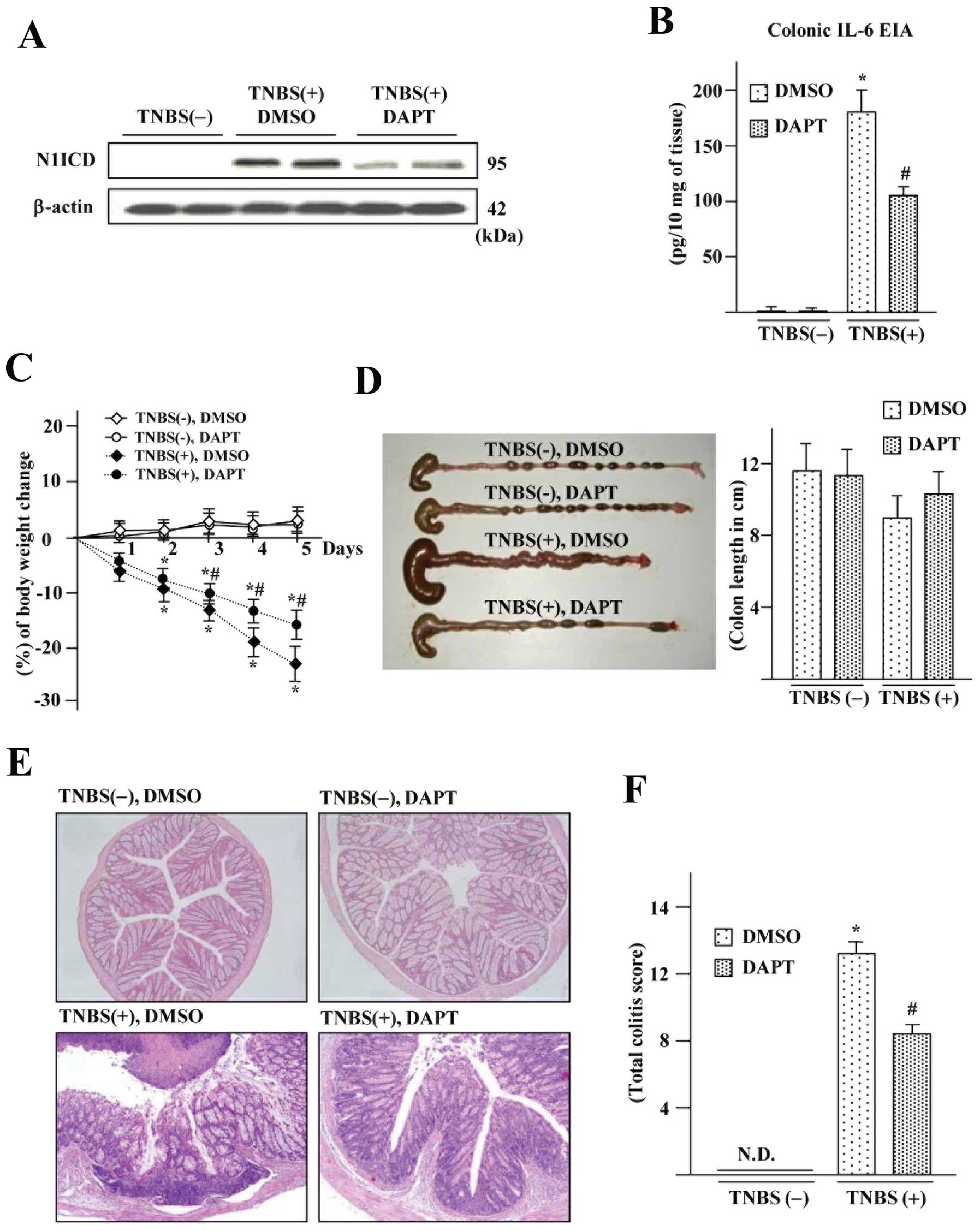
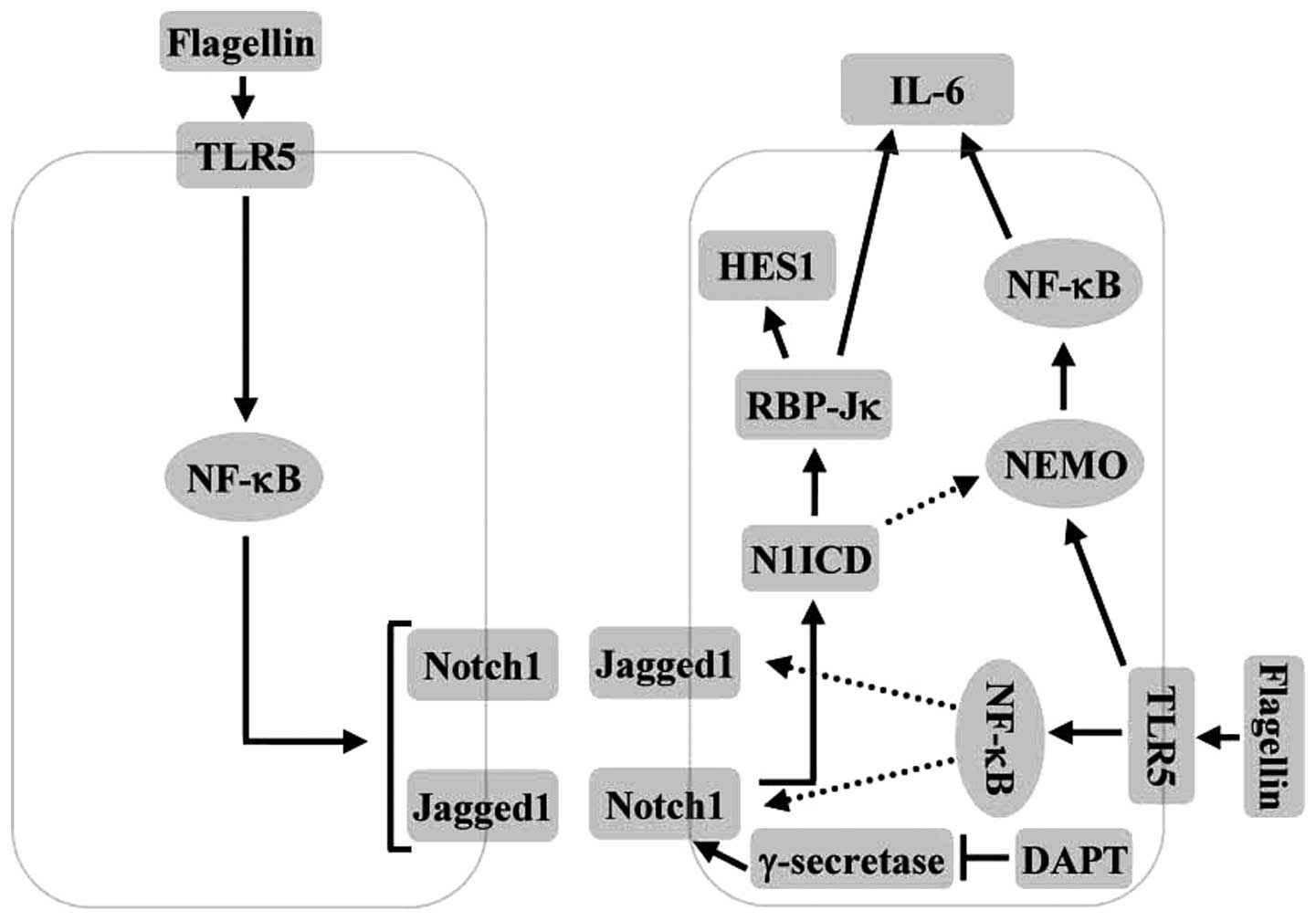
|
1
|
Ishihara S, Aziz MM, Yuki T, Kazumori H
and Kinoshita Y: Inflammatory bowel disease: review from the aspect
of genetics. J Gastroenterol. 44:1097–1108. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mizoguchi A and Mizoguchi E: Inflammatory
bowel disease: past, present, and future: lessons from animal
models. J Gastroenterol. 43:1–17. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xavier RJ and Podolsky DK: Unravelling the
pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 448:427–434.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P and
Janeway CA Jr: A human homologue of the Drosophila Toll
protein signals activation of adaptive immunity. Nature.
