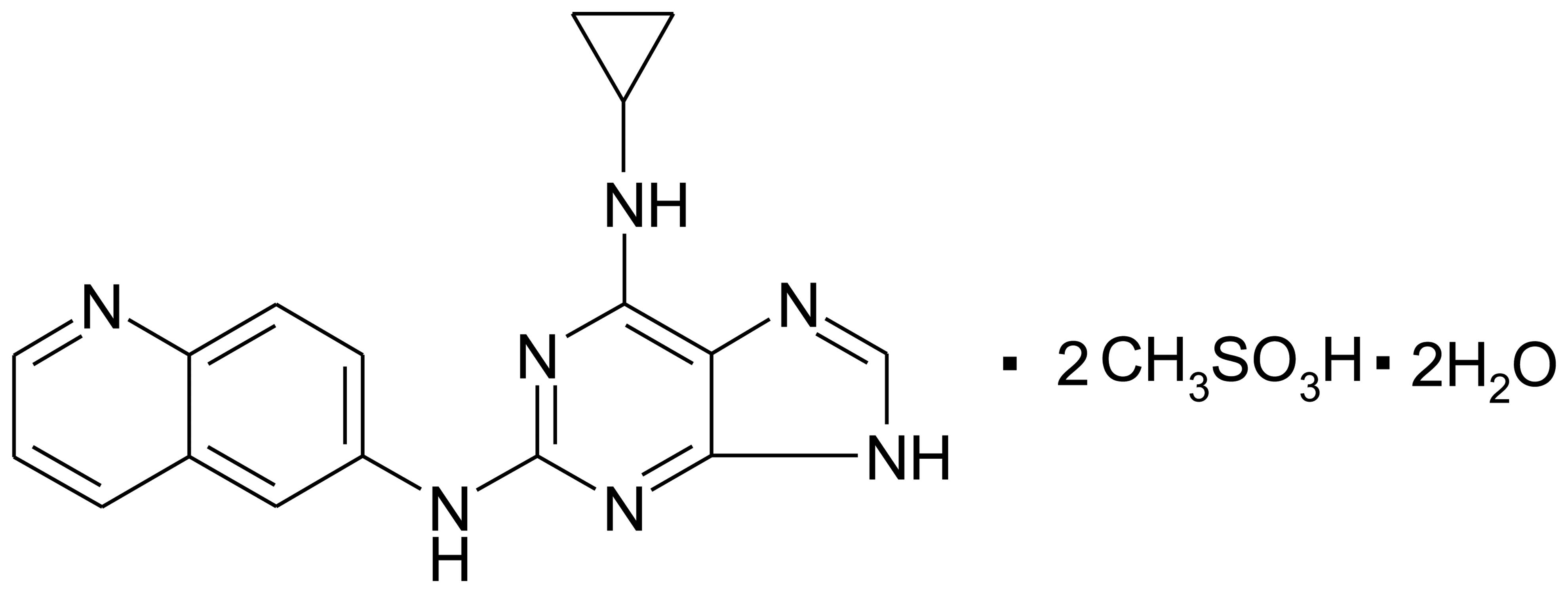
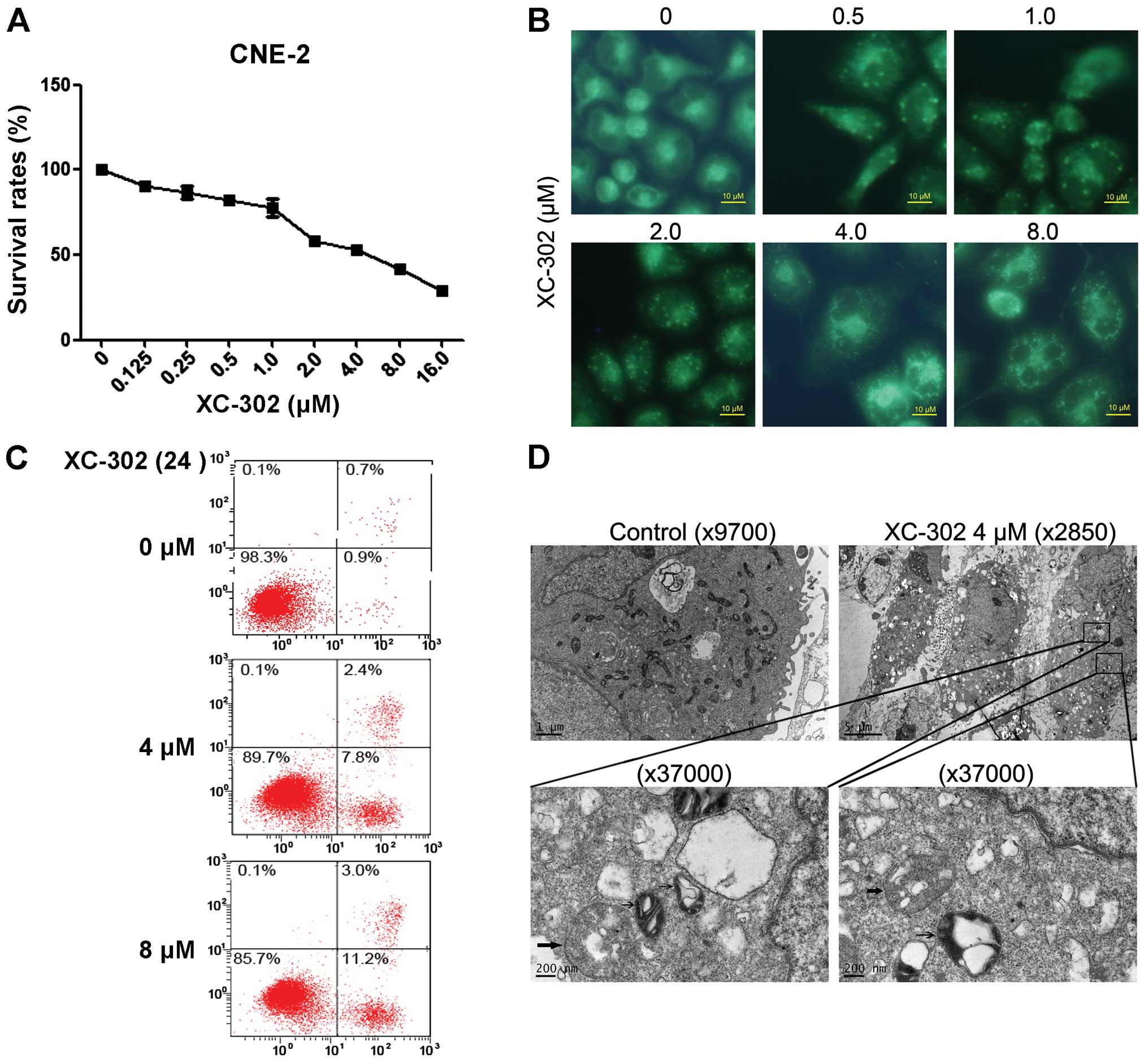
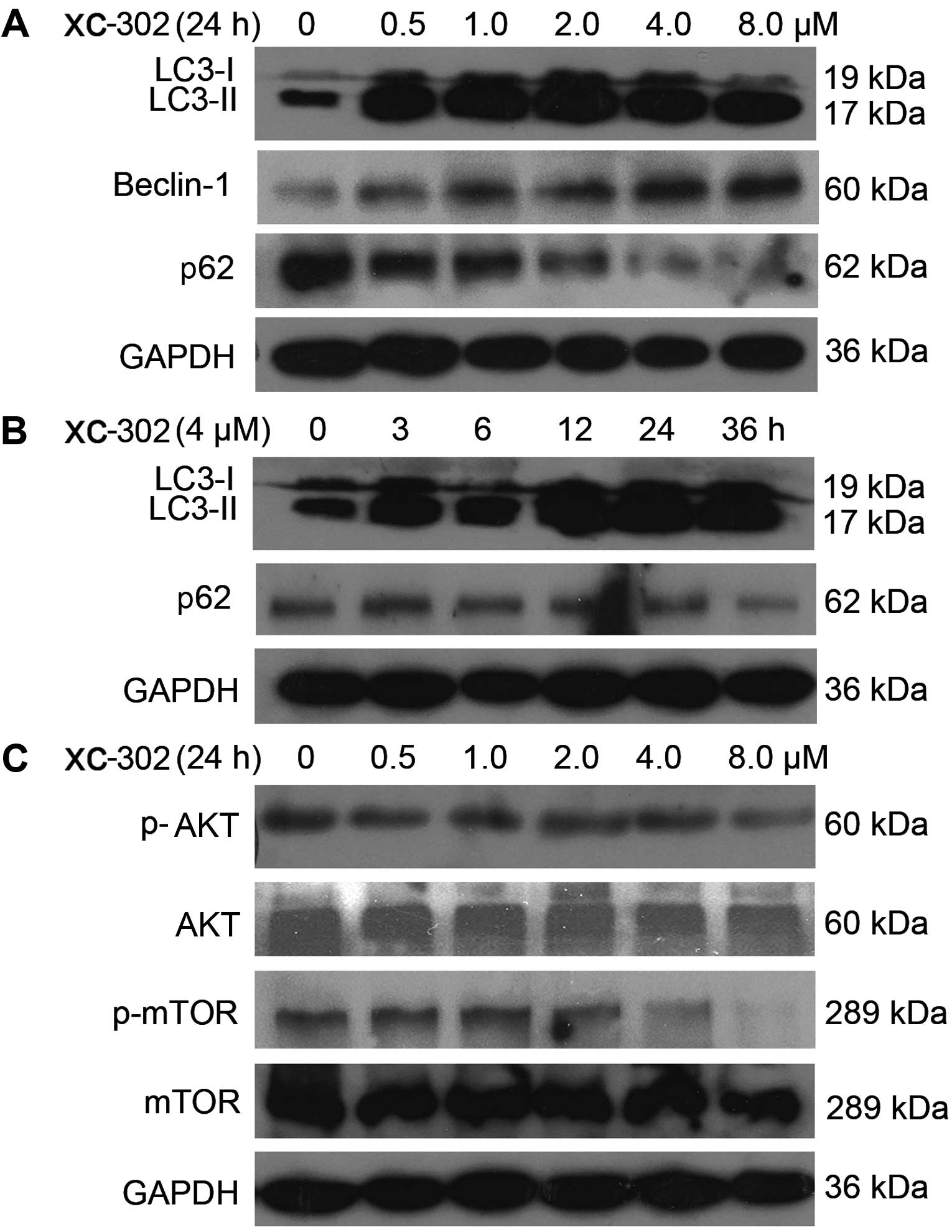
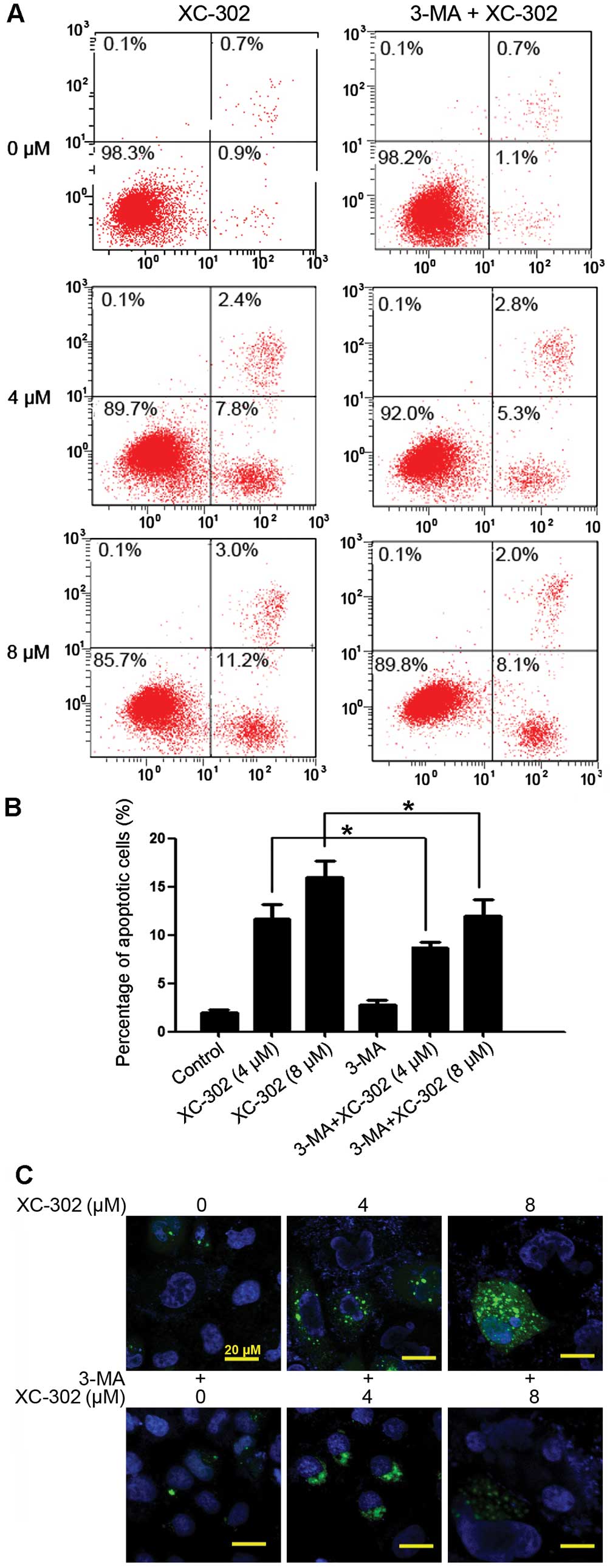
|
1
|
Cantley LC: The phosphoinositide 3-kinase
pathway. Science. 296:1655–1657. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Luo J, Manning BD and Cantley LC:
Targeting the PI3K-Akt pathway in human cancer: Rationale and
promise. Cancer Cell. 4:257–262. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Courtney KD, Corcoran RB and Engelman JA:
The PI3K pathway as drug target in human cancer. J Clin Oncol.
28:1075–1083. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chang ET and Adami HO: The enigmatic
epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 15:1765–1777. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Spratt DE and Lee N: Current and emerging
treatment options for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther.
5:297–308. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lin S, Pan J, Han L, Guo Q, Hu C, Zong J,
Zhang X and Lu JJ: Update report of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
