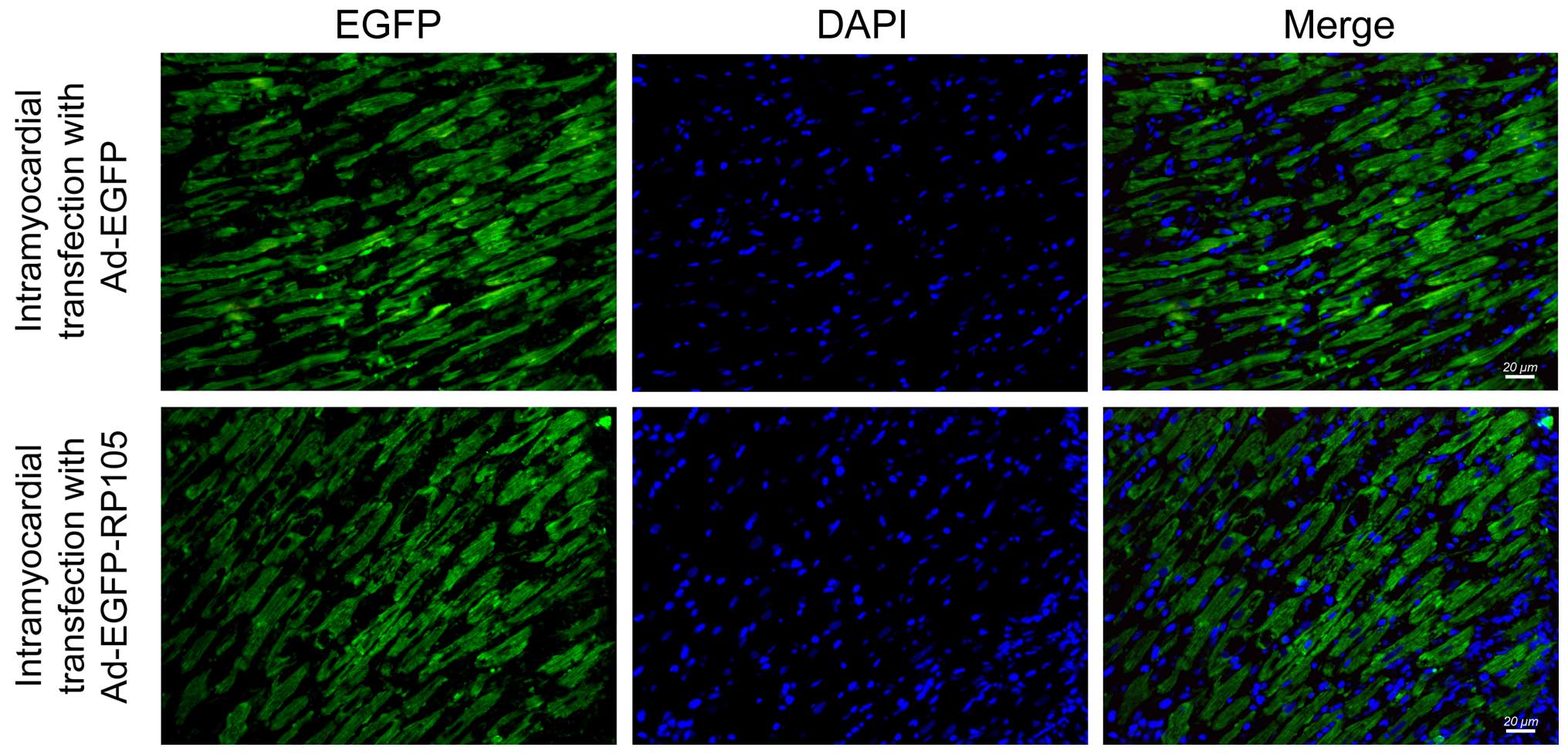
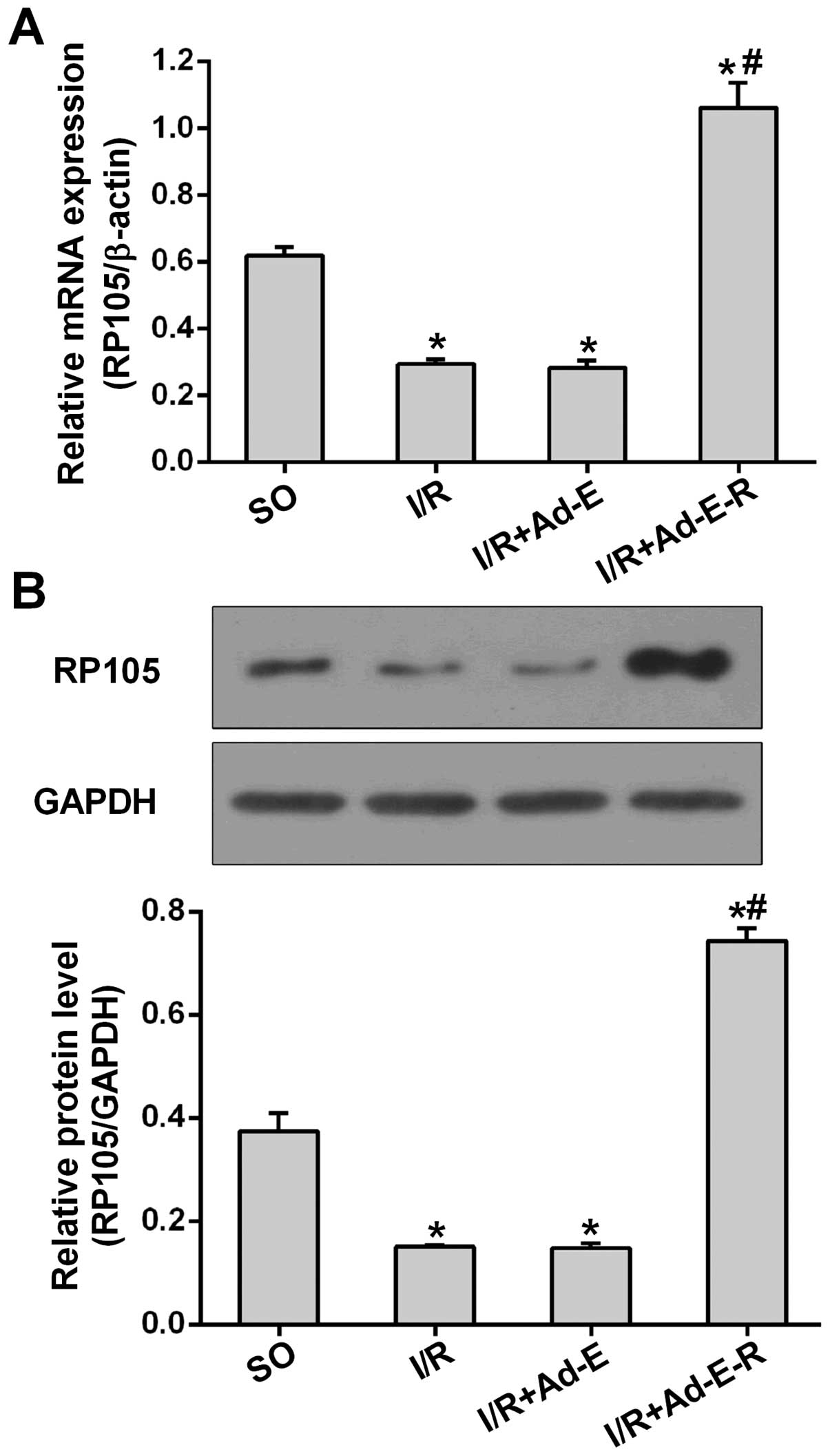
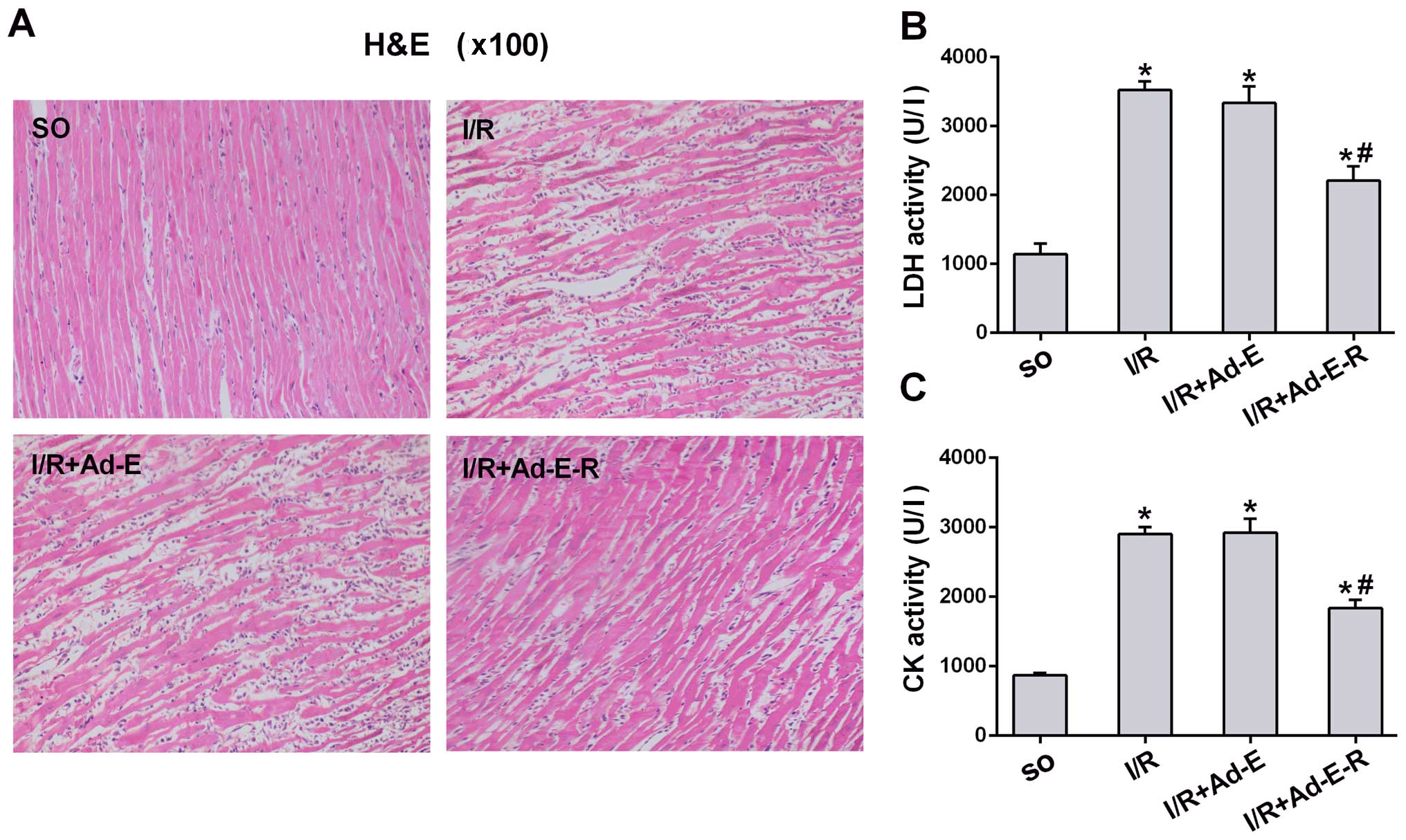
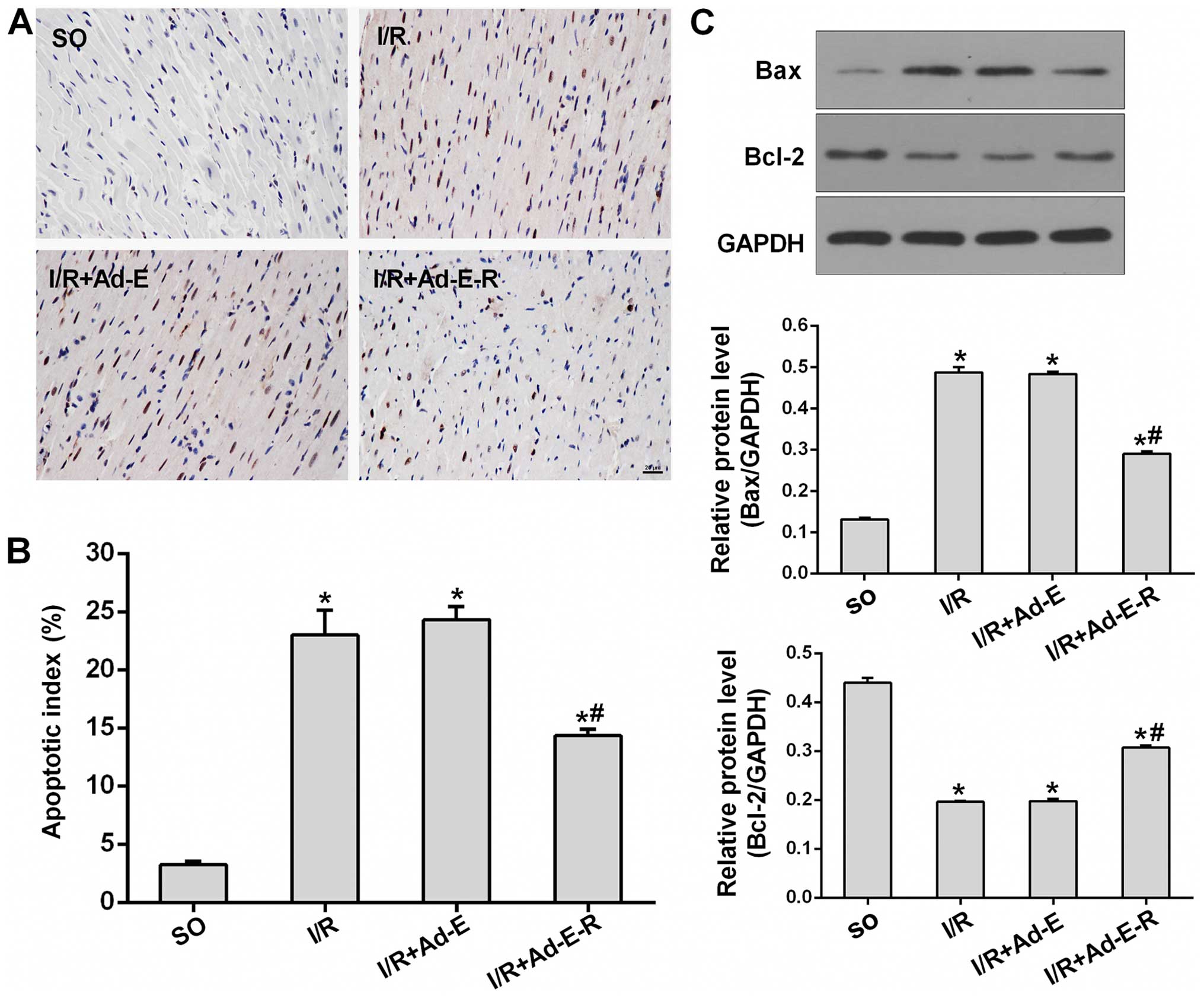
