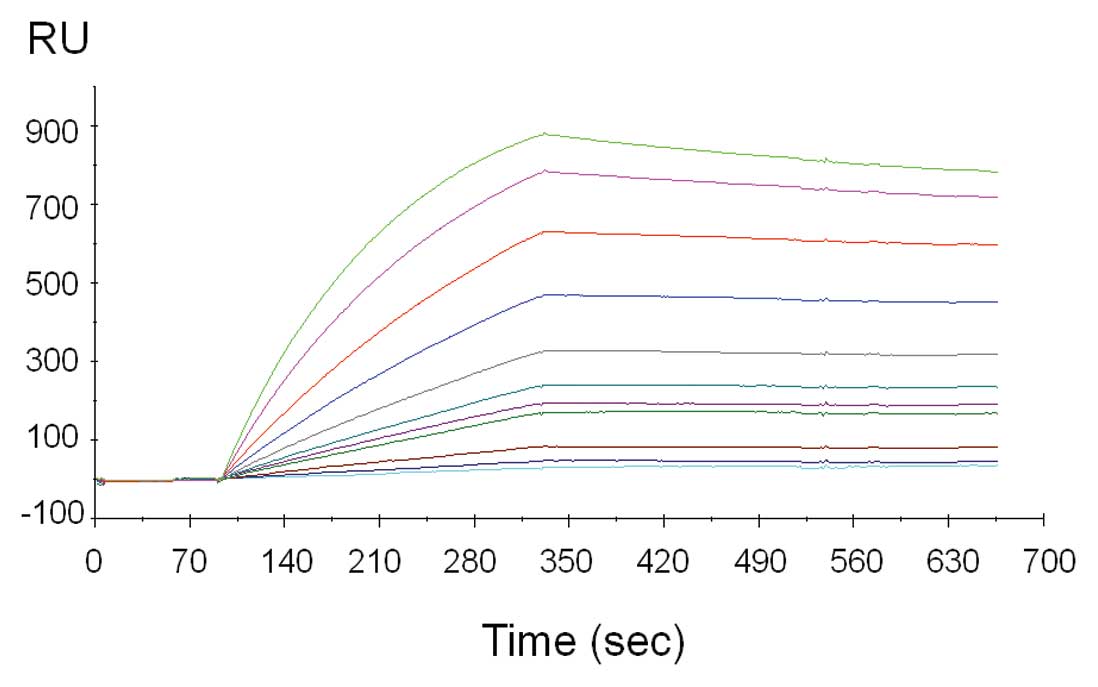
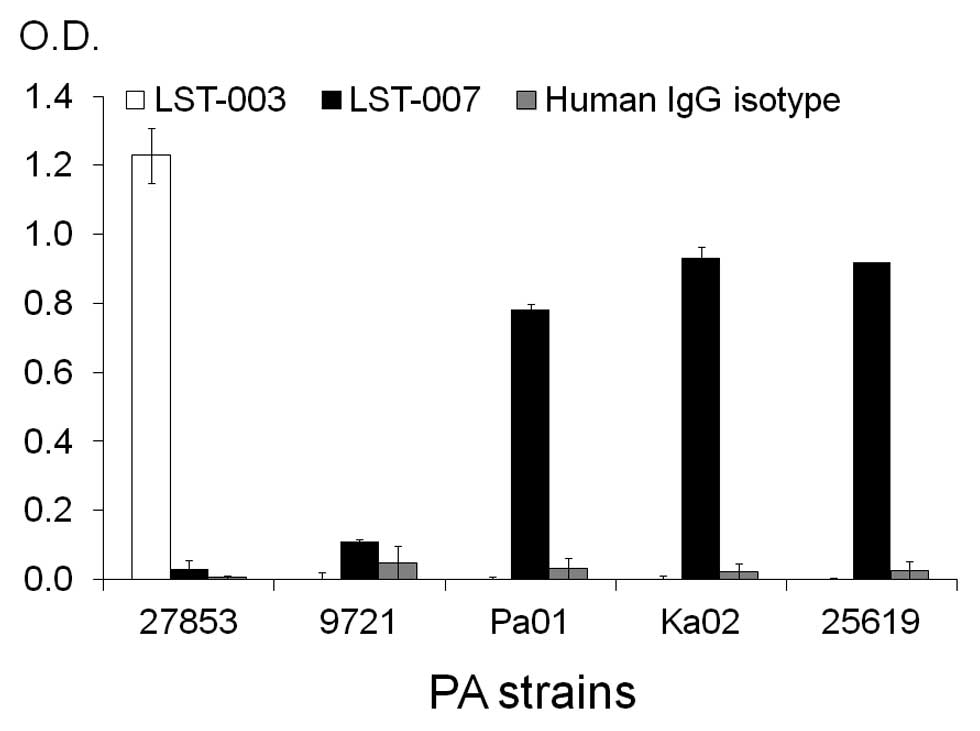
