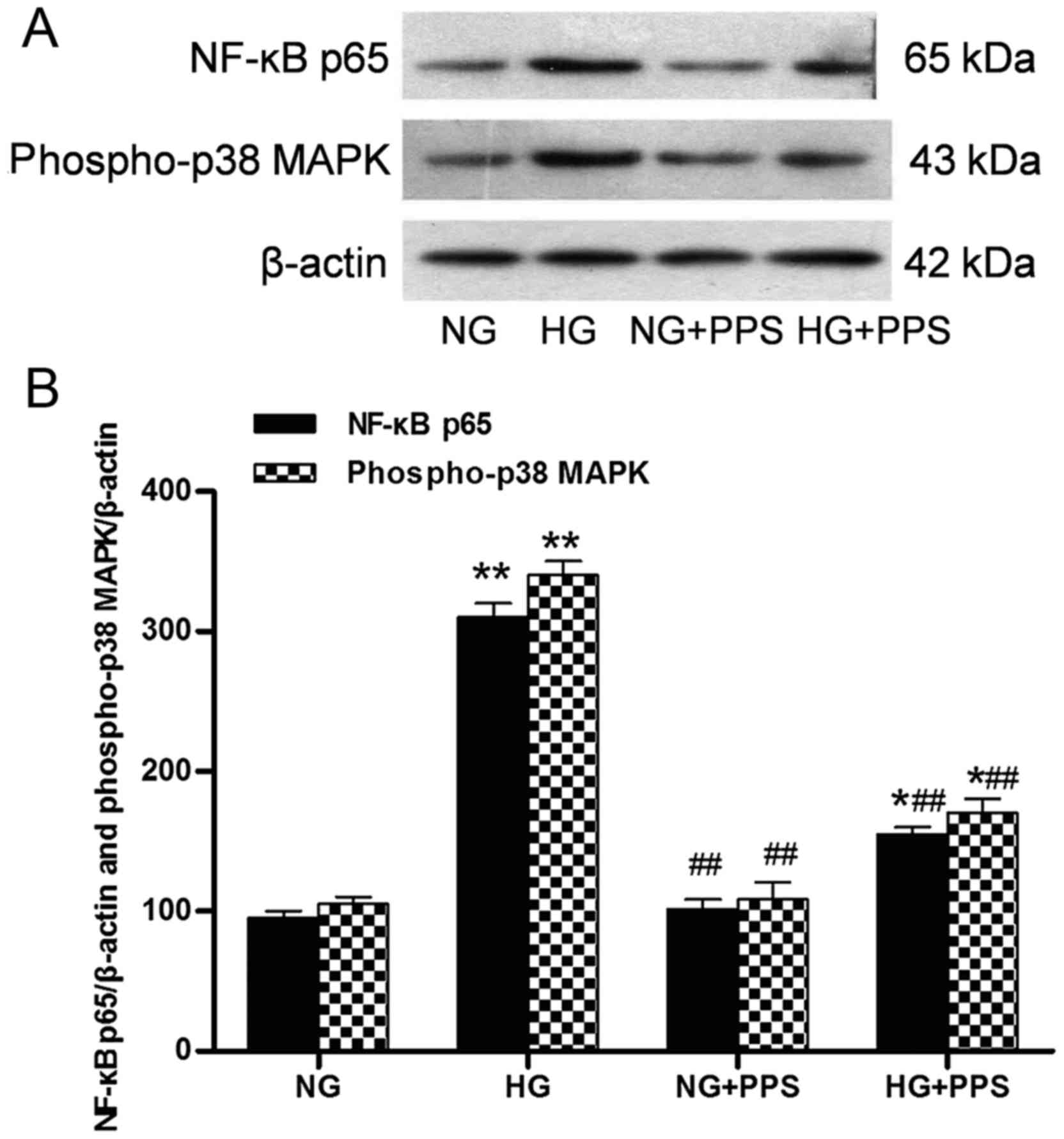
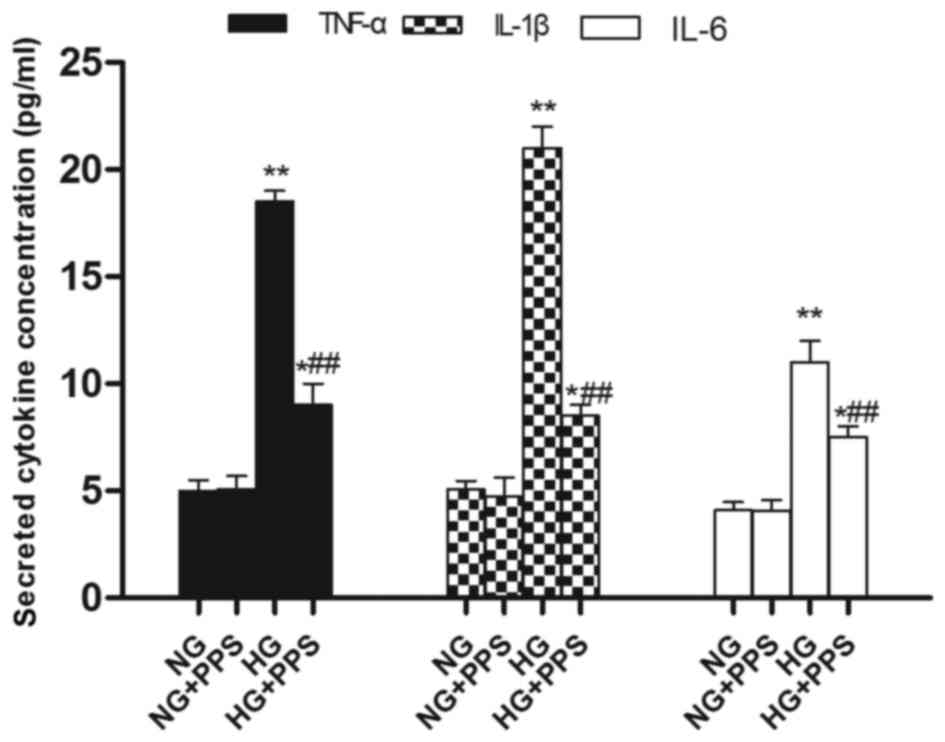
|
1
|
Gross JL, de Azevedo MJ, Silveiro SP,
Canani LH, Caramori ML and Zelmanovitz T: Diabetic nephropathy:
Diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care. 28:164–176.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tan AL, Forbes JM and Cooper ME: AGE,
RAGE, and ROS in diabetic nephropathy. Semin Nephrol. 27:130–143.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Magee GM, Bilous RW, Cardwell CR, Hunter
SJ, Kee F and Fogarty DG: Is hyperfiltration associated with the
future risk of developing diabetic nephropathy? A meta-analysis.
Diabetologia. 52:691–697. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nishikawa T, Edelstein D, Du XL, Yamagishi
S, Matsumura T, Kaneda Y, Yorek MA, Beebe D, Oates PJ, Hammes HP,
et al: Normalizing mitochondrial superoxide production blocks three
pathways of hyperglycaemic damage. Nature. 404:787–790. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Navarro-González JF and Mora-Fernández C:
The role of inflammatory cytokines in diabetic nephropathy. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 19:433–442. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Noh H and King GL: The role of protein
kinase C activation in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int Suppl.
72(Suppl): S49–S53. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Magri CJ and Fava S: The role of tubular
injury in diabetic nephropathy. Eur J Intern Med. 20:551–555. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gilbert RE and Cooper ME: The
tubulointerstitium in progressive diabetic kidney disease: More
than an aftermath of glomerular injury. Kidney Int. 56:1627–1637.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mora C and Navarro JF: Inflammation and
diabetic nephropathy. Curr Diab Rep. 6:463–468. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tuttle KR: Linking metabolism and
immunology: Diabetic nephropathy is an inflammatory disease. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 16:1537–1538. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kumar D, Robertson S and Burns KD:
Evidence of apoptosis in human diabetic kidney. Mol Cell Biochem.
