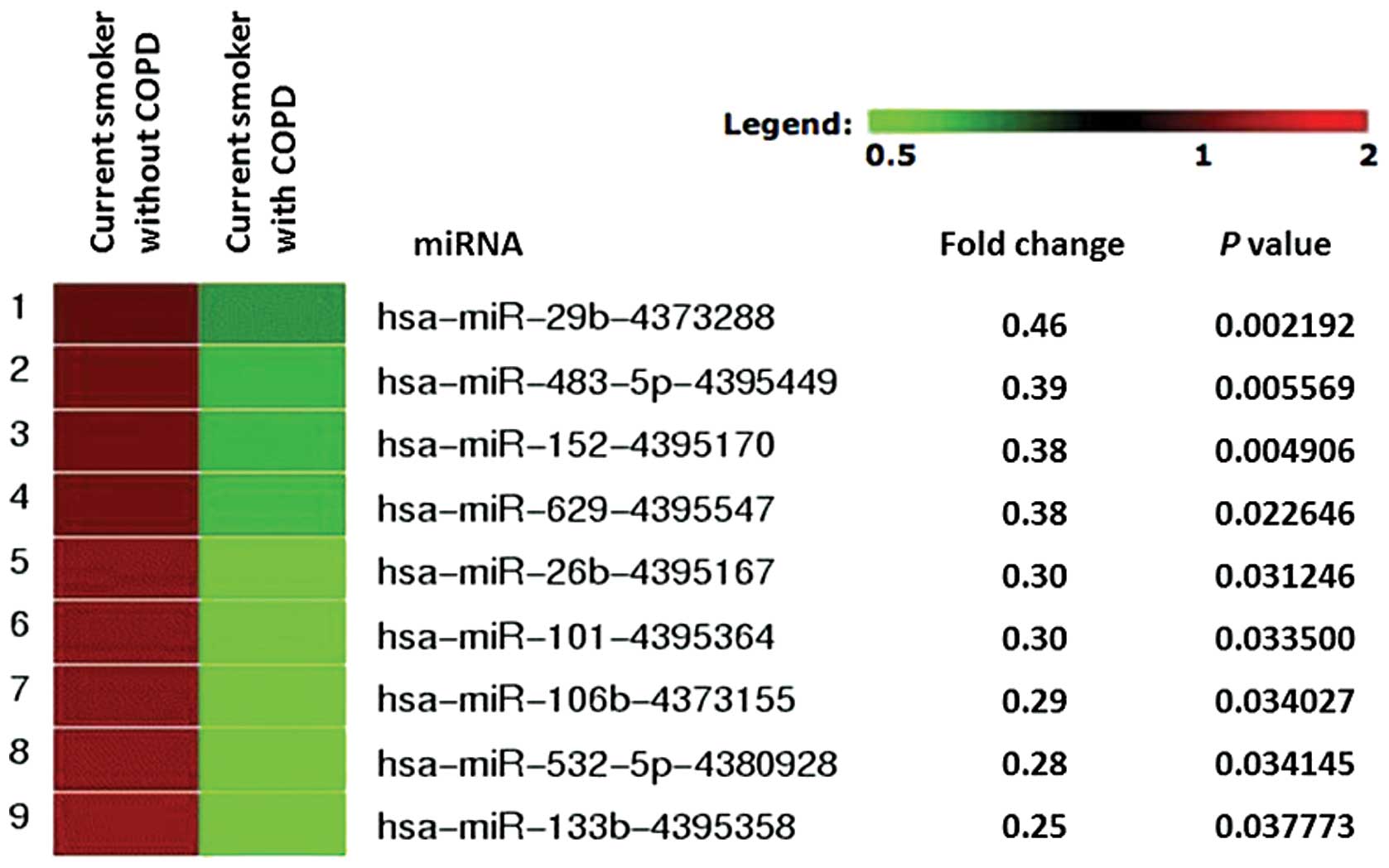
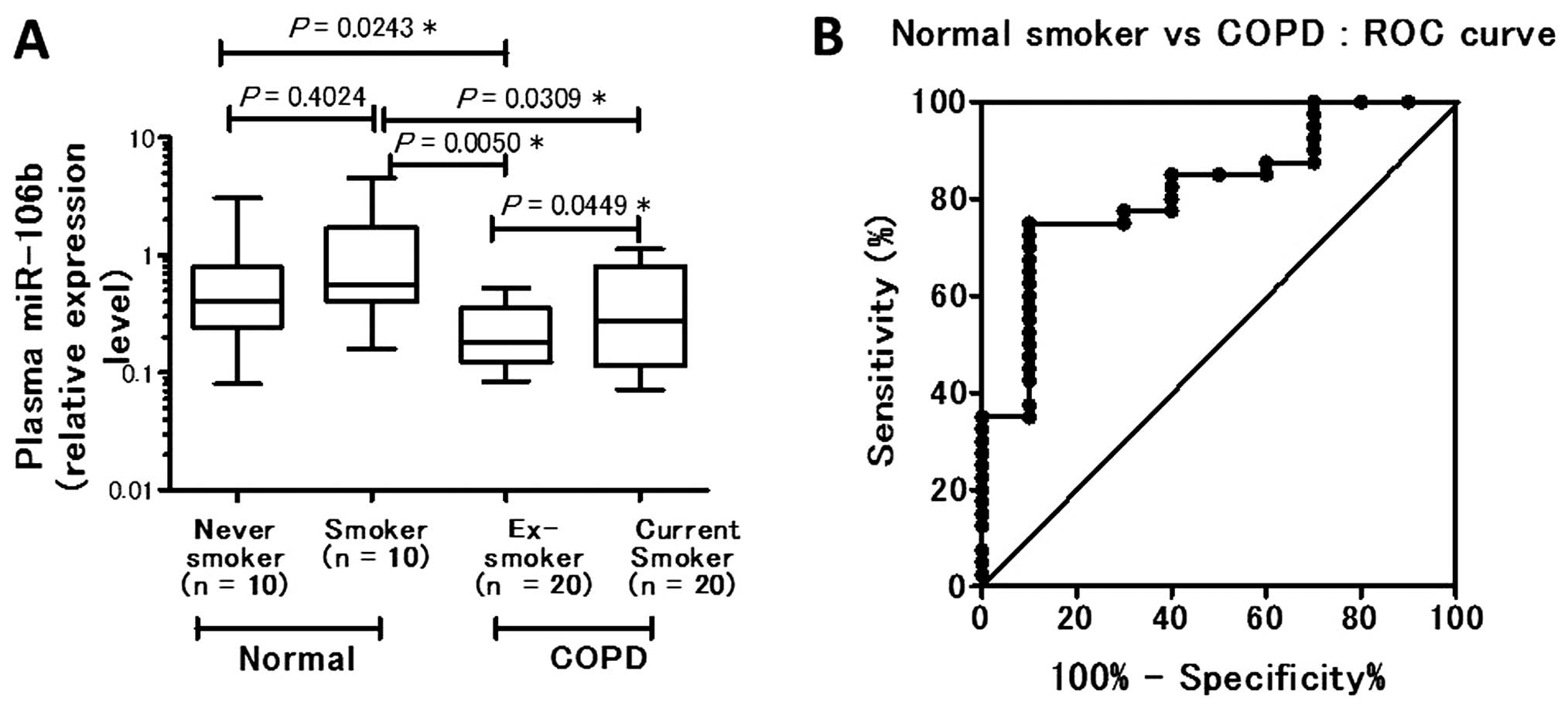
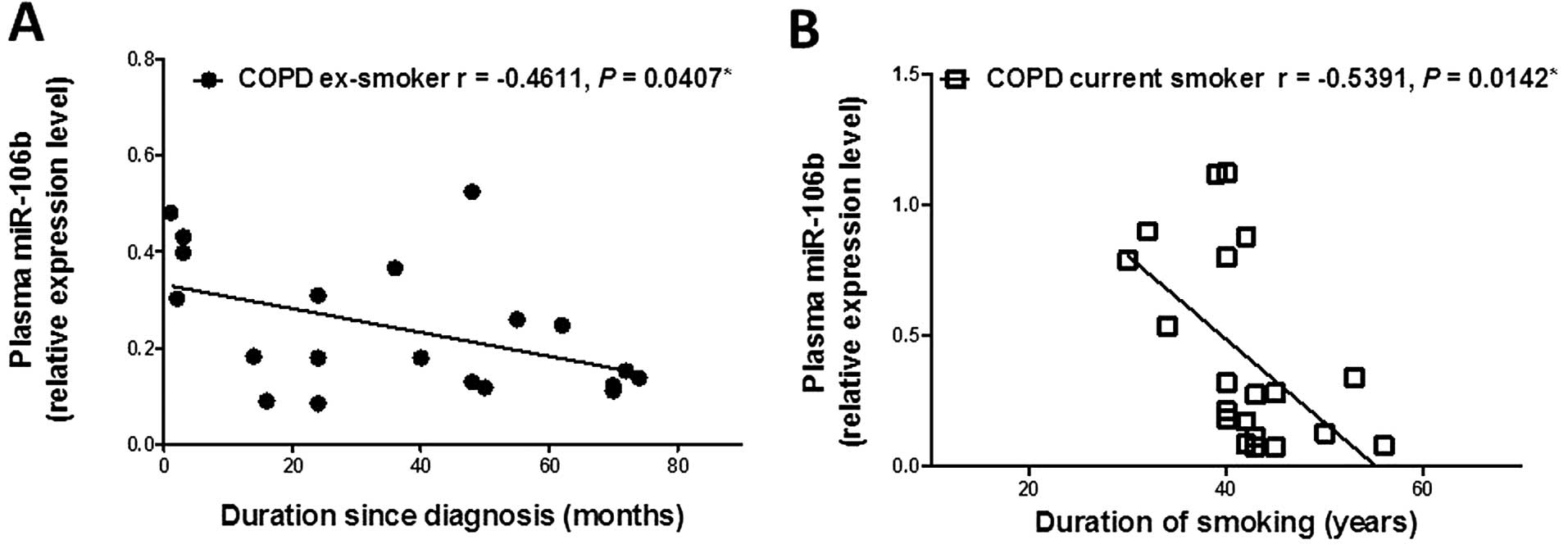
|
1
|
Agusti A and Soriano JB: COPD as a
systemic disease. COPD. 5:133–138. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Fabbri LM, Luppi F, Beghe B and Rabe KF:
Complex chronic comorbidities of COPD. Eur Respir J. 31:204–212.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Celli BR, Cote CG, Marin JM, et al: The
body-mass index, airflow obstruction, dyspnea, and exercise
capacity index in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J
Med. 350:1005–1012. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Barnes PJ and Celli BR: Systemic
manifestations and comorbidities of COPD. Eur Respir J.
33:1165–1185. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sinden NJ and Stockley RA: Systemic
inflammation and comorbidity in COPD: a result of ‘overspill’ of
inflammatory mediators from the lungs? Review of the evidence.
Thorax. 65:930–936. 2010.
|
|
6
|
Decramer M, Janssens W and Miravitlles M:
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet. 379:1341–1351. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chen HY, Yu SL, Li KC and Yang PC:
Biomarkers and transcriptome profiling of lung cancer. Respirology.
17:620–626. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Katoh Y and Katoh M: Hedgehog signaling,
epithelial-tomesenchymal transition and miRNA (Review). Int J Mol
Med. 22:271–275. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee EM, Shin S, Cha HJ, et al:
Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) changes microRNA expression
profiles in A549 human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int J Mol
Med. 24:45–50. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, et al:
Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer
detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:10513–10518. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Etheridge A, Lee I, Hood L, Galas D and
Wang K: Extracellular microRNA: a new source of biomarkers. Mutat
Res. 717:85–90. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ezzie ME, Crawford M, Cho JH, et al: Gene
expression networks in COPD: microRNA and mRNA regulation. Thorax.
