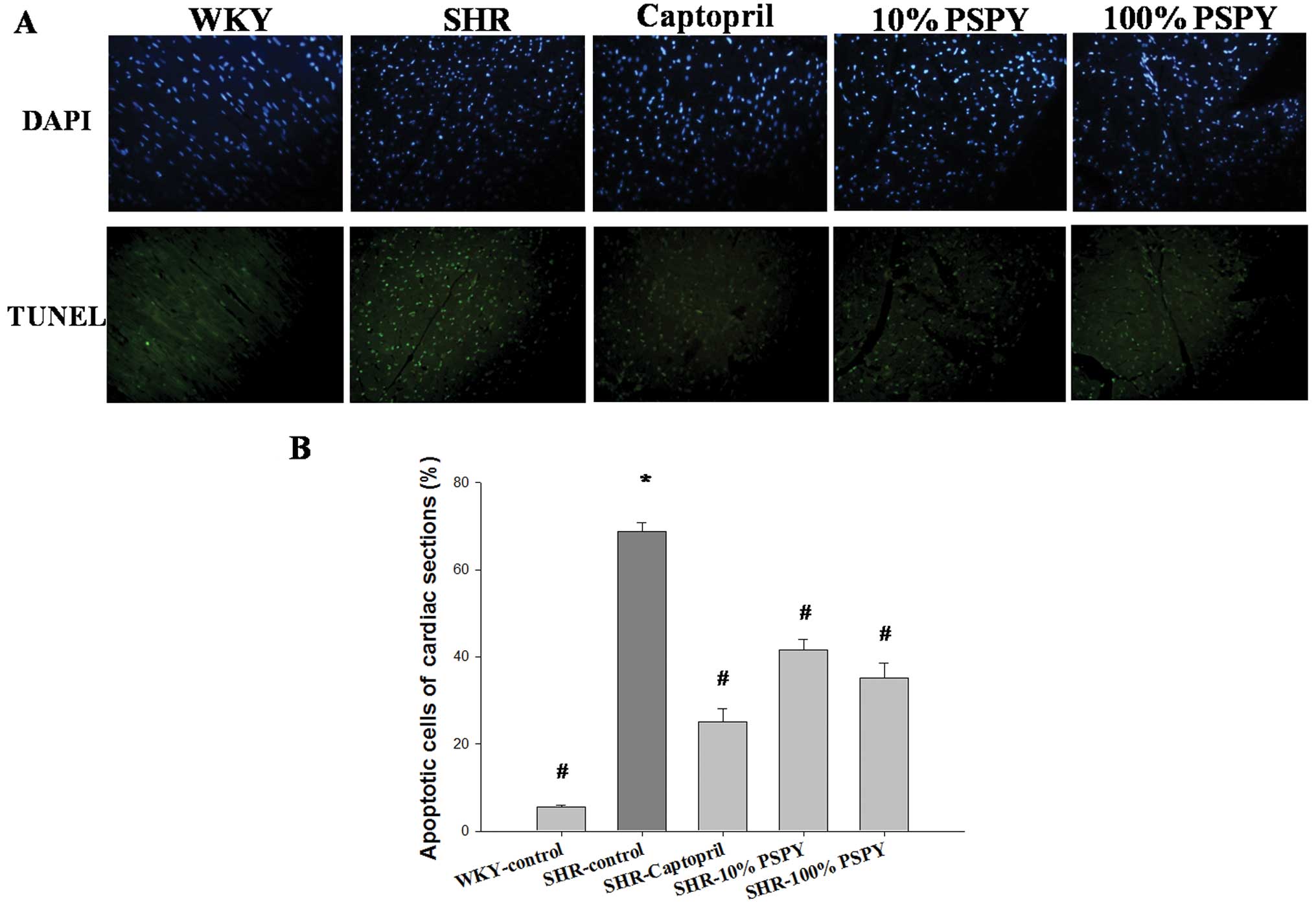
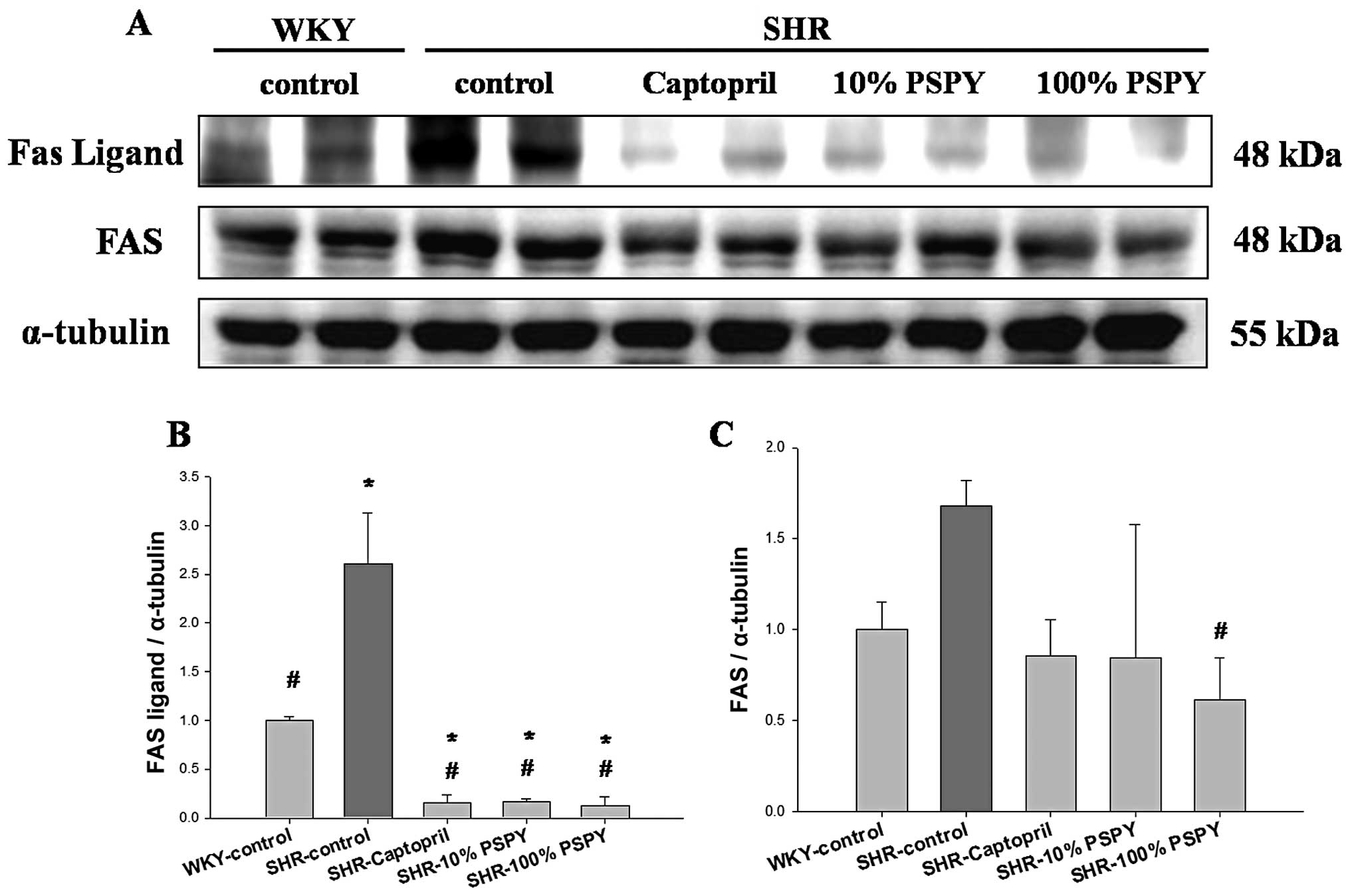
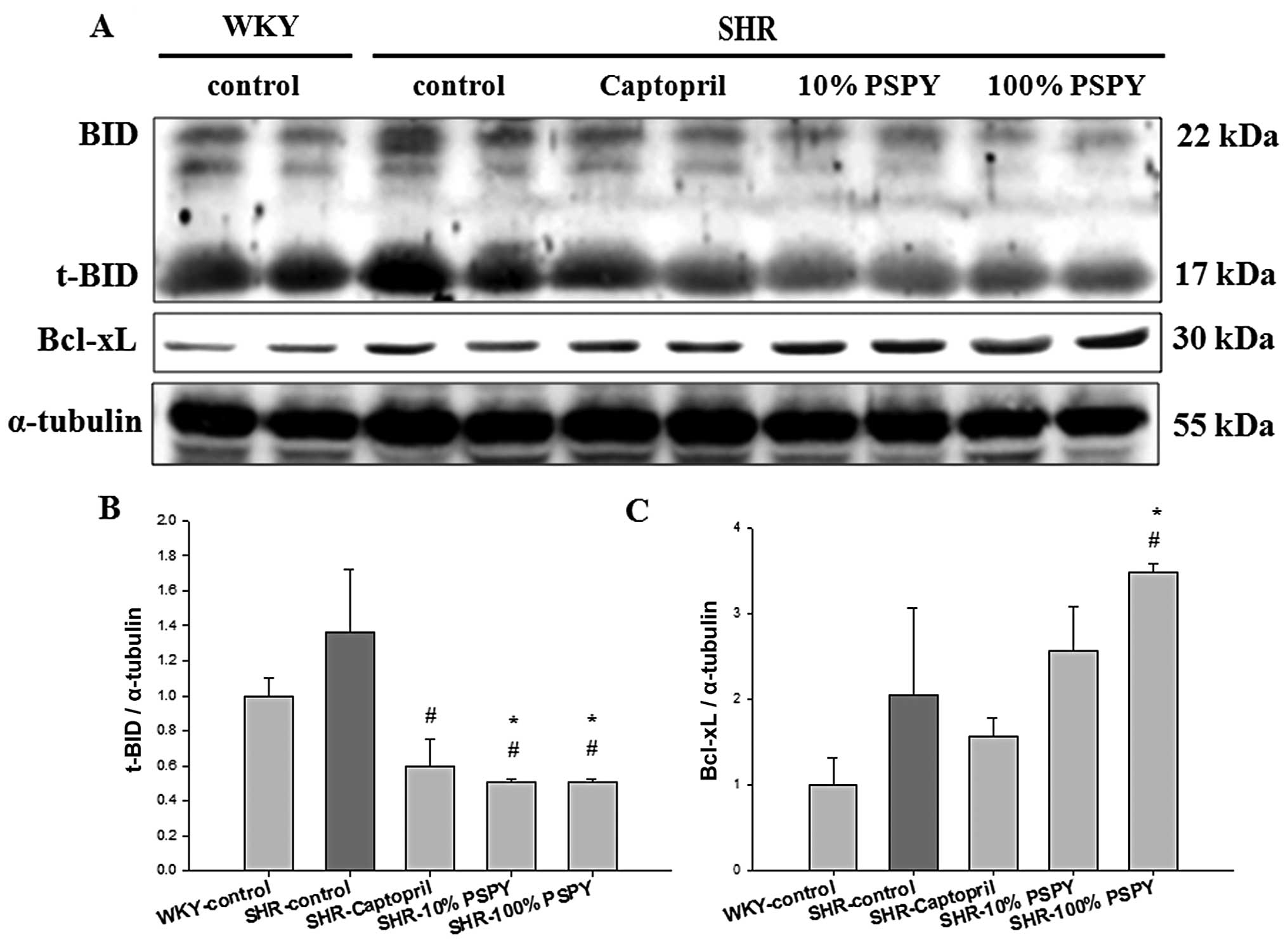
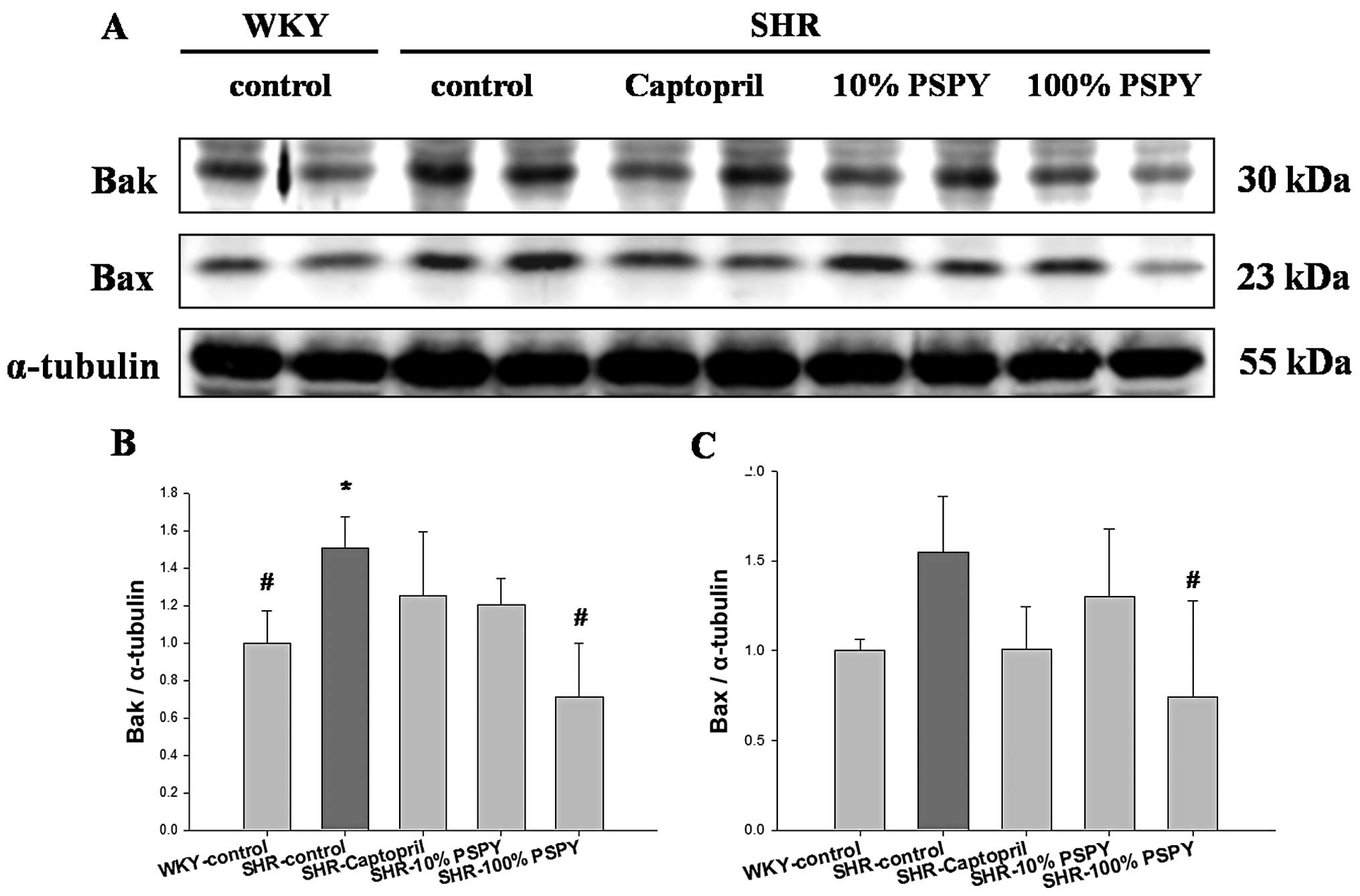
|
1
|
Tocci G, Sciarretta S and Volpe M:
Development of heart failure in recent hypertension trials. J
Hypertens. 26:1477–1486. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Morillas P, de Andrade H, Castillo J,
Quiles J, Bertomeu-González V, Cordero A, Tarazón E, Roselló E,
Portolés M, Rivera M and Bertomeu-Martínez V: Inflammation and
apoptosis in hypertension. Relevance of the extent of target organ