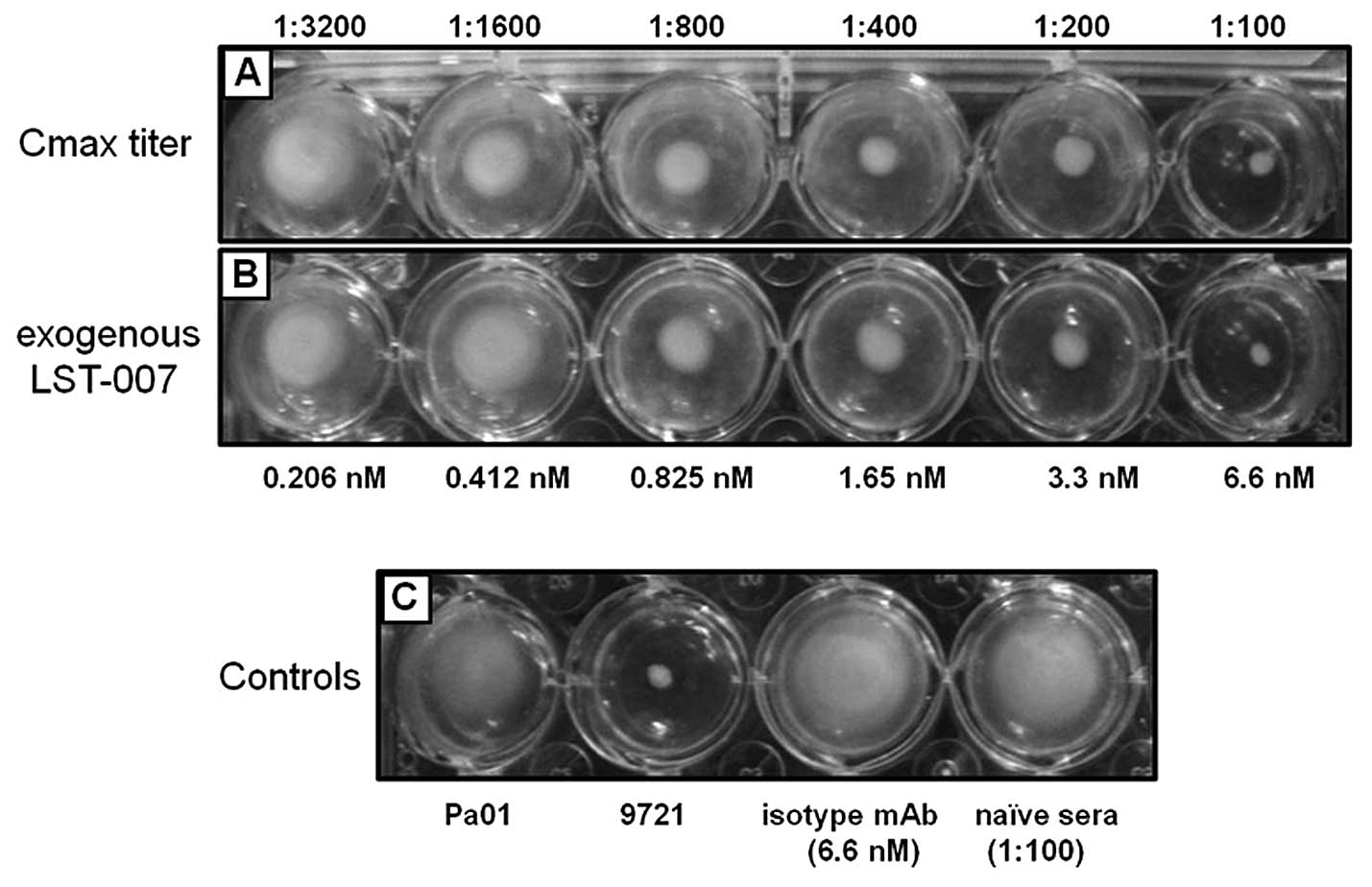
|
1.
