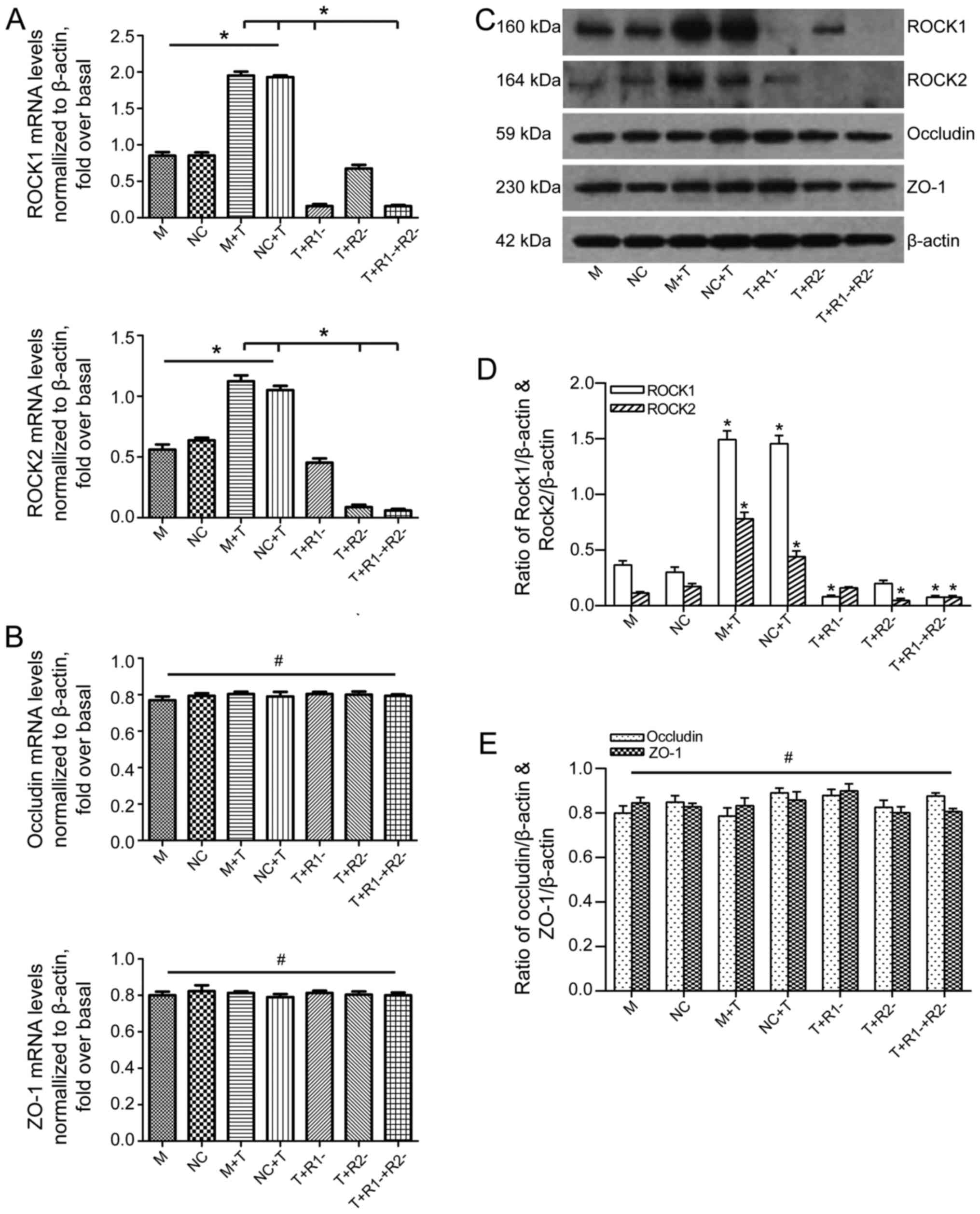
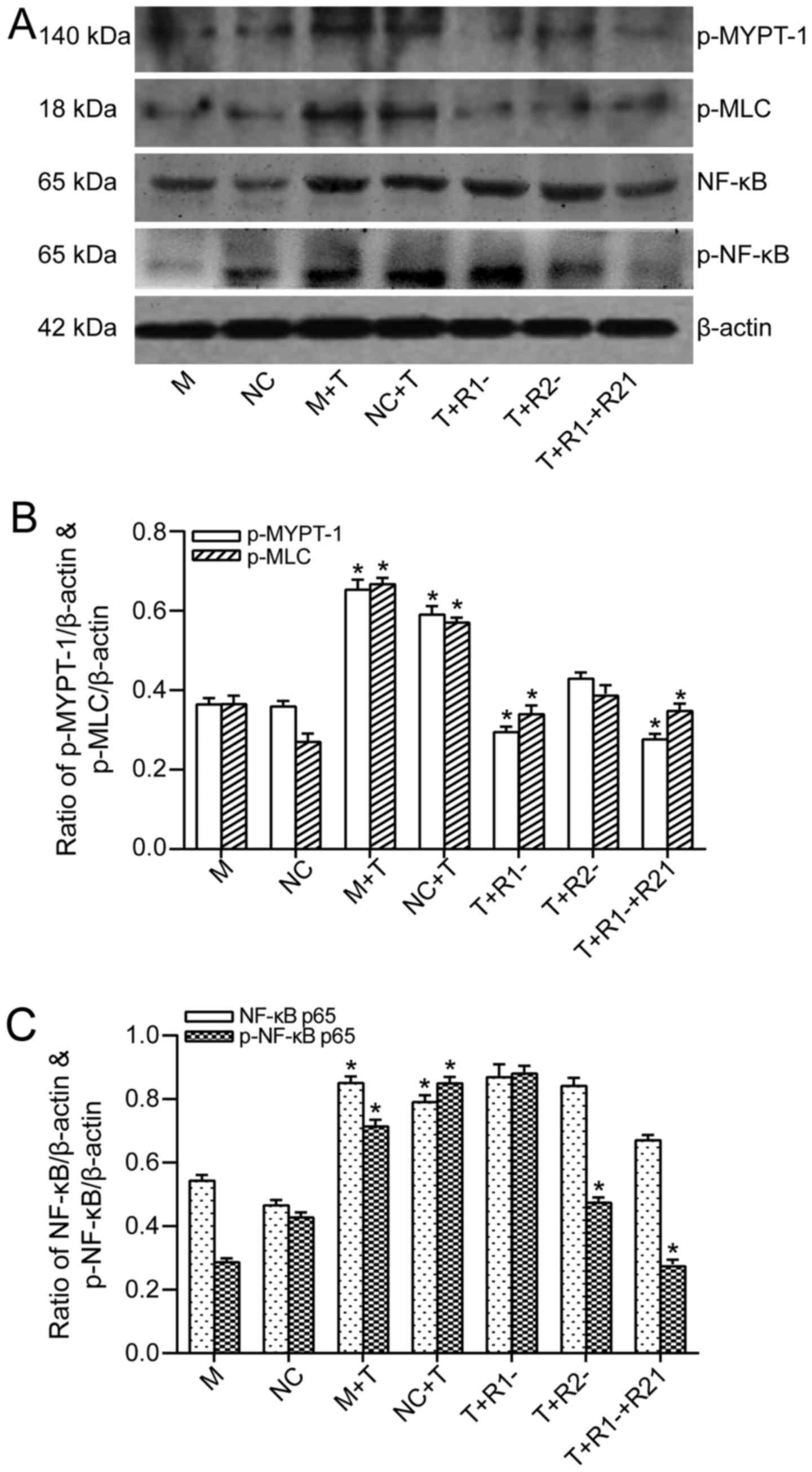
|
1
|
Zeissig S, Bojarski C, Buergel N, Mankertz
J, Zeitz M, Fromm M and Schulzke JD: Downregulation of epithelial
apoptosis and barrier repair in active Crohn's disease by tumour
necrosis factor alpha antibody treatment. Gut. 53:1295–1302. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Turck D, Ythier H, Maquet E, Deveaux M,
Marchandise X, Farriaux JP and Fontaine G: Intestinal permeability
to [51Cr] EDTA in children with Crohn's disease and celiac disease.
