Introduction
Obesity is a serious health problem worldwide,
because it is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes,
hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and cancer (1). Overaccumulation of adipose tissue is
the fundamental phenomenon of obesity (2,3).
Therefore, the understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying
adipose tissue formation, i.e., adipogenesis, is required for the
effective prevention and treatment of obesity. Adipogenesis is a
complex process accompanying the differentiation of preadipocytes
into adipocytes followed by the intracellular fat accumulation
(4–6). 3T3-L1 preadipocyte has been used as
an in vitro model of adipogenesis for decades (7), and its adipogenic differentiation
was mediated by the upregulations of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)γ and CCAAT/enhancer binding
protein (C/EBP)α followed by the inductions of lipid metabolizing
enzymes such as fatty acid binding protein (FABP)4, lipoprotein
lipase (LPL) and fatty acid synthase (4–6).
Vitamin D is produced from 7-dehydrocholesterol in
the skin by ultraviolet radiation and converted in the liver to
25-hydroxyvitamin D, followed by its conversion to
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25(OH)2D3) in kidney and other tissues.
1,25(OH)2D3, the bioactive form of vitamin D, plays multiple
physiological roles including the maintenance of calcium and
phosphorus levels for bone homeostasis (8). Accumulating evidence suggests that a
potential link exists between vitamin D deficiency and obesity in
human population (9), and vitamin
D deficiency was proposed as one of the causes of common obesity
(10). Anti-obesity effect of
vitamin D was suggested by the finding that 1,25(OH)2D3 efficiently
inhibit adipogenesis at nanomolar concentration (11). 1,25(OH)2D3, the bioactive form of
vitamin D, was found to inhibit the adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells
and primary cultures of mouse epididymal fat (12). It is necessary to understand the
anti-adipogenic mechanism of vitamin D for the effective prevention
and treatment of obesity, however, the molecular mechanism for the
anti-adipogenic effect of 1,25(OH)2D3 was not fully elucidated
until now.
As a possible candidate of the mediator for the
anti-adipogenic effect of vitamin D, we focused on the
wingless-type MMTV integration site (WNT)/β-catenin pathway. The
WNT/β-catenin pathway is known to be involved in various cellular
processes such as differentiation, development, proliferation and
tumorigenesis (13–15). Recently, an additional function of
the WNT/β-catenin pathway was identified: the negative regulator of
adipogenesis (16,17). When the WNT/β-catenin pathway is
inactive, β-catenin is proteasomally degraded by the destruction
complex composed of adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), glycogen
synthase kinase (GSK)3β and AXIN. Activation of the WNT/β-catenin
pathway enhances the interaction between disheveled (DVL)s and
AXIN. Consequently, the APC-GSK3β-AXIN destruction complex is
disrupted, thereby increasing stabilization and nuclear
translocation of β-catenin (18,19). In the nucleus, β-catenin induces
the expression of cyclin D1, c-Myc and PPARδ, which have been
reported to inhibit PPARγ, a major adipogenic transcription factor
(20–23). Until now, no study reported the
association between the anti-obesity effects of vitamin D and the
WNT/β-catenin pathway. In this study, we found that the
anti-adipogenic effect of 1,25(OH)2D3 was accompanied by the
maintenance of the WNT/β-catenin pathway signaling, which was
normally downregulated during adipogenesis.
Materials and methods
Chemicals and reagents
Cell culture reagents were obtained from Life
Technologies Inc. (Grand Island, NY, USA). Anti-PPARγ, anti-FABP4,
anti-phospho-GSK3β and anti-GSK3β antibodies and secondary antibody
were obtained from Cell Signaling (Beverly, MA, USA). Anti-C/EBPα,
anti-DVL2, anti-β actin and anti-TBP antibody were purchased from
Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. (Santa Cruz, CA, USA).
Anti-β-catenin antibody was purchased from BD Transduction
Laboratories (Lexington, KY, USA). All other chemicals including
1,25(OH)2D3 were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO,
USA).
Cell culture and differentiation
3T3-L1 preadipocytes were purchased from the
American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA) and were
subcultured every 2 or 3 days. The cells were seeded in 6-well
plates at a density of 1.5×105 cells/well. Two days
after reaching confluence (day 0), the 3T3-L1 cells were
differentiated in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM)
containing 1 μg/ml insulin, 0.25 μM dexamethasone, 0.5 mM
3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine and 10% fetal bovine serum
(differentiation-induction medium) for 2 days. The cells were then
maintained in DMEM containing 1 μg/ml insulin and 10% fetal bovine
serum (differentiation maintenance medium). The differentiation
maintenance medium was changed every 2 days until the cells were
harvested. To test its effects on adipo-genesis, 1,25(OH)2D3 was
added to the differentiation induction medium and differentiation
maintenance medium until the cells were harvested. Lipid droplets
in the cells were stained with Oil Red O as previously described
(24).