|
HW BoucherGH TalbotJS BradleyBad bugs, no
drugs: no ESKAPE! An update from the Infectious Diseases Society of
AmericaClin Infect Dis481122009
|
|
2.
|
ECDC/EMEA JointTechnical ReportThe
Bacterial Challenge: Time to React. A call to narrow the gap
between multidrug-resistant bacteria in the EU and the development
of new antibacterial agents1422009EMEA doc. ref. EMEA/576176/2009
Stockholm, September 2009.10.2900/2518
|
|
3.
|
JA DriscollSL BrodyMH KollefThe
epidemiology, pathogenesis and treatment of Pseudomonas
aeruginosa
infectionsDrugs67351368200710.2165/00003495-200767030-0000317335295
|
|
4.
|
AS LevinMS OliveiraThe challenge of
multidrug resistance: the treatment of gram-negative rod
infectionsShock303033200810.1097/SHK.0b013e3181819cb818704012
|
|
5.
|
S FujitaniHY SunVL YuJA
WeingartenPneumonia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: part I:
epidemiology, clinical diagnosis, and sourceChest1399099192011
|
|
6.
|
A PallettK HandComplicated urinary tract
infections: practical solutions for the treatment of multiresistant
Gram-negative bacteriaJ Antimicrob
Chemother65S25S33201010.1093/jac/dkq29820876625
|
|
7.
|
PA FlumeBP O’SullivanKA RobinsonCystic
fibrosis pulmonary guidelines: chronic medications for maintenance
of lung healthAm J Respir Crit Care
Med176957969200710.1164/rccm.200705-664OC17761616
|
|
8.
|
M Cohen-CymberknohD ShoseyovE
KeremManaging cystic fibrosis: strategies that increase life
expectancy and improve quality of lifeAm J Respir Crit Care
Med18314631471201110.1164/rccm.201009-1478CI21330455
|
|
9.
|
N HoibyRecent advances in the treatment of
Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in cystic fibrosisBMC
Med9322011
|
|
10.
|
CK StoverXQ PhamAL ErwinComplete genome
sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, an opportunistic
pathogenNature406959964200010.1038/3502307910984043
|
|
11.
|
CR DeanMA VisalliSJ ProjanPE SumPA
BradfordEfflux-mediated resistance to tigecycline (GAR-936) in
Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1Antimicrob Agents
Chemother47972978200310.1128/AAC.47.3.972-978.200312604529
|
|
12.
|
J ChastreJY FagonVentilator-associated
pneumoniaAm J Resp Crit Care
Med165867903200210.1164/ajrccm.165.7.2105078
|
|
13.
|
L CegelskiGR MarshallGR EldridgeSJ
HultgrenThe biology and future prospects of antivirulence
therapiesNature Rev
Microbiol61727200810.1038/nrmicro181818079741
|
|
14.
|
M ChartrainL ChuDevelopment and production
of commercial therapeutic monoclonal antibodies in mammalian cell
expression systems: an overview of the current upstream
methodologiesCurr Pharm
Biotechnol9447467200810.2174/138920108786786367
|
|
15.
|
M De JesusFM WurmManufacturing recombinant
proteins in kg-ton quantities using animal cells in bioreactorsEur
J Pharm Biopharm78184188201121256214
|
|
16.
|
M BaerT SawaP FlynnAn engineered human
antibody fab fragment specific for Pseudomonas aeruginosa
PcrV antigen has potent antibacterial activityInfect
Immun7710831090200910.1128/IAI.00815-0819103766
|
|
17.
|
T SecherL FauconnierA
SzadeAnti-Pseudomonas aeruginosa serotype O11 LPS
immunoglobulin M monoclonal antibody panobacumab (KBPA101) confers
protection in a murine model of acute lung infectionJ Antimicrob
Chemother66110011092011
|
|
18.
|
MP HornAW ZuercherMA ImbodenPreclinical in
vitro and in vivo characterization of the fully human monoclonal
IgM antibody KBPA101 specific for Pseudomonas aeruginosa
serotype IATS-O11Antimicrob Agents
Chemother5423382344201010.1128/AAC.01142-0920308370
|
|
19.