treated with reduced-volume intensity-modulated radiation therapy
and hypothesis of the optimal margin. Radiother Oncol. 110:385–389.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xiao WW, Huang SM, Han F, Wu SX, Lu LX,
Lin CG, Deng XW, Lu TX, Cui NJ and Zhao C: Local control, survival,
and late toxicities of locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma
treated by simultaneous modulated accelerated radiotherapy combined
with cisplatin concurrent chemotherapy: Long-term results of a
phase 2 study. Cancer. 117:1874–1883. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gupta AK1, McKenna WG, Weber CN, Feldman
MD, Goldsmith JD, Mick R, Machtay M, Rosenthal DI, Bakanauskas VJ,
Cerniglia GJ, et al: Local recurrence in head and neck cancer:
relationship to radiation resistance and signal transduction. Clin
Cancer Res. 8:885–892. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu T, Sun Q, Li Q, Yang H, Zhang Y, Wang
R, Lin X, Xiao D, Yuan Y, Chen L, et al: Dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors,
GSK2126458 and PKI-587, suppress tumor progression and increase
radio-sensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther.
14:429–439. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yang F, Qian XJ, Qin W, Deng R, Wu XQ, Qin
J, Feng GK and Zhu XF: Dual phosphoinositide 3-kinase/mammalian
target of rapamycin inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 has a therapeutic
potential and sensitizes cisplatin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
PLoS One. 8:e598792013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu Y, Chen LH, Yuan YW, Li QS, Sun AM and
Guan J: Activation of AKT is associated with metastasis of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 33:241–245. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Abrams JM, Alnemri
ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, El-Deiry
WS, Fulda S, et al: Molecular definitions of cell death
subroutines: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell
Death 2012. Cell Death Differ. 19:107–120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Deng Q, Yu X, Xiao L, Hu Z, Luo X, Tao Y,
Yang L, Liu X, Chen H, Ding Z, et al: Neoalbaconol induces energy
depletion and multiple cell death in cancer cells by targeting
PDK1-PI3-K/Akt signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 4:e8042013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhao YY, Tian Y, Zhang J, Xu F, Yang YP,
Huang Y, Zhao HY, Zhang JW, Xue C, Lam MH, et al: Effects of an
oral allosteric AKT inhibitor (MK-2206) on human nasopharyngeal
cancer in vitro and in vivo. Drug Des Devel Ther. 8:1827–1837.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Munafó DB and Colombo MI: A novel assay to
study autophagy: Regulation of autophagosome vacuole size by amino
acid deprivation. J Cell Sci. 114:3619–3629. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ma BB, Lui VW, Hui EP, Lau CP, Ho K, Ng
MH, Cheng SH, Tsao SW and Chan AT: The activity of mTOR inhibitor
RAD001 (everolimus) in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and
cisplatin-resistant cell lines. Invest New Drugs. 28:413–420. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ma BB, Lui VW, Hui CW, Lau CP, Wong CH,
Hui EP, Ng MH, Tsao SW, Li Y and Chan AT: Preclinical evaluation of
the AKT inhibitor MK-2206 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines.
