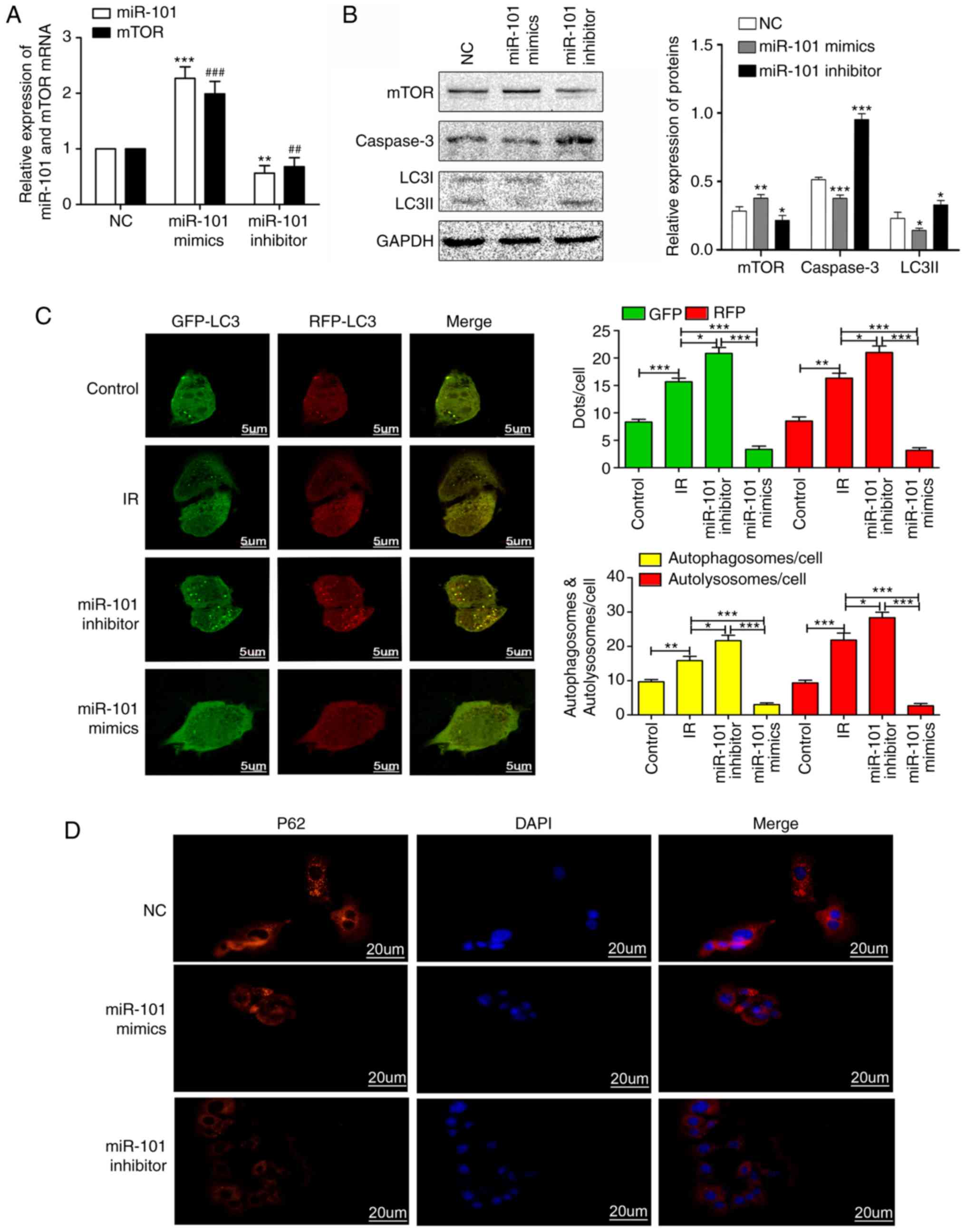
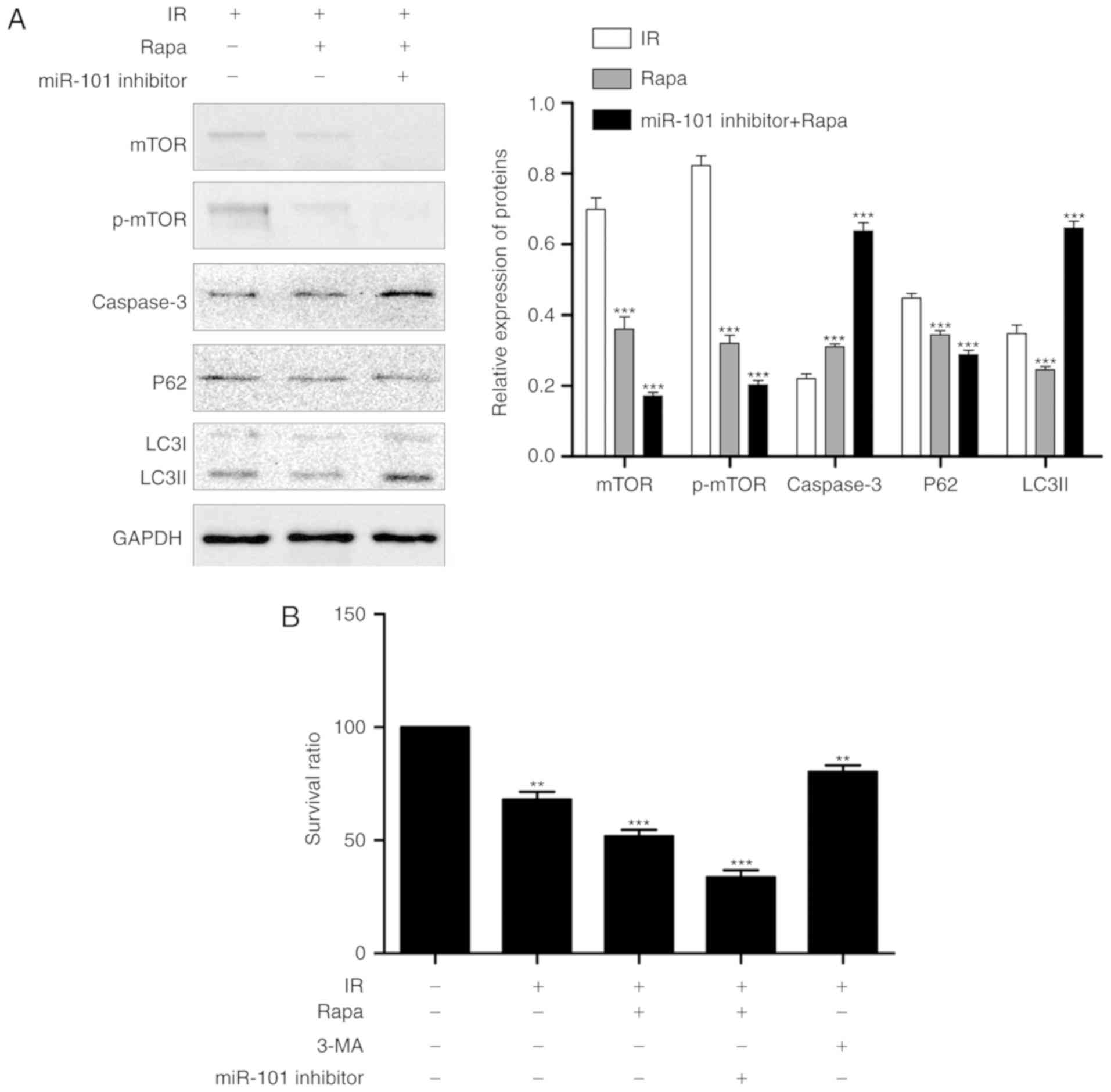
|
1
|
Cursio R, Colosetti P and Gugenheim J:
Autophagy and liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biomed Res Int.
2015:4175902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rautou PE, Mansouri A, Lebrec D, Durand F,
Valla D and Moreau R: Autophagy in liver diseases. J Hepatol.
53:1123–1134. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sun P, Zhang P, Wang PX, Zhu LH, Du Y,
Tian S, Zhu X and Li H: Mindin deficiency protects the liver
against ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Hepatol. 63:1198–1211. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Clavien PA: How far can we go with
marginal donors? J Hepatol. 45:483–484. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Halazun KJ, Quillin RC, Rosenblatt R,
Bongu A, Griesemer AD, Kato T, Smith C, Michelassi F, Guarrera JV,
Samstein B, et al: Expanding the margins: High volume utilization
of marginal liver grafts among ≥2000 liver transplants at a single
institution. Ann Surg. 266:441–449. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lentsch AB, Kato A, Yoshidome H, McMasters
KM and Edwards MJ: Inflammatory mechanisms and therapeutic
strategies for warm hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Hepatology. 32:169–173. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Qu Y, Zhang Q, Cai X, Li F, Ma Z, Xu M and
Lu L: Exosomes derived from miR-181-5p-modified adipose-derived
mesenchymal stem cells prevent liver fibrosis via autophagy
activation. J Cell Mol Med. 21:2491–2502. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tang B, Bao N, He G and Wang J: Long
noncoding RNA HOTAIR regulates autophagy via the miR-20b-5p/ATG7
axis in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Gene. 686:56–62. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Chen J, Yu Y, Li S, Liu Y, Zhou S, Cao S,
Yin J and Li G: MicroRNA-30a ameliorates hepatic fibrosis by
inhibiting beclin1-mediated autophagy. J Cell Mol Med.
