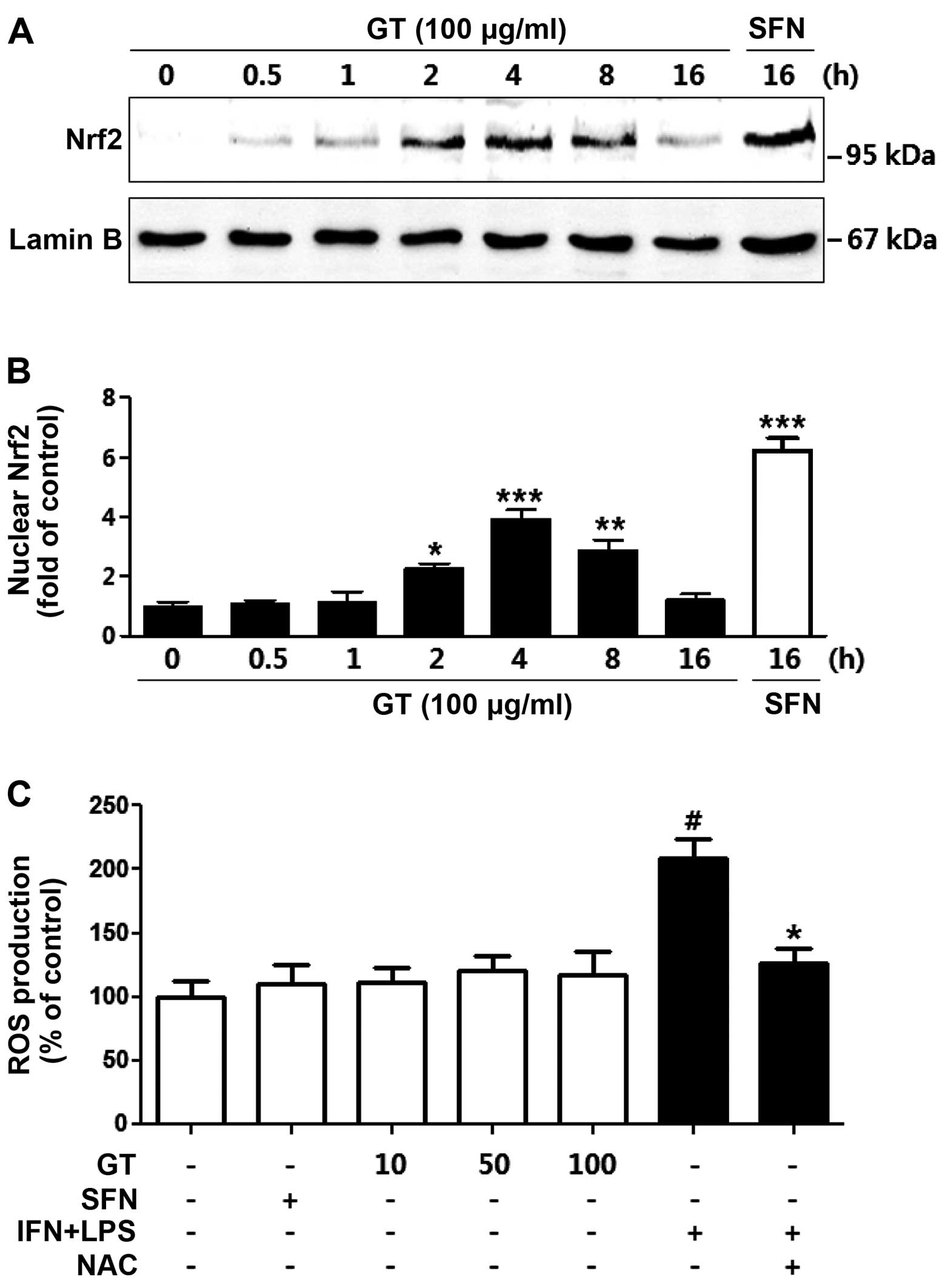
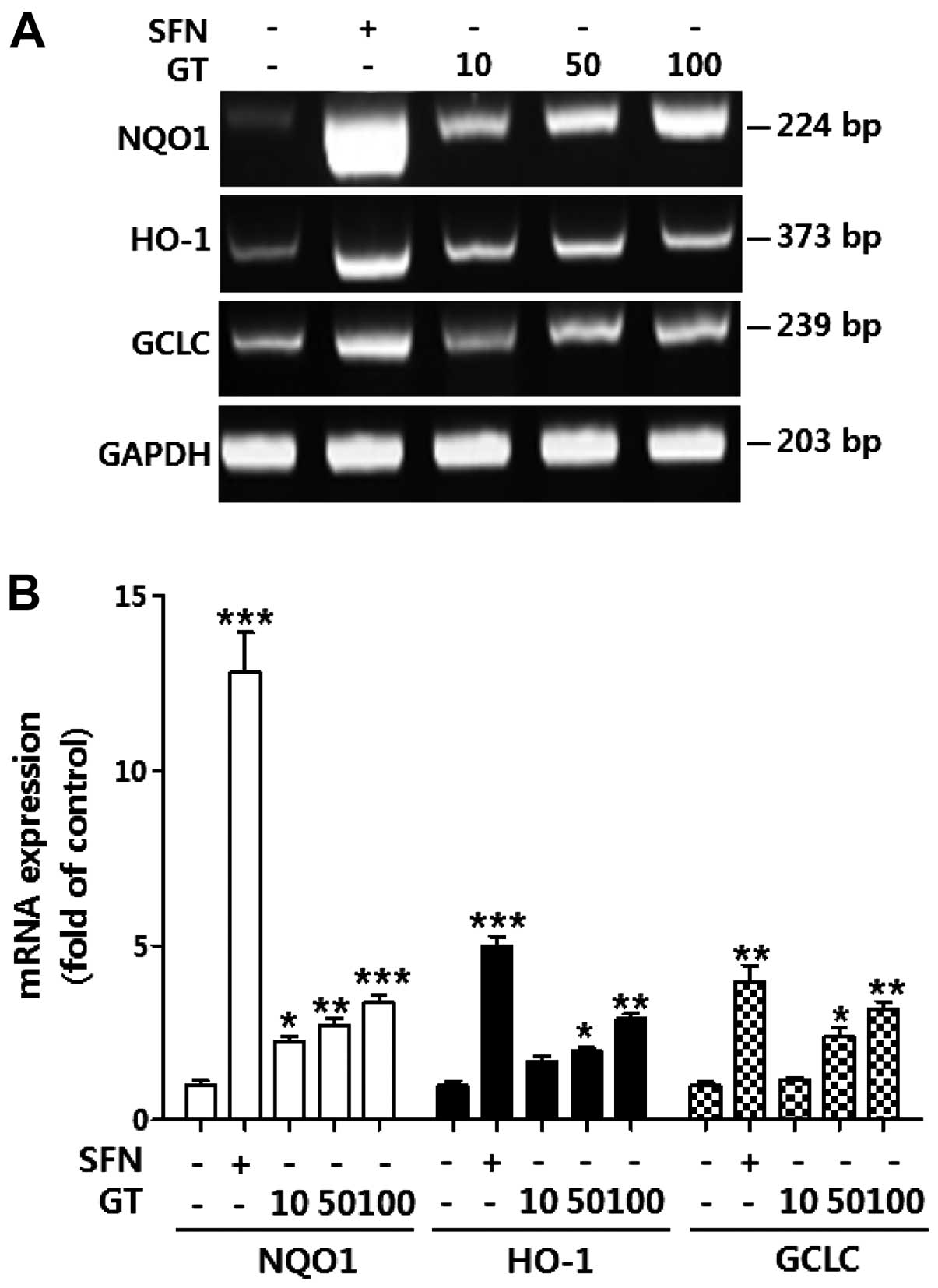
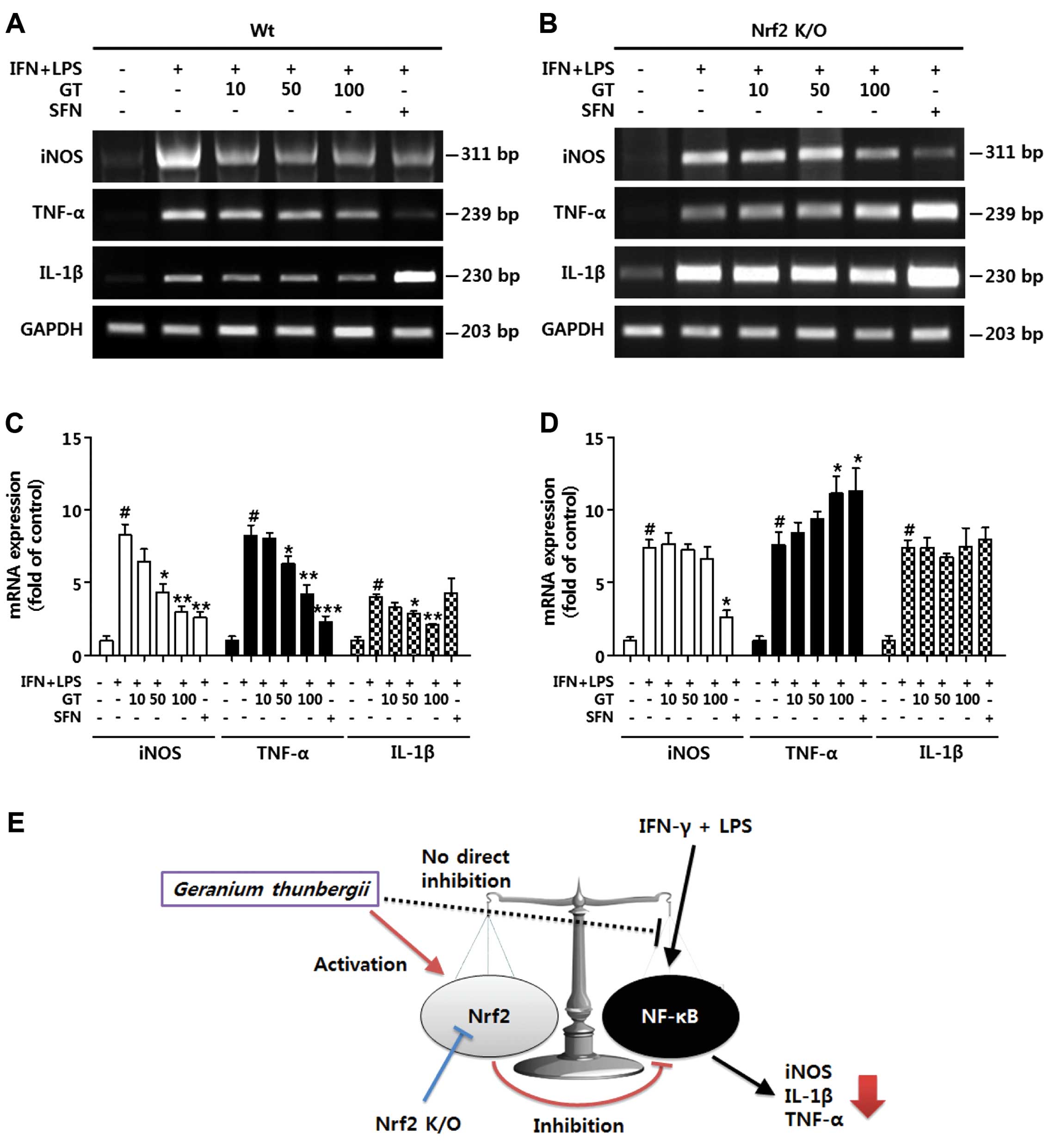
|
1
|
Reuter S, Gupta SC, Chaturvedi MM and
Aggarwal BB: Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: How are
they linked? Free Radic Biol Med. 49:1603–1616. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nathan C and Ding A: Nonresolving
inflammation. Cell. 140:871–882. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Laskin DL, Sunil VR, Gardner CR and Laskin
JD: Macrophages and tissue injury: Agents of defense or
destruction? Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 51:267–288. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Davignon JL, Hayder M, Baron M, Boyer JF,
Constantin A, Apparailly F, Poupot R and Cantagrel A: Targeting
monocytes/macrophages in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 52:590–598. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Alam J, Stewart D, Touchard C, Boinapally
S, Choi AM and Cook JL: Nrf2, a Cap‘n’Collar transcription factor,
regulates induction of the heme oxygenase-1 gene. J Biol Chem.
274:26071–26078. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Baird L and Dinkova-Kostova AT: The
cytoprotective role of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Arch Toxicol.
