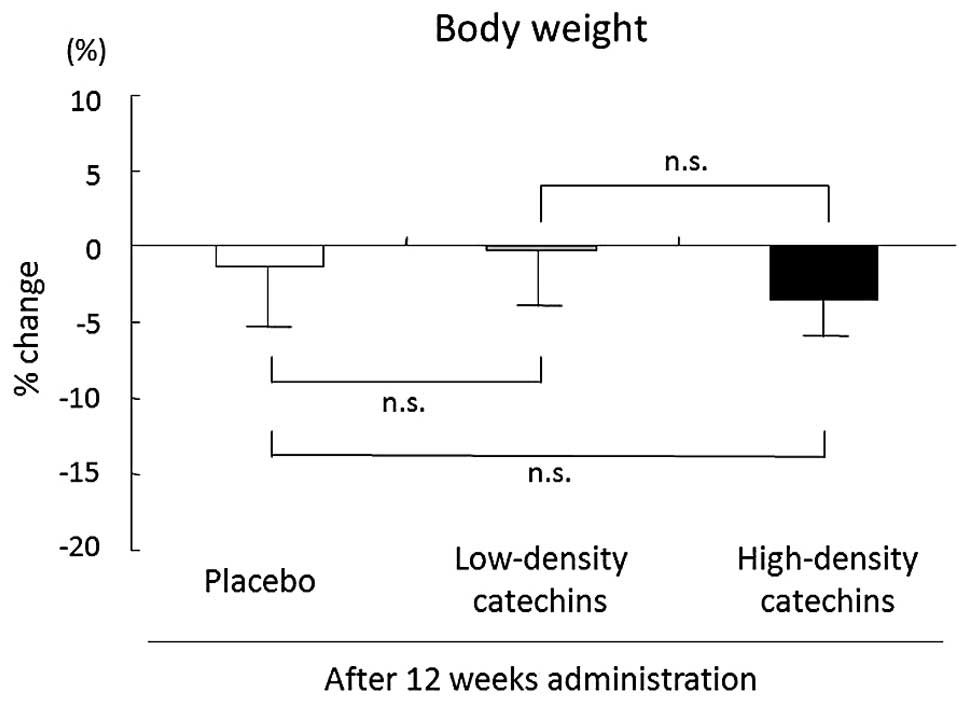
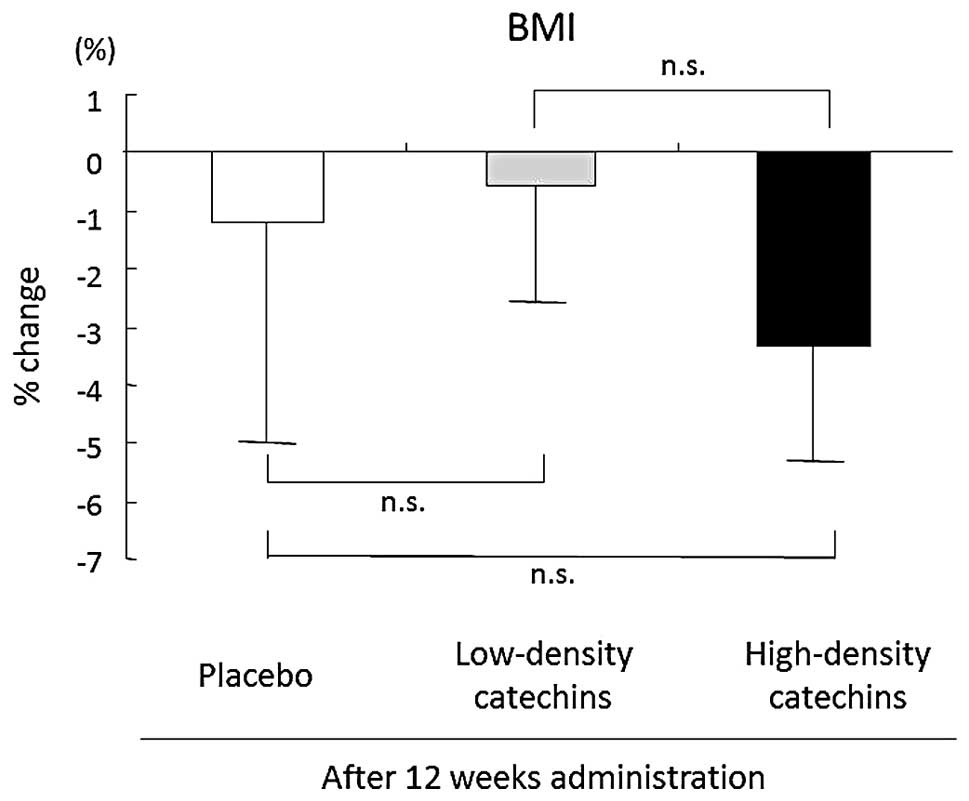
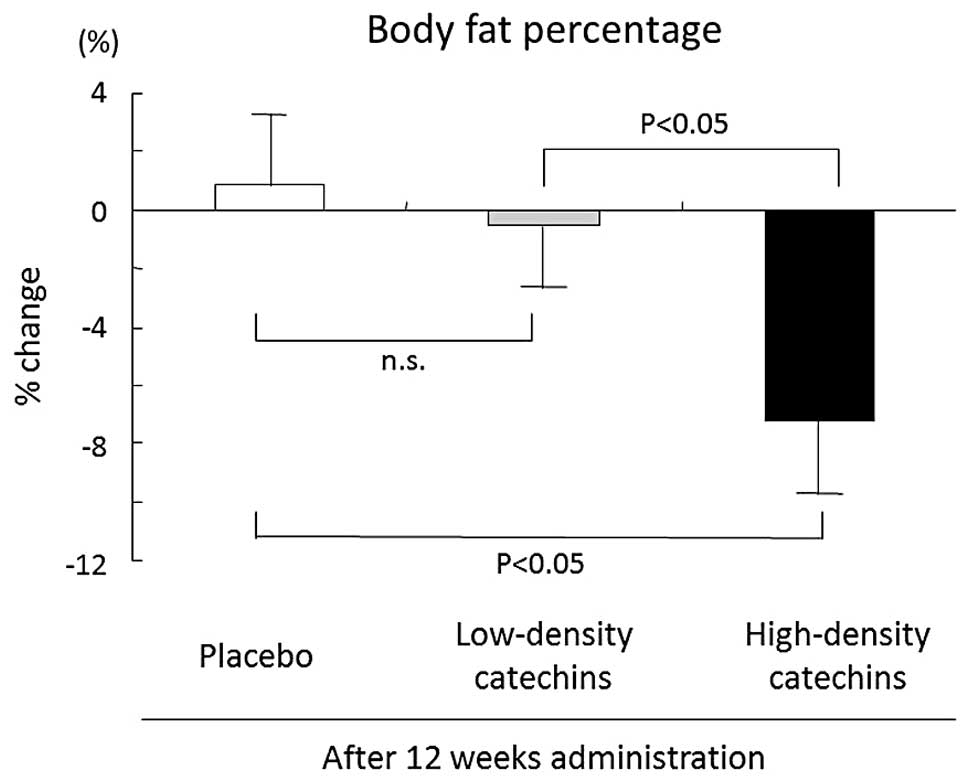
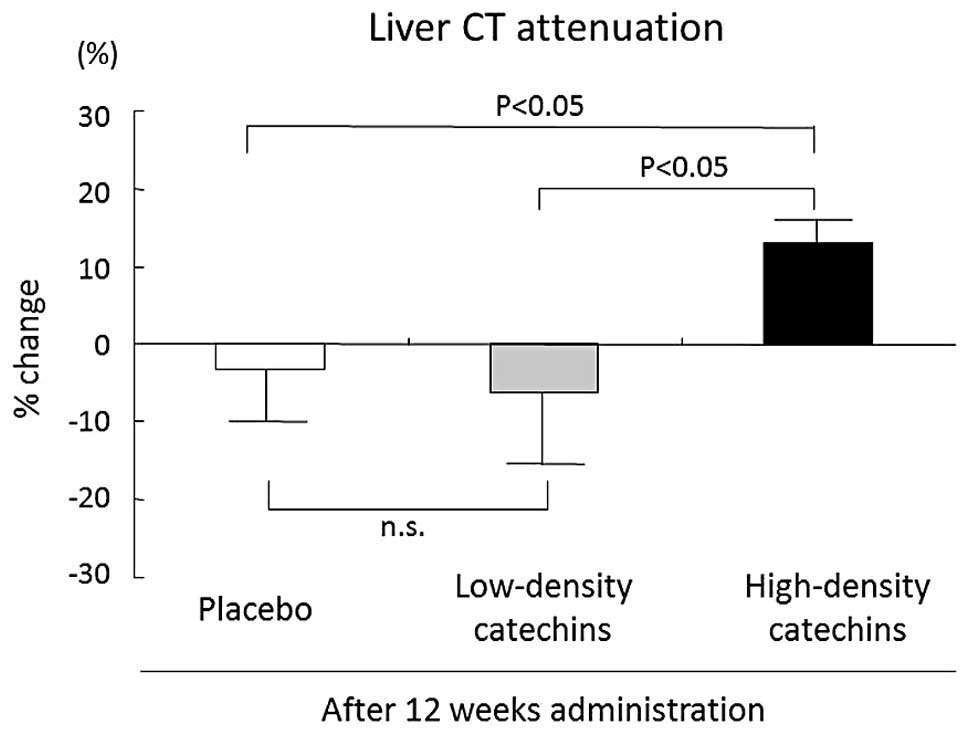
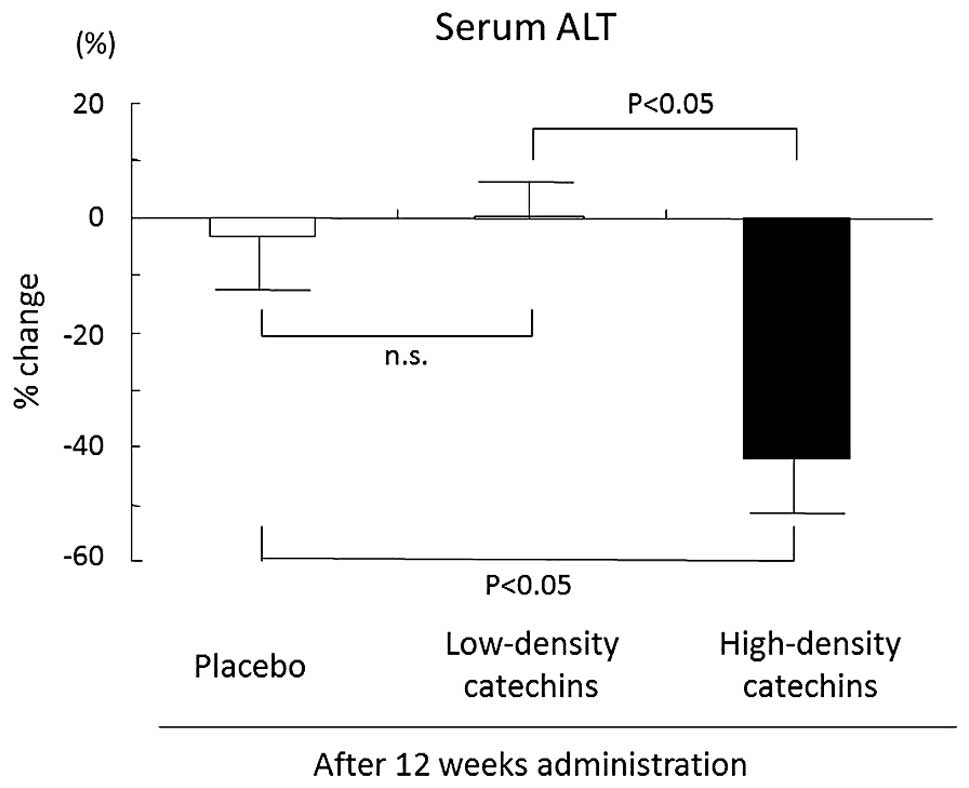
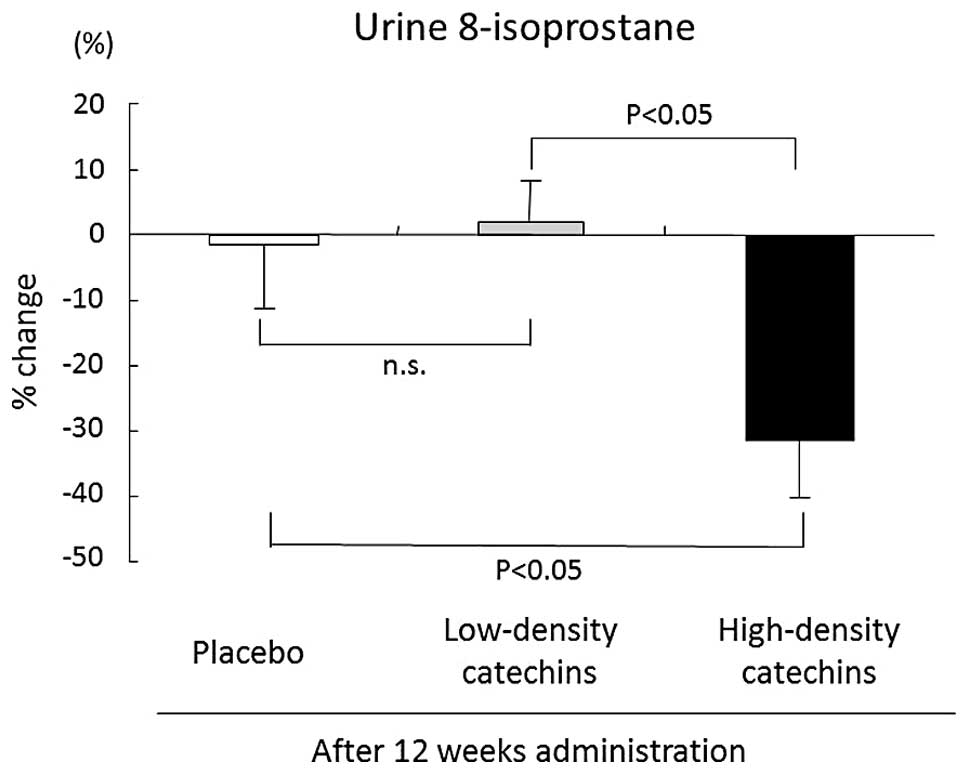
|
1
|
Neuschwander-Tetri BA and Caldwell SH:
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: summary of an AASLD single topic
conference. Hepatology. 38:1202–1219. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hakim IA, Harris RB, Brown S, et al:
Effect of increased tea consumption on oxidative DNA damage among
smokers: a randomized controlled study. J Nutr. 133:3303S–3309S.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hamza A and Zhan CG: How can