259:67–70. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Verzola D, Bertolotto MB, Villaggio B,
Ottonello L, Dallegri F, Salvatore F, Berruti V, Gandolfo MT,
Garibotto G and Deferrari G: Oxidative stress mediates apoptotic
changes induced by hyperglycemia in human tubular kidney cells. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 15(Suppl 1): S85–S87. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Verzola D, Bertolotto MB, Villaggio B,
Ottonello L, Dallegri F, Frumento G, Berruti V, Gandolfo MT,
Garibotto G and Deferran G: Taurine prevents apoptosis induced by
high ambient glucose in human tubule renal cells. J Investig Med.
50:443–451. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stambe C, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Hill PA,
Dowling J and Atkins RC: p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
activation and cell localization in human glomerulonephritis:
Correlation with renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 15:326–336. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Adhikary L, Chow F, Nikolic-Paterson DJ,
Stambe C, Dowling J, Atkins RC and Tesch GH: Abnormal p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling in human and
experimental diabetic nephropathy. Diabetologia. 47:1210–1222.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen H, Brahmbhatt S, Gupta A and Sharma
AC: Duration of streptozotocin-induced diabetes differentially
affects p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphorylation
in renal and vascular dysfunction. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 4:32005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Du Y, Tang J, Li G, Berti-Mattera L, Lee
CA, Bartkowski D, Gale D, Monahan J, Niesman MR, Alton G, et al:
Effects of p38 MAPK inhibition on early stages of diabetic
retinopathy and sensory nerve function. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
51:2158–2164. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nickel JC, Barkin J, Forrest J, Mosbaugh
PG, Hernandez-Graulau J, Kaufman D, Lloyd K, Evans RJ, Parsons CL
and Atkinson LE; Elmiron Study Group: Randomized, double-blind,
dose-ranging study of pentosan polysulfate sodium for interstitial
cystitis. Urology. 65:654–658. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu J, Guan TJ, Zheng S, Grosjean F, Liu W,
Xiong H, Gordon R, Vlassara H, Striker GE and Zheng F: Inhibition
of inflammation by pentosan polysulfate impedes the development and
progression of severe diabetic nephropathy in aging C57B6 mice. Lab
Invest. 91:1459–1471. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu H, Shi Y, Deng X, Su Y, Du C, Wei J,
Ren Y, Wu M, Hou Y and Duan H: Inhibition of c-Src/p38 MAPK pathway
ameliorates renal tubular epithelial cells apoptosis in db/db mice.
Mol Cell Endocrinol. 417:27–35. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rane MJ, Song Y, Jin S, Barati MT, Wu R,
Kausar H, Tan Y, Wang Y, Zhou G, Klein JB, et al: Interplay between
Akt and p38 MAPK pathways in the regulation of renal tubular cell
apoptosis associated with diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 298:F49–F61. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Iwayama H and Ueda N: Role of
mitochondrial Bax, caspases, and MAPKs for ceramide-induced
apoptosis in renal proximal tubular cells. Mol Cell Biochem.
379:37–42. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Blantz RC and Singh P: Glomerular and
tubular function in the diabetic kidney. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis.