J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 6:535–537. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
May GR, Sutherland LR and Meddings JB: Is
small intestinal permeability really increased in relatives of
patients with Crohn's disease? Gastroenterology. 104:1627–1632.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Clayburgh DR, Shen L and Turner JR: A
porous defense: The leaky epithelial barrier in intestinal disease.
Lab Invest. 84:282–291. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Katz KD, Hollander D, Vadheim CM, McElree
C, Delahunty T, Dadufalza VD, Krugliak P and Rotter JI: Intestinal
permeability in patients with Crohn's disease and their healthy
relatives. Gastroenterology. 97:927–931. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Edelblum KL and Turner JR: The tight
junction in inflammatory disease: Communication breakdown. Curr
Opin Pharmacol. 9:715–720. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shen L, Weber CR and Turner JR: The tight
junction protein complex undergoes rapid and continuous molecular
remodeling at steady state. J Cell Biol. 181:683–695. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hering NA and Schulzke JD: Therapeutic
options to modulate barrier defects in inflammatory bowel disease.
Dig Dis. 27:450–454. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Steed E, Balda MS and Matter K: Dynamics
and functions of tight junctions. Trends Cell Biol. 20:142–149.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ivanov AI: Structure and regulation of
intestinal epithelial tight junctions: Current concepts and
unanswered questions. Adv Exp Med Biol. 763:132–148. 2012.
|
|
11
|
Sebbagh M, Renvoizé C, Hamelin J, Riché N,
Bertoglio J and Bréard J: Caspase-3-mediated cleavage of ROCK I
induces MLC phosphorylation and apoptotic membrane blebbing. Nat
Cell Biol. 3:346–352. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chaturvedi LS, Marsh HM and Basson MD:
Role of RhoA and its effectors ROCK and mDia1 in the modulation of
deformation-induced FAK, ERK, p38, and MLC motogenic signals in
human Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 301:C1224–C1238. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sapet C, Simoncini S, Loriod B, Puthier D,
Sampol J, Nguyen C, Dignat-George F and Anfosso F: Thrombin-induced
endothelial microparticle generation: Identification of a novel
pathway involving ROCK-II activation by caspase-2. Blood.
108:1868–1876. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Turner MS, Fen-Fen-Lin, Trauger JW,
Stephens J and LoGrasso P: Characterization and purification of
truncated human Rho-kinase II expressed in Sf-21 cells. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 405:13–20. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen XQ, Tan I, Ng CH, Hall C, Lim L and
Leung T: Characterization of RhoA-binding kinase ROKalpha
implication of the pleckstrin homology domain in ROKalpha function
using region-specific antibodies. J Biol Chem. 277:12680–12688.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Matsui T, Amano M, Yamamoto T, Chihara K,
Nakafuku M, Ito M, Nakano T, Okawa K, Iwamatsu A and Kaibuchi K:
Rho-associated kinase, a novel serine/threonine kinase, as a
putative target for small GTP binding protein Rho. EMBO J.
15:2208–2216. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ward Y, Yap SF, Ravichandran V, Matsumura
F, Ito M, Spinelli B and Kelly K: The GTP binding proteins Gem and
Rad are negative regulators of the Rho-Rho kinase pathway. J Cell
Biol. 157:291–302. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Leung T, Chen XQ, Manser E and Lim L: The
p160 RhoA-binding kinase ROK alpha is a member of a kinase family
and is involved in the reorganization of the cytoskeleton. Mol Cell
Biol. 16:5313–5327. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ivanov AI, Parkos CA and Nusrat A:
Cytoskeletal regulation of epithelial barrier function during
inflammation. Am J Pathol. 177:512–524. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Segain JP, Raingeard de la Blétière D,
Sauzeau V, Bourreille A, Hilaret G, Cario-Toumaniantz C, Pacaud P,
Galmiche JP and Loirand G: Rho kinase blockade prevents
inflammation via nuclear factor kappa B inhibition: Evidence in
Crohn's disease and experimental colitis. Gastroenterology.
