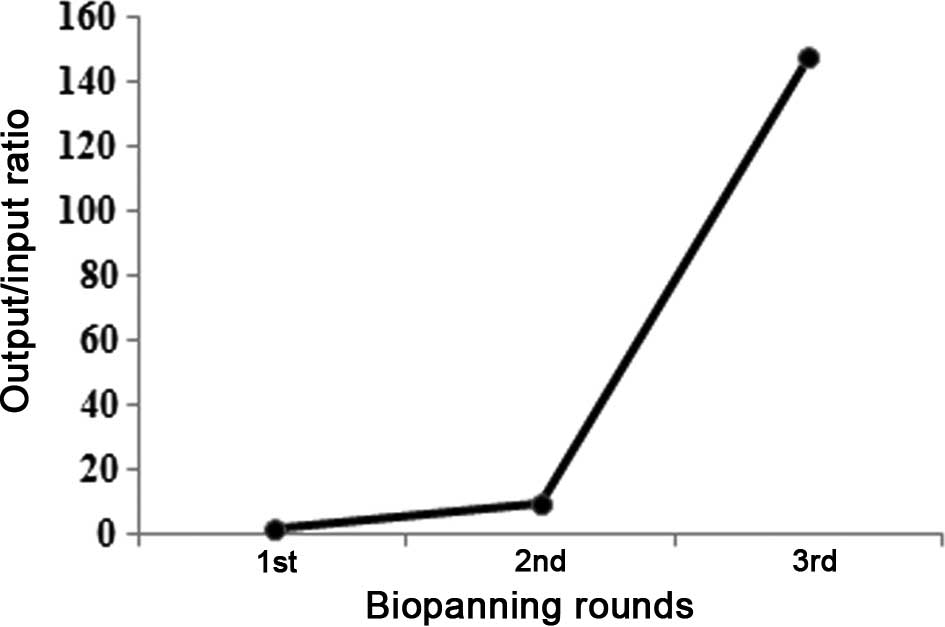
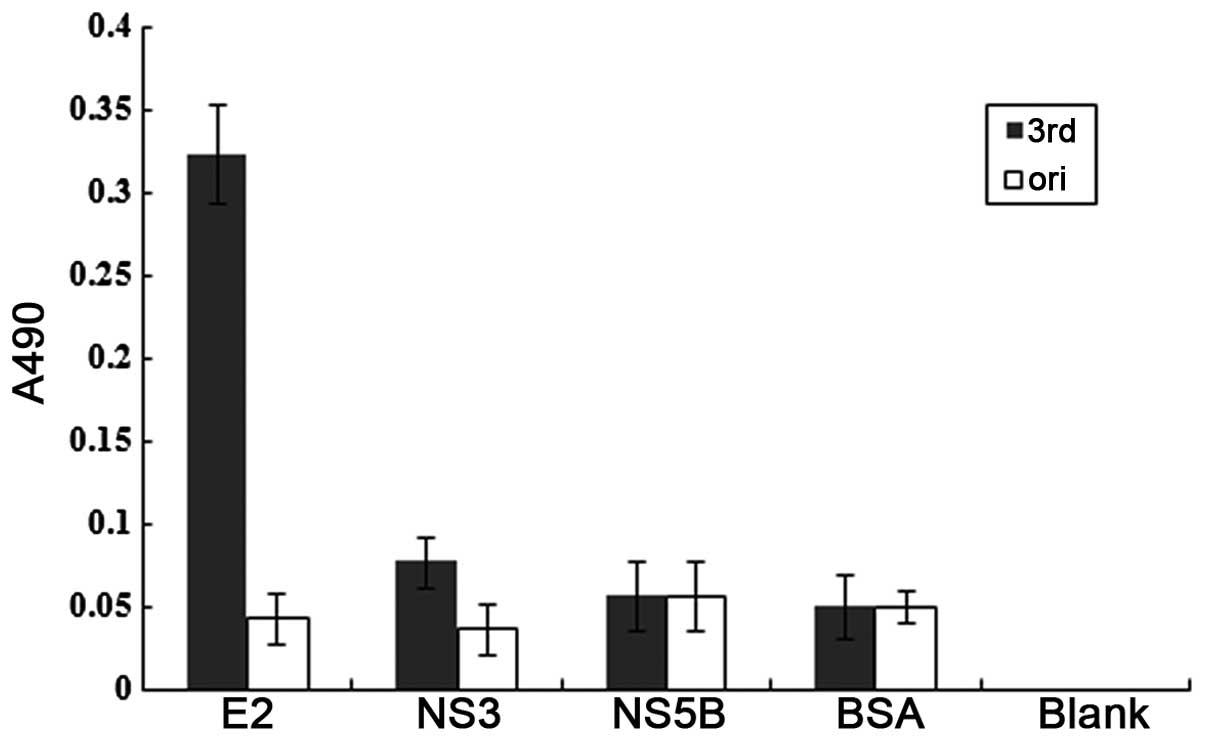
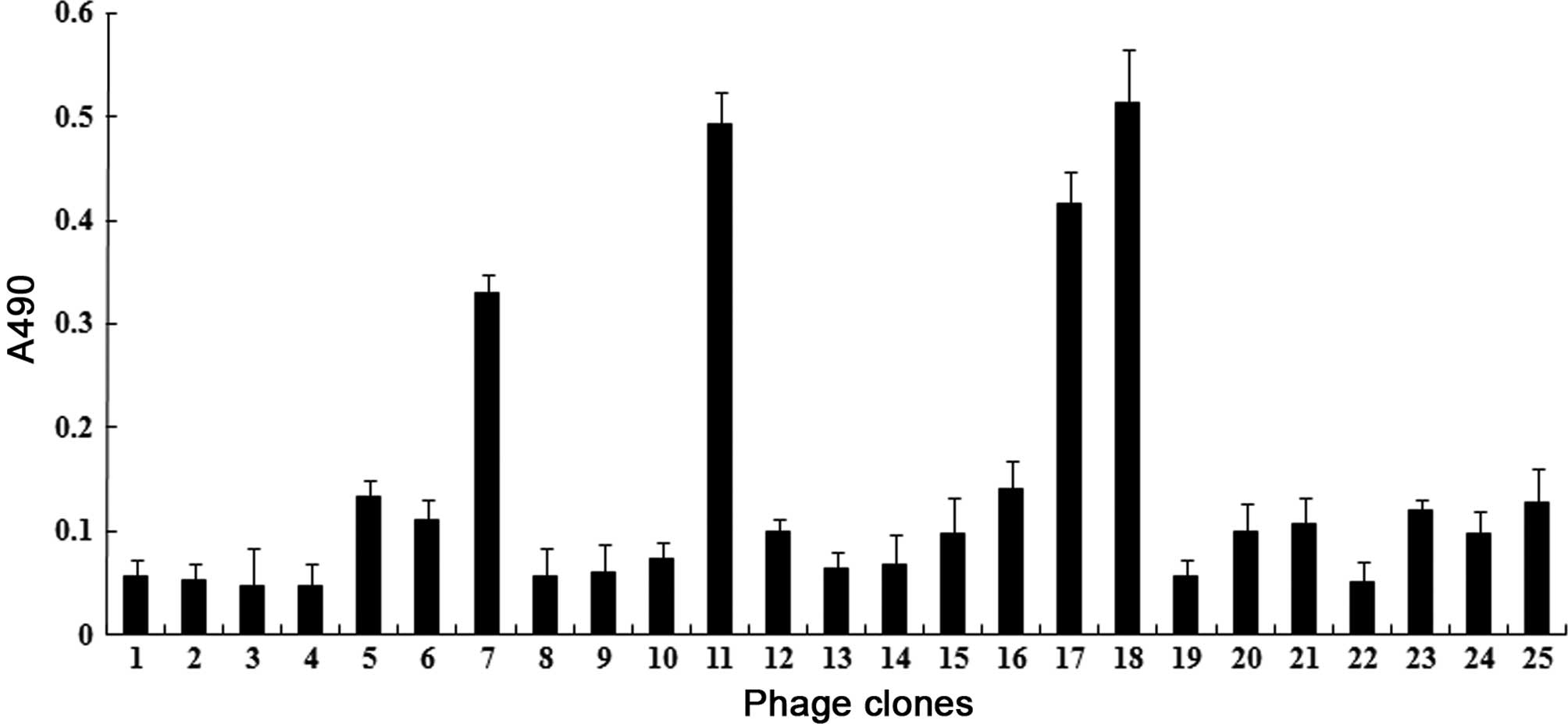
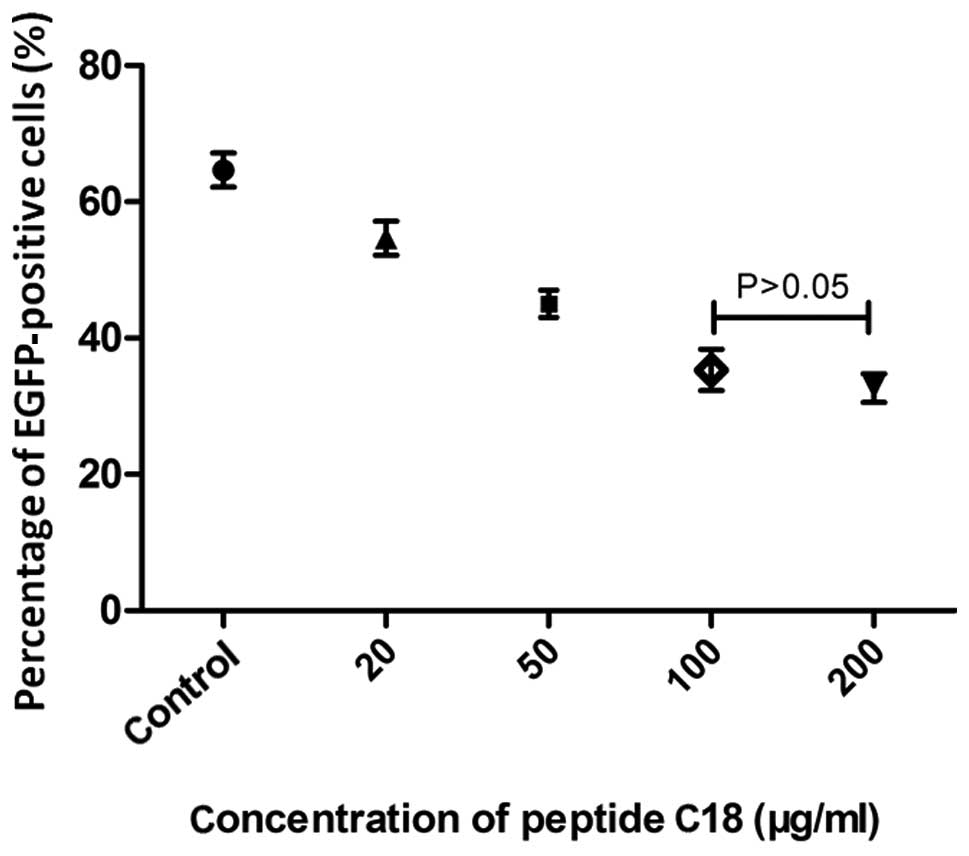
|
1
|
McGivern DR and Lemon SM: Virus-specific
mechanisms of carcinogenesis in hepatitis C virus associated liver
cancer. Oncogene. 30:1969–1983. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bacon BR and McHutchison JG: Into the
light: strategies for battling hepatitis C. Am J Manag Care.
13(Suppl 12): S319–S326. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Berwyn C: Molecular virology of hepatitis
C virus. J Gen Virol. 78:2397–2410. 1997.
|
|
4
|
Penin F, Dubuisson J, Rey FA, Moradpour D
and Pawlotsky JM: Structural biology of hepatitis C virus.
Hepatology. 39:5–19. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Reed KE and Rice CM: Overview of hepatitis
C virus genome structure, polyprotein processing, and protein
properties. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 242:55–84. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Flint M and McKeating JA: The role of the
hepatitis C virus glycoproteins in infection. Rev Med Virol.
10:101–117. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Simmonds P: Genetic diversity and
evolution of hepatitis C virus - 15 years on. J Gen Virol.
