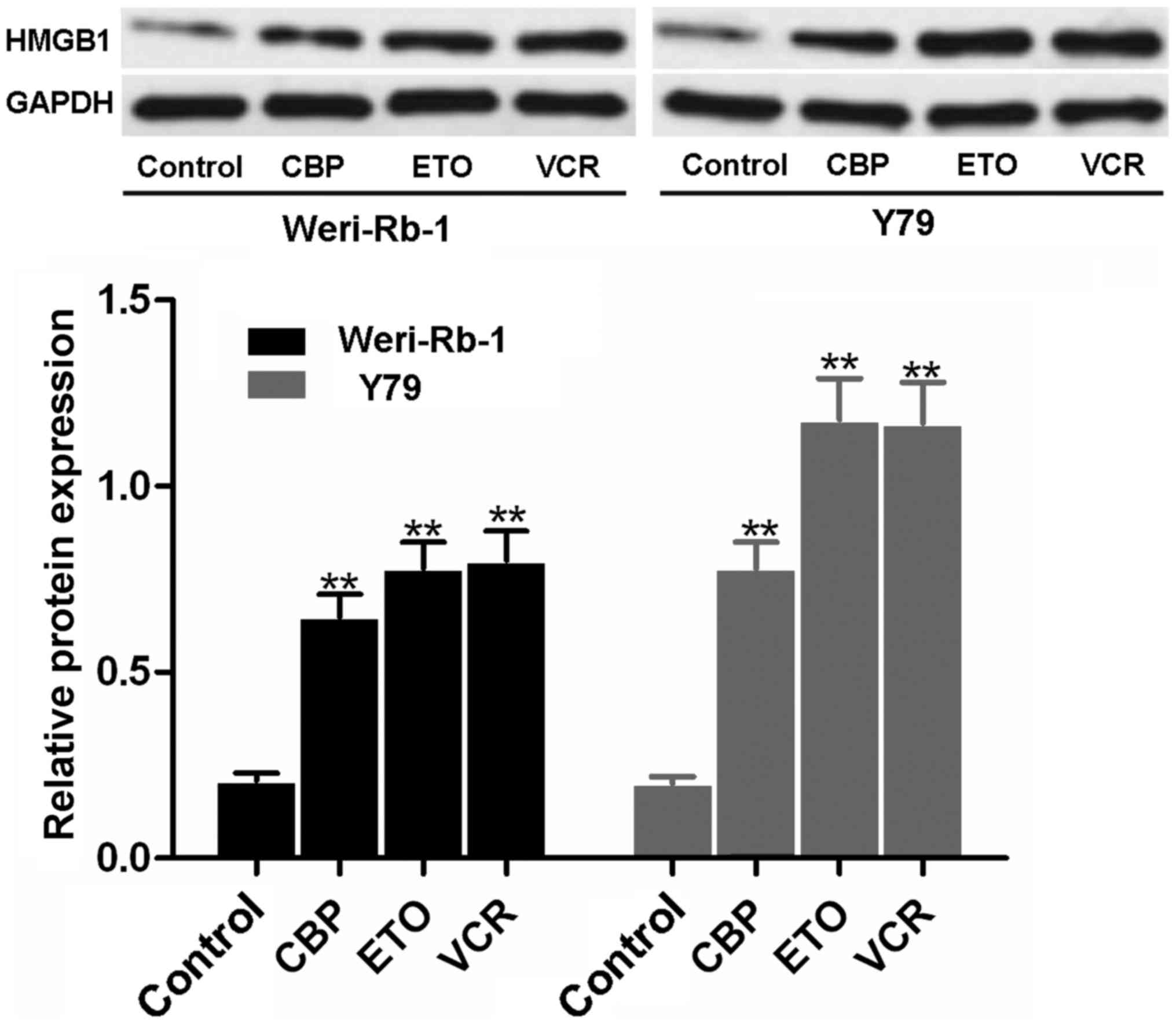
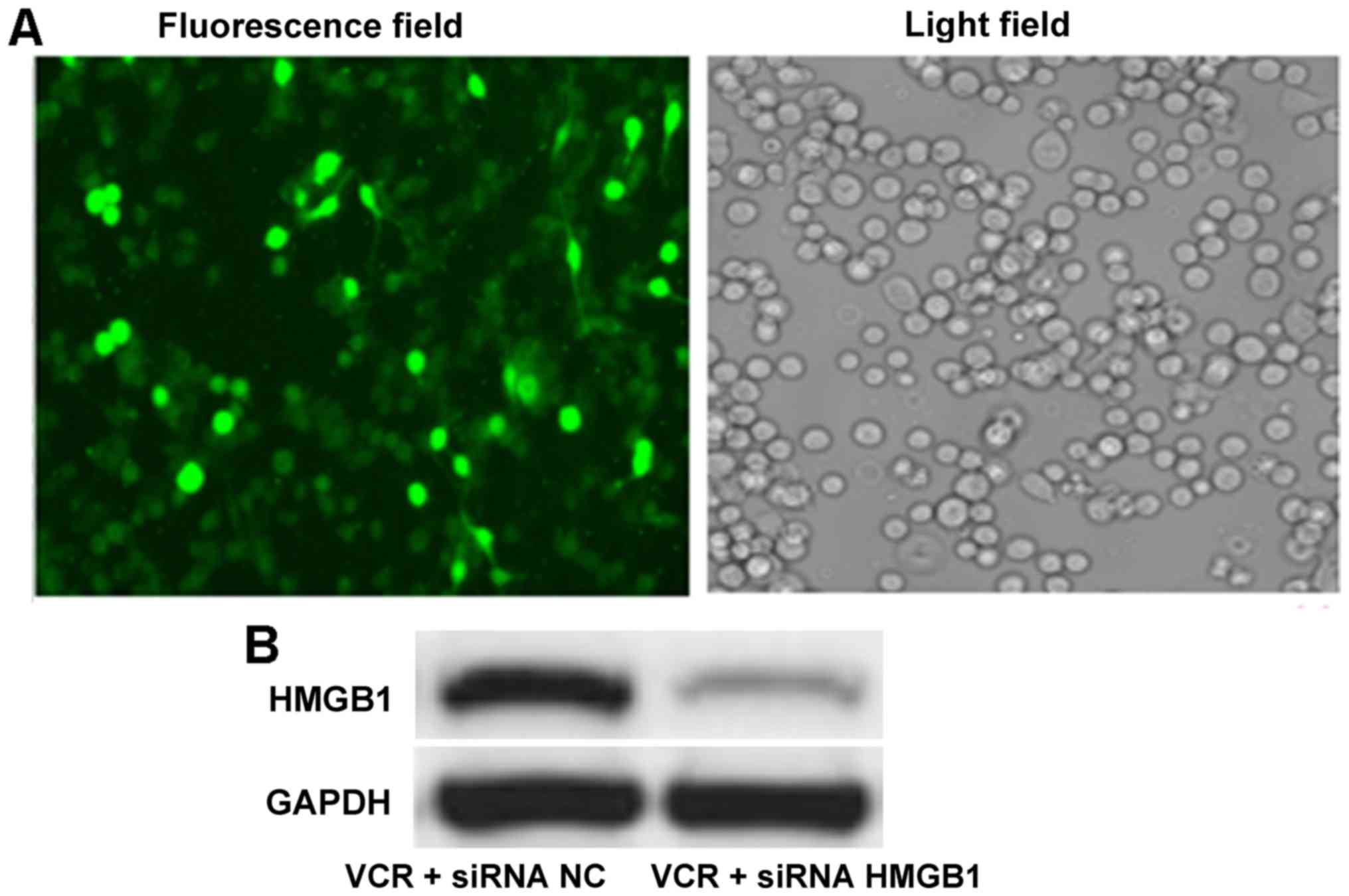
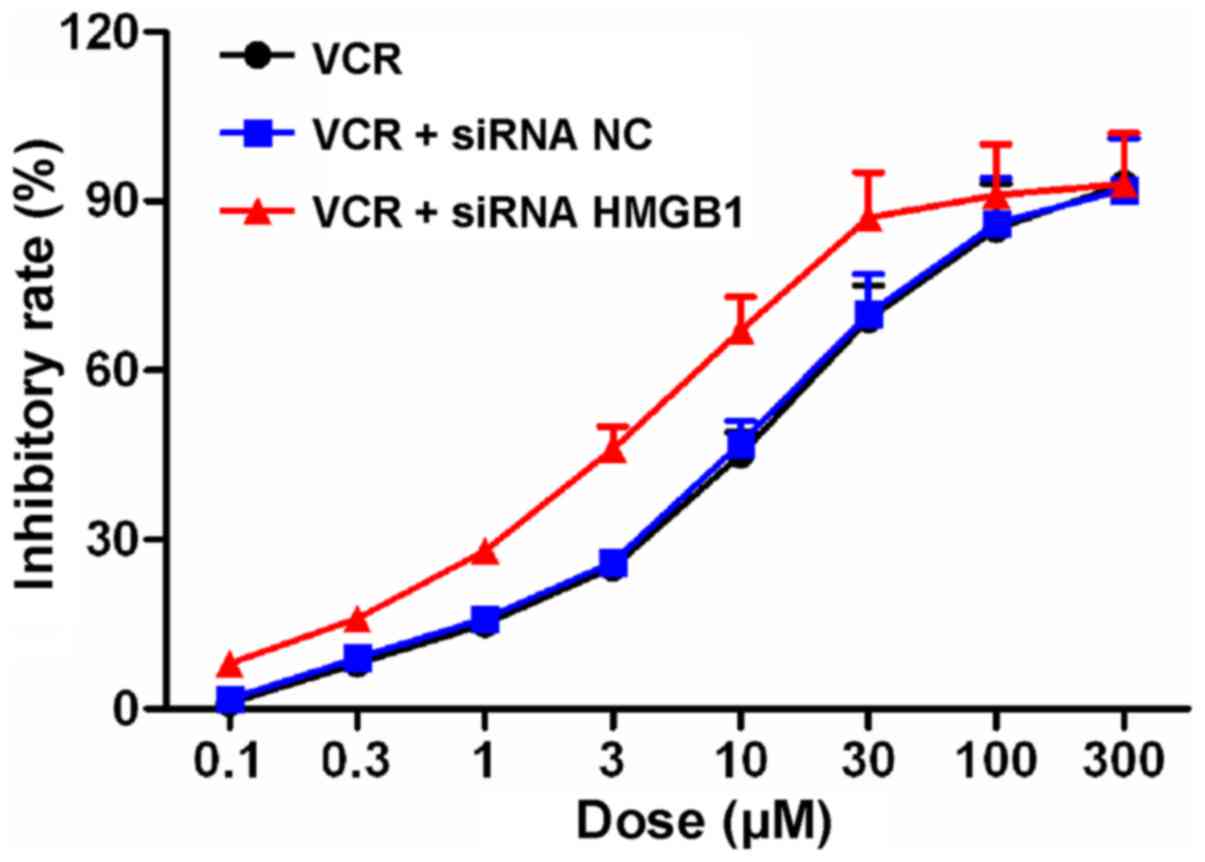
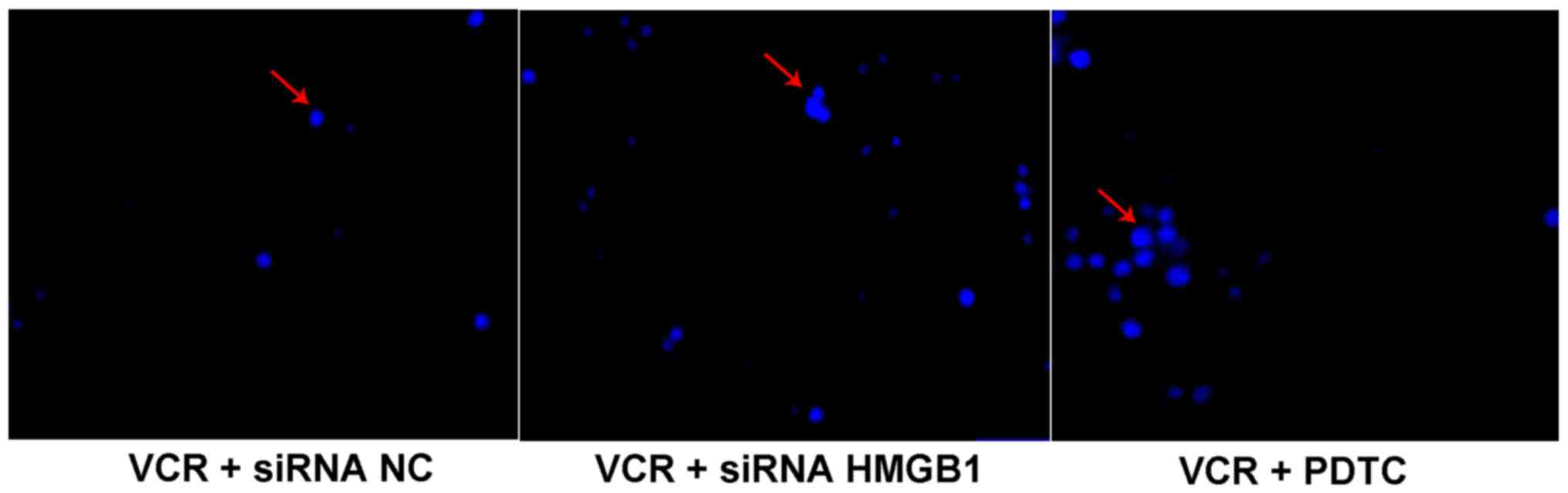
|
1
|
Zheng M, Wu H, Wang J, Jin G, Jiang W and
Sha O: Progress of retinoblastoma pathogenesis. Anat Res.
37:223–228. 2015.In Chinese.
|
|
2
|
Li J and Bo L: Progress in therapy and
research in retinoblastoma. J Clin Ophthalmol. 22:185–188. 2014.In
Chinese.
|
|
3
|
Liu J and Zhu Y: Recent advances in
retinoblastoma treatment. Recent Adv Ophthalmol. 33:91–94. 2013.In
Chinese.
|
|
4
|
Manjandavida FP and Shields CL: The role
of intravitreal chemotherapy for retinoblastoma. Indian J
Ophthalmol. 63:141–145. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huang J, Liu K, Song D, Ding M, Wang J,
Jin Q and Ni J: Krüppel-like factor 4 promotes high-mobility group
box 1-induced chemotherapy resistance in osteosarcoma cells. Cancer
Sci. 107:242–249. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Li X, Wang S, Chen Y, Liu G and Yang X:
miR-22 targets the 3′UTR of HMGB1 and inhibits the HMGB1-associated
autophagy in osteosarcoma cells during chemotherapy. Tumour Biol.