388:394–397. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ortega-Cava CF, Ishihara S, Rumi MA, et
al: Strategic compartmentalization of Toll-like receptor 4 in the
mouse gut. J Immunol. 170:3977–3985. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Uematsu S and Akira S: Immune responses of
TLR5(+) lamina propira dendritic cells in enterobacterial
infection. J Gastroenterol. 44:803–811. 2009.
|
|
7
|
Ishihara S, Rumi MA, Kadowaki Y, et al:
Essential role of MD-2 in TLR4-dependent signaling during
Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis. J Immunol.
173:1406–416. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vijay-Kumar M, Sanders CJ, Taylor RT, et
al: Deletion of TLR5 results in spontaneous colitis in mice. J Clin
Invest. 117:3909–3921. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cario E: Therapeutic impact of toll-like
receptors on inflammatory bowel diseases: a multiple-edged sword.
Inflamm Bowel Dis. 14:411–421. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gribar SC, Anand RJ, Sodhi CP and Hackam
DJ: The role of epithelial Toll-like receptor signaling in the
pathogenesis of intestinal inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 83:493–498.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Okamoto R, Tsuchiya K, Nemoto Y, Akiyama
J, Nakamura T, Kanai T and Watanabe M: Requirement of Notch
activation during regeneration of the intestinal epithelia. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 296:G23–G35. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kuhnert F, Davis CR, Wang HT, et al:
Essential requirement for Wnt signaling in proliferation of adult
small intestine and colon revealed by adenoviral expression of
Dickkopf-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:266–271. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lees CW, Zacharias WJ, Tremelling M, et
al: Analysis of germline GLI1 variation implicates hedgehog
signalling in the regulation of intestinal inflammatory pathways.
PLoS Med. 5:e2392008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Matsuno K and
Fortini ME: Notch signaling. Science. 268:225–232. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD and Lake RJ:
Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in
development. Science. 284:770–776. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Krebs LT, Xue Y, Norton CR, et al: Notch
signaling is essential for vascular morphogenesis in mice. Genes
Dev. 14:1343–1352. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fung E, Tang SM, Canner JP, et al:
Delta-like 4 induces notch signaling in macrophages: implications
for inflammation. Circulation. 115:2948–2956. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bedogni B, Warneke JA, Nickoloff BJ, et
al: Notch1 is an effector of Akt and hypoxia in melanoma
development. J Clin Invest. 118:3660–3670. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schroder N and Gossler A: Expression of
Notch pathway components in fetal and adult mouse small intestine.
Gene Expr Patterns. 2:247–250. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: Notch signaling in
gastrointestinal tract (Review). Int J Oncol. 30:247–251.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nakamura T, Tsuchiya K and Watanabe M:
Crosstalk between Wnt and Notch signaling in intestinal epithelial
cell fate decision. J Gastroenterol. 42:705–710. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ishizuya-Oka A and Hasebe T: Sonic
hedgehog and bone morphogenetic protein-4 signaling pathway
involved in epithelial cell renewal along the radial axis of the
intestine. Digestion. 77:42–47. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang H, Patel PH, Kohlmaier A, Grenley
MO, McEwen DG and Edgar BA: Cytokine/Jak/Stat signaling mediates
regeneration and homeostasis in the Drosophila midgut. Cell.