(−)-epigallocatechin gallate from green tea prevent HIV-1
infection? Mechanistic insights from computational modeling and the
implication for rational design of anti-HIV-1 entry inhibitors. J
Phys Chem B. 110:2910–2917. 2006.
|
|
4
|
Xu J, Wang J, Deng F, Hu Z and Wang H:
Green tea extract and its major component epigallocatechin gallate
inhibits hepatitis B virus in vitro. Antiviral Res. 78:242–249.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stangl V, Lorenz M and Stangl K: The role
of tea and tea flavonoids in cardiovascular health. Mol Nutr Food
Res. 50:218–228. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Maeda-Yamamoto M, Inagaki N, Kitaura J, et
al: O-methylated catechins from tea leaves inhibit multiple protein
kinases in mast cells. J Immunol. 172:4486–4492. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Khan N and Mukhtar H: Multitargeted
therapy of cancer by green tea polyphenols. Cancer Lett.
269:269–280. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim JA, Formoso G, Li Y, et al:
Epigallocatechin gallate, a green tea polyphenol, mediates
NO-dependent vasodilation using signaling pathways in vascular
endothelium requiring reactive oxygen species and Fyn. J Biol Chem.
282:13736–13745. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wolfram S: Effects of green tea and EGCG
on cardiovascular and metabolic health. J Am Coll Nutr.
26:373S–388S. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ueda M, Nishiumi S, Nagayasu H, Fukuda I,
Yoshida K and Ashida H: Epigallocatechin gallate promotes GLUT4
translocation in skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
377:286–290. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Koo SI and Noh SK: Green tea as inhibitor
of the intestinal absorption of lipids: potential mechanism for its
lipid-lowering effect. J Nutr Biochem. 18:179–183. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Murase T, Haramizu S, Shimotoyodome A,
Tokimitsu I and Hase T: Green tea extract improves running
endurance in mice by stimulating lipid utilization during exercise.
Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 290:R1550–R1556. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kyle UG, Genton L, Hans D and Pichard C:
Validation of a bioelectrical impedance analysis equation to
predict appendicular skeletal muscle mass (ASMM). Clin Nutr.
22:537–543. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lukaski HC: Applications of bioelectrical
impedance analysis: a critical review. Basic Life Sci. 55:365–374.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Duman DG, Celikel C, Tuney D, Imeryuz N,
Avsar E and Tozun N: Computed tomography in nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease: a useful tool for hepatosteatosis assessment? Dig
Dis Sci. 51:346–351. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Church TS, Kuk JL, Ross R, Priest EL,
Biltoft E and Blair SN: Association of cardiorespiratory fitness,
body mass index, and waist circumference to nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease. Gastroenterology. 130:2023–2030. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Oliva MR, Mortele KJ, Segatto E, et al:
Computed tomography features of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with
histopathologic correlation. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 30:37–43.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Devaraj S, Hirany SV, Burk RF and Jialal
I: Divergence between LDL oxidative susceptibility and urinary
F(2)-isoprostanes as measures of oxidative stress in type 2
diabetes. Clin Chem. 47:1974–1979. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Patrono C and FitzGerald GA: Isoprostanes:
potential markers of oxidant stress in atherothrombotic disease.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 17:2309–2315. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Powell EE, Cooksley WG, Hanson R, Searle
J, Halliday JW and Powell LW: The natural history of nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis: a follow-up study of forty-two patients for up to
21 years. Hepatology. 11:74–80. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Brunt EM: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis:
definition and pathology. Semin Liver Dis. 21:3–16. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bugianesi E, Leone N, Vanni E, et al:
Expanding the natural history of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: from
cryptogenic cirrhosis to hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 123:134–140. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Brunt EM: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis:
pathologic features and differential diagnosis. Semin Diagn Pathol.
22:330–338. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Marrero JA, Fontana RJ, Su GL, Conjeevaram
HS, Emick DM and Lok AS: NAFLD may be a common underlying liver
disease in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in the United
States. Hepatology. 36:1349–1354. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Caldwell SH, Oelsner DH, Iezzoni JC,
Hespenheide EE, Battle EH and Driscoll CJ: Cryptogenic cirrhosis:
clinical characterization and risk factors for underlying disease.
Hepatology. 29:664–669. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kersten S, Seydoux J, Peters JM, Gonzalez
FJ, Desvergne B and Wahli W: Peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor alpha mediates the adaptive response to fasting. J Clin
Invest. 103:1489–1498. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nakai M, Fukui Y, Asami S, et al:
Inhibitory effects of oolong tea polyphenols on pancreatic lipase
in vitro. J Agric Food Chem. 53:4593–4598. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Matsui T, Yoshimoto C, Osajima K, Oki T
and Osajima Y: In vitro survey of alpha-glucosidase inhibitory food
components. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 60:2019–2022. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Unno T, Tago M, Suzuki Y, et al: Effect of
tea catechins on postprandial plasma lipid responses in human
subjects. Br J Nutr. 93:543–547. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Murase T, Nagasawa A, Suzuki J, Hase T and
Tokimitsu I: Beneficial effects of tea catechins on diet-induced
obesity: stimulation of lipid catabolism in the liver. Int J Obes
Relat Metab Disord. 26:1459–1464. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ullmann U, Haller J, Bakker GC, Brink EJ
and Weber P: Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) (TEAVIGO) does not
impair nonhaem-iron absorption in man. Phytomedicine. 12:410–415.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kohgo Y, Ohtake T, Ikuta K, Suzuki Y,
Torimoto Y and Kato J: Dysregulation of systemic iron metabolism in
alcoholic liver diseases. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23(Suppl 1):
S78–S81. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sumida Y, Kanemasa K, Fukumoto K, et al:
Effect of iron reduction by phlebotomy in Japanese patients with
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A pilot study. Hepatol Res.
36:315–321. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, et al:
The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease:
practice guideline by the American Gastroenterological Association,
American Association for the study of liver diseases, and American
College of Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology. 142:1592–1609. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Farrell GC, van Rooyen D, Gan L and
Chitturi S: NASH is an inflammatory disorder: pathogenic,
prognostic and therapeutic implications. Gut Liver. 6:149–171.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|