85:241–272. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Maicas N, Ferrándiz ML, Brines R, Ibáñez
L, Cuadrado A, Koenders MI, van den Berg WB and Alcaraz MJ:
Deficiency of Nrf2 accelerates the effector phase of arthritis and
aggravates joint disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 15:889–901. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Khor TO, Huang MT, Kwon KH, Chan JY, Reddy
BS and Kong AN: Nrf2-deficient mice have an increased
susceptibility to dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. Cancer
Res. 66:11580–11584. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chan K and Kan YW: Nrf2 is essential for
protection against acute pulmonary injury in mice. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 96:12731–12736. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kaplan M, Mutlu EA, Benson M, Fields JZ,
Banan A and Keshavarzian A: Use of herbal preparations in the
treatment of oxidant-mediated inflammatory disorders. Complement
Ther Med. 15:207–216. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee SE, Jeong SI, Yang H, Jeong SH, Jang
YP, Park CS, Kim J and Park YS: Extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza
(Danshen) induces Nrf2-mediated heme oxygenase-1 expression as a
cytoprotective action in RAW 264.7 macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol.
139:541–548. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lee JA, Lee MY, Shin IS, Seo CS, Ha H and
Shin HK: Anti-inflammatory effects of Amomum compactum on RAW 264.7
cells via induction of heme oxygenase-1. Arch Pharm Res.
35:739–746. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Choi JY, Kwun MJ, Kim KH, et al:
Protective Effect of the fruit hull of Gleditsia sinensis on
LPS-induced acute lung injury is associated with Nrf2 activation.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012:9747132012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Han CW, Kwun MJ, Kim KH, Choi JY, Oh SR,
Ahn KS, Lee JH and Joo M: Ethanol extract of Alismatis Rhizoma
reduces acute lung inflammation by suppressing NF-κB and activating
Nrf2. J Ethnopharmacol. 146:402–410. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ju MS, Jeong HU, Kim HG, et al:
Anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of Geranii Herba.
Kor J Herbol. 25:97–101. 2010.
|
|
16
|
Liu QH, Jeong JE, Choi EJ, Moon YH and Woo
ER: A new furofuran lignan from Geranium thunbergii Sieb. et Zucc.
Arch Pharm Res. 29:1109–1113. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hiramatsu N, Xiufen W, Takechi R, Itoh Y,
Mamo J and Pal S: Antimutagenicity of Japanese traditional herbs,
gennoshoko, yomogi, senburi and iwa-tobacco. Biofactors.
22:123–125. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Xiufen W, Hiramatsu N and Matsubara M: The
antioxidative activity of traditional Japanese herbs. Biofactors.
21:281–284. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Sung YY, Yoon T, Yang WK, Kim SJ and Kim
HK: Anti-obesity effects of Geranium thunbergii extract via
improvement of lipid metabolism in high-fat diet-induced obese
mice. Mol Med Rep. 4:1107–1113. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu QH and Woo ER: Inhibitory activity of
IL-6 production by flavonoids and phenolic compounds. Nat Prod Sci.
14:1–5. 2008.
|
|
21
|
Okuda T, Mori K and Murakami R:
Constituents of Geranium thunbergii Sieb. et Zucc. VI. Difference
of tannin activity caused by structural differences. (2).
Colorimetry with methylene blue (author’s transl). Yakugaku Zasshi.
97:1273–1278. 1977.In Japanese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Okuda T, Yoshida T and Mori K:
Consitutents of Geranium thunbergii Sieb. et Zucc. II.
Ellagitannins. (1) (author’s transl). Yakugaku Zasshi.
95:1462–1466. 1975.In Japanese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Harborne JB, Baxter H and Moss GP:
Phytochemical Dictionary: A Handbook of Bioactive Compounds from
Plants. Taylor and Francis; London, Philadelphia: 1999
|
|
24
|
Barthwal MK, Anzinger JJ, Xu Q, Bohnacker
T, Wymann MP and Kruth HS: Fluid-phase pinocytosis of native low
density lipoprotein promotes murine M-CSF differentiated macrophage
foam cell formation. PLoS One. 8:e580542013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lyu JH, Lee GS, Kim KH, et al:
ent-kaur-16-en-19-oic Acid, isolated from the roots of Aralia
continentalis, induces activation of Nrf2. J Ethnopharmacol.
137:1442–1449. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Okuda T, Mori K and Ishino M: Constituents
of Geranium thunbergii Sieg. et Zucc. VIII. Transformations of
geraniin upon decoction (author’s transl). Yakugaku Zasshi.