67:122–131. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schembri F, Sridhar S, Perdomo C, et al:
MicroRNAs as modulators of smoking-induced gene expression changes
in human airway epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:2319–2324.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hunter MP, Ismail N, Zhang X, et al:
Detection of microRNA expression in human peripheral blood
microvesicles. PloS One. 3:e36942008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ohyashiki JH, Umezu T, Kobayashi C, et al:
Impact on cell to plasma ratio of miR-92a in patients with acute
leukemia: in vivo assessment of cell to plasma ratio of miR-92a.
BMC Res Notes. 3:3472010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yoshizawa S, Ohyashiki JH, Ohyashiki M, et
al: Downregulated plasma miR-92a levels have clinical impact on
multiple myeloma and related disorders. Blood Cancer J. 2:e532012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vestbo J and Rennard S: Chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease biomarker(s) for disease activity
needed urgently. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 182:863–864. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Han MK: Update in chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease in 2010. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
183:1311–1315. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sakao S and Tatsumi K: The importance of
epigenetics in the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease. Respirology. 16:1056–1063. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pottelberge GR, Mestdagh P, Bracke KR, et
al: MicroRNA expression in induced sputum of smokers and patients
with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 183:898–906. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sato T, Liu X, Nelson A, et al: Reduced
miR-146a increases prostaglandin E in chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease fibroblasts. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 182:1020–1029.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lewis A, Riddoch-Contreras J, Natanek SA,
et al: Downregulation of the serum response factor/miR-1 axis in
the quadriceps of patients with COPD. Thorax. 67:26–34. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Izzotti A, Calin GA, Arrigo P, Steele VE,
Croce CM and De Flora S: Downregulation of microRNA expression in
the lungs of rats exposed to cigarette smoke. FASEB J. 23:806–812.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cushing L, Kuang PP, Qian J, et al: miR-29
is a major regulator of genes associated with pulmonary fibrosis.
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 45:287–294. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Akbas F, Coskunpinar E, Aynaci E, Oltulu
YM and Yildiz P: Analysis of serum micro-RNAs as potential
biomarker in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Exp Lung Res.
38:286–294. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rutgers SR, Postma DS, ten Hacken NH, et
al: Ongoing airway inflammation in patients with COPD who do not
currently smoke. Thorax. 55:12–18. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lapperre TS, Postma DS, Gosman MM, et al:
Relation between duration of smoking cessation and bronchial
inflammation in COPD. Thorax. 61:115–121. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Margadant C and Sonnenberg A:
Integrin-TGF-beta crosstalk in fibrosis, cancer and wound healing.
EMBO Rep. 11:97–105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Takizawa H, Tanaka M, Takami K, et al:
Increased expression of transforming growth factor-beta1 in small
airway epithelium from tobacco smokers and patients with chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
163:1476–1483. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mak JC, Chan-Yeung MM, Ho SP, et al:
Elevated plasma TGF-beta1 levels in patients with chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Med. 103:1083–1089. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gong Y, Fan L, Wan H, et al: Lack of
association between the TGF-β(1) gene and development of COPD in
Asians: a case-control study and meta-analysis. Lung. 189:213–223.
2011.
|
|
32
|
Marwick JA, Kirkham P, Gilmour PS,
Donaldson K, Mac NW and Rahman I: Cigarette smoke-induced oxidative
stress and TGF-beta1 increase p21waf1/cip1 expression in alveolar
epithelial cells. Ann NY Acad Sci. 973:278–283. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ivanovska I, Ball AS, Diaz RL, et al:
MicroRNAs in the miR-106b family regulate p21/CDKN1A and promote
cell cycle progression. Mol Cell Biol. 28:2167–2174. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|