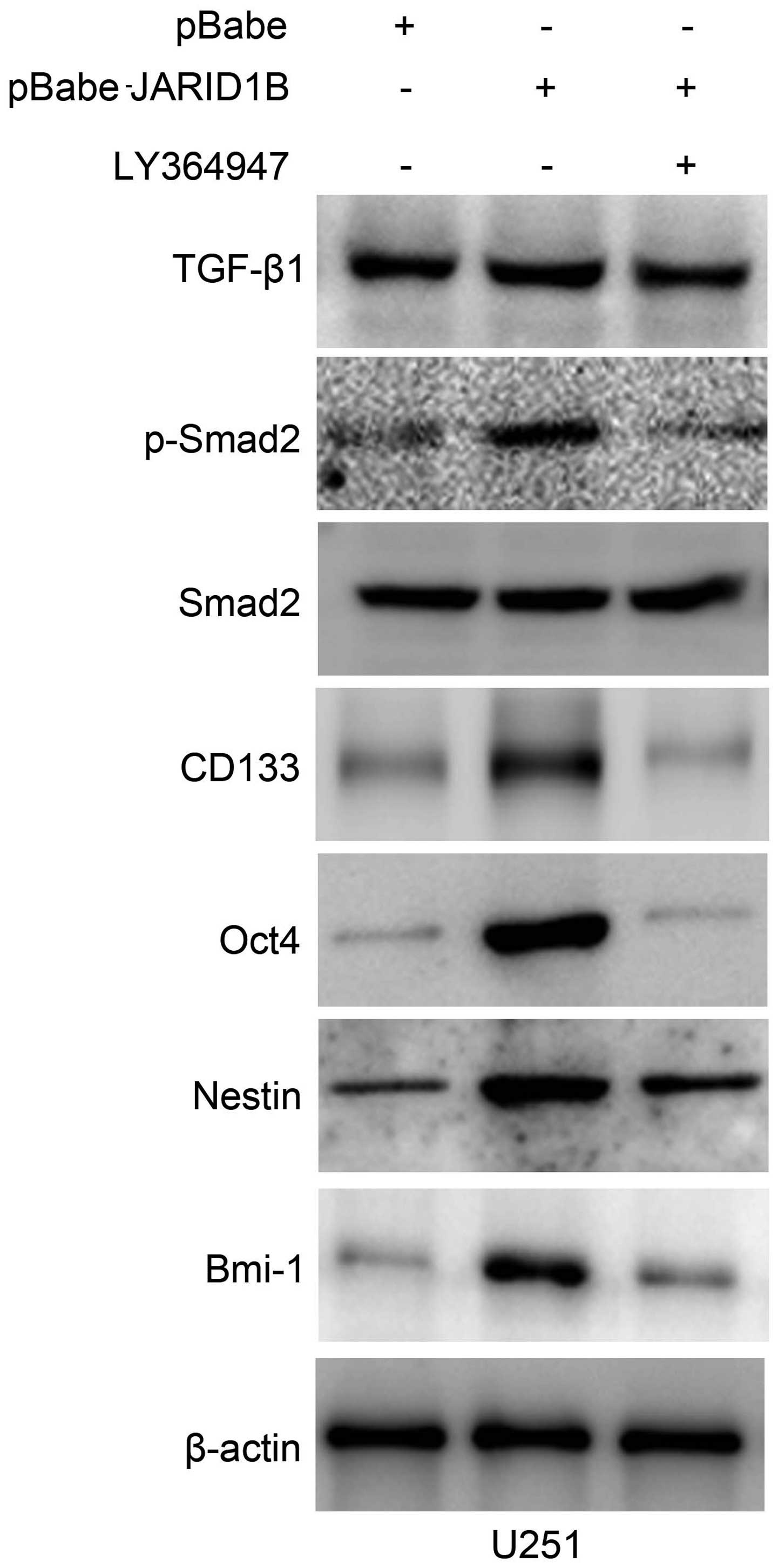
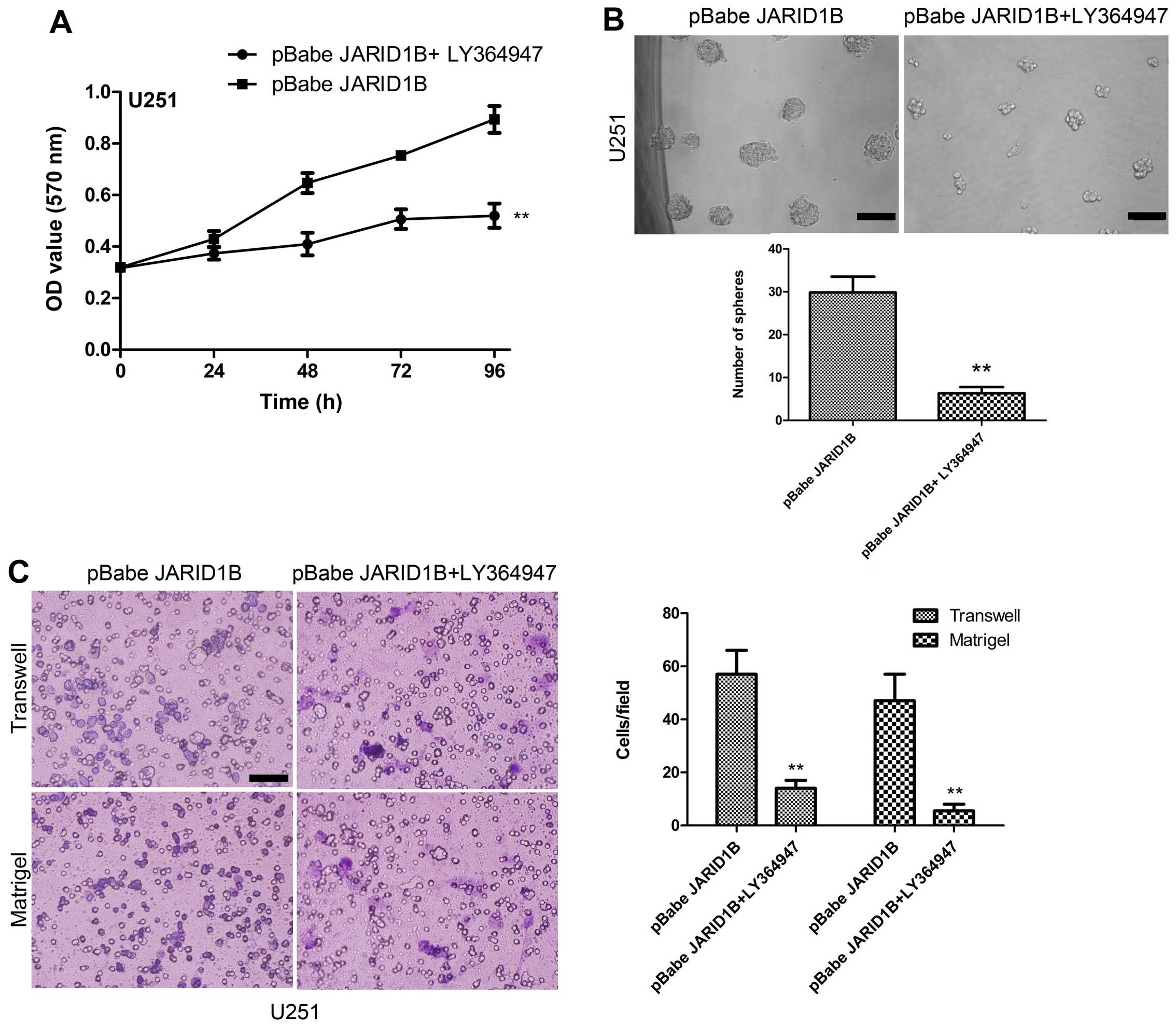
|
1
|
Opocher E, Kremer LC, Da Dalt L, van de
Wetering MD, Viscardi E, Caron HN and Perilongo G: Prognostic
factors for progression of childhood optic pathway glioma: a
systematic review. Eur J Cancer. 42:1807–1816. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Weiler M and Wick W: Molecular predictors
of outcome in low-grade glioma. Curr Opin Neurol. 25:767–773. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Siegel
RL, Stein KD, Kramer JL, Alteri R, Robbins AS and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin.
64:252–271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen R, Ravindra VM, Cohen AL, Jensen RL,
Salzman KL, Prescot AP and Colman H: Molecular features assisting
in diagnosis, surgery, and treatment decision making in low-grade
gliomas. Neurosurg Focus. 38:E22015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Seward DJ, Cubberley G, Kim S, Schonewald
M, Zhang L, Tripet B and Bentley DL: Demethylation of trimethylated
histone H3 Lys4 in vivo by JARID1 JmjC proteins. Nat Struct Mol
Biol. 14:240–242. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wynder C, Stalker L and Doughty ML: Role
of H3K4 demethylases in complex neurodevelopmental diseases.