Real-time polymerase chain reaction
(PCR)
Cells were harvested, and total RNA was extracted
using an RNeasy kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). One microgram of
total RNA was reverse-transcribed at 37°C using the cDNA Reverse
Transcription kit (Applied Biosystems, Inc., Foster City, CA, USA).
Briefly, the reaction was performed in a final volume of 20 μl,
which included reverse transcriptase reaction buffer, 100 mM dNTP
mix, random primers, MultiScribe™ Reverse Transcriptase, RNase
inhibitor and total RNA. The reaction mixtures were heated at 25°C
for 10 min, 37°C for 120 min and 85°C for 5 min. Real-time PCR was
performed using the 7000 Real-Time PCR system (Applied Biosystems)
in a final volume of 20 μl, which included TaqMan gene expression
master mix, 250 nM of TaqMan probe, an optimized concentration of
each primer, and 2 μl of the reverse transcription product
containing cDNA. The reaction mixtures were preheated at 95°C for
10 min to activate the enzyme and then subjected to 40 cycles of
melting at 95°C for 15 sec and annealing/extension at 60°C for 1
min. The assay-on-demand gene expression products (Applied
Biosystems, Inc.) were used to evaluate the mRNA levels of PPARγ
(Mm00440945_m1), C/EBPα (Mm01265914_ s1), FABP4 (Mm00445880_m1),
LPL (Mm00434764_m1), WNT10B (Mm00442104_m1), LRP6 (Mm00999795_m1),
DVL2 (Mm00432899_m1), GSK3β (Mm00444911_m1) as well as the level of
18S rRNA (Hs99999901_s1). The 18S rRNA was used as an internal
control as previously described (25). For each sample, the mRNA level was
normalized against the level of 18S rRNA, and the ratio of
normalized mRNA to the preadipocytes (day 0) was determined using
the comparative Ct method (26).
Protein extraction and western
blotting
Cells were harvested using a cell scraper and lysed
with ice-cold RIPA buffer containing 25 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.6), 150
mM NaCl, 1% Nonidet P-40, 1% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS and a
protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma-Aldrich) to obtain total cell
lysates. The total cell lysates were then centrifuged at 20,000 × g
for 20 min at 4°C to remove the insoluble materials. The protein
concentrations were determined using a BCA protein assay kit
(Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA). Fifty micrograms of each protein
extract was separated using 12% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
and electrotransferred to nitrocellulose membranes at 150 mA for 1
h. The membranes were then blocked for 2 h at room temperature with
phosphate buffered saline containing 5% skim milk and 0.1%
Tween-20, and incubated with 1:1,000-dilutions of primary antibody
overnight at 4°C followed by a 1:1,000-dilution of horseradish
peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody for 1 h at room
temperature. Peroxidase activity was visualized using an ECL kit
(Pierce). β-actin was used as a loading control for cytosolic
proteins.
Analysis of nuclear β-catenin level
Cells were harvested using a cell scraper and then
nuclear extracts were prepared using a nuclear extract kit (Active
Motif, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Protein concentrations in the nuclear
extracts were determined using a BCA protein assay kit (Pierce).
Ten micrograms of nuclear protein were separated using 12%
polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and analyzed by western blotting
using an anti-β-catenin antibody followed by a secondary antibody.
TATA-box binding protein (TBP) was used as a loading control for
nuclear proteins.
Statistical analysis
All data are expressed as means ± standard
deviations from at least three replicate experiments. Statistically
significant differences between treated and untreated samples were
detected using an unpaired t-test. All analyses were performed
using SPSS ver. 19 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA).
