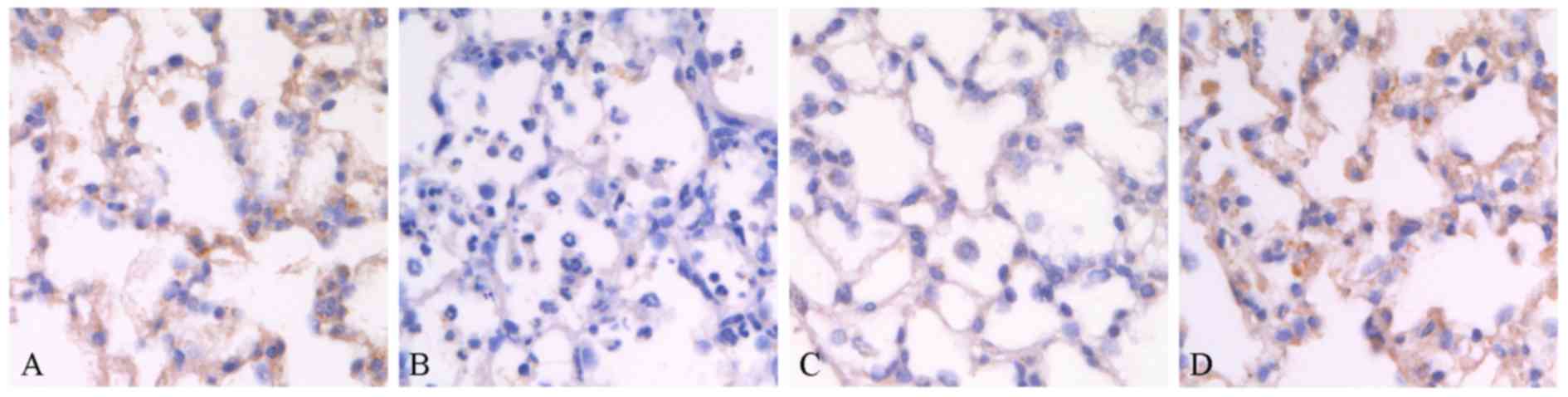
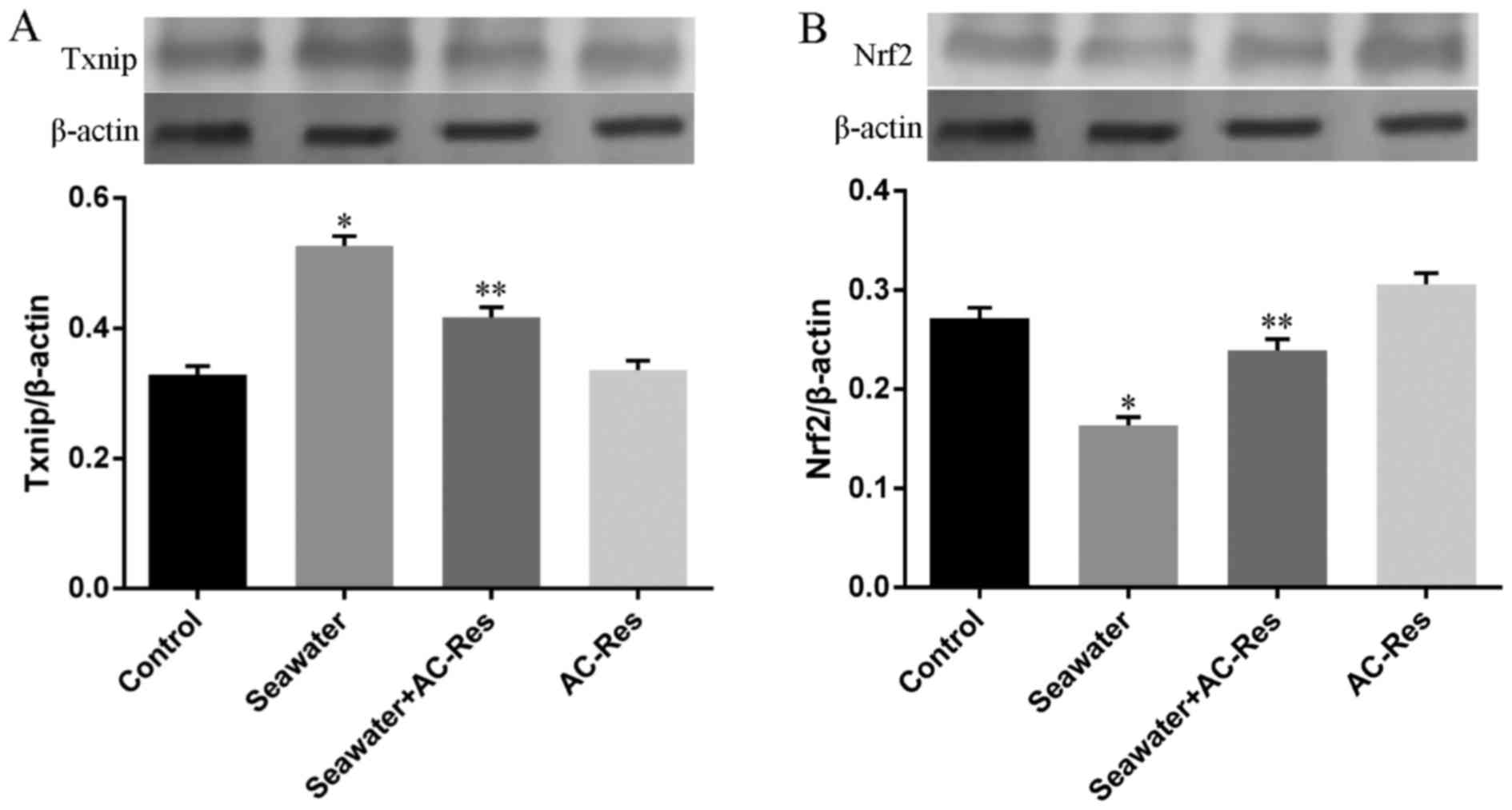
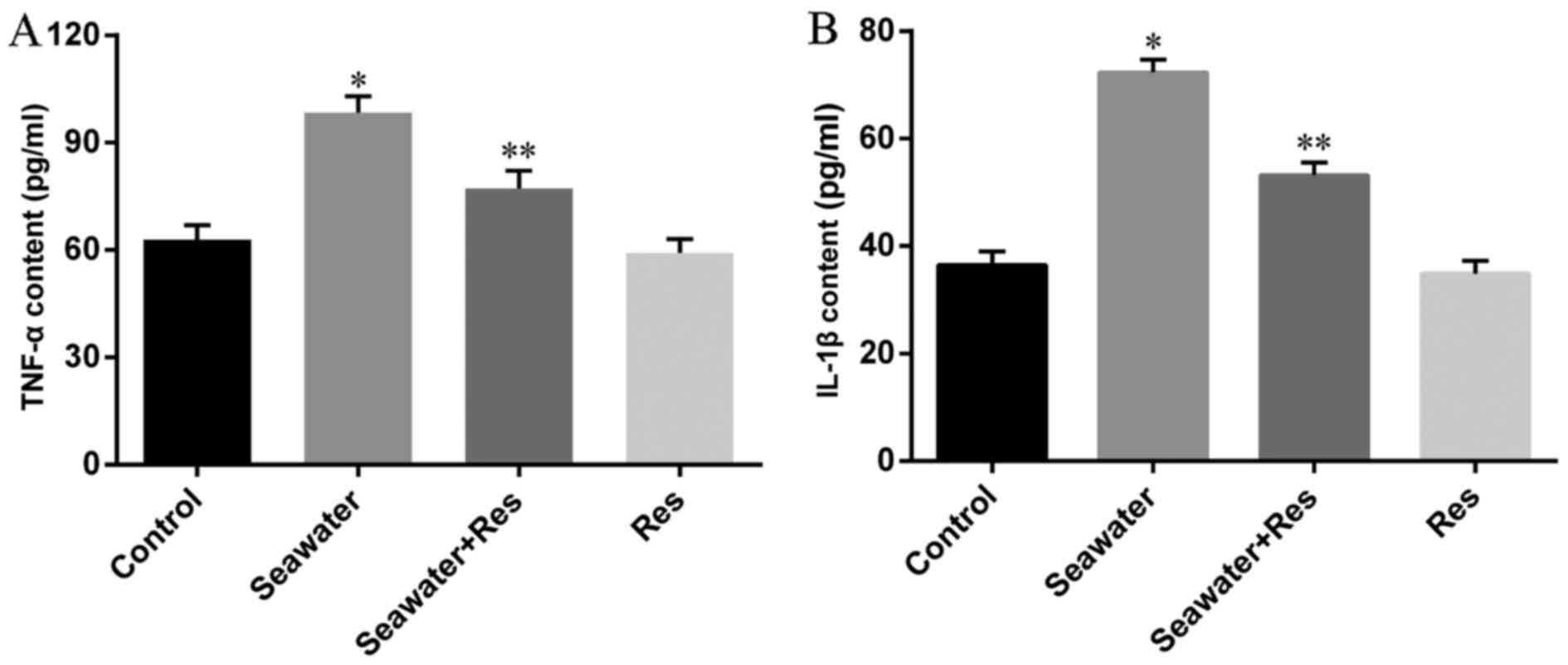
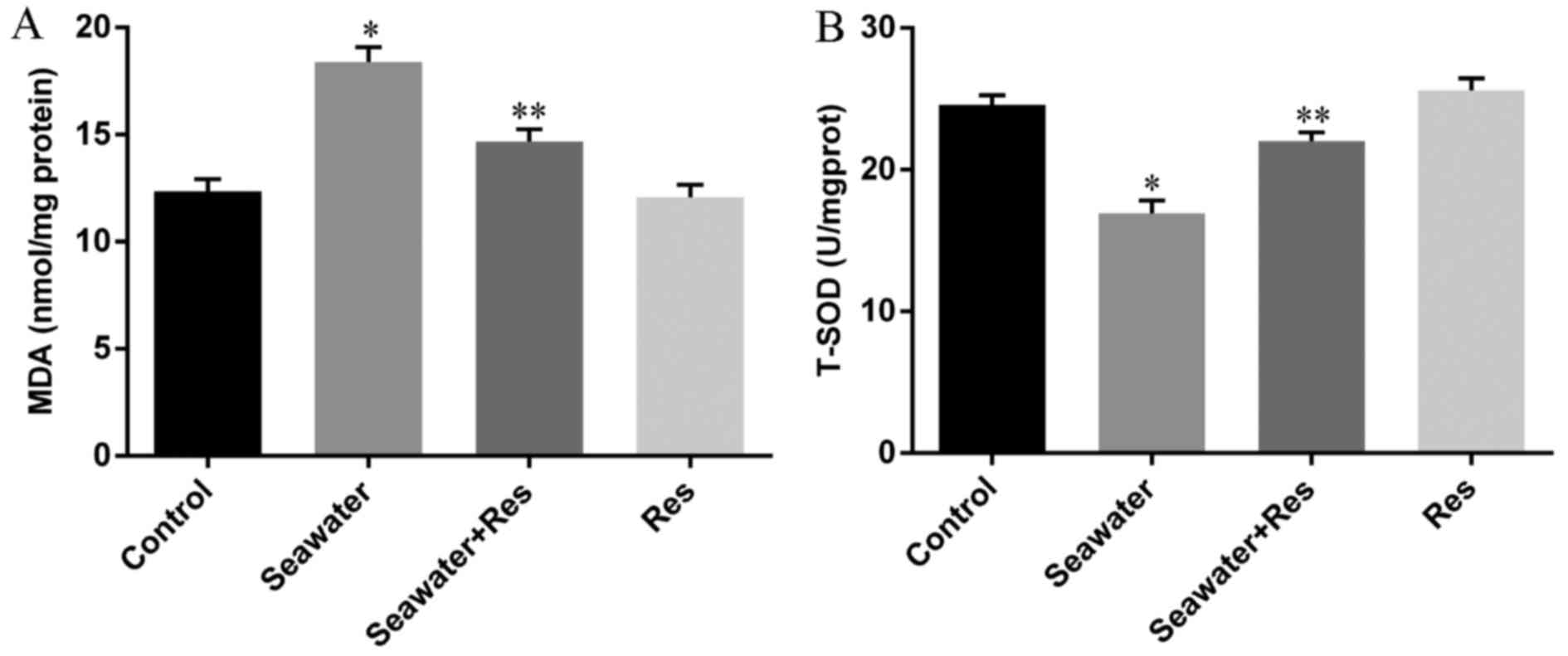
|
1
|
Koh Y: Update in acute respiratory
distress syndrome. J Intensive Care. 2:22014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Organisation, World Health: Disease and
injury regional mortality estimates for 2000-2011. Global summary
estimates. 2015-1-20. 2013.