21:297–303. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Baba K, Minatoguchi S, Sano H, Kagawa T,
Murata I, Takemura G, Hirano T, Ohashi H, Takemura M, Fujiwara T,
et al: Involvement of apoptosis in patients with diabetic
nephropathy: A study on plasma soluble Fas levels and pathological
findings. Nephrology (Carlton). 9:94–99. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Habib SL: Diabetes and renal tubular cell
apoptosis. World J Diabetes. 4:27–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sakai N, Wada T, Furuichi K, Iwata Y,
Yoshimoto K, Kitagawa K, Kokubo S, Kobayashi M, Hara A, Yamahana J,
et al: Involvement of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38
in human diabetic nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 45:54–65. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fujita H, Omori S, Ishikura K, Hida M and
Awazu M: ERK and p38 mediate high-glucose-induced hypertrophy and
TGF-beta expression in renal tubular cells. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 286:F120–F126. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Bocanegra V, Gil Lorenzo AF, Cacciamani V,
Benardón ME, Costantino VV and Vallés PG: RhoA and MAPK signal
transduction pathways regulate NHE1-dependent proximal tubule cell
apoptosis after mechanical stretch. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
307:F881–F889. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Galkina E and Ley K: Leukocyte recruitment
and vascular injury in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol.
17:368–377. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chow F, Ozols E, Nikolic-Paterson DJ,
Atkins RC and Tesch GH: Macrophages in mouse type 2 diabetic
nephropathy: Correlation with diabetic state and progressive renal
injury. Kidney Int. 65:116–128. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sassy-Prigent C, Heudes D, Mandet C,
Bélair MF, Michel O, Perdereau B, Bariéty J and Bruneval P: Early
glomerular macrophage recruitment in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats. Diabetes. 49:466–475. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Furuta T, Saito T, Ootaka T, Soma J, Obara
K, Abe K and Yoshinaga K: The role of macrophages in diabetic
glomerulosclerosis. Am J Kidney Dis. 21:480–485. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bohle A, Wehrmann M, Bogenschütz O, Batz
C, Müller CA and Müller GA: The pathogenesis of chronic renal
failure in diabetic nephropathy. Investigation of 488 cases of
diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Pathol Res Pract. 187:251–259. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Viedt C and Orth SR: Monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) in the kidney: Does it more than
simply attract monocytes. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 17:2043–2047.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chow FY, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Ozols E,
Atkins RC, Rollin BJ and Tesch GH: Monocyte chemoattractant
protein-1 promotes the development of diabetic renal injury in
streptozotocin-treated mice. Kidney Int. 69:73–80. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chow FY, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Ma FY, Ozols
E, Rollins BJ and Tesch GH: Monocyte chemoattractant
protein-1-induced tissue inflammation is critical for the
development of renal injury but not type 2 diabetes in obese db/db
mice. Diabetologia. 50:471–480. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lim AK and Tesch GH: Inflammation in
diabetic nephropathy. Mediators Inflamm. 146154:2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chow FY, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Ozols E,
Atkins RC and Tesch GH: Intercellular adhesion molecule-1
deficiency is protective against nephropathy in type 2 diabetic
db/db mice. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:1711–1722. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Okada S, Shikata K, Matsuda M, Ogawa D,
Usui H, Kido Y, Nagase R, Wada J, Shikata Y and Makino H:
Intercellular adhesion molecule-1-deficient mice are resistant
against renal injury after induction of diabetes. Diabetes.
52:2586–2593. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sanchez AP and Sharma K: Transcription
factors in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Expert Rev Mol
Med. 11:e132009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Saklatvala J: The p38 MAP kinase pathway
as a therapeutic target in inflammatory disease. Curr Opin
Pharmacol. 4:372–377. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mezzano S, Aros C, Droguett A, Burgos ME,
Ardiles L, Flores C, Schneider H, Ruiz-Ortega M and Egido J:
NF-kappaB activation and overexpression of regulated genes in human
diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 19:2505–2512. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yang B, Hodgkinson A, Oates PJ, Millward
BA and Demaine AG: High glucose induction of DNA-binding activity
of the transcription factor NFkappaB in patients with diabetic
nephropathy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1782:295–302. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lewko B and Stepinski J: Hyperglycemia and
mechanical stress: Targeting the renal podocyte. J Cell Physiol.
221:288–295. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|