Results
Inhibitory effects of 1,25(OH)2D3 on the
adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells
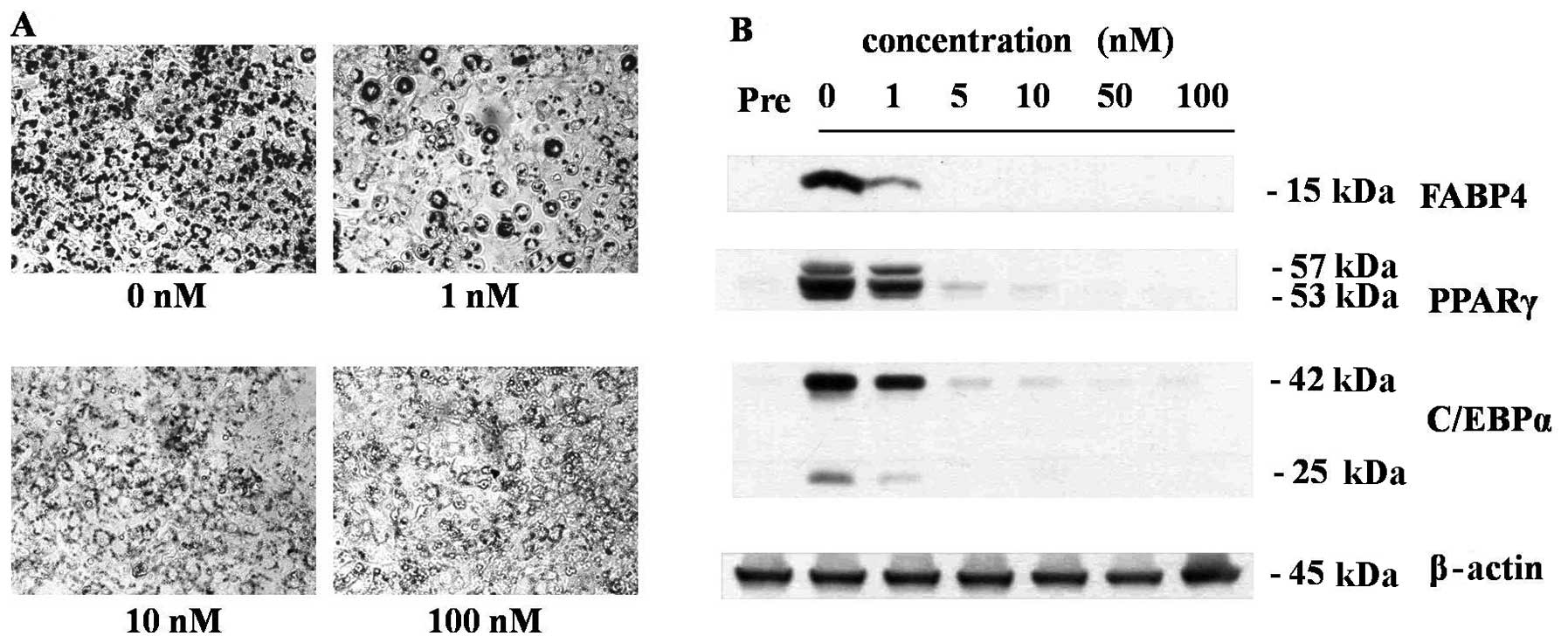
As shown in Fig.
1, treatments of nanomolar concentrations of 1,25(OH)2D3 during
the adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells effectively inhibited the
adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells in a dose-dependent manner. At the
concentration of 10 nM, 1,25(OH)2D3 completely inhibited lipid
droplet formation (Fig. 1A) as
well as the expressions of adipocyte maker protein, FABP4, PPARγ
and C/EBPα (Fig. 1B). Because 10
nM is the optimal anti-adipogenic concentration of 1,25(OH)2D3, all
further experiments were conducted at this concentration. In
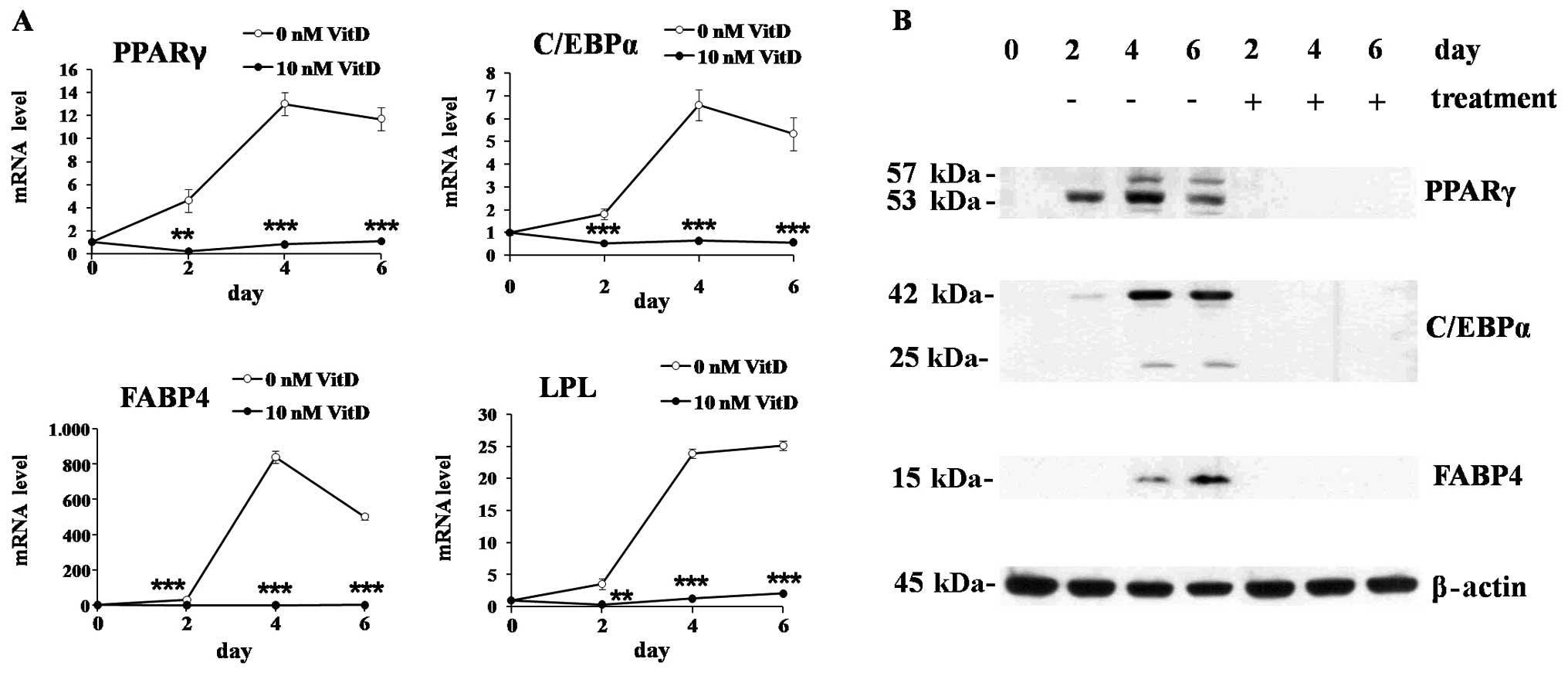
time-course experiments, 1,25(OH)2D3 treatment significantly
suppressed the mRNA expression of major transcription factors of
adipogenesis, PPARγ and C/EBPα, as well as the proteins involved in