137:1343–1355. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fre S, Pallavi SK, Huyghe M, et al: Notch
and Wnt signals cooperatively control cell proliferation and
tumorigenesis in the intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:6309–6314. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Oshima N, Ishihara S, Rumi MA, et al: A20
is an early responding negative regulator of Toll-like receptor 5
signalling in intestinal epithelial cells during inflammation. Clin
Exp Immunol. 159:185–198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rhee SH, Im E, Riegler M, Kokkotou E,
O’Brien M and Pothoulakis C: Pathophysiological role of Toll-like
receptor 5 engagement by bacterial flagellin in colonic
inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:13610–13615. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Aziz MM, Ishihara S, Rumi MA, et al:
Prolactin induces MFG-E8 production in macrophages via
transcription factor C/EBPbeta-dependent pathway. Apoptosis.
13:609–620. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gewirtz AT, Navas TA, Lyons S, Godowski PJ
and Madara JL: Cutting edge: bacterial flagellin activates
basolaterally expressed TLR5 to induce epithelial proinflammatory
gene expression. J Immunol. 167:1882–1885. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Solt LA and May MJ: The IkappaB kinase
complex: master regulator of NF-kappaB signaling. Immunol Res.
42:3–18. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Verma UN, Yamamoto Y, Prajapati S and
Gaynor RB: Nuclear role of I kappa B Kinase-gamma/NF-kappa B
essential modulator (IKK gamma/NEMO) in NF-kappa B-dependent gene
expression. J Biol Chem. 279:3509–3515. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rudolph D, Yeh WC, Wakeham B, et al:
Severe liver degeneration and lack of NF-kappaB activation in
NEMO/IKKgamma-deficient mice. Genes Dev. 14:854–862.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shifera AS, Friedman JM and Horwitz MS:
IKK gamma (NEMO) is involved in the coordination of the AP-1 and
NF-kappa B pathways. Mol Cell Biochem. 310:181–190. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vales LD and Friedl EM: Binding of C/EBP
and RBP (CBF1) to overlapping sites regulates interleukin-6 gene
expression. J Biol Chem. 277:42438–42446. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Moriyama I, Ishihara S, Rumi MA, et al:
Decoy oligodeoxynucleotide targeting activator protein-1 (AP-1)
attenuates intestinal inflammation in murine experimental colitis.
Lab Invest. 88:652–663. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Aziz MM, Ishihara S, Mishima Y, et al:
MFG-E8 attenuates intestinal inflammation in murine experimental
colitis by modulating osteopontin-dependent alphavbeta3 integrin
signaling. J Immunol. 182:7222–7232. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
van Es JH and Clevers H: Notch and Wnt
inhibitors as potential new drugs for intestinal neoplastic
disease. Trends Mol Med. 11:496–502. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Radtke F, Schweisguth F and Pear W: The
Notch ‘gospel’. EMBO Rep. 6:1120–1125. 2005.
|
|
38
|
Hurlbut GD, Kankel MW, Lake RJ and
Artavanis-Tsakonas S: Crossing paths with Notch in the
hyper-network. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 19:166–175. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Palaga T, Buranaruk C, Rengpipat S, Fauq
AH, Golde TE, Kaufmann SH and Osborne BA: Notch signaling is
activated by TLR stimulation and regulates macrophage functions.
Eur J Immunol. 38:174–183. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shin HM, Minter LM, Cho OH, et al: Notch1
augments NF-kappaB activity by facilitating its nuclear retention.
EMBO J. 25:129–138. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Osipo C, Golde TE, Osborne BA and Miele
LA: Off the beaten pathway: the complex cross talk between Notch
and NF-kappaB. Lab Invest. 88:11–17. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cheng P, Zlobin A, Volgina V, et al:
Notch-1 regulates NF-kappaB activity in hemopoietic progenitor
cells. J Immunol. 167:4458–4467. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Amsen D, Antov A and Flavell RA: The
different faces of Notch in T-helper-cell differentiation. Nat Rev
Immunol. 9:116–124. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Abreu MT, Fukata M and Arditi M: TLR
signaling in the gut in health and disease. J Immunol.
174:4453–4460. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|