damage. Rev Esp Cardiol. 65:819–825. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee SD, Chu CH, Huang EJ, Lu MC, Liu JY,
Liu CJ, Hsu HH, Lin JA, Kuo WW and Huang CY: Roles of insulin-like
growth factor II in cardiomyoblast apoptosis and in hypertensive
rat heart with abdominal aorta ligation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 291:E306–E314. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kuo WW, Hsu TC, Chain MH, Lai CH, Wang WH,
Tsai FJ, Tsai CH, Wu CH, Huang CY and Tzang BS: Attenuated cardiac
mitochondrial-dependent apoptotic effects by li-fu formula in
hamsters fed with a hypercholesterol diet. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2011:5303452011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Haunstetter A and Izumo S: Apoptosis:
basic mechanisms and implications for cardiovascular disease. Circ
Res. 82:1111–1129. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Narula J, Haider N, Arbustini E and
Chandrashekhar Y: Mechanisms of disease: apoptosis in heart failure
- seeing hope in death. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 3:681–688.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Harrison DG, Cai H, Landmesser U and
Griendling KK: Interactions of angiotensin II with NAD(P)H oxidase,
oxidant stress and cardiovascular disease. J Renin Angiotensin
Aldosterone Syst. 4:51–61. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Filippatos G, Tilak M, Pinillos H and Uhal
BD: Regulation of apoptosis by angiotensin II in the heart and
lungs (Review). Int J Mol Med. 7:273–280. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fujio Y, Nguyen T, Wencker D, Kitsis RN
and Walsh K: Akt promotes survival of cardiomyocytes in vitro and
protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury in mouse heart.