lipid metabolism, FABP4 and LPL (Fig.
2A). The protein expression was also suppressed by 1,25(OH)2D3
showing similar patterns with mRNA expression (Fig. 2B).
Maintenance of the WNT signaling by
1,25(OH)2D3
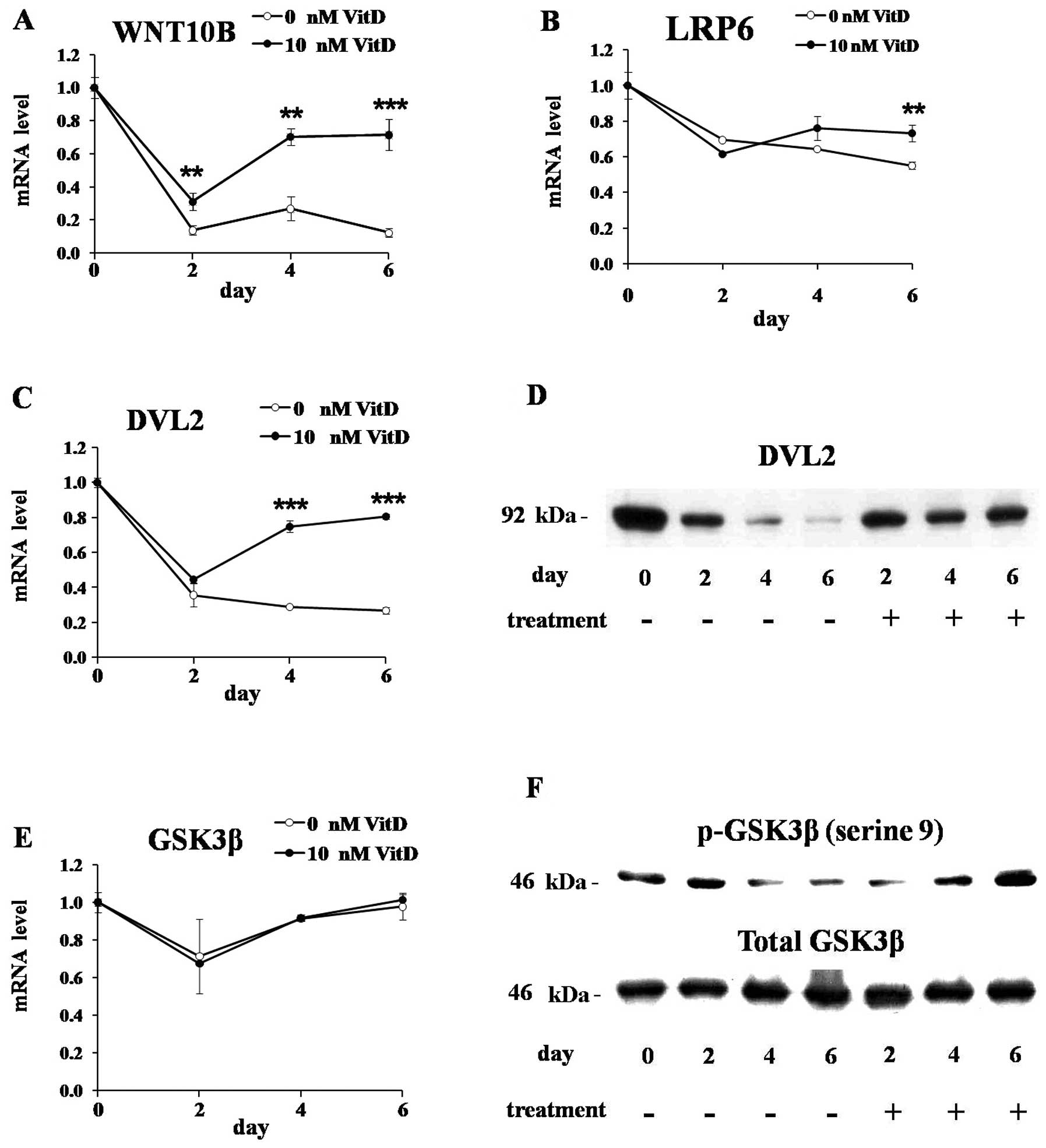
To investigate the effects of 1,25(OH)2D3 on the WNT
signaling, we measured the expressions of the genes involved in the
WNT signaling in 3T3-L1 cells differentiated for 0, 2, 4 and 6 days
in the presence or absence of 1,25(OH)2D3. The mRNA level of WNT10B
was markedly downregulated during adipogenesis of untreated cells,
but the treatment of 1,25(OH)2D3 maintained its expression levels
(Fig. 3A). The mRNA level of LRP6
was mildly decreased during adipogenesis of untreated cells, but
1,25(OH)2D3 maintained its level (Fig. 3B). DVL2 is reported to be
activated by WNT signaling and prevent the formation of the
APC-GSK3β-AXIN destruction complex which degrade β-catenin
(27). The mRNA and protein
levels of DVL2 were markedly downregulated during adipogenesis of
untreated cells, but 1,25(OH)2D3 maintained their mRNA and protein
levels during adipogenesis (Fig. 3C
and D). During adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells, treated or
untreated, the mRNA and protein levels of GSK3β were not
significantly changed (Fig. 3E and
F, lower panel), but its phosphorylation on serine 9 residue
was significantly decreased in untreated cells (Fig. 3F, upper panel). 1,25(OH)2D3
efficiently elevated GSK3β phosphorylation even though it has no
effects on total GSK3β protein levels as well as its mRNA levels.
GSK3β is a component of APC-GSK3β-AXIN destruction complex which is
involved in the proteolytic degradation of β-catenin, and it is
also well-known that GSK3β is inactivated by its phosphorylation
(15,19). We found that GSK3β was activated
by its dephosphorylation during adipogenesis of untreated 3T3-L1
cells, but the treatment of 1,25(OH)2D3 efficiently elevated its
phosphorylation levels resulting in its inactivation.