21:3679–3692. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lim LP, Glasner ME, Yekta S, Burge CB and
Bartel DP: Vertebrate microRNA genes. Science. 299:15402003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Weiss JB, Eisenhardt SU, Stark GB, Bode C,
Moser M and Grundmann S: MicroRNAs in ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2:237–247. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Valinezhad Orang A, Safaralizadeh R and
Kazemzadeh-Bavili M: Mechanisms of miRNA-mediated gene regulation
from common downregulation to mRNA-specific upregulation. Int J
Genomics. 2014:9706072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang Y and Liang C: MicroRNAs: An emerging
player in autophagy. ScienceOpen Res. 2015:14293/S2199–1006.
2015.
|
|
14
|
Bartel DP: Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell.
173:20–51. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Frankel LB, Wen J, Lees M, Høyer-Hansen M,
Farkas T, Krogh A, Jäättelä M and Lund AH: microRNA-101 is a potent
inhibitor of autophagy. EMBO J. 30. pp. 4628–4641. 2011, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Valera E, Spencer B, Mott J, Trejo M,
Adame A, Mante M, Rockenstein E, Troncoso JC, Beach TG, Masliah E
and Desplats P: MicroRNA-101 modulates autophagy and
oligodendroglial alpha-synuclein accumulation in multiple system
atrophy. Front Mol Neurosci. 10:3292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu Y, An Y, Wang Y, Zhang C, Zhang H,
Huang C, Jiang H, Wang X and Li X: miR-101 inhibits autophagy and
enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Oncol Rep. 29:2019–2024. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
National Research Council (US) Institute
for Laboratory Animal Research: Guide for the Care and Use of
Laboratory Animals. National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC:
1996
|
|
19
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. National
Academies Press (US); Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
20
|
Ji H, Shen X, Gao F, Ke B, Freitas MC,
Uchida Y, Busuttil RW, Zhai Y and Kupiec-Weglinski JW: Programmed
death-1/B7-H1 negative costimulation protects mouse liver against
ischemia and reperfusion injury. Hepatology. 52:1380–1389. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Coleman MC, Olivier AK, Jacobus JA,
Mapuskar KA, Mao G, Martin SM, Riley DP, Gius D and Spitz DR:
Superoxide mediates acute liver injury in irradiated mice lacking
sirtuin 3. Antioxid Redox Signal. 20:1423–1435. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Suzuki S, Toledo-Pereyra LH, Rodriguez FJ
and Cejalvo D: Neutrophil infiltration as an important factor in
liver ischemia and reperfusion injury. modulating effects of FK506
and cyclosporine. Transplantation. 55:1265–1272. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Vergne I, Roberts E, Elmaoued RA, Tosch V,
Delgado MA, Proikas-Cezanne T, Laporte J and Deretic V: Control of
autophagy initiation by phosphoinositide 3-phosphatase jumpy. EMBO
J. 28:2244–2258. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhou C, Zhong W, Zhou J, Sheng F, Fang Z,
Wei Y, Chen Y, Deng X, Xia B and Lin J: Monitoring autophagic flux
by an improved tandem fluorescent-tagged LC3 (mTagRFP-mWasabi-LC3)
reveals that high-dose rapamycin impairs autophagic flux in cancer
cells. Autophagy. 8:1215–1226. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu C, Yu C and Li Y: Current studies on
therapeutic approaches for ischemia/reperfusion injury in steatotic
livers. Hepatol Res. 38:851–859. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li CX, Ng KT, Shao Y, Liu XB, Ling CC, Ma
YY, Geng W, Qi X, Cheng Q, Chung SK, et al: The inhibition of
aldose reductase attenuates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury
through reducing inflammatory response. Ann Surg. 260:317–328.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ohsumi Y: Historical landmarks of
autophagy research. Cell Res. 24:9–23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Ohsumi Y: Molecular dissection of
autophagy: Two ubiquitin-like systems. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
2:211–216. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Weidberg H, Shpilka T, Shvets E, Abada A,
Shimron F and Elazar Z: LC3 and GATE-16 N termini mediate membrane
fusion processes required for autophagosome biogenesis. Dev Cell.
20:444–454. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li S, Zhang J, Wang Z, Wang T, Yu Y, He J,
Zhang H, Yang T and Shen Z: MicroRNA-17 regulates autophagy to
promote hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury via suppression of
signal transductions and activation of transcription-3 expression.
