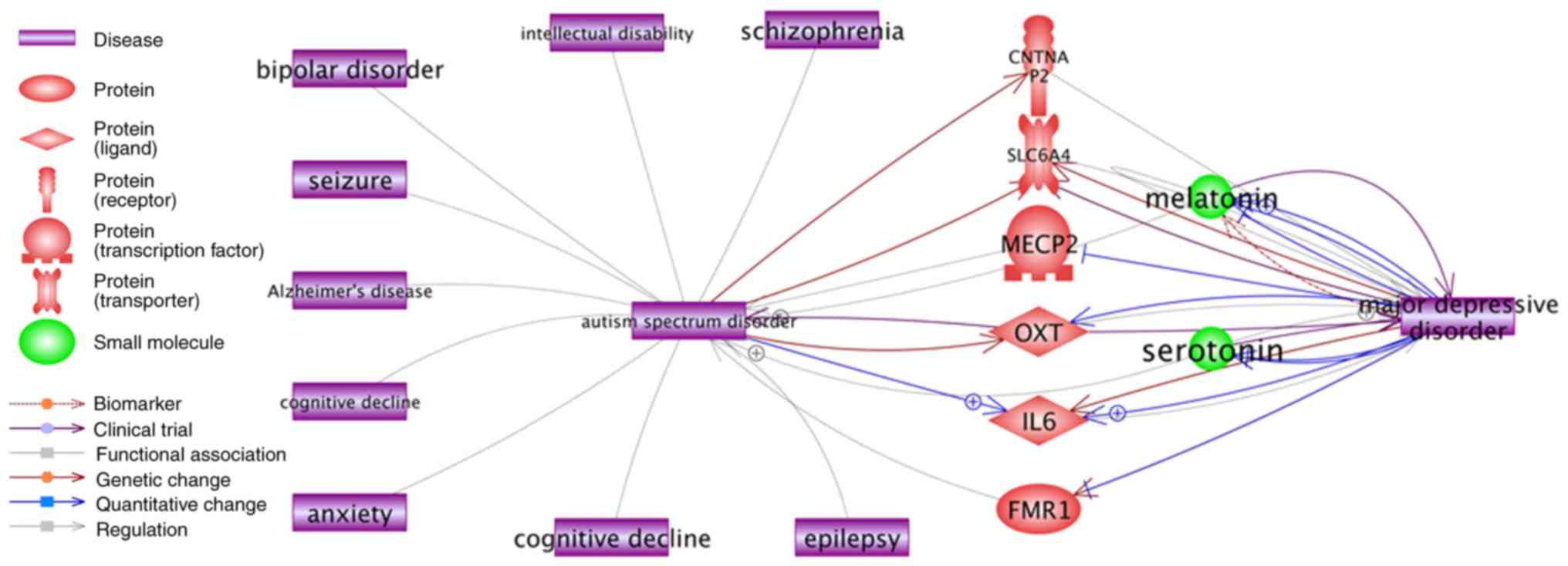
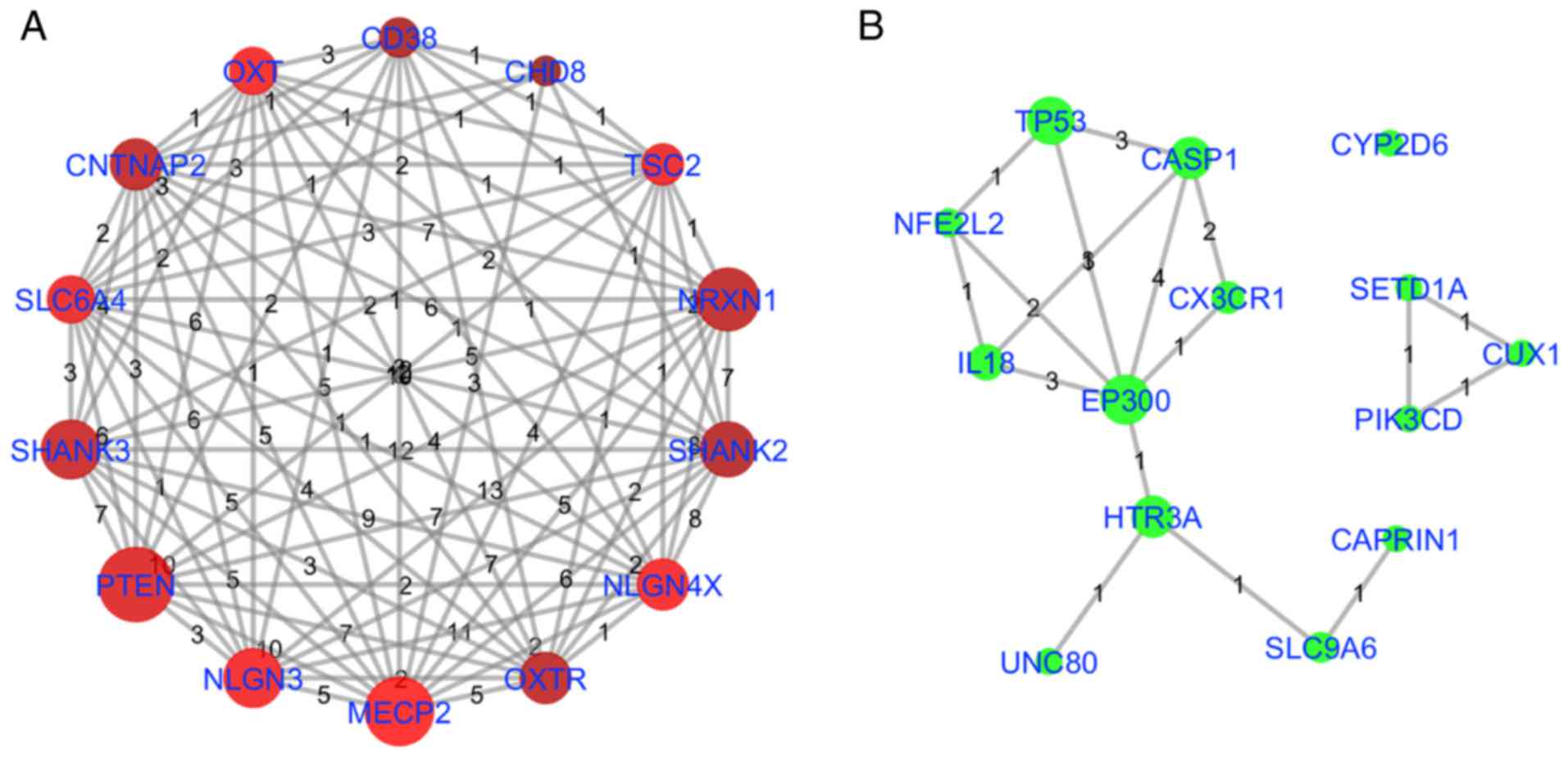
|
1
|
Chaste P and Leboyer M: Autism risk
factors: Genes, environment, and gene-environment interactions.
Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 14:281–292. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rutter M: Genetic studies of autism: From
the 1970s into the millennium. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 28:3–14.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Aronson M, Hagberg B and Gillberg C:
Attention deficits and autistic spectrum problems in children
exposed to alcohol during gestation: A follow-up study. Dev Med
Child Neurol. 39:583–587. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kolevzon A, Gross R and Reichenberg A:
Prenatal and perinatal risk factors for autism: A review and
integration of findings. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 161:326–333.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Minshew NJ: Brief report: Brain mechanisms
in autism: Functional and structural abnormalities. J Autism Dev
Disord. 26:205–209. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tager-Flusberg H: The origins of social
impairments in autism spectrum disorder: Studies of infants at
risk. Neural Netw. 23:1072–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Businaro R, Corsi M, Azzara G, Di Raimo T,
Laviola G, Romano E, Ricci L, Maccarrone M, Aronica E, Fuso A, et
al: Interleukin-18 modulation in autism spectrum disorders. J
Neuroinflammation. 13:22016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hu VW: Subphenotype-dependent disease
markers for diagnosis and personalized treatment of autism spectrum
disorders. Dis Markers. 33:277–288. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Parker-Athill EC and Tan J: Maternal