Maintenance of nuclear β-catenin levels
by 1,25(OH)2D3
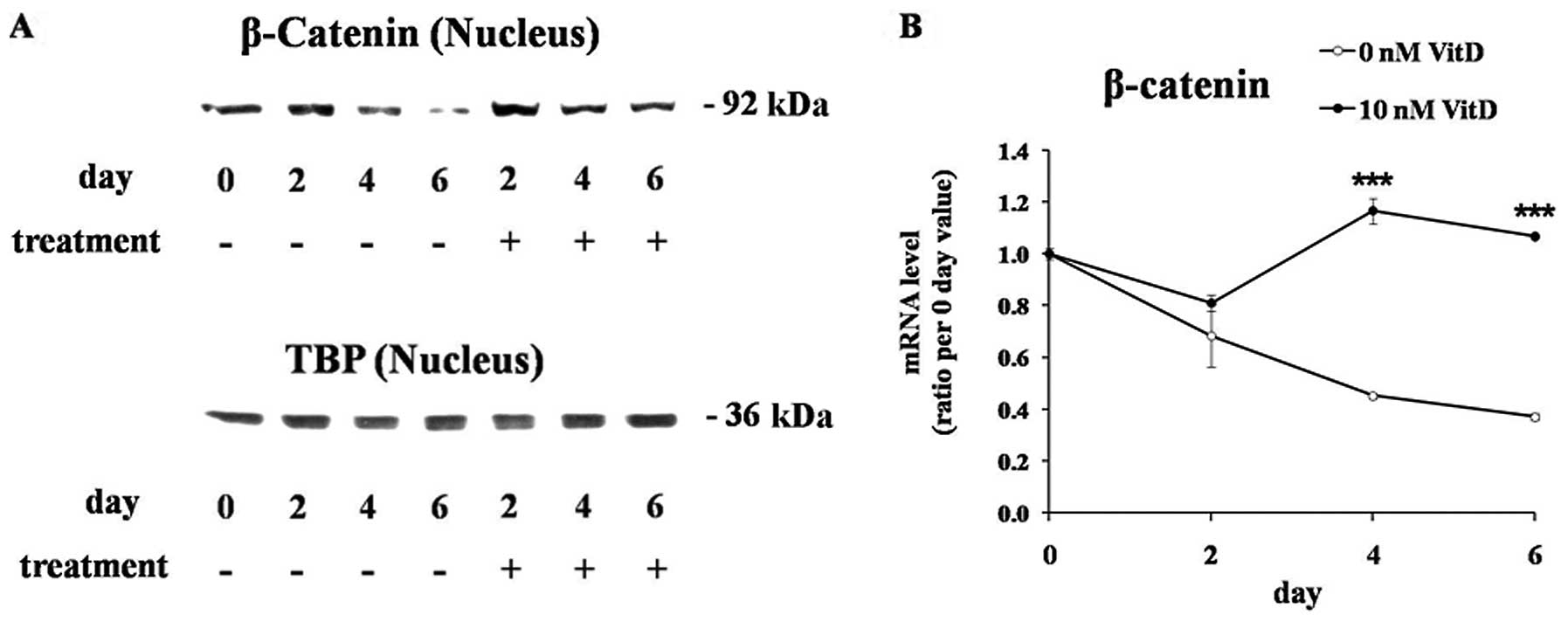
β-catenin is a transcriptional cofactor which plays
a central role in the WNT/β-catenin pathway (20). The nuclear level of β-catenin
protein was significantly reduced during adipogenesis of untreated
cells, but 1,25(OH)2D3 treatment maintained the nuclear β-catenin
levels (Fig. 4A). TBP protein was
used as an endogenous control for the loading of equal amounts of
the nuclear protein. The levels of the β-catenin mRNA, which were
significantly downregulated during the adipogenesis of untreated
cells, were also maintained by 1,25(OH)2D3 treatment (Fig. 4B).
Discussion
The effects of vitamin D on WNT signaling in
relation to adipo-genesis were not reported until now. The relation
of vitamin D and WNT signaling has only been reported in relation
to cancer: vitamin D was reported to have a protective effect
against colorectal cancer by its inhibitory action on the
WNT/β-catenin pathway (28). In
the present study on the anti-adipogenic mechanisms of vitamin D,
our interest in the WNT/β-catenin pathway was prompted by recent
findings of its role as a negative regulator of adipogenesis
(16,17). WNT signaling was reported to
inhibit adipogenesis (29), and
was found to mediate the anti-adipogenic effects of some cytokines
and chemical compounds: anti-adipogenic cytokines, tumor necrosis
factor α and interleukin-6 inhibit adipogenesis by the activation
of WNT signaling (25).
Bisindoylmaleimide I, a specific inhibitor of protein kinase C,
inhibits adipocyte differentiation through the activation of the
WNT signaling (30), and
curcumin, a component of curry, inhibits adipogenesis via the
WNT/β-catenin pathway (31).
In this study, the induction of PPARγ, a major
transcription factor of adipogenesis, was effectively suppressed by
1,25(OH)2D3 (Figs. 1 and 2), while the nuclear level of β-catenin
was maintained by 1,25(OH)2D3 during the adipogenesis of 3T3-L1
cells (Fig. 4A). It is well-known
that the WNT singling upregulates β-catenin at post-translation
levels by protein stabilization (18,19). Few reports exist on the
transcriptional regulation of β-catenin during adipogenesis, and it
is interesting that 1,25(OH)2D3 also maintained mRNA levels of
β-catenin which were decreased during adipogenesis of untreated
cells (Fig. 4B). Even though
further study is necessary to elucidate the transcriptional
modulation of β-catenin by 1,25(OH)2D3, these experimental data can
provide an explanation for the anti-adipogenic mechanism of
1,25(OH)2D3, considering that β-catenin inhibits PPARγ directly
(32), and indirectly by inducing
its target genes (21–23). Our data suggest that the
anti-adipogenic effect of 1,25(OH)2D3 is mediated by the
maintenance of the nuclear β-catenin levels, which results in the
suppression of PPARγ, the major adipogenic transcription factor
playing a central role in the expressions of lipid-metabolizing
enzymes (4–6,33).
