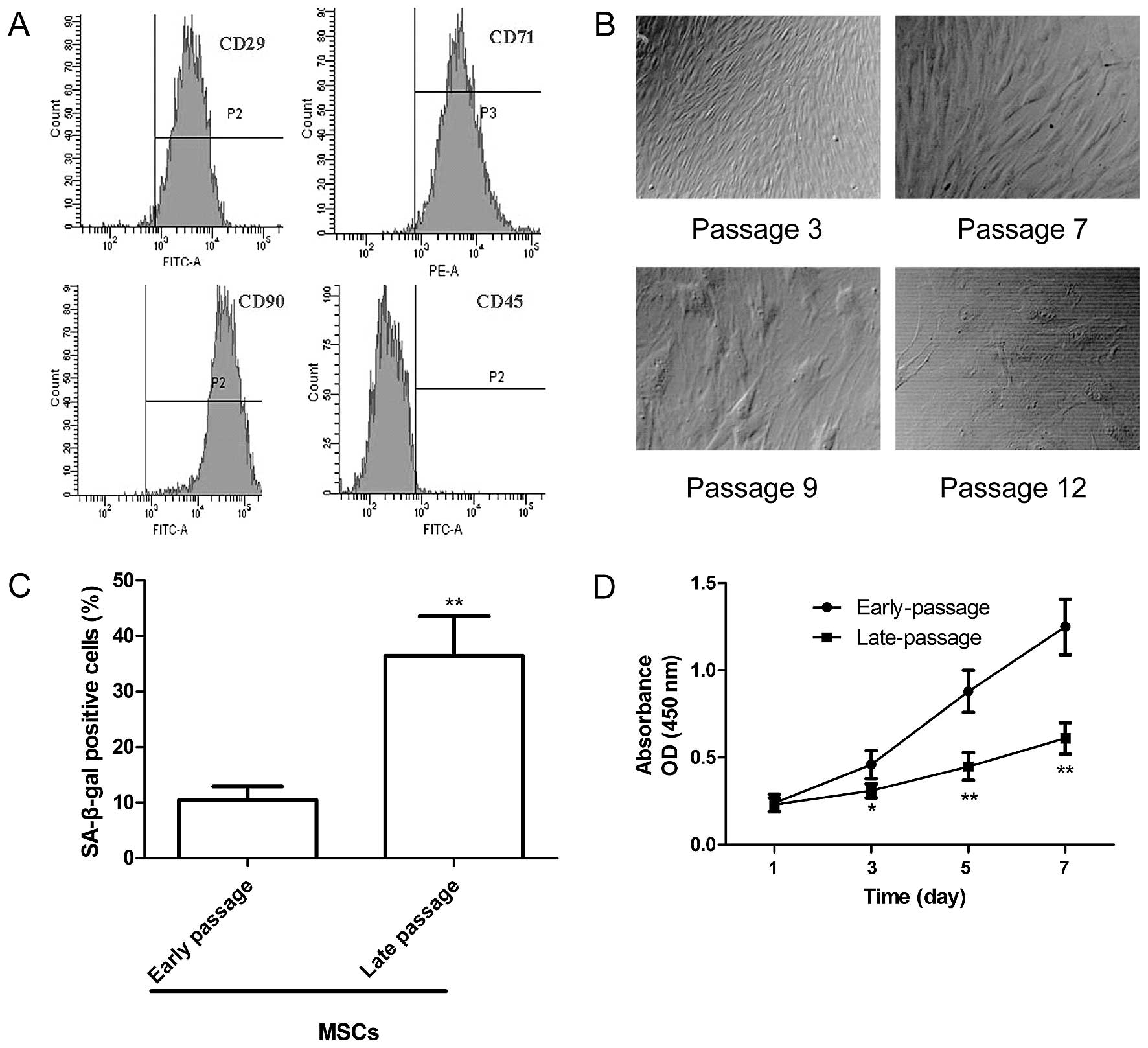
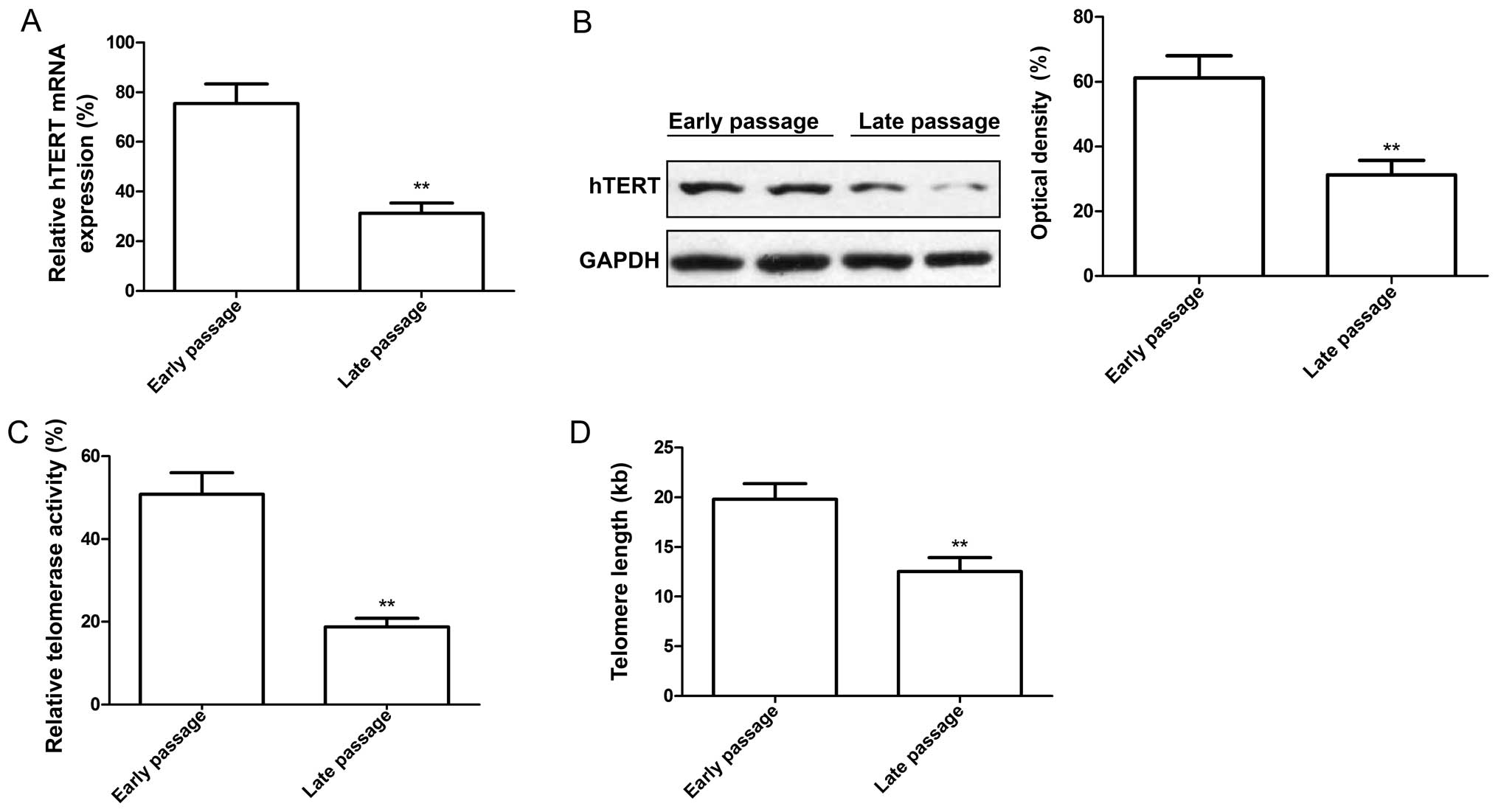
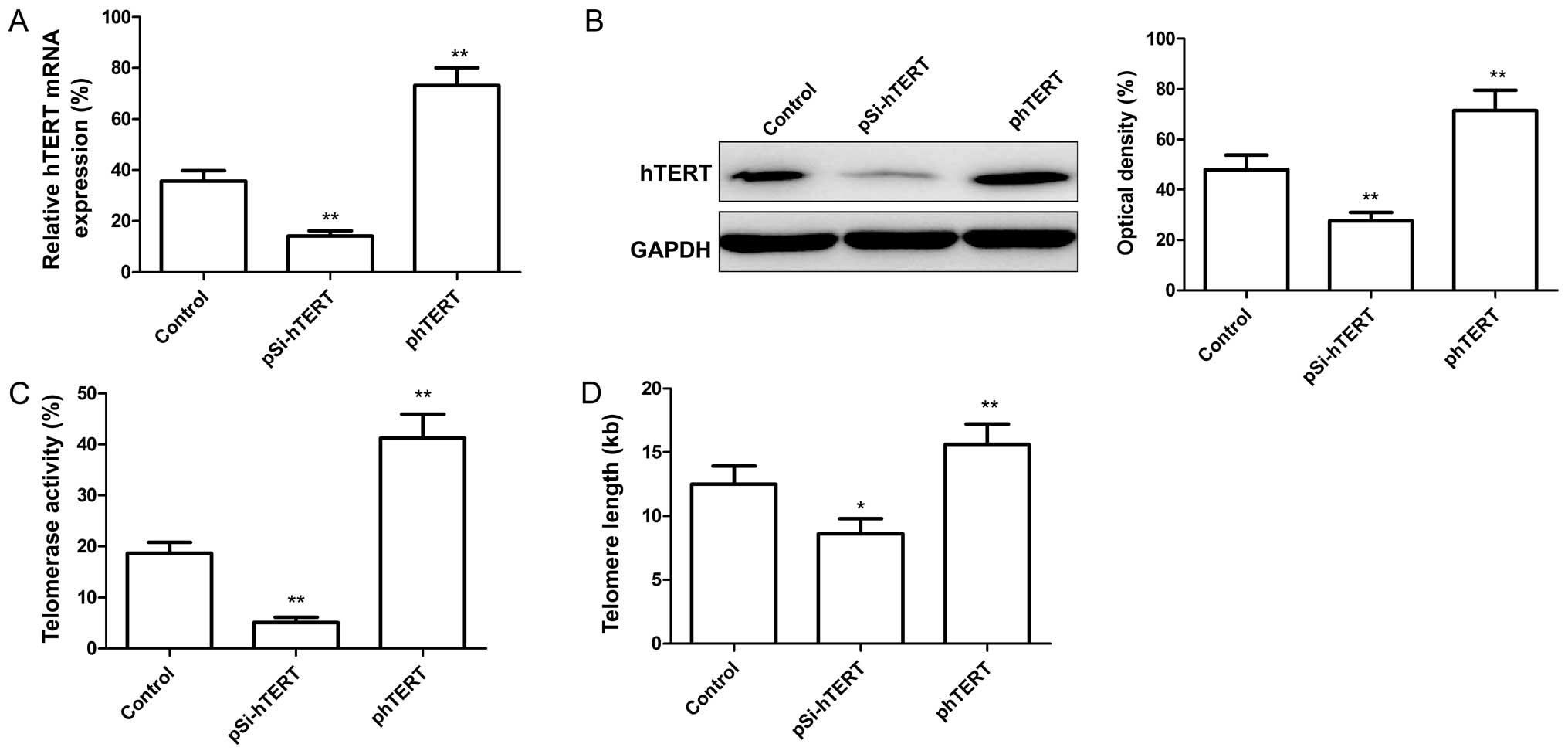
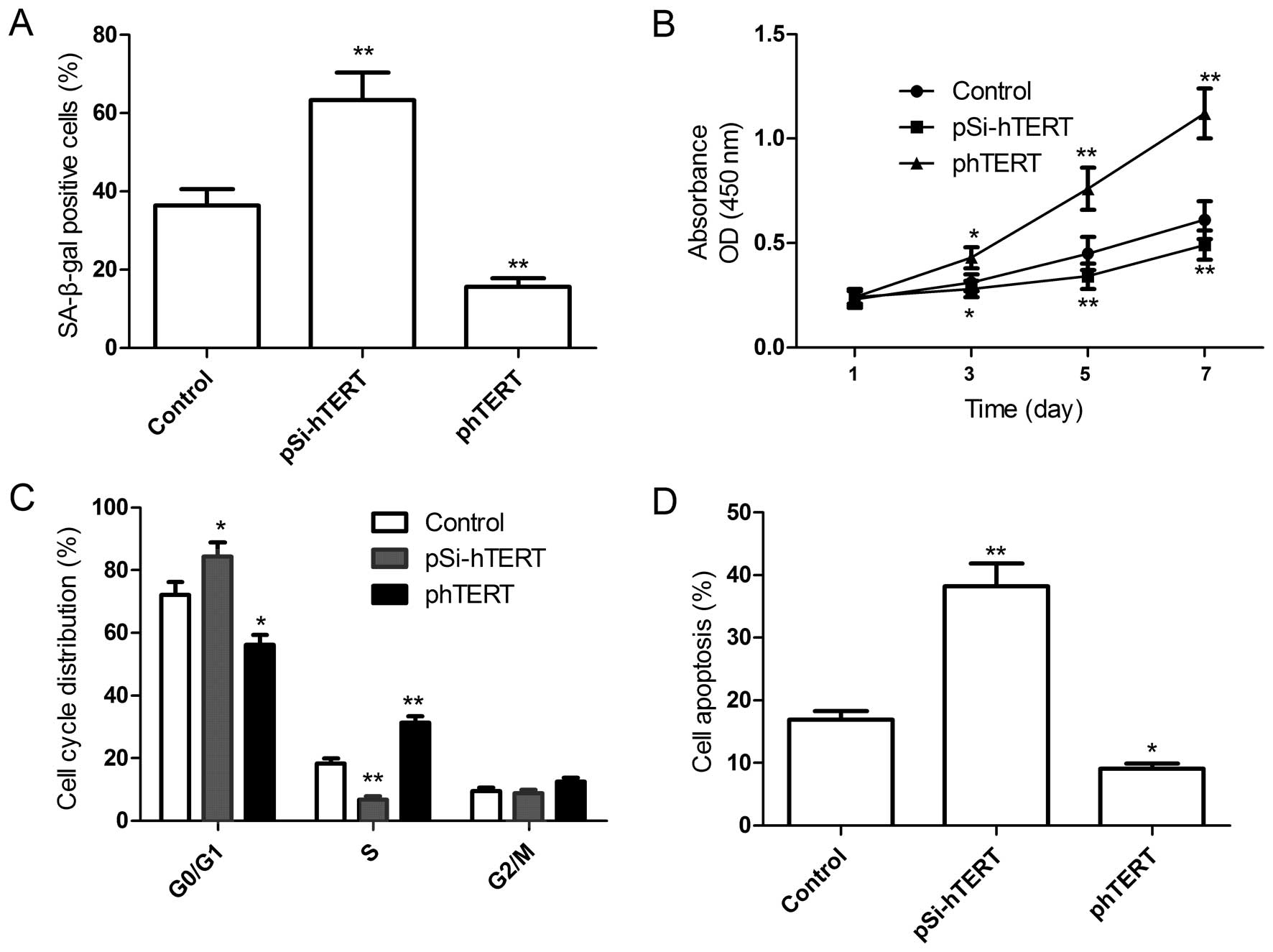
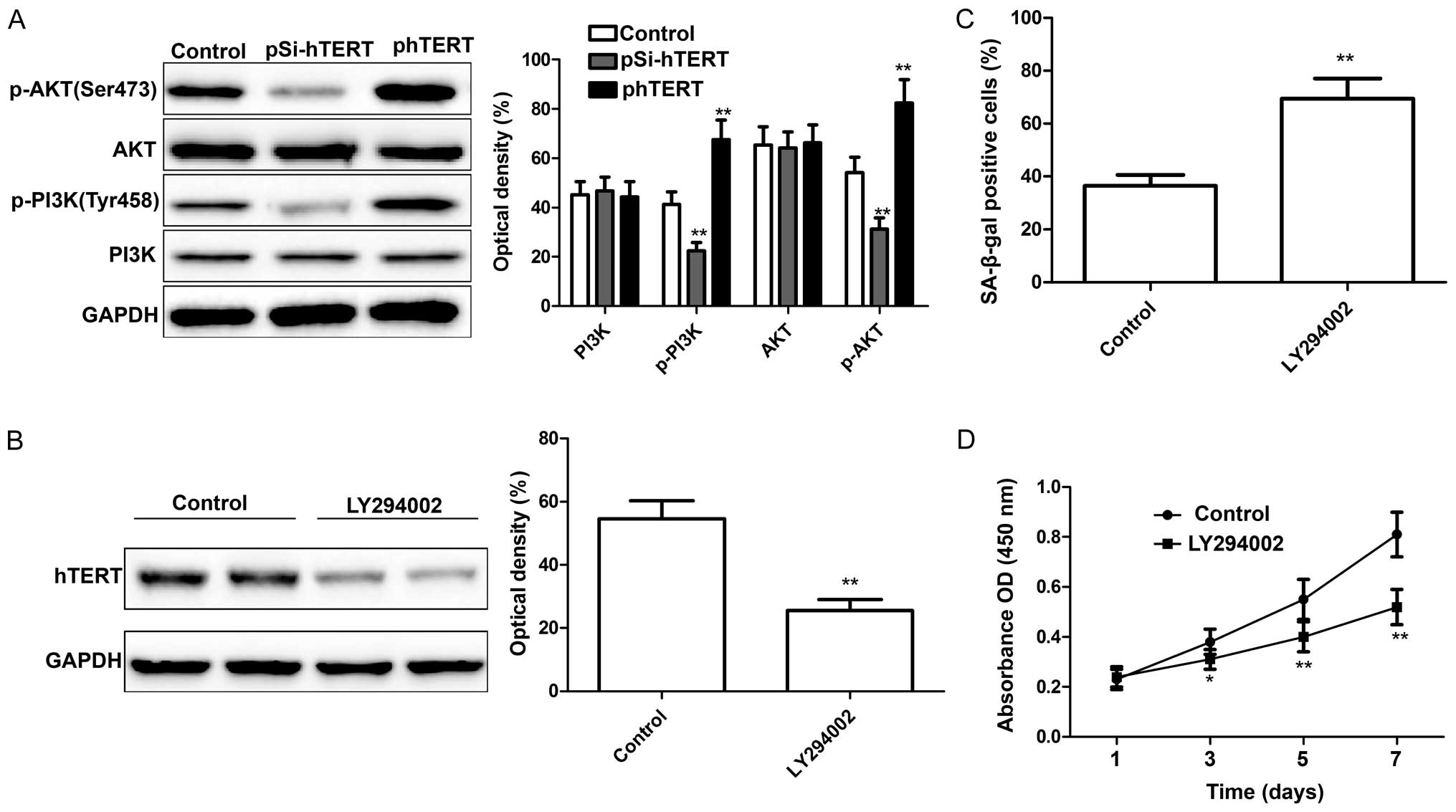
|
1
|
Bayati V, Hashemitabar M, Gazor R,
Nejatbakhsh R and Bijannejad D: Expression of surface markers and
myogenic potential of rat bone marrow- and adipose-derived stem
cells: a comparative study. Anat Cell Biol. 46:113–121. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wakitani S, Saito T and Caplan AI:
Myogenic cells derived from rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
exposed to 5-azacytidine. Muscle Nerve. 18:1417–1426. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Javazon EH, Colter DC, Schwarz EJ and
Prockop DJ: Rat marrow stromal cells are more sensitive to plating
density and expand more rapidly from single-cell-derived colonies
than human marrow stromal cells. Stem Cells. 19:219–225. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Beyer Nardi N and da Silva Meirelles L:
Mesenchymal stem cells: isolation, in vitro expansion and
characterization. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 174:249–282. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Brighton CT and Hunt RM: Early
histological and ultrastructural changes in medullary fracture
callus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 73:832–847. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Caplan AI: Mesenchymal stem cells. J
Orthop Res. 9:641–650. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li J and Pei M: Cell senescence: A
challenge in cartilage engineering and regeneration. Tissue Eng
Part B Rev. 18:270–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Allsopp RC, Vaziri H, Patterson C,
Goldstein S, Younglai EV, Futcher AB, Greider CW and Harley CB:
Telomere length predicts replicative capacity of human fibroblasts.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:10114–10118. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Broccoli D, Young JW and de Lange T:
Telomerase activity in normal and malignant hematopoietic cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:9082–9086. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Counter CM, Avilion AA, LeFeuvre CE,
Stewart NG, Greider CW, Harley CB and Bacchetti S: Telomere
shortening associated with chromosome instability is arrested in
immortal cells which express telomerase activity. EMBO J.