|
Q LuJJ RoubyPF LaterrePharmacokinetics and
safety of panobacumab: specific adjunctive immunotherapy in
critical patients with nosocomial Pseudomonas aeruginosa O11
pneumoniaJ Antimicrob
Chemother6611101116201110.1093/jac/dkr04621398296
|
|
20.
|
CE MillaFJ AccursoJ ChmielModulating
Pseudomonas aeruginosa chronic inflammation with the
anti-PcrV antibody KB001: Results of a pilot clinical and
pharmacodynamic study in subjects with cystic fibrosisAm J Respir
Crit Care Med181A18452010
|
|
21.
|
FA SamateyK ImadaS NagashimaStructure of
the bacterial flagellar protofilament and implications for a switch
for supercoilingNature410331337200110.1038/3506650411268201
|
|
22.
|
K YonekuraS Maki-YonekuraK NambaComplete
atomic model of the bacterial flagellar filament by electron
cryomicroscopyNature424643650200310.1038/nature0183012904785
|
|
23.
|
KD SmithE Andersen-NissenF
HayashiToll-like receptor 5 recognizes a conserved site on
flagellin required for protofilament formation and bacterial
motilityNat Immunol412471253200310.1038/ni101114625549
|
|
24.
|
RA AnsorgME KnocheAF SpiesCJ
KrausDifferentiation of the major flagellar antigens of
Pseudomonas aeruginosa by the slide coagglutination
techniqueJ Clin Microbiol20848819846430957
|
|
25.
|
TJ MontieTR AndersonEnzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay for detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
H (flagellar) antigenEur J Clin Microbiol Infect
Dis7256260198810.1007/BF019630972455641
|
|
26.
|
JA MorganNF BellinghamC WinstanleyMA
OusleyCA HartJR SaundersComparison of flagellin genes from clinical
and environmental Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolatesAppl
Environ Microbiol6511751179199910049879
|
|
27.
|
MJ RosokMR StebbinsK ConnellyME LostromAW
SiadakGeneration and characterization of murine anti flagellum
monoclonal antibodies that are protective against lethal challenge
with Pseudomonas aeruginosaInfect Immun58381938281990
|
|
28.
|
H OchiH OhtsukaS YokotaInhibitory activity
on bacterial motility and in vivo protective activity of human
monoclonal antibodies against flagella of Pseudomonas
aeruginosaInfect Immun5955055419911898908
|
|
29.
|
WJ LandspergerKD Kelly-WintenbergTC
MontieInhibition of bacterial motility with human antiflagellar
monoclonal antibodies attenuates Pseudomonas
aeruginosa-induced pneumonia in the immunocompetent ratInfect
Immun624825483019947927761
|
|
30.
|
LF NevilleY BarneaO Hammer-MunzAntibodies
raised against N’-terminal Pseudomonas aeruginosa flagellin
prevent mortality in lethal murine models of infectionInt J Mol
Med161651712005
|
|
31.
|
Y BarneaY CarmeliLF NevilleTherapy with
anti-flagellin A monoclonal antibody limits Pseudomonas
aeruginosa invasiveness in a mouse burn wound sepsis
modelBurns35390396200910.1016/j.burns.2008.08.01418951715
|
|
32.
|
R ErenD LandsteinD TerkieltaubPreclinical
evaluation of two neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies against
hepatitis C virus (HCV): a potential treatment to prevent HCV
reinfection in liver transplant patientsJ
Virol8026542664200610.1128/JVI.80.6.2654-2664.2006
|
|
33.
|
V NeuhoffN AroldD TaubeW EhrhardtImproved
staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels including isoelectric
focusing gels with clear background at nanogram sensitivity using
Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 and
R-250Electrophoresis9255262198810.1002/elps.1150090603
|
|
34.
|
MH RashidA KornbergInorganic polyphosphate
is needed for swimming, swarming, and twitching motilities of
Pseudomonas aeruginosaProc Natl Acad Sci
USA9748854890200010.1073/pnas.06003009710758151
|
|
35.
|
CA BoswellDB TesarK MukhyalaFP TheilPJ
FielderLA KhawliEffects of charge on antibody tissue distribution
and pharmacokineticsBioconjug
Chem2121532163201010.1021/bc100261d21053952
|
|
36.