Among members of WNT family, WNT10B is most closely
related to adipogenesis and obesity, and previous studies have
established the role of WNT10B as an endogenous regulator of
adipogenesis (34). WNT10B
transgenic mice which express WNT10B from the adipocyte-specific
promoter, showed 50% reduction of the total body fat and resisted
the accumulation of adipose tissue when fed a high fat diet
(35). Human obesity phenotype in
various populations were reported to be associated with the genetic
polymorphisms of WNT10B (36,37). In the present study, it was found
that 1,25(OH)2D3 maintained the expression level of WNT10B, a WNT
family member most closely related to adipogenesis and obesity
(Fig. 3A).
In conclusion, 1,25(OH)2D3 maintained WNT10B
expression levels resulting in the maintenance of the nuclear
levels of β-catenin which is a suppressor of adipogenesis,
suggesting that the WNT/β-catenin pathway plays a role as a
mediator for the anti-adipogenic and anti-obesity effects of
vitamin D.
Abbreviations:
|
APC
|
adenomatous polyposis coli;
|
|
C/EBP
|
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein;
|
|
DVL
|
disheveled; 1,25(OH)2D3,
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3;
|
|
FABP
|
fatty acid binding protein;
|
|
GSK
|
glycogen synthase kinase;
|
|
LPL
|
lipoprotein lipase;
|
|
LRP
|
low density lipoprotein
receptor-related protein;
|
|
PPAR
|
peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor;
|
|
WNT
|
wingless-type MMTV integration
site
|
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Basic
Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation
of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and
Technology (2010-0007729).
References
|
1.
|
A MustJ SpadanoEH CoakleyAE FieldG
ColditzWH DietzThe disease burden associated with overweight and
obesityJAMA28215231529199910.1001/jama.282.16.152310546691
|
|
2.
|
FX Pi-SunyerThe obesity epidemic:
pathophysiology and consequences of obesityObes Res10Suppl
2S97S104200210.1038/oby.2002.20212490658
|
|
3.
|
BM SpiegelmanJS FlierObesity and the
regulation of energy
balanceCell104531543200110.1016/S0092-8674(01)00240-911239410
|
|
4.
|
SR FarmerTranscriptional control of
adipocyte formationCell
Metab4263273200610.1016/j.cmet.2006.07.00117011499
|
|
5.
|
ED RosenOA MacDougaldAdipocyte
differentiation from the inside outNat Rev Mol Cell
Biol7885896200610.1038/nrm206617139329
|
|
6.
|
ED RosenCJ WalkeyP PuigserverBM
SpiegelmanTranscriptional regulation of adipogenesisGenes
Dev1412931307200010837022
|
|
7.
|
H GreenM MeuthAn established pre-adipose
cell line and its differentiation in
cultureCell3127133197410.1016/0092-8674(74)90116-04426090
|
|
8.
|
AL SuttonPN MacDonaldVitamin D: more than
a ‘bone-afide’ hormoneMol Endocrinol177777912003
|
|
9.
|
LA MartiniRJ WoodVitamin D status and the
metabolic syndromeNutr
Rev64479486200610.1111/j.1753-4887.2006.tb00180.x17131943
|
|
10.
|
YJ FossVitamin D deficiency is the cause
of common obesityMed
Hypotheses72314321200910.1016/j.mehy.2008.10.00519054627
|
|
11.
|
Y IshidaH TaniguchiS BabaPossible
involvement of 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in proliferation and
differentiation of 3T3-L1 cellsBiochem Biophys Res
Commun15111221127198810.1016/S0006-291X(88)80482-03355544
|
|
12.
|
J KongYC LiMolecular mechanism of
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibition of adipogenesis in 3T3-L1
cellsAm J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab290E916E924200610.1152/ajpendo.00410.200516368784
|
|
13.
|
RT MoonB BowermanM BoutrosN PerrimonThe
promise and perils of Wnt signaling through
beta-cateninScience29616441646200210.1126/science.107154912040179
|
|
14.
|
MT VeemanJD AxelrodRT MoonA second
canonFunctions and mechanisms of beta-catenin-independent Wnt
signaling Dev Cell53673772003
|
|
15.
|
A WodarzR NusseMechanisms of Wnt signaling
in developmentAnnu Rev Cell Dev
Biol145988199810.1146/annurev.cellbio.14.1.59
|
|
16.
|
CN BennettSE RossKA LongoL BajnokN
HematiKW JohnsonSD HarrisonOA MacDougaldRegulation of Wnt signaling
during adipogenesisJ Biol
Chem2773099831004200210.1074/jbc.M20452720012055200
|
|
17.