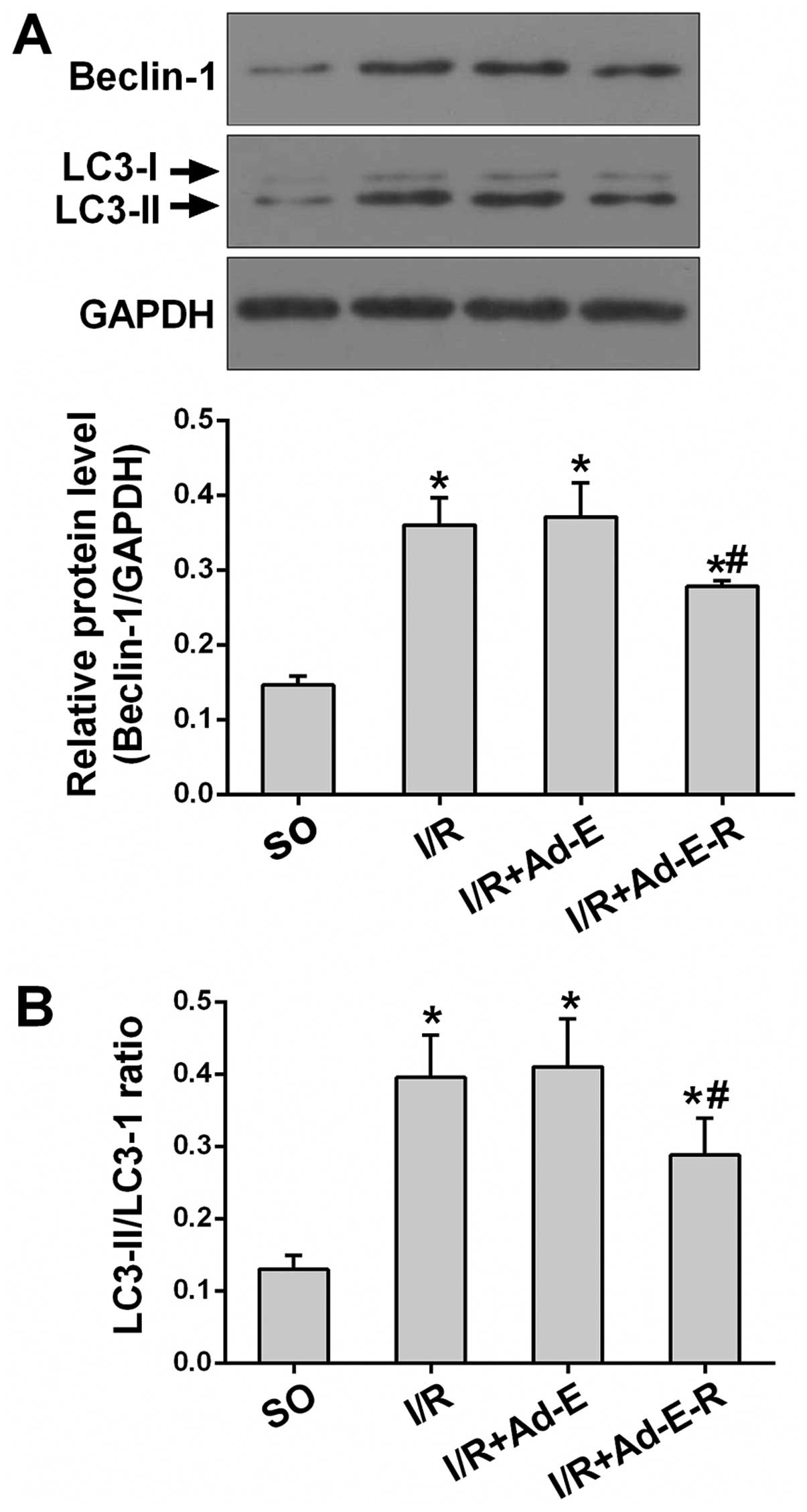
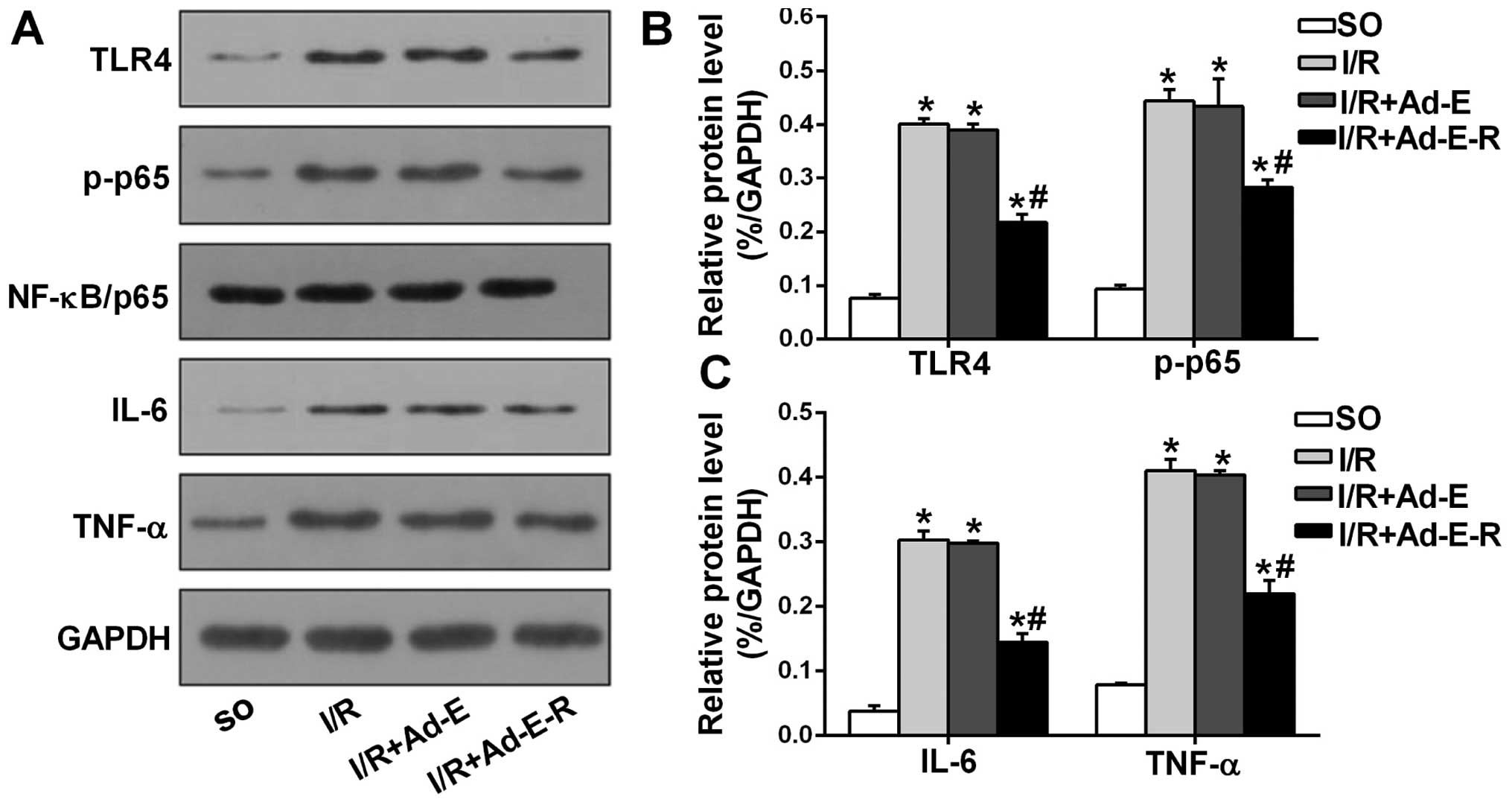
|
1
|
Zhou X, Chen M, Wang S, Yu L and Jiang H:
MG53 protein: a promising novel therapeutic target for myocardial
ischemia reperfusion injury. Int J Cardiol. 199:424–425. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Han XJ, He D, Xu LJ, Chen M, Wang YQ, Feng
JG, Wei MJ, Hong T and Jiang LP: Knockdown of connexin 43
attenuates balloon injury-induced vascular restenosis through the
inhibition of the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth
muscle cells. Int J Mol Med. 36:1361–1368. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Thapalia BA, Zhou Z and Lin X: Autophagy,
a process within reperfusion injury: an update. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 7:8322–8341. 2014.