11:1921–1929. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vaziri H and Benchimol S: Reconstitution
of telomerase activity in normal human cells leads to elongation of
telomeres and extended replicative life span. Curr Biol. 8:279–282.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bodnar AG, Ouellette M, Frolkis M, Holt
SE, Chiu CP, Morin GB, Harley CB, Shay JW, Lichtsteiner S and
Wright WE: Extension of life-span by introduction of telomerase
into normal human cells. Science. 279:349–352. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Greider CW and Blackburn EH: A telomeric
sequence in the RNA of Tetrahymena telomerase required for telomere
repeat synthesis. Nature. 337:331–337. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Feng J, Funk WD, Wang SS, Weinrich SL,
Avilion AA, Chiu CP, Adams RR, Chang E, Allsopp RC, Yu J, et al:
The RNA component of human telomerase. Science. 269:1236–1241.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kassem M, Abdallah BM, Yu Z, Ditzel N and
Burns JS: The use of hTERT-immortalized cells in tissue
engineering. Cytotechnology. 45:39–46. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tao Q, Lv B, Qiao B, Zheng CQ and Chen ZF:
Immortalization of ameloblastoma cells via reactivation of
telomerase function: Phenotypic and molecular characteristics. Oral
Oncol. 45:e239–e244. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Morales CP, Holt SE, Ouellette M, Kaur KJ,
Yan Y, Wilson KS, White MA, Wright WE and Shay JW: Absence of
cancer-associated changes in human fibroblasts immortalized with
telomerase. Nat Genet. 21:115–118. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rajamani K, Lin YC, Wen TC, Hsieh J, Subeq
YM, Liu JW, Lin PC, Harn HJ, Lin SZ and Chiou TW: The
antisenescence effect of trans-cinnamaldehyde on adipose-derived
stem cells. Cell Transplant. 24:493–507. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang J, Chang E, Cherry AM, Bangs CD, Oei
Y, Bodnar A, Bronstein A, Chiu CP and Herron GS: Human endothelial
cell life extension by telomerase expression. J Biol Chem.