|
Y VugmeysterD DeFrancoDD PittmanX
XuPharmacokinetics and lung distribution of a humanized anti-RAGE
antibody in wild-type and RAGE−/ −
miceMAbs2571575201010.4161/mabs.2.5.1308920978371
|
|
37.
|
L Freire-MoranB AronssonC ManzCritical
shortage of new antibiotics in development against
multidrug-resistant bacteria - time to react is nowDrug Resist
Updat14118124201110.1016/j.drup.2011.02.00321435939
|
|
38.
|
MG PageJ HeimProspects for the next
anti-Pseudomonas drugCurr Opin
Pharmacol9558565200910.1016/j.coph.2009.08.00619748829
|
|
39.
|
GH TalbotWhat is in the pipeline for
Gram-negative pathogens?Expert Rev Anti Infect
Ther63949200810.1586/14787210.6.1.3918251663
|
|
40.
|
JW MoutonPG AmbroseR CantonConserving
antibiotics for the future: New ways to use old and new drugs from
a pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic perspectiveDrug Resist
Updat14107117201110.1016/j.drup.2011.02.00521440486
|
|
41.
|
JM ReichertMonoclonal antibodies as
innovative therapeuticsCurr Pharm
Biotechnol9423430200810.2174/13892010878678635819075682
|
|
42.
|
I LowyDC MolrineBA LeavTreatment with
monoclonal antibodies against Clostridium difficile toxinsN
Engl J Med362197205201010.1056/NEJMoa090763520089970
|
|
43.
|
EL LopezMM ContriniE GlatsteinSafety and
pharmacokinetics of urtoxazumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody,
against Shiga-like toxin 2 in healthy adults and in pediatric
patients infected with Shiga-like toxin-producing Escherichia
coliAntimicrob Agents
Chemother54239243201010.1128/AAC.00343-09
|
|
44.
|
A VermaM SchirmSK AroraP ThibaultSM LoganR
RamphalGlycosylation of b-type flagellin of Pseudomonas
aeruginosa: structural and genetic basisJ
Bacteriol18843954403200610.1128/JB.01642-0516740946
|
|
45.
|
KK ShanksW GuangKC KimEP
LillehojInterleukin-8 production by human airway epithelial cells
in response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates
expressing type a or type b flagellinsClin Vaccine
Immunol1711961202201010.1128/CVI.00167-1020592113
|
|
46.
|
D BannisterB PopovicS SridharanEpitope
mapping and key amino acid identification of anti-CD22 immunotoxin
CAT-8015 using hybrid β-lactamase displayProtein Eng Des
Sel24351360201121159620
|
|
47.
|
RC BoneMonoclonal antibodies to endotoxin.
New allies against
sepsis?JAMA26611251126199110.1001/jama.1991.034700800950381865548
|
|
48.
|
RC BoneWhy sepsis trials
failJAMA276565566199610.1001/jama.1996.035400700610328709407
|
|
49.
|
D HolmesBuy buy bispecific antibodiesNat
Rev Drug Discov10798800201110.1038/nrd358122037028
|
|
50.
|
AT GewirtzM Vijay-KumarSR BrantRH DuerrDL
NicolaeJH ChoDominant-negative TLR5 polymorphism reduces adaptive
immune response to flagellin and negatively associates with Crohn’s
diseaseAm J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol290G1157G1163200616439468
|
|
51.
|
CJ BlohmkeJ ParkAF HirschfeldTLR5 as an
anti-inflammatory target and modifier gene in cystic fibrosisJ
Immunol18577317738201010.4049/jimmunol.100151321068401
|
|
52.
|
TR HawnH WuJM GrossmanBH HahnBP TsaoA
AderemA stop codon polymorphism of Toll-like receptor 5 is
associated with resistance to systemic lupus erythematosusProc Natl
Acad Sci USA1021059310597200510.1073/pnas.050116510216027372
|
|
53.
|
E NilssonA LarssonHV OlesenPE WejakerH
KollbergGood effect of IgY against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
infections in cystic fibrosis patientsPediatr
Pulmonol438928992008
|
|
54.
|
E NilssonA AminiB WretlindA
LarssonPseudomonas aeruginosa infections are prevented in
cystic fibrosis patients by avian antibodies binding Pseudomonas
aeruginosa flagellinJ Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life
Sci8567580200710.1016/j.jchromb.2007.05.029
|