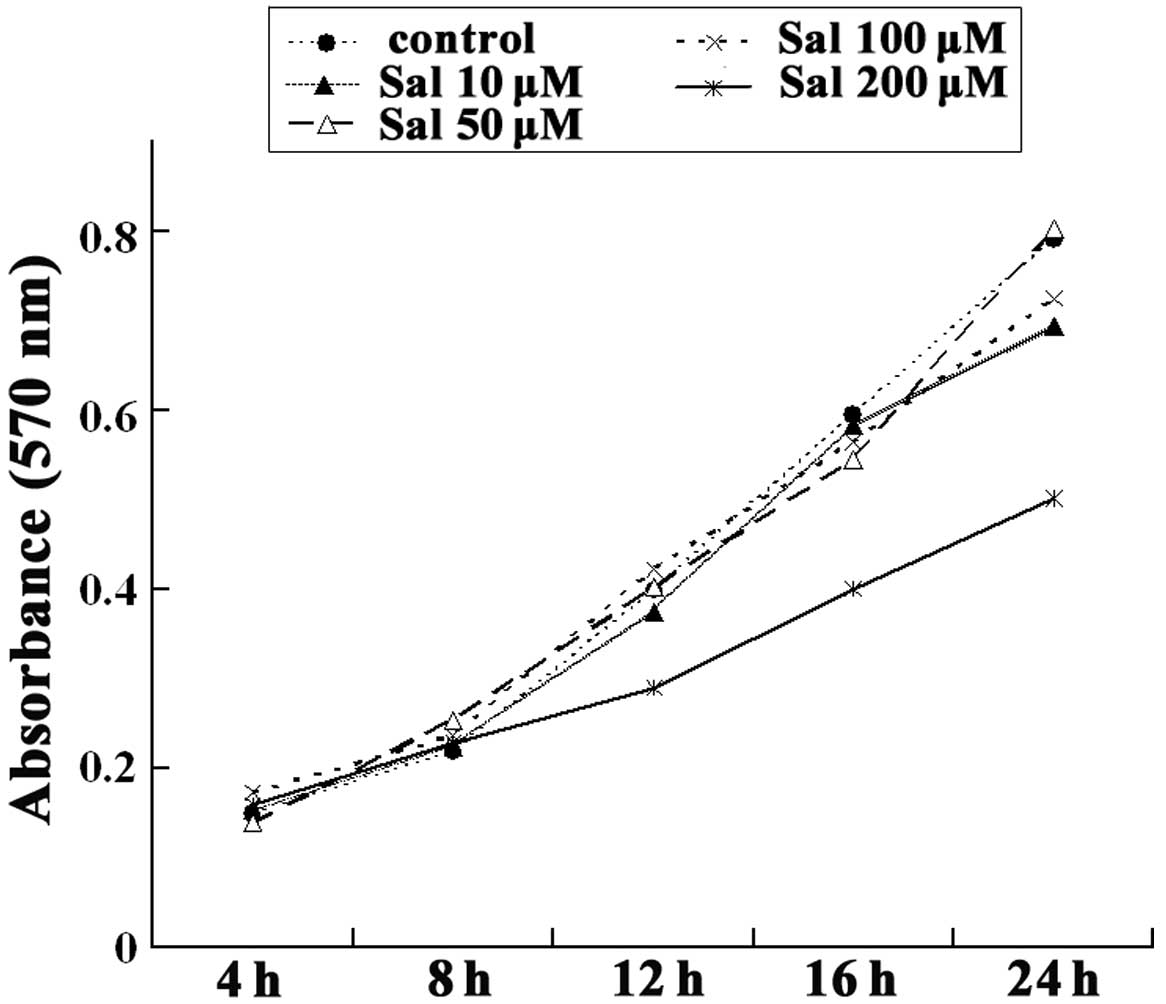
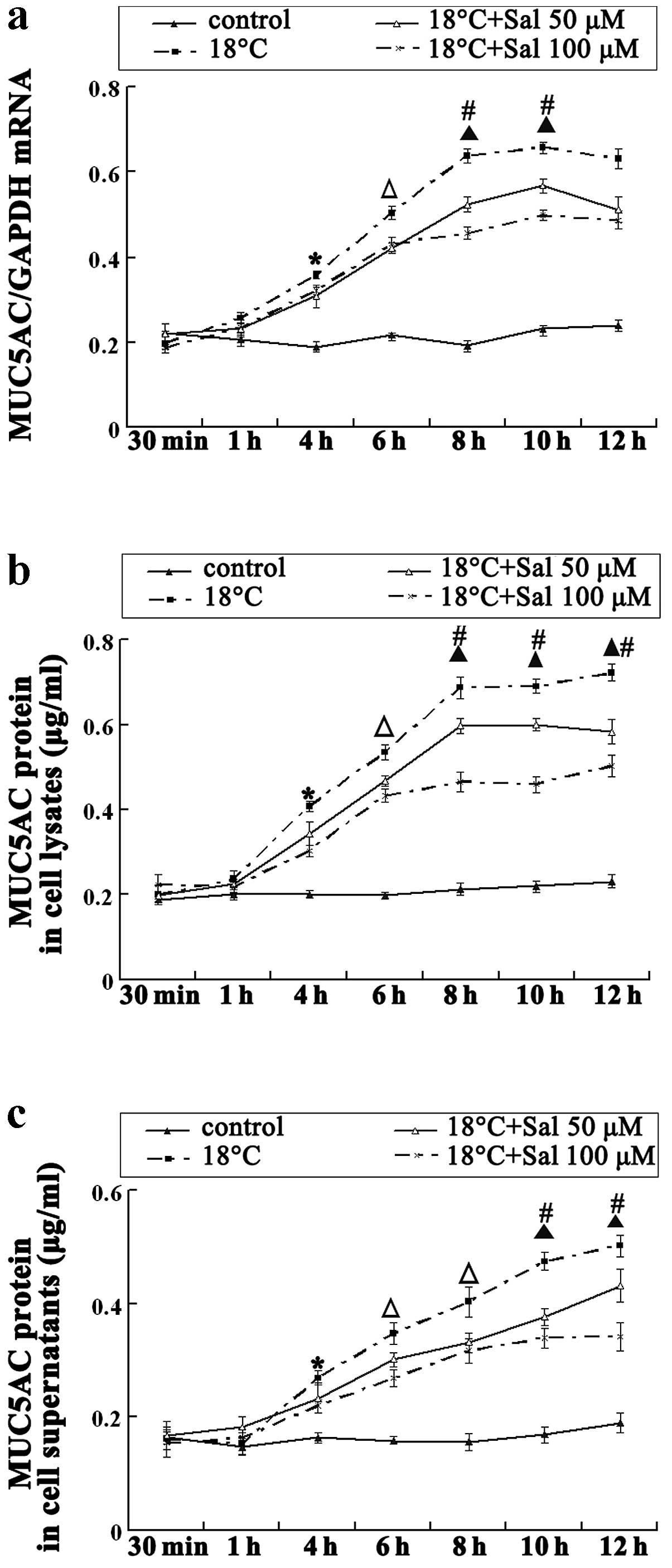
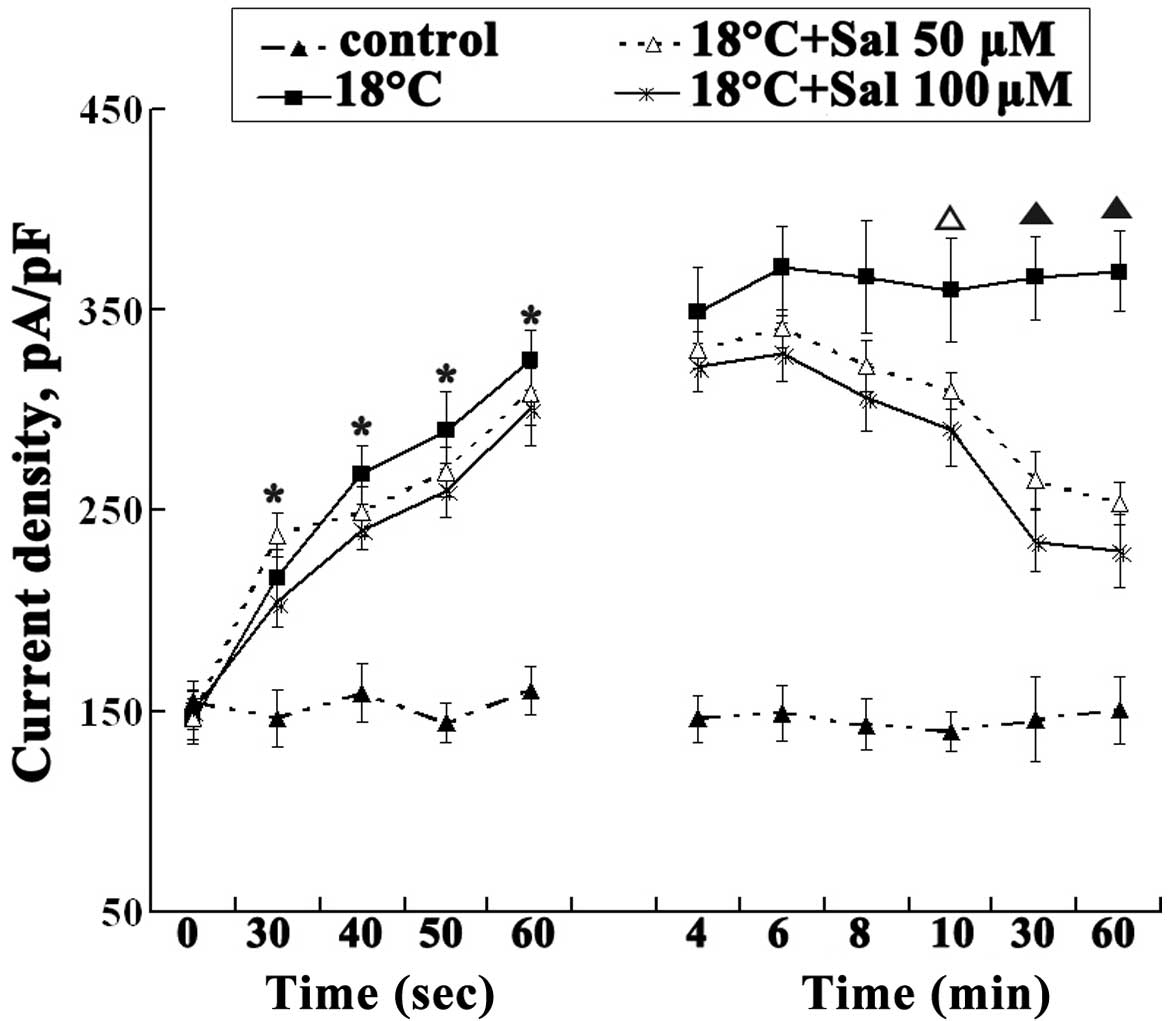
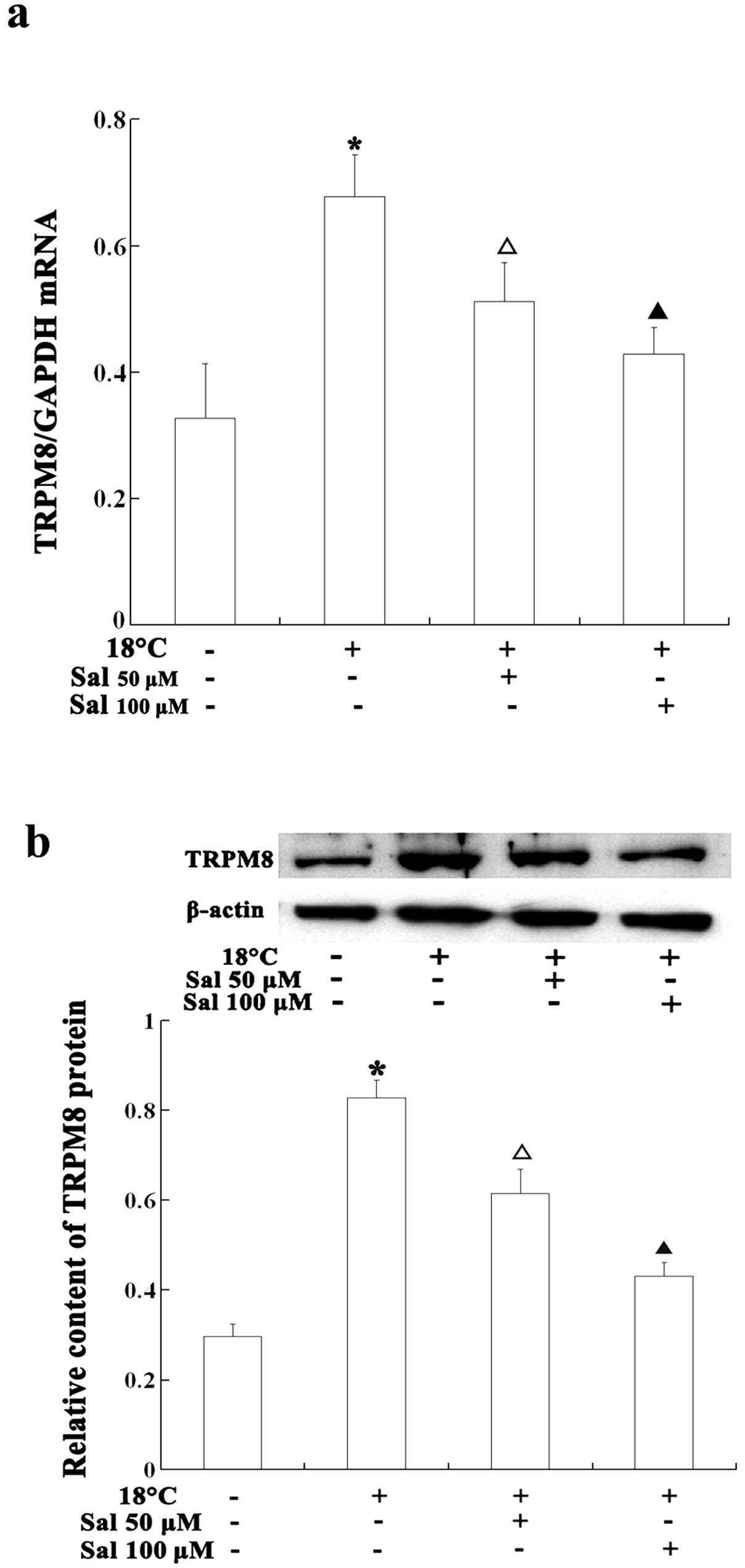
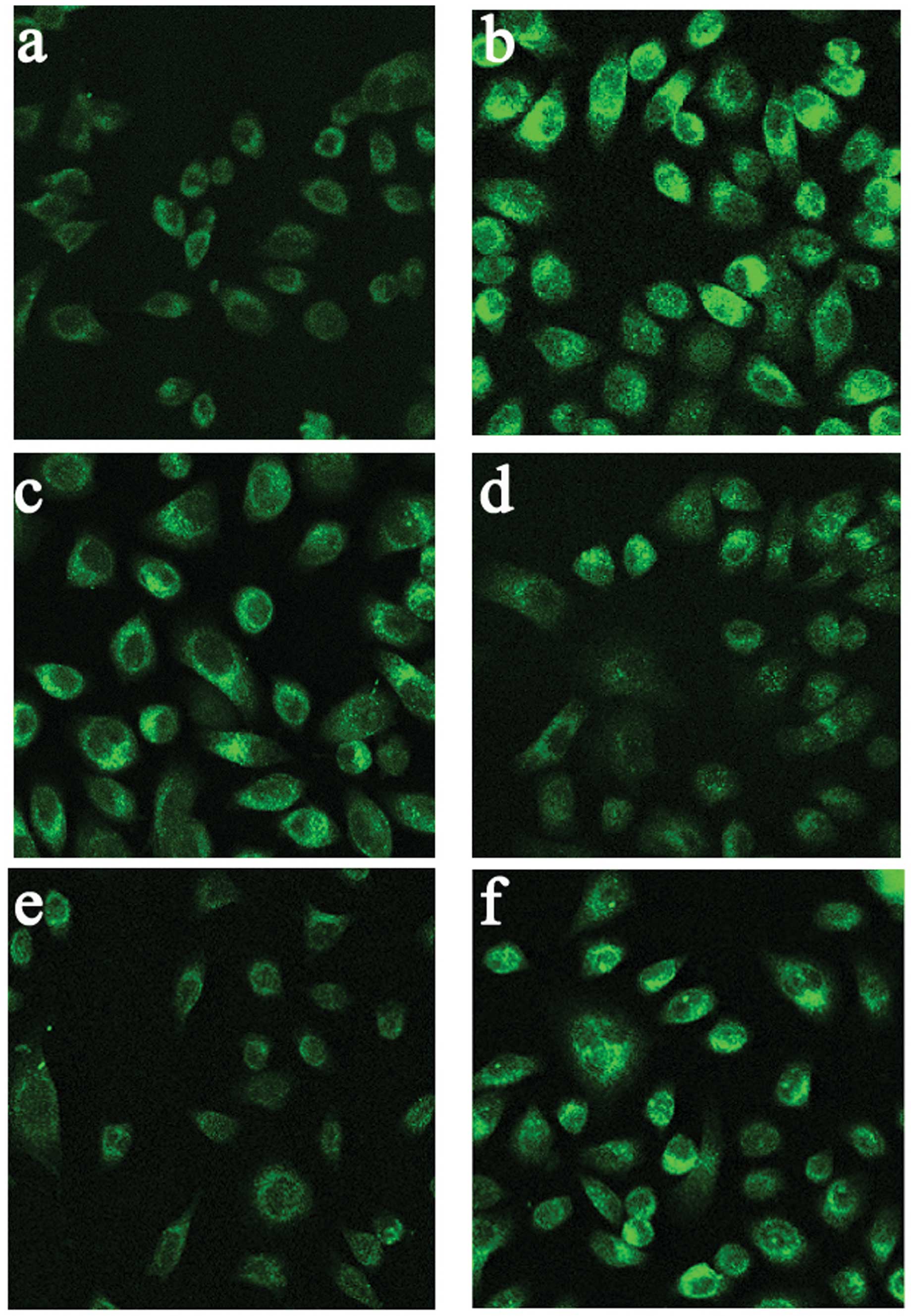
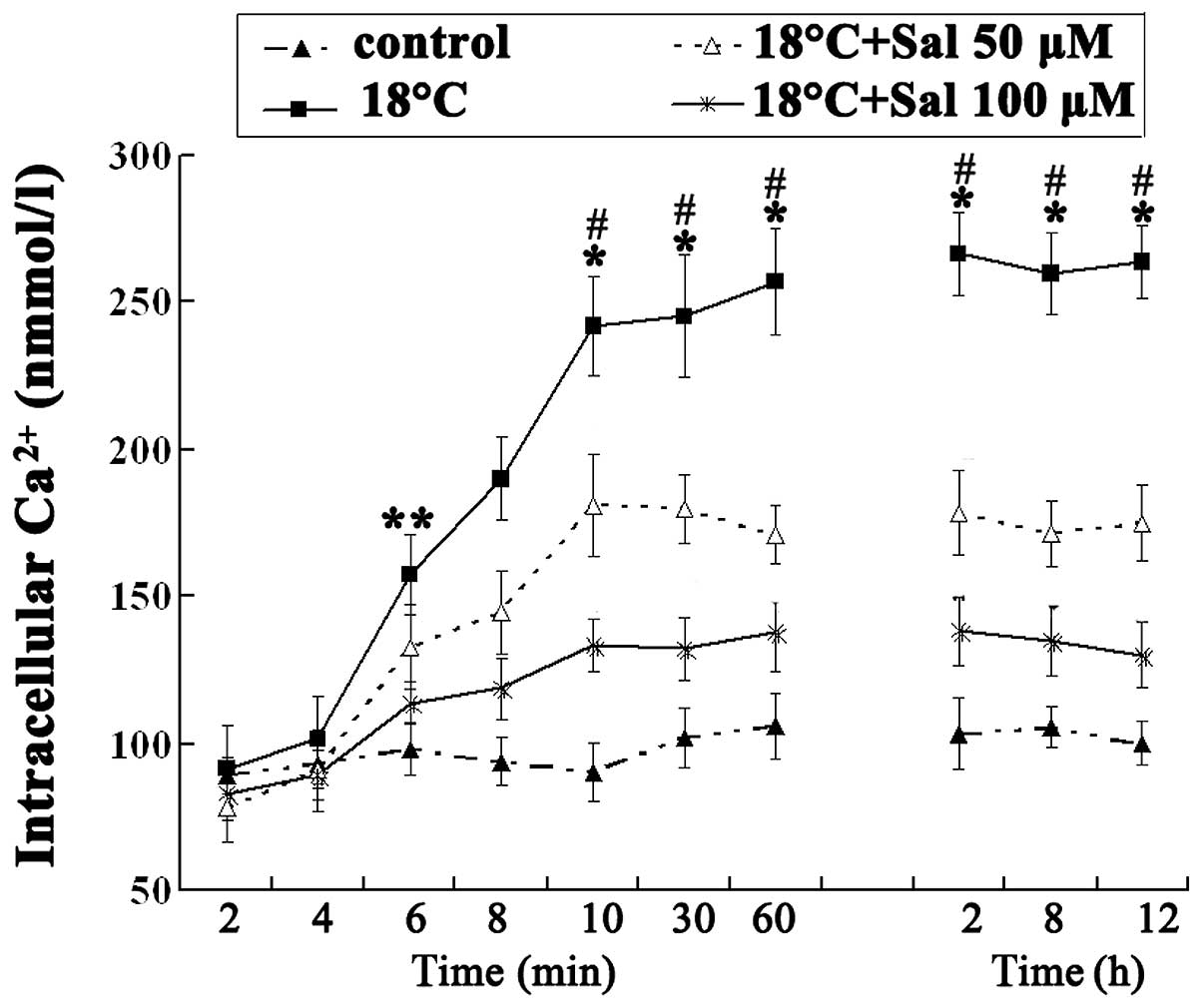
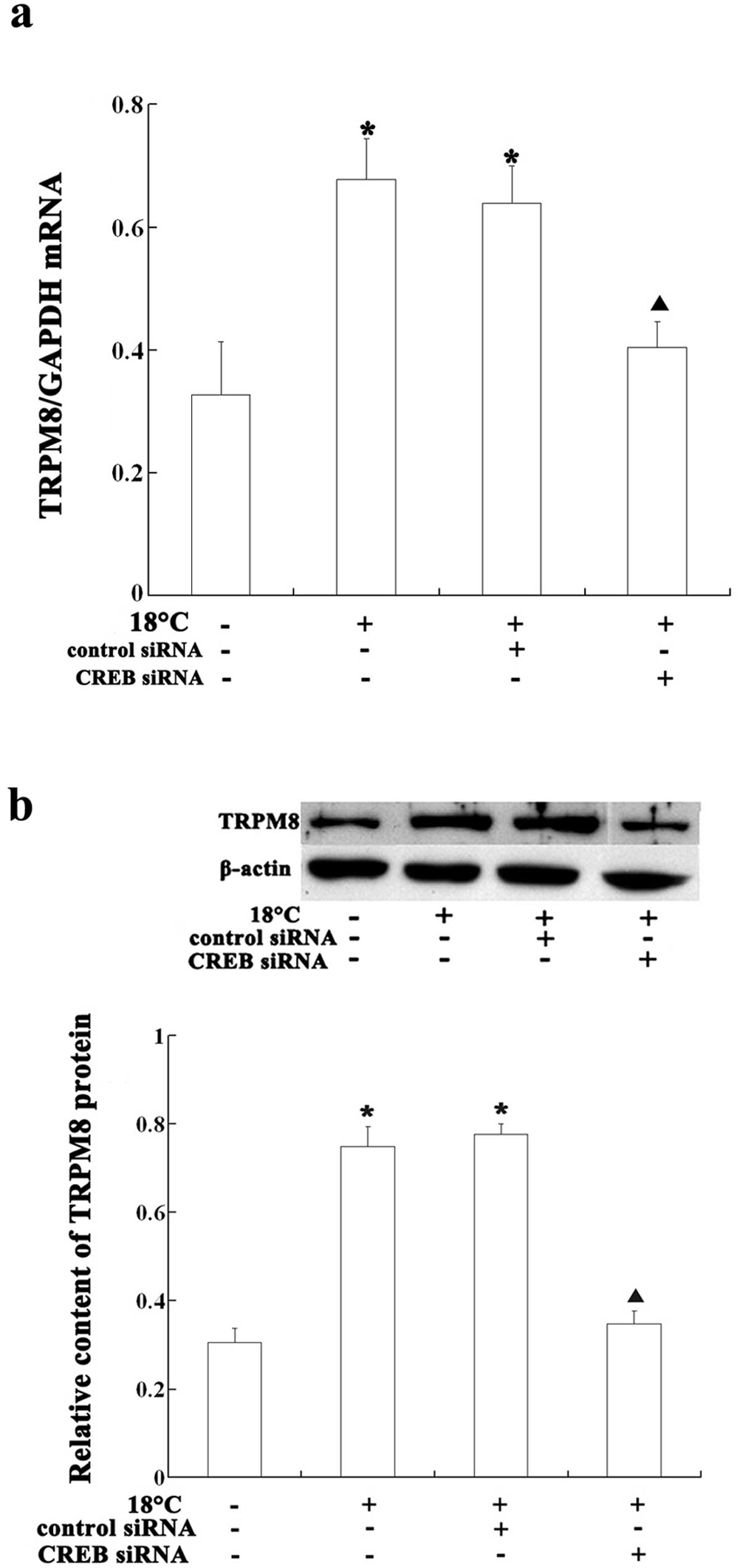
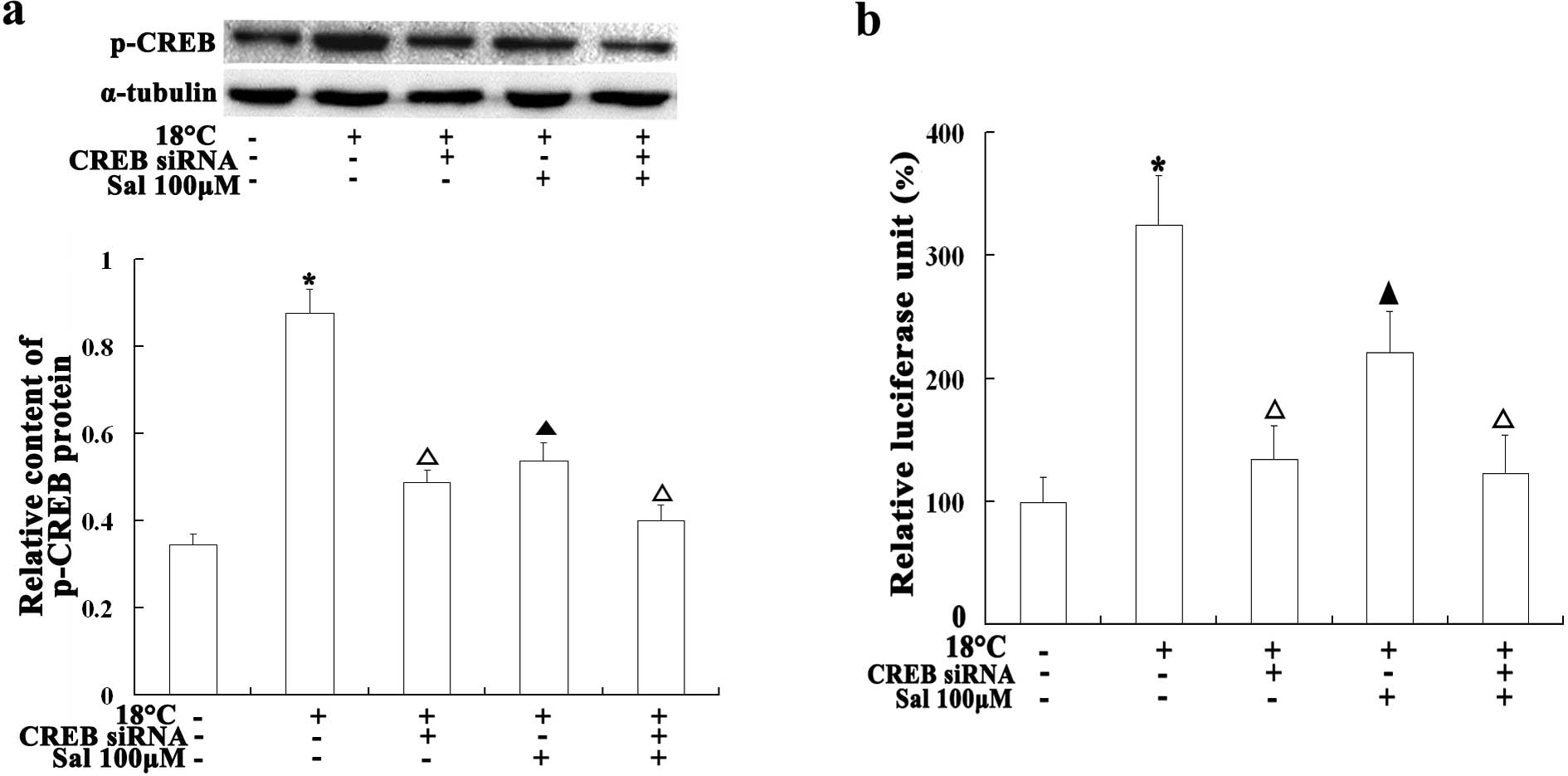
|
1
|