85:3173–3188. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartosch B, Verney G, Dreux M, Donot P,
Morice Y, Penin F, Pawlotsky JM, Lavillette D and Cosset FL: An
interplay between hypervariable region 1 of the hepatitis C virus
E2 glycoprotein, the scavenger receptor BI, and high-density
lipoprotein promotes both enhancement of infection and protection
against neutralizing antibodies. J Virol. 79:8217–8229. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Callens N, Ciczora Y, Bartosch B, Vu-Dac
N, Cosset FL and Pawlotsky JM: Basic residues in hypervariable
region 1 of hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein E2 contribute
to virus entry. J Virol. 79:15331–15341. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zeisel MB, Fofana I, Fafi-Kremer S and
Baumert TF: Hepatitis C virus entry into hepatocytes: molecular
mechanisms and targets for antiviral therapies. J Hepatol.
54:566–576. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Owsianka A, Clayton RF, Loomis-Price LD,
McKeating JA and Patel AH: Functional analysis of hepatitis C virus
E2 glycoproteins and virus-like particles reveals structural
dissimilarities between different forms of E2. J Gen Virol.
82:1877–1883. 2001.
|
|
12
|
Lavillette D, Tarr AW, Voisset C, Donot P,
Bartosch B, Bain C, Patel AH, Dubuisson J, Ball JK and Cosset FL:
Characterization of host-range and cell entry properties of the
major genotypes and subtypes of hepatitis C virus. Hepatology.
41:265–274. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Flint M, Dubuisson J, Maidens C, Harrop R,
Guile GR, Borrow P and McKeating JA: Functional characterization of
intracellular and secreted forms of a truncated hepatitis C virus
E2 glycoprotein. J Virol. 74:702–709. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yao M, Fang HL, Yin W, Lei YF, Yang J, Sun
MN, Tian JH and Lü X: Prokaryotic expression and purification of
truncated hepatitis c virus envelope glycoprotein E2. Sci Technol
Eng. 9:2296–2298. 2009.
|
|
15
|
Bartosch B, Dubuisson J and Cosset FL:
Infectious hepatitis C virus pseudo-particles containing functional
E1–E2 envelope protein complexes. J Exp Med. 197:633–642.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hsu M, Zhang J, Flint M, Logvinoff C,
Cheng-Mayer C, Rice CM and McKeating JA: Hepatitis C virus
glycoproteins mediate pH-dependent cell entry of pseudotyped
retroviral particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:7271–7276. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lindenbach BD, Evans MJ, Syder AJ, Wölk B,
Tellinghuisen TL, Liu CC, Maruyama T, Hynes RO, Burton DR,
McKeating JA and Rice CM: Complete replication of hepatitis C virus
in cell culture. Science. 309:623–626. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lindenbach BD, Meuleman P, Ploss A,
Vanwolleghem T, Syder AJ, McKeating JA, Lanford RE, Feinstone SM,
Major ME, Leroux-Roels G and Rice CM: Cell culture-grown hepatitis
C virus is infectious in vivo and can be recultured in vitro. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:3805–3809. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang J, Lei YF, Yin W, Wei SH, An QX, Lv
X, Hu XB and Xu ZK: Production and characterization of monoclonal
antibody specific for NS3 helicase of hepatitis C virus. Hybridoma.
27:181–186. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pileri P, Uematsu Y, Campagnoli S, Galli
G, Falugi F, Petracca R, Weiner AJ, Houghton M, Rosa D, Grandi G
and Abrignani S: Binding of hepatitis C virus to CD81. Science.
282:938–941. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang J, Randall G, Higginbottom A, Monk
P, Rice CM and McKeating JA: CD81 is required for hepatitis C virus
glycoprotein-mediated viral infection. J Virol. 78:1448–1455. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Scarselli E, Ansuini H, Cerino R,
Roccasecca RM, Acali S, Filocamo G, Traboni C, Nicosia A, Cortese R
and Vitelli A: The human scavenger receptor class B type I is a
novel candidate receptor for the hepatitis C virus. EMBO J.