immune activation and autism spectrum disorder: Interleukin-6
signaling as a key mechanistic pathway. Neurosignals. 18:113–128.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Andari E, Duhamel JR, Zalla T, Herbrecht
E, Leboyer M and Sirigu A: Promoting social behavior with oxytocin
in high-functioning autism spectrum disorders. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 107:4389–4394. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kolevzon A, Bush L, Wang AT, Halpern D,
Frank Y, Grodberg D, Rapaport R, Tavassoli T, Chaplin W, Soorya L,
et al: A pilot controlled trial of insulin-like growth factor-1 in
children with Phelan-McDermid syndrome. Mol Autism. 5:542014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
LoParo D and Waldman ID: The oxytocin
receptor gene (OXTR) is associated with autism spectrum disorder: A
meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry. 20:640–646. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhou Y, Kaiser T, Monteiro P, Zhang X, Van
der Goes MS, Wang D, Barak B, Zeng M, Li C, Lu C, et al: Mice with
Shank3 mutations associated with ASD and Schizophrenia display both
shared and distinct defects. Neuron. 89:147–162. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Cotney J, Muhle RA, Sanders SJ, Liu L,
Willsey AJ, Niu W, Liu W, Klei L, Lei J, Yin J, et al: The
autism-associated chromatin modifier CHD8 regulates other autism
risk genes during human neurodevelopment. Nat Commun. 6:64042015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
King LB, Walum H, Inoue K, Eyrich NW and
Young LJ: Variation in the oxytocin receptor gene predicts brain
region-specific expression and social attachment. Biol Psychiatry.