Giesbrecht GG: The respiratory system in a
cold environment. Aviat Space Environ Med. 66:890–902.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Voynow JA and Rubin BK: Mucins, mucus, and
sputum. Chest. 135:505–512. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhen G, Park SW, Nguyenvu LT, Rodriguez
MW, Barbeau R, Paquet AC and Erle DJ: IL-13 and epidermal growth
factor receptor have critical but distinct roles in epithelial cell
mucin production. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 36:244–253. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhu L, Lee PK, Lee WM, Zhao Y, Yu D and
Chen Y: Rhinovirus-induced major airway mucin production involves a
novel TLR3-EGFR-dependent pathway. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
40:610–619. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Turner J and Jones CE: Regulation of mucin
expression in respiratory diseases. Biochem Soc Trans. 37:877–881.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Caterina MJ, Leffler A, Malmberg AB,
Martin WJ, Trafton J, Petersen-Zeitz KR, Koltzenburg M, Basbaum AI
and Julius D: Impaired nociception and pain sensation in mice
lacking the capsaicin receptor. Science. 288:306–313. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Caterina MJ, Rosen TA, Tominaga M, Brake
AJ and Julius D: A capsaicin-receptor homologue with a high
threshold for noxious heat. Nature. 398:436–441. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Smith GD, Gunthorpe MJ, Kelsell RE, Hayes
PD, Reilly P, Facer P, Wright JE, Jerman JC, Walhin JP, Ooi L,
Egerton J, Charles KJ, Smart D, Randall AD, Anand P and Davis JB:
TRPV3 is a temperature-sensitive vanilloid receptor-like protein.