Epigenomics. 2:407–418. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yamamoto S, Wu Z, Russnes HG, Takagi S,
Peluffo G, Vaske C, Zhao X, Moen Vollan HK, Maruyama R, Ekram MB,
et al: JARID1B is a luminal lineage-driving oncogene in breast
cancer. Cancer Cell. 25:762–777. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xiang Y, Zhu Z, Han G, Ye X, Xu B, Peng Z,
Ma Y, Yu Y, Lin H, Chen AP and Chen CD: JARID1B is a histone H3
lysine 4 demethylase up-regulated in prostate cancer. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 104:19226–19231. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li Q, Shi L, Gui B, Yu W, Wang J, Zhang D,
Han X, Yao Z and Shang Y: Binding of the JmjC demethylase JARID1B
to LSD1/NuRD suppresses angiogenesis and metastasis in breast
cancer cells by repressing chemokine CCL14. Cancer Res.
71:6899–6908. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mitra D, Das PM, Huynh FC and Jones FE:
Jumonji/ARID1 B (JARID1B) protein promotes breast tumor cell cycle
progression through epigenetic repression of microRNA let-7e. J
Biol Chem. 286:40531–40535. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Catchpole S, Spencer-Dene B, Hall D,
Santangelo S, Rosewell I, Guenatri M, Beatson R, Scibetta AG,
Burchell JM and Taylor-Papadimitriou J: PLU-1/JARID1B/KDM5B is
required for embryonic survival and contributes to cell
proliferation in the mammary gland and in ER+ breast
cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 38:1267–1277. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang Y, Wen M, Kwon Y, Xu Y, Liu Y, Zhang
P, He X, Wang Q, Huang Y, Jen KY, et al: CUL4A induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes cancer metastasis by
regulating ZEB1 expression. Cancer Res. 74:520–531. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Wang Y, Zhang P, Liu Z, Wang Q, Wen M,
Wang Y, Yuan H, Mao JH and Wei G: CUL4A overexpression enhances
lung tumor growth and sensitizes lung cancer cells to erlotinib via
transcriptional regulation of EGFR. Mol Cancer. 13:2522014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun Y, Wang Y, Fan C, Gao P, Wang X, Wei G
and Wei J: Estrogen promotes stemness and invasiveness of
ER-positive breast cancer cells through Gli1 activation. Mol
Cancer. 13:1372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Q, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Zhang Y and Xiao
W: Involvement of urokinase in cigarette smoke extract-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human small airway epithelial
cells. Lab Invest. 95:469–479. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kano Y, Konno M, Ohta K, Haraguchi N,
Nishikawa S, Kagawa Y, Hamabe A, Hasegawa S, Ogawa H, Fukusumi T,
et al: Jumonji/Arid1b (Jarid1b) protein modulates human esophageal
cancer cell growth. Mol Clin Oncol. 1:753–757. 2013.
|
|
17
|
Roesch A, Vultur A, Bogeski I, Wang H,
Zimmermann KM, Speicher D, Körbel C, Laschke MW, Gimotty PA,
Philipp SE, et al: Overcoming intrinsic multidrug resistance in
melanoma by blocking the mitochondrial respiratory chain of
slow-cycling JARID1B(high) cells. Cancer Cell. 23:811–825. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Albert M, Schmitz SU, Kooistra SM,
Malatesta M, Morales Torres C, Rekling JC, Johansen JV, Abarrategui
I and Helin K: The histone demethylase Jarid1b ensures faithful
mouse development by protecting developmental genes from aberrant
H3K4me3. PLoS Genet. 9:e10034612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wendt MK, Allington TM and Schiemann WP:
Mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by TGF-beta.
Future Oncol. 5:1145–1168. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Parvani JG, Taylor MA and Schiemann WP:
Noncanonical TGF-β signaling during mammary tumorigenesis. J
Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 16:127–146. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim HM, Haraguchi N, Ishii H, Ohkuma M,
Okano M, Mimori K, Eguchi H, Yamamoto H, Nagano H, Sekimoto M, et
al: Increased CD13 expression reduces reactive oxygen species,
promoting survival of liver cancer stem cells via an
epithelial-mesenchymal transition-like phenomenon. Ann Surg Oncol.
19(Suppl 3): S539–S548. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Grzmil M, Morin P Jr, Lino MM, Merlo A,
Frank S, Wang Y, Moncayo G and Hemmings BA: MAP kinase-interacting
kinase 1 regulates SMAD2-dependent TGF-β signaling pathway in human
glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 71:2392–2402. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun J, Liu SZ, Lin Y, Cao XP and Liu JM:
TGF-β promotes glioma cell growth via activating Nodal expression
through Smad and ERK1/2 pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
443:1066–1072. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|