Invest New Drugs. 31:567–575. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Morrison JA, Gulley ML, Pathmanathan R and
Raab-Traub N: Differential signaling pathways are activated in the
Epstein-Barr virus-associated malignancies nasopharyngeal carcinoma
and Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer Res. 64:5251–5260. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang XM, Dai CB, Mou ZL, Wang LJ, Wen WP,
Lin SG, Xu G and Li HB: Overproduction of cyclin D1 is dependent on
activated mTORC1 signal in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Implication
for therapy. Cancer Lett. 279:47–56. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen J, Hu CF, Hou JH, Shao Q, Yan LX, Zhu
XF, Zeng YX and Shao JY: Epstein-Barr virus encoded latent membrane
protein 1 regulates mTOR signaling pathway genes which predict poor
prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Transl Med. 8(30)2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liu P, Cheng H, Roberts TM and Zhao JJ:
Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 8:627–644. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tekirdag KA, Korkmaz G, Ozturk DG, Agami R
and Gozuacik D: MIR181A regulates starvation- and rapamycin-induced
autophagy through targeting of ATG5. Autophagy. 9:374–385. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mizushima N: Methods for monitoring
autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 36:2491–2502. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fujiwara K, Iwado E, Mills GB, Sawaya R,
Kondo S and Kondo Y: Akt inhibitor shows anticancer and
radiosensitizing effects in malignant glioma cells by inducing
autophagy. Int J Oncol. 31:753–760. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hung JY, Hsu YL, Li CT, Ko YC, Ni WC,
Huang MS and Kuo PL: 6-Shogaol, an active constituent of dietary
ginger, induces autophagy by inhibiting the AKT/mTOR pathway in
human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. J Agric Food Chem.
57:9809–9816. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shin SY, Lee KS, Choi YK, Lim HJ, Lee HG,
Lim Y and Lee YH: The antipsychotic agent chlorpromazine induces
autophagic cell death by inhibiting the Akt/mTOR pathway in human
U-87MG glioma cells. Carcinogenesis. 34:2080–2089. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Seglen PO and Gordon PB: 3-Methyladenine:
Specific inhibitor of autophagic/lysosomal protein degradation in
isolated rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 79:1889–1892.
1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lum JJ, Bauer DE, Kong M, Harris MH, Li C,
Lindsten T and Thompson CB: Growth factor regulation of autophagy
and cell survival in the absence of apoptosis. Cell. 120:237–248.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Eisenberg-Lerner A and Kimchi A: The
paradox of autophagy and its implication in cancer etiology and
therapy. Apoptosis. 14:376–391. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, Garuti R,
Liang XH, Mizushima N, Packer M, Schneider MD and Levine B: Bcl-2
antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell.
122:927–939. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Levine B, Sinha S and Kroemer G: Bcl-2
family members: Dual regulators of apoptosis and autophagy.
Autophagy. 4:600–606. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chang NC, Nguyen M, Germain M and Shore
GC: Antagonism of Beclin 1-dependent autophagy by BCL-2 at the
endoplasmic reticulum requires NAF-1. EMBO J. 29:606–618. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Marquez RT and Xu L: Bcl-2:Beclin 1
complex: multiple, mechanisms regulating autophagy/apoptosis toggle
switch. Am J Cancer Res. 2:214–221. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mukhopadhyay S, Panda PK, Sinha N, Das DN
and Bhutia SK: Autophagy and apoptosis: where do they meet?
Apoptosis. 19:555–566. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tolkovsky AM, Xue L, Fletcher GC and
Borutaite V: Mitochondrial disappearance from cells: A clue to the
role of autophagy in programmed cell death and disease? Biochimie.
84:233–240. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|