|
|
3
|
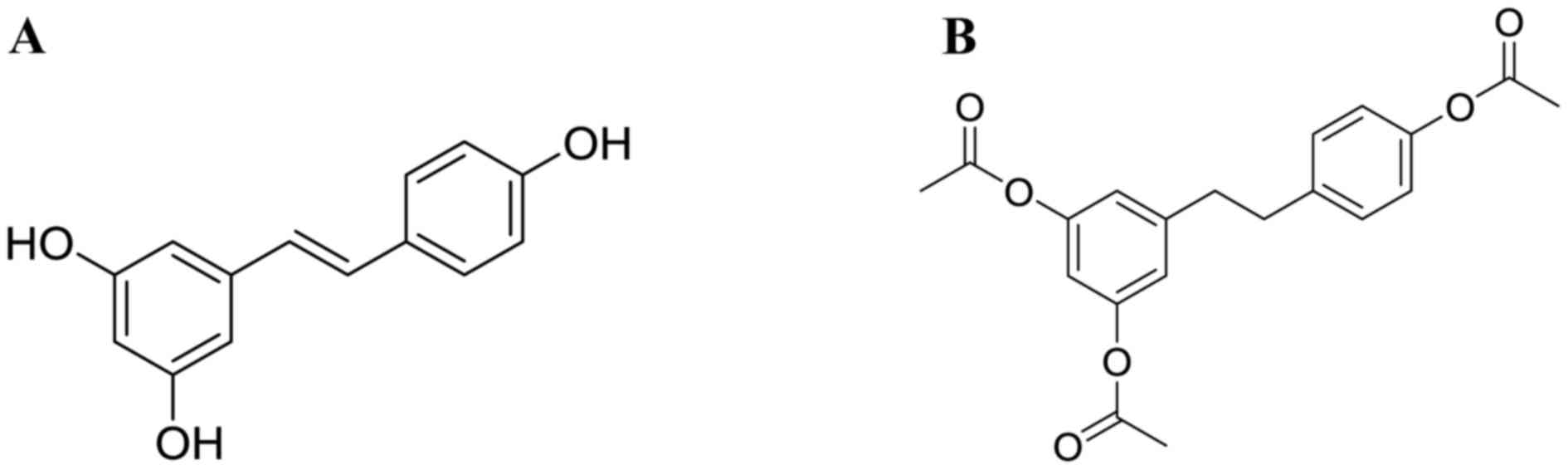
Simcock AD: Treatment of near drowning - a
review of 130 cases. Anaesthesia. 41:643–648. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gregorakos L, Markou N, Psalida V,
Kanakaki M, Alexopoulou A, Sotiriou E, Damianos A and Myrianthefs
P: Near-drowning: Clinical course of lung injury in adults. Lung.
187:93–97. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang Y, Zhang B, Xu DQ, Li WP, Xu M, Li
JH, Xie XY, Fan QX, Liu W, Mu DG, et al: Tanshinone IIA attenuates
seawater aspiration-induced lung injury by inhibiting macrophage
migration inhibitory factor. Biol Pharm Bull. 34:1052–1057. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang T, Zhang A, Honeggar M, Kohan DE,
Mizel D, Sanders K, Hoidal JR, Briggs JP and Schnermann JB:
Hypertonic induction of COX-2 in collecting duct cells by reactive
oxygen species of mitochondrial origin. J Biol Chem.
280:34966–34973. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yu HL, Zhao TF, Wu H, Pan YZ, Zhang Q,
Wang KL, Zhang CC and Jin YP: Pinellia ternata lectin exerts a
pro-inflammatory effect on macrophages by inducing the release of
pro-inflammatory cytokines, the activation of the nuclear factor-κB
signaling pathway and the overproduction of reactive oxygen
species. Int J Mol Med. 36:1127–1135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lortz S, Gurgul-Convey E, Lenzen S and
Tiedge M: Importance of mitochondrial superoxide dismutase
expression in insulin-producing cells for the toxicity of reactive
oxygen species and proinflammatory cytokines. Diabetologia.