Nature. 418:186–190. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Güler AD, Lee H, Iida T, Shimizu I,
Tominaga M and Caterina M: Heat-evoked activation of the ion
channel, TRPV4. J Neurosci. 2:6408–6414. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
McKemy DD, Neuhausser WM and Julius D:
Identification of a cold receptor reveals a general role for TRP
channels in thermosensation. Nature. 416:52–58. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Peier AM, Moqrich A, Hergarden AC, Reeve
AJ, Andersson DA, Story GM, Earley TJ, Dragoni I, McIntyre P, Bevan
S and Patapoutian A: A TRP channel that senses cold stimuli and
menthol. Cell. 108:705–715. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li MC, Li Q, Yang G, Kolosov VP, Perelman
JM and Zhou XD: Cold temperature induces mucin hypersecretion from
normal human bronchial epithelial cells in vitro through a
transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8)-mediated
mechanism. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 128:626–634. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Li YR, Cao W, Guo J, Miao S, Ding GR, Li
KC, Wang J and Guo GZ: Comparative investigations on the protective
effects of rhodioside, ciwujianoside-B and astragaloside IV on
radiation injuries of the hematopoietic system in mice. Phytother
Res. 25:644–653. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Díaz Lanza AM, Abad Martínez MJ, Fernández
Matellano L, Recuero Carretero C, Villaescusa Castillo L, Silván
Sen AM and Bermejo Benito P: Lignan and phenylpropanoid glycosides
from Phillyrea latifolia and their in vitro anti
inflammatory activity. Planta Med. 67:219–223. 2001.
|
|
15
|
Kelly GS: Rhodiola rosea: a
possible plant adaptogen. Altern Med Rev. 6:293–302. 2001.
|
|
16
|
Kucinskaite A, Briedis V and Savickas A:
Experimental analysis of therapeutic properties of Rhodiola
rosea L. and its possible application in medicine. Medicina
(Kaunas). 40:614–619. 2004.(In Lithuanian).
|
|
17
|
Bavencoffe A, Kondratskyi A, Gkika D,
Mauroy B, Shuba Y, Prevarskaya N and Skryma R: Complex regulation
of the TRPM8 cold receptor channel: role of arachidonic acid
release following M3 muscarinic receptor stimulation. J Biol Chem.
286:9849–9855. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bidaux G, Roudbaraki M, Merle C, Crépin A,
Delcourt P, Slomianny C, Thebault S, Bonnal JL, Benahmed M, Cabon
F, Mauroy B and Prevarskaya N: Evidence for specific TRPM8
expression in human prostate secretory epithelial cells: functional
androgen receptor requirement. Endocr Relat Cancer. 12:367–382.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sabnis AS, Shadid M, Yost GS and Reilly
CA: Human lung epithelial cells express a functional cold-sensing
TRPM8 variant. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 39:466–474. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McCoy DD, Knowlton WM and McKemy DD:
Scraping through the ice: uncovering the role of TRPM8 in cold
transduction. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
300:R1278–R1287. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang L and Barritt GJ: TRPM8 in prostate
cancer cells: a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker with a
secretory function? Endocr Relat Cancer. 13:27–38. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Behrendt HJ, Germann T, Gillen C, Hatt H
and Jostock R: Characterization of the mouse cold-menthol receptor
TRPM8 and vanilloid receptor type-1 VR1 using a fluorometric
imaging plate reader (FLIPR) assay. Br J Pharmacol. 141:737–745.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Andersson DA, Chase HW and Bevan S: TRPM8
activation by menthol, icilin, and cold is differentially modulated
by intracellular pH. J Neurosci. 24:5364–5369. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tolonen A, Pakonen M, Hohtola A and
Jalonen J: Phenylpropanoid glycosides from Rhodiola rosea.