99:505–509. 1979.In Japanese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Johnson JA, Johnson DA, Kraft AD, Calkins
MJ, Jakel RJ, Vargas MR and Chen PC: The Nrf2-ARE pathway: An
indicator and modulator of oxidative stress in neurodegeneration.
Ann NY Acad Sci. 1147:61–69. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wakabayashi N, Slocum SL, Skoko JJ, Shin S
and Kensler TW: When NRF2 talks, who’s listening? Antioxid Redox
Signal. 13:1649–1663. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Drexler SK, Kong PL, Wales J and Foxwell
BM: Cell signalling in macrophages, the principal innate immune
effector cells of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther.
10:2162008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schroder K, Sweet MJ and Hume DA: Signal
integration between IFNgamma and TLR signalling pathways in
macrophages. Immunobiology. 211:511–524. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Korhonen R, Lahti A, Kankaanranta H and
Moilanen E: Nitric oxide production and signaling in inflammation.
Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 4:471–479. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gupta SC, Sundaram C, Reuter S and
Aggarwal BB: Inhibiting NF-κB activation by small molecules as a
therapeutic strategy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1799:775–787. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tornatore L, Thotakura AK, Bennett J,
Moretti M and Franzoso G: The nuclear factor-kappa B signaling
pathway: Integrating metabolism with inflammation. Trends Cell
Biol. 22:557–566. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Spehlmann ME and Eckmann L: Nuclear
factor-kappa B in intestinal protection and destruction. Curr Opin
Gastroenterol. 25:92–99. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Saito H: Toxico-pharmacological
perspective of the Nrf2-Keap1 defense system against oxidative
stress in kidney diseases. Biochem Pharmacol. 85:865–872. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim J, Cha YN and Surh YJ: A protective
role of nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2 (Nrf2) in
inflammatory disorders. Mutat Res. 690:12–23. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Jin W, Wang H, Yan W, Xu L, Wang X, Zhao
X, Yang X, Chen G and Ji Y: Disruption of Nrf2 enhances
upregulation of nuclear factor-kappaB activity, proinflammatory
cytokines, and inter-cellular adhesion molecule-1 in the brain
after traumatic brain injury. Mediators Inflamm. 2008:7251742008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Turpaev KT: Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway:
Mechanisms of regulation and role in protection of cells against
toxicity caused by xenobiotics and electrophiles. Biochem Mosc.
78:111–126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Jeong WS, Kim IW, Hu R and Kong AN:
Modulatory properties of various natural chemopreventive agents on
the activation of NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Pharm Res.
21:661–670. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Márquez N, Sancho R, Macho A, Calzado MA,
Fiebich BL and Muñoz E: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester inhibits
T-cell activation by targeting both nuclear factor of activated
T-cells and NF-kappaB transcription factors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
308:993–1001. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Xu YX, Pindolia KR, Janakiraman N, Chapman
RA and Gautam SC: Curcumin inhibits IL1 alpha and TNF-alpha
induction of AP-1 and NF-κB DNA-binding activity in bone marrow
stromal cells. Hematopathol Mol Hematol. 11:49–62. 1997–1998.
|
|
42
|
Moreira AJ, Fraga C, Alonso M, Collado PS,
Zetller C, Marroni C, Marroni N and González-Gallego J: Quercetin
prevents oxidative stress and NF-kappaB activation in gastric
mucosa of portal hypertensive rats. Biochem Pharmacol.
68:1939–1946. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xu C, Shen G, Chen C, Gélinas C and Kong
AN: Suppression of NF-kappaB and NF-kappaB-regulated gene
expression by sulforaphane and PEITC through IkappaBalpha, IKK
pathway in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Oncogene.
24:4486–4495. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Manandhar S, You A, Lee ES, Kim JA and
Kwak MK: Activation of the Nrf2-antioxidant system by a novel
cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor furan-2-yl-3-pyridin-2-yl-propenone:
Implication in anti-inflammatory function by Nrf2 activator. J
Pharm Pharmacol. 60:879–887. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li B, Abdalrahman A, Lai Y, Janicki JS,
Ward KW, Meyer CJ, Wang XL, Tang D and Cui T:
Dihydro-CDDO-trifluoroethyl amide suppresses inflammatory responses
in macrophages via activation of Nrf2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
444:555–561. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|