48:1541–1548. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu Y, Qiu J, Wang Z, You W, Wu L, Ji C
and Chen G: Dimethylfumarate alleviates early brain injury and
secondary cognitive deficits after experimental subarachnoid
hemorrhage via activation of Keap1-Nrf2-ARE system. J Neurosurg.
123:915–923. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Niso-Santano M, González-Polo RA,
Bravo-San Pedro JM, Gómez-Sánchez R, Lastres-Becker I, Ortiz-Ortiz
MA, Soler G, Morán JM, Cuadrado A and Fuentes JM; Centro de
Investigación Biomédica en Red sobre Enfermedades
Neurodegenerativas (CIBERNED): Activation of apoptosis
signal-regulating kinase 1 is a key factor in paraquat-induced cell
death: Modulation by the Nrf2/Trx axis. Free Radic Biol Med.
48:1370–1381. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ogata FT, Batista WL, Sartori A, Gesteira
TF, Masutani H, Arai RJ, Yodoi J, Stern A and Monteiro HP:
Nitrosative/oxidative stress conditions regulate
thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) expression and
thioredoxin-1 (TRX-1) nuclear localization. PLoS One. 8:e845882013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Zhang C, Li Q, Kang L, Lei X, Zhai X, Zhao
S, Zhang C and Dong W: Resveratrol inhibits hyperxia-induced cell
apoptosis through up-regulating SIRT1 expression in HPAECs. Xi Bao
Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 31:590–595. 2015.In Chinese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kuno A, Tanno M and Horio Y: The effects
of resveratrol and SIRT1 activation on dystrophic cardiomyopathy.
Ann NY Acad Sci. 1348:46–54. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tvrda E, Kovacik A, Tusimova E, Massanyi P
and Lukac N: Resveratrol offers protection to oxidative stress
induced by ferrous ascorbate in bovine spermatozoa. J Environ Sci
Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 50:1440–1451. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Walle T, Hsieh F, DeLegge MH, Oatis JE Jr
and Walle UK: High absorption but very low bioavailability of oral
resveratrol in humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 32:1377–1382. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liang L, Liu X, Wang Q, Cheng S, Zhang S
and Zhang M: Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and excretion
study of resveratrol and its prodrug 3,5,4′-tri-O-acetylresveratrol
in rats. Phytomedicine. 20:558–563. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ma L, Zhao Y, Li B, Wang Q, Liu X, Chen X,
Nan Y, Liang L, Chang R, Liang L, et al:
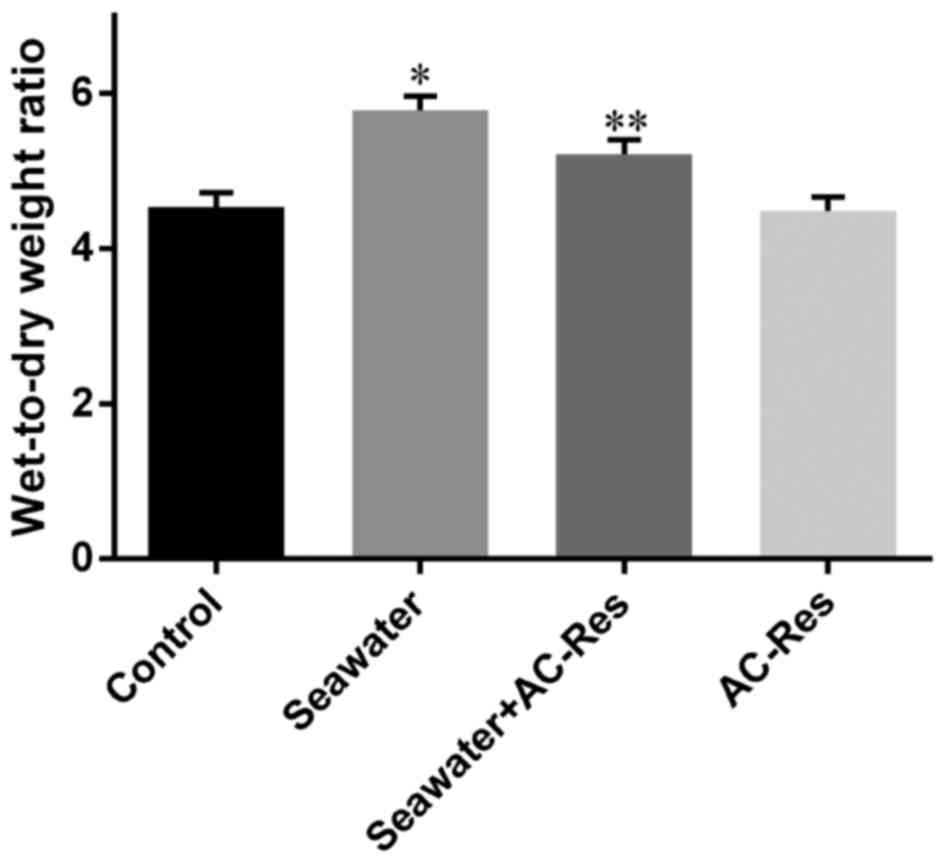
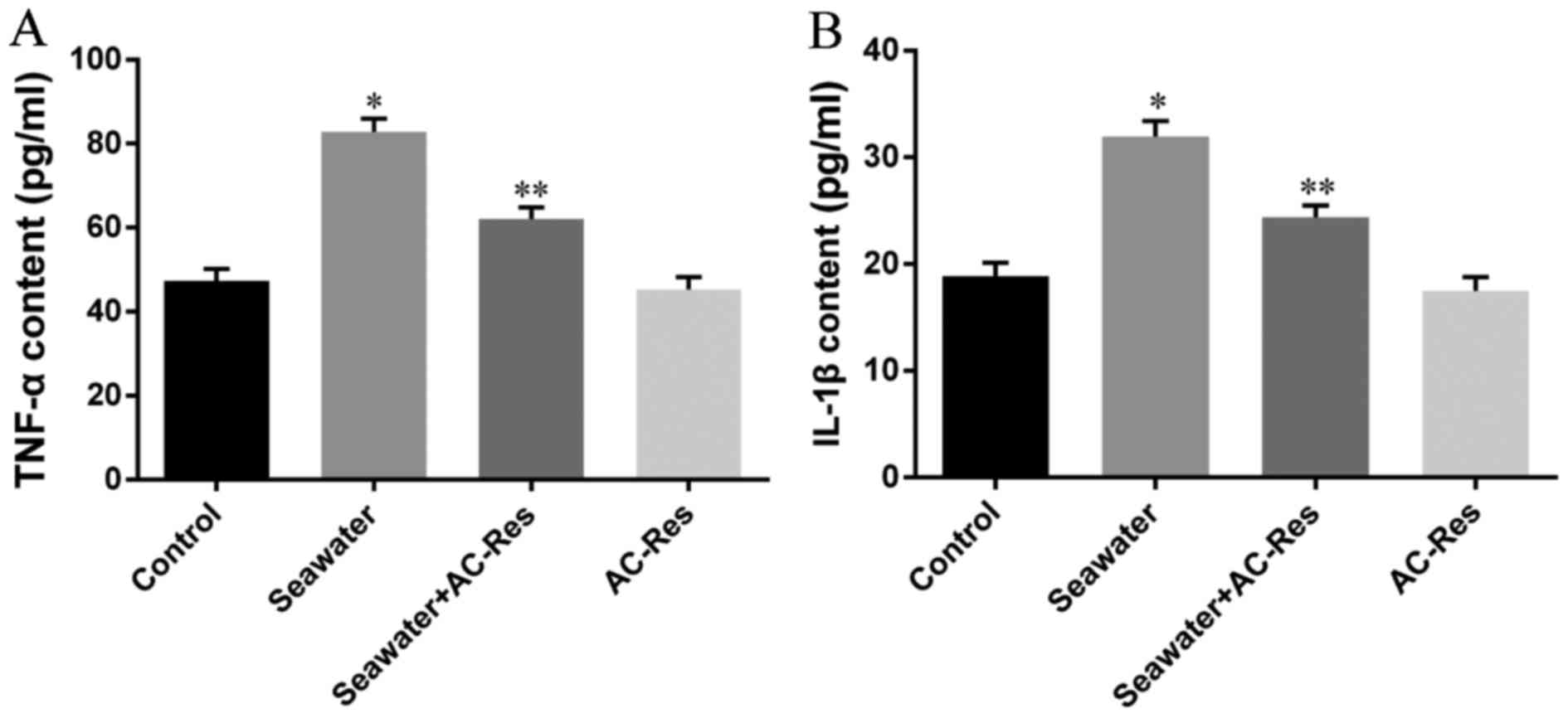
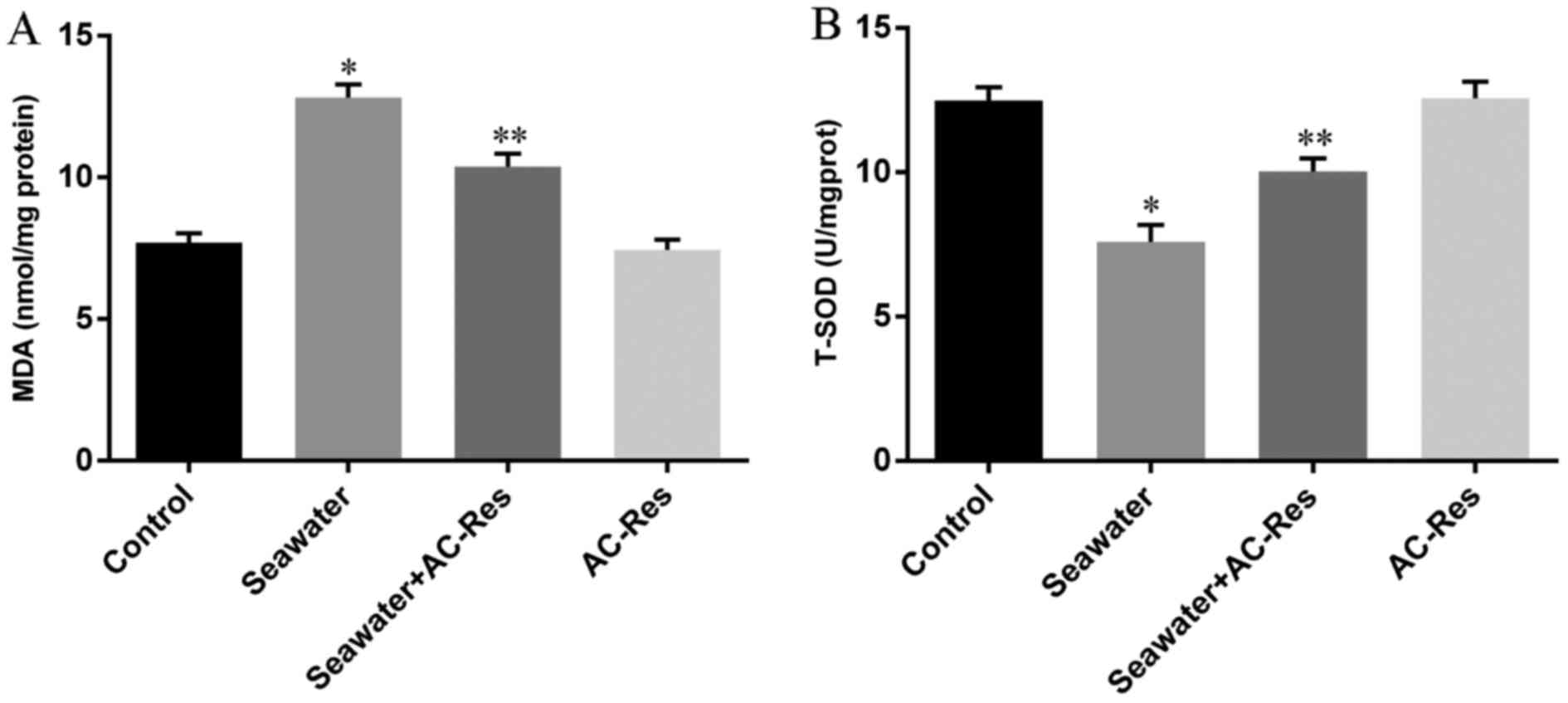
3,5,4′-Tri-O-acetylresveratrol attenuates seawater
aspiration-induced lung injury by inhibiting activation of nuclear
factor-kappa B and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Respir Physiol
Neurobiol. 185:608–614. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ibsen LM and Koch T: Submersion and
asphyxial injury. Crit Care Med. 30(Suppl 11): S402–S408. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Janz DR and Ware LB: Biomarkers of
ALI/ARDS: Pathogenesis, discovery, and relevance to clinical
trials. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 34:537–548. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ware LB: Autopsy in ARDS: Insights into
natural history. Lancet Respir Med. 1:352–354. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Tang PC, NG YF, Ho S, Gyda M and Chan SW:
Resveratrol and cardiovascular health - promising therapeutic or
hopeless illusion? Pharmacol Res. 90:88–115. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fu DG: Regulation of redox signalling and