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 51:467–470. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mao GX, Wang Y, Qiu Q, Deng HB, Yuan LG,
Li RG, Song DQ, Li YY, Li DD and Wang Z: Salidroside protects human
fibroblast cells from premature senescence induced by H(2)O(2)
partly through modulating oxidative status. Mech Ageing Dev.
131:723–731. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li X, Ye X, Li X, Sun X, Liang Q, Tao L,
Kang X and Chen J: Salidroside protects against MPP(+)-induced
apoptosis in PC12 cells by inhibiting the NO pathway. Brain Res.
1382:9–18. 2011.
|
|
27
|
Zhang L, Yu H, Sun Y, Lin X, Chen B, Tan
C, Cao G and Wang Z: Protective effects of salidroside on hydrogen
peroxide-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells.
Eur J Pharmacol. 564:18–25. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Koskela HO: Cold air-provoked respiratory
symptoms: the mechanisms and management. Int J Circumpolar Health.
66:91–100. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rodway GW and Windsor JS: Airway
mucociliary function at high altitude. Wilderness Environ Med.
17:271–275. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dada LA and Sznajder JI: Mitochondrial
Ca2+ and ROS take center stage to orchestrate
TNF-α-mediated inflammatory responses. J Clin Invest.
121:1683–1685. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gusarova GA, Trejo HE, Dada LA, Briva A,
Welch LC, Hamanaka RB, Mutlu GM, Chandel NS, Prakriya M and
Sznajder JI: Hypoxia leads to Na,K-ATPase downregulation via Ca(2+)
release-activated Ca(2+) channels and AMPK activation. Mol Cell
Biol. 31:3546–3556. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Galli GL, Lipnick MS, Shiels HA and Block
BA: Temperature effects on Ca2+ cycling in scombrid
cardiomyocytes: a phylogenetic comparison. J Exp Biol.
214:1068–1076. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cho Y, Jang Y, Yang YD, Lee CH, Lee Y and
Oh U: TRPM8 mediates cold and menthol allergies associated with
mast cell activation. Cell Calcium. 48:202–208. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Abe J, Hosokawa H, Sawada Y, Matsumura K
and Kobayashi S: Ca2+-dependent PKC activation mediates
menthol-induced desensitization of transient receptor potential M8.
Neurosci Lett. 397:140–144. 2006.
|
|
35
|
Premkumar LS, Raisinghani M, Pingle SC,
Long C and Pimentel F: Downregulation of transient receptor
potential melastatin 8 by protein kinase C-mediated
dephosphorylation. J Neurosci. 25:11322–11329. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Daniels RL, Takashima Y and McKemy DD:
Activity of the neuronal cold sensor TRPM8 is regulated by
phospholipase C via the phospholipid phosphoinositol
4,5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 84:1570–1582. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rohács T, Lopes CM, Michailidis I and
Logothetis DE: PI(4,5)P2 regulates the activation and
desensitization of TRPM8 channels through the TRP domain. Nat
Neurosci. 8:626–634. 2005.
|
|
38
|
Andersson DA, Nash M and Bevan S:
Modulation of the cold-activated channel TRPM8 by lysophospholipids
and polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Neurosci. 27:3347–3355. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Vanden Abeele F, Zholos A, Bidaux G, Shuba
Y, Thebault S, Beck B, Flourakis M, Panchin Y, Skryma R and
Prevarskaya N: Ca2+-independent phospholipase
A2-dependent gating of TRPM8 by lysophospholipids. J Biol Chem.
281:40174–40182. 2006.
|
|
40
|
Bavencoffe A, Gkika D, Kondratskyi A, Beck
B, Borowiec AS, Bidaux G, Busserolles J, Eschalier A, Shuba Y,
Skryma R and Prevarskaya N: The transient receptor potential
channel TRPM8 is inhibited via the alpha 2A adrenoreceptor
signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 285:9410–9419. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
De Petrocellis L, Starowicz K, Moriello
AS, Vivese M, Orlando P and Di Marzo V: Regulation of transient
receptor potential channels of melastatin type 8 (TRPM8): effect of
cAMP, cannabinoid CB(1) receptors and endovanilloids. Exp Cell Res.
313:1911–1920. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Andrisani OM: CREB-mediated
transcriptional control. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 9:19–32.
1999.
|
|
43
|
Johannessen M and Moens U: Multisite
phosphorylation of the cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB)
by a diversity of protein kinases. Front Biosci. 12:1814–1832.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Johannessen M, Delghandi MP, Seternes OM,
Johansen B and Moens U: Synergistic activation of CREB-mediated
transcription by forskolin and phorbol ester requires PKC and
depends on the glutamine-rich Q2 transactivation domain. Cell
Signal. 16:1187–1199. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Shaywitz AJ and Greenberg ME: CREB: a
stimulus-induced transcription factor activated by a diverse array
of extracellular signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 68:821–861. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang L and Barritt GJ: Evidence that
TRPM8 is an androgen-dependent Ca2+ channel required for
the survival of prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 64:8365–8373.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|