35:6021–6028. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Naumnik W, Nilklińska W, Ossolińska M and
Chyczewska E: Serum levels of HMGB1, survivin, and VEGF in patients
with advanced non-small cell lung cancer during chemotherapy. Folia
Histochem Cytobiol. 47:703–709. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ran X, Yang J, Liu C, Zhou P, Xiao L and
Zhang K: MiR-218 inhibits HMGB1-mediated autophagy in endometrial
carcinoma cells during chemotherapy. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:6617–6626. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Luo Y, Chihara Y, Fujimoto K, Sasahira T,
Kuwada M, Fujiwara R, Fujii K, Ohmori H and Kuniyasu H: High
mobility group box 1 released from necrotic cells enhances regrowth
and metastasis of cancer cells that have survived chemotherapy. Eur
J Cancer. 49:741–751. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hu Y, Yang L and Zhang C: HMGB1-a as
potential target for therapy of hematological malignancies-review.
J Exp Hematol. 24:560–564. 2014.In Chinese.
|
|
11
|
Cao Q, Liu Y and Ling C: Research progress
of the correlation between HMGB1 and tumor. Chin Clin Oncol.
17:282–285. 2012.In Chinese.
|
|
12
|
Stoetzer OJ, Fersching DM, Salat C,
Steinkohl O, Gabka CJ, Hamann U, Braun M, Feller AM, Heinemann V,
Siegele B, et al: Circulating immunogenic cell death biomarkers
HMGB1 and RAGE in breast cancer patients during neoadjuvant
chemotherapy. Tumour Biol. 34:81–90. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Goodwin GH, Sanders C and Johns EW: A new
group of chromatin-associated proteins with a high content of
acidic and basic amino acids. Eur J Biochem. 38:14–19. 1973.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang X, Xiang L, Li H, Chen P, Feng Y,
Zhang J, Yang N, Li F, Wang Y, Zhang Q, et al: The role of HMGB1
signaling pathway in the development and progression of
hepatocellular carcinoma: A review. Int J Mol Sci. 16:22527–22540.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Erlandsson Harris H and Andersson U:
Mini-review: The nuclear protein HMGB1 as a proinflammatory
mediator. Eur J Immunol. 34:1503–1512. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Singh MK, Singh L, Pushker N, Sen S,
Sharma A, Chauhan FA and Kashyap S: Correlation of high mobility
group box-1 protein (HMGB1) with clinicopathological parameters in
primary retinoblastoma. Pathol Oncol Res. 21:1237–1242. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu L, Yang M, Kang R, Wang Z, Zhao Y, Yu
Y, Xie M, Yin X, Livesey KM, Lotze MT, et al: HMGB1-induced
autophagy promotes chemotherapy resistance in leukemia cells.
Leukemia. 25:23–31. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang R, Li Y, Wang Z, Chen L, Dong X and
Nie X: Interference with HMGB1 increases the sensitivity to
chemotherapy drugs by inhibiting HMGB1-mediated cell autophagy and
inducing cell apoptosis. Tumour Biol. 36:8585–8592. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Prajoko YW and Aryandono T: Expression of
nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) as a predictor of poor pathologic
response to chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced breast
cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:595–598. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Endo F, Nishizuka SS, Kume K, Ishida K,
Katagiri H, Ishida K, Sato K, Iwaya T, Koeda K and Wakabayashi G: A
compensatory role of NF-κB to p53 in response to 5-FU-based
chemotherapy for gastric cancer cell lines. PLoS One. 9:e901552014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wu Y, Fang W and Li Y: Mechanisms and
reversing drugs of cancer multidrug resistance. Pharma Clin Res.
24:43–47. 2016.In Chinese.
|
|
22
|
Pan G and Yan L: Research advancement on
mechanism of tumor multidrug resistance. Med Recapitulate.
15:1162–1164. 2009.In Chinese.
|
|
23
|
Liu K, Huang J, Xie M, Yu Y, Zhu S, Kang
R, Cao L, Tang D and Duan X: MIR34A regulates autophagy and
apoptosis by targeting HMGB1 in the retinoblastoma cell. Autophagy.
10:442–452. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang Y and Zhang J and Zhang J:
Progresses on autophagy and drug resistance of tumor. Life Sci Res.
19:62–67. 2015.In Chinese.
|