|
TC PrestwichOA MacDougaldWnt/beta-catenin
signaling in adipogenesis and metabolismCurr Opin Cell
Biol19612617200710.1016/j.ceb.2007.09.01417997088
|
|
18.
|
KM CadiganYI LiuWnt signaling: complexity
at the surfaceJ Cell Sci119395402200610.1242/jcs.0282616443747
|
|
19.
|
J HuelskenJ BehrensThe Wnt signalling
pathwayJ Cell Sci11539773978200210.1242/jcs.0008912356903
|
|
20.
|
J BehrensJP von KriesM KuhlL BruhnD
WedlichR GrosschedlW BirchmeierFunctional interaction of
beta-catenin with the transcription factor
LEF-1Nature382638642199610.1038/382638a08757136
|
|
21.
|
SO FreytagTJ GeddesReciprocal regulation
of adipogenesis by Myc and C/EBP
alphaScience256379382199210.1126/science.256.5055.3791566086
|
|
22.
|
M FuM RaoT BourasC WangK WuX ZhangZ LiTP
YaoRG PestellCyclin D1 inhibits peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor gamma-mediated adipogenesis through histone deacetylase
recruitmentJ Biol Chem2801693416941200510.1074/jbc.M500403200
|
|
23.
|
Y ShiM HonRM EvansThe peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor delta, an integrator of
transcriptional repression and nuclear receptor signalingProc Natl
Acad Sci USA9926132618200210.1073/pnas.05270709911867749
|
|
24.
|
R KasturiVC JoshiHormonal regulation of
stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase activity and lipogenesis during
adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cellsJ Biol
Chem257122241223019826181064
|
|
25.
|
B GustafsonU SmithCytokines promote Wnt
signaling and inflammation and impair the normal differentiation
and lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytesJ Biol
Chem28195079516200610.1074/jbc.M51207720016464856
|
|
26.
|
KJ LivakTD SchmittgenAnalysis of relative
gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the
2(-Delta Delta C(T))
methodMethods25402408200110.1006/meth.2001.126211846609
|
|
27.
|
C GaoYG ChenDishevelled: the hub of Wnt
signalingCell
Signal22717727201010.1016/j.cellsig.2009.11.02120006983
|
|
28.
|
N Pendas-FrancoO AguileraF PereiraJM
Gonzalez-SanchoA MunozVitamin D and Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in
colon cancer: role and regulation of DICKKOPF genesAnticancer
Res2826132623200819035286
|
|
29.
|
SE RossN HematiKA LongoCN BennettPC
LucasRL EricksonOA MacDougaldInhibition of adipogenesis by Wnt
signalingScience289950953200010.1126/science.289.5481.95010937998
|
|
30.
|
M ChoS ParkJ GwakDE KimSS YeaJG ShinS
OhBisindoylmaleimide I suppresses adipocyte differentiation through
stabilization of intracellular beta-catenin proteinBiochem Biophys
Res Commun367195200200810.1016/j.bbrc.2007.12.14718174026
|
|
31.
|
J AhnH LeeS KimT HaCurcumin-induced
suppression of adipogenic differentiation is accompanied by
activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signalingAm J Physiol Cell
Physiol298C15101516201010.1152/ajpcell.00369.200920357182
|
|
32.
|
J LiuH WangY ZuoSR FarmerFunctional
interaction between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
gamma and beta-cateninMol Cell
Biol2658275837200610.1128/MCB.00441-0616847334
|
|
33.
|
SR FarmerRegulation of PPARgamma activity
during adipo-genesisInt J Obes29Suppl
1S13S16200510.1038/sj.ijo.080290715711576
|
|
34.
|
P WendK WendSA KrumGA Miranda-CarboniThe
role of WNT10B in physiology and diseaseActa
Physiol2043451201210.1111/j.1748-1716.2011.02296.x21447090
|
|
35.
|
KA LongoWS WrightS KangI GerinSH ChiangPC
LucasMR OppOA MacDougaldWnt10b inhibits development of white and
brown adipose tissuesJ Biol
Chem2793550335509200410.1074/jbc.M40293720015190075
|
|
36.
|
JK Van CampS BeckersD ZegersA VerrijkenLF
Van GaalW Van HulGenetic association between WNT10B polymorphisms
and obesity in a Belgian case-control population is restricted to
malesMol Genet Metab105489493201222189080
|
|
37.
|
IC KimMH ChaDM KimH LeeJS MoonSM ChoiKS
KimY YoonA functional promoter polymorphism -607G>C of WNT10B is
associated with abdominal fat in Korean female subjectsJ Nutr
Biochem22252258201220579865
|