21:5017–5025. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bartosch B, Vitelli A, Granier C, Goujon
C, Dubuisson J, Pascale S, Scarselli E, Cortese R, Nicosia A and
Cosset FL: Cell entry of hepatitis C virus requires a set of
co-receptors that include the CD81 tetraspanin and the SR-B1
scavenger receptor. J Biol Chem. 278:41624–41630. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Agnello V, Abel G, Elfahal M, Knight GB
and Zhang QX: Hepatitis C virus and other flaviviridae viruses
enter cells via low density lipoprotein receptor. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 96:12766–12771. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cormier EG, Durso RJ, Tsamis F, Boussemart
L, Manix C, Olson WC, Gardner JP and Dragic T: L-SIGN (CD209L) and
DC-SIGN (CD209) mediate transinfection of liver cells by hepatitis
C virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:14067–14072. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Garson JA, Lubach D, Passas J, Whitby K
and Grant PR: Suramin blocks hepatitis C binding to human hepatoma
cells in vitro. J Med Virol. 57:238–242. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Evans MJ, von Hahn T, Tscherne DM, Syder
AJ, Panis M, Wölk B, Hatziioannou T, McKeating JA, Bieniasz PD and
Rice CM: Claudin-1 is a hepatitis C virus co-receptor required for
a late step in entry. Nature. 446:801–805. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ploss A, Evans MJ, Gaysinskaya VA, Panis
M, You H, de Jong YP and Rice CM: Human occludin is a hepatitis C
virus entry factor required for infection of mouse cells. Nature.
457:882–886. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cervia JS and Smith MA: Enfuvirtide
(T-20): a novel human immunodeficiency virus type 1 fusion
inhibitor. Clin Infect Dis. 37:1102–1106. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dorr P, Westby M, Dobbs S, Griffin P,
Irvine B, Macartney M, Mori J, Rickett G, Smith-Burchnell C, Napier
C, Webster R, Armour D, Price D, Stammen B, Wood A and Perros M:
Maraviroc (UK-427, 857), a potent, orally bioavailable, and
selective small-molecule inhibitor of chemokine receptor CCR5 with
broad-spectrum antihuman immunodeficiency virus type 1 activity.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 49:4721–4732. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Fätkenheuer G, Pozniak AL, Johnson MA,
Plettenberg A, Staszewski S, Hoepelman AI, Saag MS, Goebel FD,
Rockstroh JK, Dezube BJ, Jenkins TM, Medhurst C, Sullivan JF,
Ridgway C, Abel S, James IT, Youle M and van der Ryst E: Efficacy
of short-term monotherapy with maraviroc, a new CCR5 antagonist, in
patients infected with HIV-1. Nat Med. 11:1170–1172.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shimizu YK, Hijikata M, Iwamoto A, Alter
HJ, Purcell RH and Yoshikura H: Neutralizing antibodies against
hepatitis C virus and the emergence of neutralization escape mutant
viruses. J Virol. 68:1494–1500. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cao J, Zhao P, Miao XH, Zhao LJ, Xue LJ
and Qi ZT: Phage display selection on whole cells yields a small
peptide specific for HCV receptor human CD81. Cell Res. 13:473–479.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cao J, Liao XL, Wu SM, Zhao P, Zhao LJ, Wu
WB and Qi ZT: Selection of a phage-displayed peptide recognized by
monoclonal antibody directed blocking the site of hepatitis C virus
E2 for human CD81. J Microbiol Methods. 68:601–604. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Molek P, Strukelj B and Bratkovic T:
Peptide phage display as a tool for drug discovery: targeting
membrane receptors. Molecules. 16:857–887. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim MS, Park C, Lee JH and Myung H:
Selection and target-site mapping of peptides inhibiting HCV NS5B
polymerase using phage display. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 18:328–333.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Baldick CJ, Wichroski MJ, Pendri A, Walsh
AW, Fang J, Mazzucco CE, Pokornowski KA, Rose RE, Eggers BJ, Hsu M,
Zhai W, Zhai G, Gerritz SW, Poss MA, Meanwell NA, Cockett MI and
Tenney DJ: A novel small molecule inhibitor of hepatitis C virus
entry. PLoS Pathog. 6:e10010862010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu R, Tewari M, Kong R, Zhang R,
Ingravallo P and Ralston R: A peptide derived from hepatitis C
virus E2 envelope protein inhibits a post-binding step in HCV
entry. Antiviral Res. 86:172–179. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hong HW, Lee SW and Myung H: Selection of
peptides binding to HCV E2 and inhibiting viral infectivity. J
Microbiol Biotechnol. 20:1769–1771. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|