|
|
4
|
Lin Y, Chen L, Li W and Fang J: Role of
high-mobility group box-1 in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury
and the effect of ethyl pyruvate. Exp Ther Med. 9:1537–1541.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yao T, Ying X, Zhao Y, Yuan A, He Q, Tong
H, Ding S, Liu J, Peng X, Gao E, et al: Vitamin D receptor
activation protects against myocardial reperfusion injury through
inhibition of apoptosis and modulation of autophagy. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 22:633–650. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Barry SP, Ounzain S, McCormick J,
Scarabelli TM, Chen-Scarabelli C, Saravolatz LI, Faggian G,
Mazzucco A, Suzuki H, Thiemermann C, et al: Enhanced IL-17
signalling following myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Int J
Cardiol. 163:326–334. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Ding HS, Yang J, Chen P, Yang J, Bo SQ,
Ding JW and Yu QQ: The HMGB1-TLR4 axis contributes to myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury via regulation of cardiomyocyte
apoptosis. Gene. 527:389–393. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang B, Zhong S, Zheng F, Zhang Y, Gao F,
Chen Y, Lu B, Xu H and Shi G: N-n-butyl haloperidol iodide protects
cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by inhibiting
autophagy. Oncotarget. 6:24709–24721. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Murphy E and Steenbergen C: Mechanisms
underlying acute protection from cardiac ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Physiol Rev. 88:581–609. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu H, Che X, Zheng Q, Wu A, Pan K, Shao A,
Wu Q, Zhang J and Hong Y: Caspases: a molecular switch node in the
crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Int J Biol Sci.
10:1072–1083. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kalogeris T, Baines CP, Krenz M and
Korthuis RJ: Cell biology of ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int Rev
Cell Mol Biol. 298:229–317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xie M, Kong Y, Tan W, May H, Battiprolu
PK, Pedrozo Z, Wang ZV, Morales C, Luo X, Cho G, et al: Histone
deacetylase inhibition blunts ischemia/reperfusion injury by
inducing cardiomyocyte autophagy. Circulation. 129:1139–1151. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gustafsson ÅB and Gottlieb RA: Eat your
heart out: role of autophagy in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion.
Autophagy. 4:416–421. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu W, Jiang H, Hu X and Fu W: Effects of
high-mobility group box 1 on the expression of Beclin-1 and LC3
proteins following hypoxia and reoxygenation injury in rat
cardiomyocytes. Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:5353–5357. 2014.
|
|
15
|
Ke J, Yao B, Li T, Cui S and Ding H: A2
adenosine receptor-mediated cardioprotection against reperfusion
injury in rat hearts is associated with autophagy downregulation. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 66:25–34. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nikoletopoulou V, Markaki M, Palikaras K
and Tavernarakis N: Crosstalk between apoptosis, necrosis and
autophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:3448–3459. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu J, Qin X, Cai X, Yang L, Xing Y, Li J,
Zhang L, Tang Y, Liu J, Zhang X and Gao F: Mitochondrial JNK
activation triggers autophagy and apoptosis and aggravates
myocardial injury following ischemia/reperfusion. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1852:262–270. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Shen M, Lu J, Dai W, Wang F, Xu L, Chen K,
He L, Cheng P, Zhang Y, Wang C, et al: Ethyl pyruvate ameliorates
hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting intrinsic pathway
of apoptosis and autophagy. Mediators Inflamm. 2013:4615362013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhao Y, Xu Y, Zhang J and Ji T:
Cardioprotective effect of carvedilol: inhibition of apoptosis in
H9c2 cardiomyocytes via the TLR4/NF-κB pathway following
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Exp Ther Med. 8:1092–1096.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu Y, Jagannath C, Liu XD, Sharafkhaneh A,
Kolodziejska KE and Eissa NT: Toll-like receptor 4 is a sensor for
autophagy associated with innate immunity. Immunity. 27:135–144.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Porakishvili N, Vispute K, Steele AJ,
Rajakaruna N, Kulikova N, Tsertsvadze T, Nathwani A, Damle RN,
Clark EA, Rai KR, et al: Rewiring of sIgM-mediated intracellular
signaling through the CD180 Toll-like receptor. Mol Med. 21:46–57.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Wezel A, van der Velden D, Maassen JM,
Lagraauw HM, de Vries MR, Karper JC, Kuiper J, Bot I and Quax PH:
RP105 deficiency attenuates early atherosclerosis via decreased
monocyte influx in a CCR2 dependent manner. Atherosclerosis.