80:160–169. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Theoharides TC, Stewart JM, Panagiotidou S
and Melamed I: Mast cells, brain inflammation and autism. Eur J
Pharmacol. 778:96–102. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Higashida H, Yokoyama S, Huang JJ, Liu L,
Ma WJ, Akther S, Higashida C, Kikuchi M, Minabe Y and Munesue T:
Social memory, amnesia, and autism: Brain oxytocin secretion is
regulated by NAD+ metabolites and single nucleotide
polymorphisms of CD38. Neurochem Int. 61:828–838. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jiang YH and Ehlers MD: Modeling autism by
SHANK gene mutations in mice. Neuron. 78:8–27. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Clipperton-Allen AE and Page DT: Decreased
aggression and increased repetitive behavior in Pten
haploinsufficient mice. Genes Brain Behav. 14:145–157. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nikitin A, Egorov S, Daraselia N and Mazo
I: Pathway studio - the analysis and navigation of molecular
networks. Bioinformatics. 19:2155–2157. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rindflesch TC, Tanabe L, Weinstein JN and
Hunter L: EDGAR: Extraction of drugs, genes and relations from the
biomedical literature. Pac Symp Biocomput. 2000:517–528. 2000.
|
|
22
|
Sivachenko AY, Yuryev A, Daraselia N and
Mazo I: Molecular networks in microarray analysis. J Bioinform
Comput Biol. 5:429–456. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pyatnitskiy M, Mazo I, Shkrob M, Schwartz
E and Kotelnikova E: Clustering gene expression regulators: New
approach to disease subtyping. PLoS One. 9:e849552014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vanwong N, Ngamsamut N, Medhasi S,
Puangpetch A, Chamnanphon M, Tan-Kam T, Hongkaew Y, Limsila P and
Sukasem C: Impact of CYP2D6 polymorphism on steady-state plasma
levels of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone in thai children and
adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. J Child Adolesc
Psychopharmacol. 27:185–191. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Cheadle C, Cao H, Kalinin A and Hodgkinson
J: Advanced literature analysis in a Big Data world. Ann NY Acad
Sci. 1387:25–33. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sanders SJ, Murtha MT, Gupta AR, Murdoch
JD, Raubeson MJ, Willsey AJ, Ercan-Sencicek AG, DiLullo NM,
Parikshak NN, Stein JL, et al: De novo mutations revealed by
whole-exome sequencing are strongly associated with autism. Nature.
485:237–241. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Katayama Y, Nishiyama M, Shoji H, Ohkawa
Y, Kawamura A, Sato T, Suyama M, Takumi T, Miyakawa T and Nakayama
KI: CHD8 haploinsufficiency results in autistic-like phenotypes in
mice. Nature. 537:675–679. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Supek F, Bošnjak M, Škunca N and Šmuc T:
REVIGO summarizes and visualizes long lists of gene ontology terms.
PLoS One. 6:e218002011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Alabdali A, Al-Ayadhi L and El-Ansary A:
Association of social and cognitive impairment and biomarkers in
autism spectrum disorders. J Neuroinflammation. 11:42014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Goldstein G, Minshew NJ, Allen DN and
Seaton BE: High-functioning autism and schizophrenia: A comparison
of an early and late onset neurodevelopmental disorder. Arch Clin
Neuropsychol. 17:461–475. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Robinson SJ: Childhood epilepsy and autism
spectrum disorders: Psychiatric problems, phenotypic expression,
and anticonvulsants. Neuropsychol Rev. 22:271–279. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|