autophagy during cardiovascular diseases-role of resveratrol. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 19:1530–1536. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ma L, Li W, Wang R, Nan Y, Wang Q, Liu W
and Jin F: Resveratrol enhanced anticancer effects of cisplatin on
non-small cell lung cancer cell lines by inducing mitochondrial
dysfunction and cell apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 47:1460–1468. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Empl MT, Albers M, Wang S and Steinberg P:
The resveratrol tetramer r-viniferin Induces a cell cycle arrest
followed by apoptosis in the prostate cancer cell line LNCaP.
Phytother Res. 29:1640–1645. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kjær TN, Thorsen K, Jessen N, Stenderup K
and Pedersen SB: Resveratrol ameliorates imiquimod-induced
psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice. PLoS One.
10:e01265992015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kimbrough CW, Lakshmanan J, Matheson PJ,
Woeste M, Gentile A, Benns MV, Zhang B, Smith JW and Harbrecht BG:
Resveratrol decreases nitric oxide production by hepatocytes during
inflammation. Surgery. 158:1095–1101. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guo S, Yao Q, Ke Z, Chen H, Wu J and Liu
C: Resveratrol attenuates high glucose-induced oxidative stress and
cardiomyocyte apoptosis through AMPK. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
412:85–94. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ates O, Cayli SR, Yucel N, Altinoz E,
Kocak A, Durak MA, Turkoz Y and Yologlu S: Central nervous system
protection by resveratrol in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
J Clin Neurosci. 14:256–260. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Venturini CD, Merlo S, Souto AA, Fernandes