238:132–139. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Louwe MC, Karper JC, de Vries MR, Nossent
AY, Bastiaansen AJ, van der Hoorn JW, Willems van Dijk K, Rensen
PC, Steendijk P, Smit JW and Quax PH: RP105 deficiency aggravates
cardiac dysfunction after myocardial infarction in mice. Int J
Cardiol. 176:788–793. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Karper JC, Ewing MM, de Vries MR, de Jager
SC, Peters EA, de Boer HC, van Zonneveld AJ, Kuiper J, Huizinga EG,
Brondijk TH, et al: TLR accessory molecule RP105 (CD180) is
involved in post-interventional vascular remodeling and soluble
RP105 modulates neointima formation. PLoS One. 8:e679232013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang J, Guo X, Yang J, Ding JW, Li S, Yang
R, Fan ZX and Yang CJ: RP105 protects against apoptosis in
ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial damage in rats by
suppressing TLR4-mediated signaling pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem.
36:2137–2148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang J, Jiang H, Chen SS, Chen J, Li WQ,
Xu SK and Wang JC: Lentivirus-mediated RNAi targeting CREB binding
protein attenuates neointimal formation and promotes
re-endothelialization in balloon injured rat carotid artery. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 26:441–448. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zeng M, Wei X, Wu Z, Li W, Li B, Zhen Y,
Chen J, Wang P and Fei Y: NF-κB-mediated induction of autophagy in
cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
436:180–185. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shyu KG, Wang BW, Lin CM and Chang H:
Cyclic stretch enhances the expression of toll-like receptor 4 gene
in cultured cardiomyocytes via p38 MAP kinase and NF-kappaB
pathway. J Biomed Sci. 17:152010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Eltzschig HK and Eckle T: Ischemia and
reperfusion - from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 17:1391–1401.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Divanovic S, Trompette A, Atabani SF,
Madan R, Golenbock DT, Visintin A, Finberg RW, Tarakhovsky A, Vogel
SN, Belkaid Y, et al: Negative regulation of Toll-like receptor 4
signaling by the Toll-like receptor homolog RP105. Nat Immunol.
6:571–578. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yazawa N, Fujimoto M, Sato S, Miyake K,
Asano N, Nagai Y, Takeuchi O, Takeda K, Okochi H, Akira S, et al:
CD19 regulates innate immunity by the toll-like receptor RP105
signaling in B lymphocytes. Blood. 102:1374–1380. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hsieh YC, Athar M and Chaudry IH: When
apoptosis meets autophagy: deciding cell fate after trauma and
sepsis. Trends Mol Med. 15:129–138. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang Y, Gao K, Hu Z, Li W, Davies H, Ling
S, Rudd JA and Fang M: Autophagy upregulation and apoptosis
downregulation in DAHP and triptolide treated cerebral ischemia.
Mediators Inflamm. 2015:1201982015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Maejima Y, Kyoi S, Zhai P, Liu T, Li H,
Ivessa A, Sciarretta S, Del Re DP, Zablocki DK, Hsu CP, et al: Mst1
inhibits autophagy by promoting Beclin1-Bcl-2 interaction. Nat Med.
19:1478–1488. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|