Circulation. 101:660–667. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Athanasiou A, Clarke AB, Turner AE,
Kumaran NM, Vakilpour S, Smith PA, Bagiokou D, Bradshaw TD,
Westwell AD, Fang L, Lobo DN, Constantinescu CS, Calabrese V,
Loesch A, Alexander SP, Clothier RH, Kendall DA and Bates TE:
Cannabinoid receptor agonists are mitochondrial inhibitors: a
unified hypothesis of how cannabinoids modulate mitochondrial
function and induce cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
364:131–137. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bishopric NH, Andreka P, Slepak T and
Webster KA: Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis in the cardiac
myocyte. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 1:141–150. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee SD, Tzang BS, Kuo WW, Lin YM, Yang AL,
Chen SH, Tsai FJ, Wu FL, Lu MC and Huang CY: Cardiac fas
receptor-dependent apoptotic pathway in obese Zucker rats. Obesity
(Silver Spring). 15:2407–2415. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Brown GC and Borutaite V: Nitric oxide,
cytochrome c and mitochondria. Nitric oxide, cytochrome c and
mitochondria. Biochem Soc Symp. 66:17–25. 1999.
|
|
14
|
Ren J, Samson WK and Sowers JR:
Insulin-like growth factor I as a cardiac hormone: physiological
and pathophysiological implications in heart disease. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 31:2049–2061. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vincent AM and Feldman EL: Control of cell
survival by IGF signaling pathways. Growth Horm IGF Res.
12:193–197. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Simoncini T, Hafezi-Moghadam A, Brazil DP,
Ley K, Chin WW and Liao JK: Interaction of oestrogen receptor with
the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase. Nature.
407:538–541. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu CF, Tung YT, Wu CL, Lee BH, Hsu WH and
Pan TM: Antihypertensive effects of Lactobacillus-fermented milk
orally administered to spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Agric
Food Chem. 59:4537–4543. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Inoue K, Shirai T, Ochiai H, Kasao M,
Hayakawa K, Kimura M and Sansawa H: Blood-pressure-lowering effect
of a novel fermented milk containing gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
in mild hypertensives. Eur J Clin Nutr. 57:490–495. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Komatsuzaki N, Nakamura T, Kimura T and
Shima J: Characterization of glutamate decarboxylase from a high
gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-producer, Lactobacillus
paracasei. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 72:278–285. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu TY, Tsai CC, Hwang YT and Chiu TH:
Effect of antioxidant activity and functional properties of
chingshey purple sweet potato fermented milk by Lactobacillus
acidophilus, L. delbrueckii subsp lactis, and L.
gasseri strains. J Food Sci. 77:M2–M8. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fortuno MA, Ravassa S, Fortuno A, Zalba G
and Diez J: Cardiomyocyte apoptotic cell death in arterial
hypertension: mechanisms and potential management. Hypertension.
38:1406–1412. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Richey PA and Brown SP: Pathological
versus physiological left ventricular hypertrophy: a review. J
Sports Sci. 16:129–141. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin PP, Hsieh YM, Kuo WW, Lin CC, Tsai FJ,
Tsai CH, Huang CY and Tsai CC: Inhibition of cardiac hypertrophy by
probiotic-fermented purple sweet potato yogurt in spontaneously
hypertensive rat hearts. Int J Mol Med. 30:1365–1375.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Díez J, Fortuño MA and Ravassa S:
Apoptosis in hypertensive heart disease. Curr Opin Cardiol.
13:317–325. 1998.
|
|
25
|
Huang CY, Yang AL, Lin YM, Wu FN, Lin JA,
Chan YS, Tsai FJ, Tsai CH, Kuo CH and Lee SD: Anti-apoptotic and
pro-survival effects of exercise training on hypertensive hearts. J
Appl Physiol. 112:883–891. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
McGowan BS, Ciccimaro EF, Chan TO and
Feldman AM: The balance between pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic
pathways in the failing myocardium. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 3:191–206.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Torella D, Rota M, Nurzynska D, Musso E,
Monsen A, Shiraishi I, Zias E, Walsh K, Rosenzweig A, Sussman MA,
Urbanek K, Nadal-Ginard B, Kajstura J, Anversa P and Leri A:
Cardiac stem cell and myocyte aging, heart failure, and
insulin-like growth factor-1 overexpression. Circ Res. 94:514–524.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Palmen M, Daemen MJ, Bronsaer R, Dassen
WR, Zandbergen HR, Kockx M, Smits JF, van der Zee R and Doevendans
PA: Cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction is impaired in
IGF-1 deficient mice. Circ Res. 50:516–524. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wong CM, Bansal G, Pavlickova L, Marcocci
L and Suzuki YJ: Reactive oxygen species and antioxidants in
pulmonary hypertension. Antioxid Redox Signal. 18:1789–1796. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lam V, Su J, Koprowski S, Hsu A, Tweddell
JS, Rafiee P, Gross GJ, Salzman NH and Baker JE: Intestinal
microbiota determine severity of myocardial infarction in rats.
FASEB J. 26:1727–1735. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sobol KV, Belostotskaya GB and Nesterov
VP: The effect of probiotics and their metabolic products on
cardiovascular system cells in vitro. Dokl Biol Sci. 436:9–12.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|