124:1180–1187. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mihaescu A, Santén S, Jeppsson B and
Thorlacius H: Rho kinase signalling mediates radiation-induced
inflammation and intestinal barrier dysfunction. Br J Surg.
98:124–131. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Anwar KN, Fazal F, Malik AB and Rahman A:
RhoA/Rho-associated kinase pathway selectively regulates
thrombin-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in
endothelial cells via activation of I kappa B kinase beta and
phosphorylation of RelA/p65. J Immunol. 173:6965–6972. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rodriguez PL, Sahay S, Olabisi OO and
Whitehead IP: ROCK I-mediated activation of NF-kappaB by RhoB. Cell
Signal. 19:2361–2369. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Voiosu T, Benguş A, Dinu R, Voiosu AM,
Bălănescu P, Băicuş C, Diculescu M, Voiosu R and Mateescu B: Rapid
fecal calprotectin level assessment and the SIBDQ score can
accurately detect active mucosal inflammation in IBD patients in
clinical remission: A prospective study. J Gastrointestin Liver
Dis. 23:273–278. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ameho CK, Adjei AA, Harrison EK, Takeshita
K, Morioka T, Arakaki Y, Ito E, Suzuki I, Kulkarni AD, Kawajiri A,
et al: Prophylactic effect of dietary glutamine supplementation on
interleukin-8 and tumour necrosis factor alpha production in
trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid induced colitis. Gut. 41:487–493.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dong X, Liu Z, Lan D, Niu J, Miao J, Yang
G, Zhang F, Sun Y, Wang K and Miao Y: Critical role of Keratin 1 in
maintaining epithelial barrier and correlation of its
down-regulation with the progression of inflammatory bowel disease.
Gene. 608:13–19. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Turner JR, Buschmann MM, Romero-Calvo I,
Sailer A and Shen L: The role of molecular remodeling in
differential regulation of tight junction permeability. Semin Cell
Dev Biol. 36:204–212. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Moyer RA, Wendt MK, Johanesen PA, Turner
JR and Dwinell MB: Rho activation regulates CXCL12 chemokine
stimulated actin rearrangement and restitution in model intestinal
epithelia. Lab Invest. 87:807–817. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Le Dréan G, haure-Mirande V, Ferrier L,
Bonnet C, hulin P, de Coppet P and Segain JP: Visceral adipose
tissue and leptin increase colonic epithelial tight junction
permeability via a RhoA-ROCK-dependent pathway. FASEB J.
28:1059–1070. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Elamin E, Masclee A, Dekker J and Jonkers
D: Ethanol disrupts intestinal epithelial tight junction integrity
through intracellular calcium-mediated Rho/ROCK activation. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 306:G677–G685. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ji R, Wang A, Shang H, Chen L, Bao C, Wu
L, Wu H and Shi Y: Herb-partitioned moxibustion upregulated the
expression of colonic epithelial tight junction-related proteins in
Crohn's disease model rats. Chin Med. 11:202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tong J, Wang Y, Chang B, Zhang D and Wang
B: Y-27632 inhibits ethanol-induced increase in intestinal
epithelial barrier permeability. Mol Med Rep. 9:2357–2361. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Furuse M, hirase T, Itoh M, Nagafuchi A,
Yonemura S and Tsukita S and Tsukita S: Occludin: A novel integral
membrane protein localizing at tight junctions. J Cell Biol.
123:1777–1788. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shimada H and Rajagopalan LE: Rho kinase-2
activation in human endothelial cells drives lysophosphatidic
acid-mediated expression of cell adhesion molecules via NF-kappaB.
65J Biol Chem. 285:12536–12542. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|