274:26141–26148. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bischoff DS, Makhijani NS and Yamaguchi
DT: Constitutive expression of human telomerase enhances the
proliferation potential of human mesenchymal stem cells. Biores
Open Access. 1:273–279. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Huang G, Zheng Q, Sun J, Guo C, Yang J,
Chen R, Xu Y, Wang G, Shen D, Pan Z, et al: Stabilization of
cellular properties and differentiation mutilpotential of human
mesenchymal stem cells transduced with hTERT gene in a long-term
culture. J Cell Biochem. 103:1256–1269. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kobune M, Kawano Y, Ito Y, Chiba H,
Nakamura K, Tsuda H, Sasaki K, Dehari H, Uchida H, Honmou O, et al:
Telomerized human multipotent mesenchymal cells can differentiate
into hematopoietic and cobblestone area-supporting cells. Exp
Hematol. 31:715–722. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Piper SL, Wang M, Yamamoto A, Malek F, Luu
A, Kuo AC and Kim HT: Inducible immortality in hTERT-human
mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 30:1879–1885. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Moffatt-Jauregui CE, Robinson B, de Moya
AV, Brockman RD, Roman AV, Cash MN, Culp DJ and Lamont RJ:
Establishment and characterization of a telomerase immortalized
human gingival epithelial cell line. J Periodontal Res. 48:713–721.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang YX, Miao ZC, Zhang HJ, Wang Y, Gao JX
and Feng MF: Establishment and characterization of a human
telomerase catalytic subunit-transduced fetal bone marrow-derived
osteoblastic cell line. Differentiation. 75:24–34. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Scutt A and Bertram P: Bone marrow cells
are targets for the anabolic actions of prostaglandin E2 on bone:
induction of a transition from nonadherent to adherent osteoblast
precursors. J Bone Miner Res. 10:474–487. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Galderisi U, Helmbold H, Squillaro T,
Alessio N, Komm N, Khadang B, Cipollaro M, Bohn W and Giordano A:
In vitro senescence of rat mesenchymal stem cells is accompanied by
downregulation of stemness-related and DNA damage repair genes.
Stem Cells Dev. 18:1033–1042. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Shi YA, Zhao Q, Zhang LH, Du W, Wang XY,
He X, Wu S and Li YL: Knockdown of hTERT by siRNA inhibits cervical
cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Int J Oncol. 45:1216–1224.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Palm W and de Lange T: How shelterin
protects mammalian telomeres. Annu Rev Genet. 42:301–334. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Follo MY, Manzoli L, Poli A, McCubrey JA
and Cocco L: PLC and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling in disease and
cancer. Adv Biol Regul. 57:10–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yoon KA, Cho HS, Shin HI and Cho JY:
Differential regulation of CXCL5 by FGF2 in osteoblastic and
endothelial niche cells supports hematopoietic stem cell migration.
Stem Cells Dev. 21:3391–3402. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal
RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S and
Marshak DR: Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem
cells. Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Stewart JA, Chaiken MF, Wang F and Price
CM: Maintaining the end: Roles of telomere proteins in
end-protection, telomere replication and length regulation. Mutat
Res. 730:12–19. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Serakinci N, Graakjaer J and Kolvraa S:
Telomere stability and telomerase in mesenchymal stem cells.
Biochimie. 90:33–40. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Fajkus J, Simícková M and Maláska J:
Tiptoeing to chromosome tips: facts, promises and perils of today's
human telomere biology. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci.
357:545–562. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dimitrova V and Arcaro A: Targeting the
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in medulloblastoma. Curr Mol Med.
15:82–93. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chell JM and Brand AH:
Nutrition-responsive glia control exit of neural stem cells from
quiescence. Cell. 143:1161–1173. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sewell GW, Marks DJ and Segal AW: The
immunopathogenesis of Crohn's disease: a three-stage model. Curr
Opin Immunol. 21:506–513. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kang SS, Kwon T, Kwon DY and Do SI: Akt
protein kinase enhances human telomerase activity through
phosphorylation of telomerase reverse transcriptase subunit. J Biol
Chem. 274:13085–13090. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kawagoe J, Ohmichi M, Takahashi T, Ohshima
C, Mabuchi S, Takahashi K, Igarashi H, Mori-Abe A, Saitoh M, Du B,
et al: Raloxifene inhibits estrogen-induced up-regulation of
telomerase activity in a human breast cancer cell line. J Biol
Chem. 278:43363–43372. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kimura A, Ohmichi M, Kawagoe J, Kyo S,
Mabuchi S, Takahashi T, Ohshima C, Arimoto-Ishida E, Nishio Y,
Inoue M, et al: Induction of hTERT expression and phosphorylation
by estrogen via Akt cascade in human ovarian cancer cell lines.
Oncogene. 23:4505–4515. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|