MC, Gomez R and Rhoden CR: Resveratrol and red wine function as
antioxidants in the nervous system without cellular proliferative
effects during experimental diabetes. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
3:434–441. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chen X, He H, Wang G, Yang B, Ren W, Ma L
and Yu Q: Stereospecific determination of cis- and
trans-resveratrol in rat plasma by HPLC: Application to
pharmacokinetic studies. Biomed Chromatogr. 21:257–265. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Koide K, Osman S, garner AL, Song F, Dixon
T, Greenberger JS and Epperly MW: The use of
3,5,4′-tri-O-acetylresveratrol as a potential pro-drug for
resveratrol protects mice from γ-irradiation-induced death. ACS Med
Chem Lett. 2:270–274. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Forsgren P, Modig J, Gerdin B, Axelsson B
and Dahlbäck M: Intrapulmonary deposition of aerosolized Evans blue
dye and liposomes in an experimental porcine model of early ARDS.
Ups J Med Sci. 95:117–136. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu H, Zhang D, Zhao B and Zhao J:
Superoxide anion, the main species of ROS in the development of
ARDS induced by oleic acid. Free Radic Res. 38:1281–1287. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kovac S, Angelova PR, Holmström KM, Zhang
Y, Dinkova-Kostova AT and Abramov AY: Nrf2 regulates ROS production
by mitochondria and NADPH oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1850:794–801. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Yu M, Geiger B, Deeb N and Rothschild MF:
Investigation of TXNIP (thioredoxin-interacting protein) and TRX
(thioredoxin) genes for growth-related traits in pigs. Mamm genome.
18:197–209. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|