Liver Transpl. 22:1697–1709. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schneider JL and Cuervo AM: Liver
autophagy: Much more than just taking out the trash. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 11:187–200. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Shin CS and Huh WK: Bidirectional
regulation between TORC1 and autophagy in saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Autophagy. 7:854–862. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu A, Huang L, Guo E, Li R, Yang J, Li A,
Yang Y, Liu S, Hu J, Jiang X, et al: Baicalein pretreatment reduces
liver ischemia/reperfusion injury via induction of autophagy in
rats. Sci Rep. 6:250422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tan L, Jiang W, Lu A, Cai H and Kong L:
miR-155 aggravates liver ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing
SOCS1 in mice. Transplant Proc. 50:3831–3839. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xiao Q, Ye QF, Wang W, Fu BQ, Xia ZP, Liu
ZZ, Zhang XJ and Wang YF: Mild hypothermia pretreatment protects
hepatocytes against ischemia reperfusion injury via down-regulating
miR-122 and IGF-1R/AKT pathway. Cryobiology. 75:100–105. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yang W, Chen J, Meng Y, Chen Z and Yang J:
Novel targets for treating ischemia-reperfusion injury in the
liver. Int J Mol Sci. 19:E13022018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li SP, He JD, Wang Z, Yu Y, Fu SY, Zhang
HM, Zhang JJ and Shen ZY: miR-30b inhibits autophagy to alleviate
hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury via decreasing the Atg12-Atg5
conjugate. World J Gastroenterol. 22:4501–4514. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim HJ, Joe Y, Yu JK, Chen Y, Jeong SO,
Mani N, Cho GJ, Pae HO, Ryter SW and Chung HT: Carbon monoxide
protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by modulating
the miR-34a/SIRT1 pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1852:1550–1559.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang G, Yao J, Li Z, Zu G, Feng D, Shan W,
Li Y, Hu Y, Zhao Y and Tian X: miR-34a-5p inhibition alleviates
intestinal ischemia/reperfusion-induced reactive oxygen species
accumulation and apoptosis via activation of SIRT1 signaling.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 24:961–973. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Vasudevan S, Tong Y and Steitz JA:
Switching from repression to activation: microRNAs can up-regulate
translation. Science. 318:1931–1934. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Carthew RW and Sontheimer EJ: Origins and
Mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell. 136:642–655. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Siomi H and Siomi MC: On the road to
reading the RNA-interference code. Nature. 457:396–404. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lin CC, Liu LZ, Addison JB, Wonderlin WF,
Ivanov AV and Ruppert JM: A KLF4-miRNA-206 autoregulatory feedback
loop can promote or inhibit protein translation depending upon cell
context. Mol Cell Biol. 31:2513–2527. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Vasudevan S and Steitz JA:
AU-rich-element-mediated upregulation of translation by FXR1 and
argonaute 2. Cell. 128:1105–1118. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Moshiri F, Salvi A, Gramantieri L,
Sangiovanni A, Guerriero P, De Petro G, Bassi C, Lupini L, Sattari
A, Cheung D, et al: Circulating miR-106b-3p miR-101-3p and miR-1246
as diagnostic biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget.
9:15350–15364. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xu L, Beckebaum S, Iacob S, Wu G, Kaiser
GM, Radtke A, Liu C, Kabar I, Schmidt HH, Zhang X, et al:
MicroRNA-101 inhibits human hepatocellular carcinoma progression
through EZH2 downregulation and increased cytostatic drug
sensitivity. J Hepatol. 60:590–598. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Zhang S, Wang M, Li Q and Zhu P: MiR-101
reduces cell proliferation and invasion and enhances apoptosis in
endometrial cancer via regulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR. Cancer Biomark.
21:179–186. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Saxton RA and Sabatini DM: mTOR signaling
in growth, metabolism, and disease. Cell. 168:960–976. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li Y, Wang S, Gao X, Zhao Y, Li Y, Yang B,
Zhang N and Ma L: Octreotide alleviates autophagy by up-regulation
of MicroRNA-101 in intestinal epithelial cell line caco-2. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 49:1352–1363. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cox LS: PCNA tightens its hold on the
nucleus. Cell Cycle. 14:2727–2728. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Melo RM, Martins YS, Luz RK, Rizzo E and
Bazzoli N: PCNA and apoptosis during post-spawning ovarian
remodeling in the teleost oreochromis niloticus. Tissue Cell.
47:541–549. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ghavami S, Hashemi M, Ande SR, Yeganeh B,
Xiao W, Eshraghi M, Bus CJ, Kadkhoda K, Wiechec E, Halayko AJ and
Los M: Apoptosis and cancer: Mutations within caspase genes. J Med
Genet. 46:497–510. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Nikoonahad Lotfabadi N, Mohseni
Kouchesfahani H, Sheikhha MH and Kalantar SM: In vitro transfection
of anti-tumor miR-101 induces BIM, a pro-apoptotic protein,
expression in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). EXCLI J. 16:1257–1267.
2017.
|
|
55
|
Guertin DA and Sabatini DM: An expanding
role for mTOR in cancer. Trends Mol Med. 11:353–361. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kim J, Kim YC, Fang C, Russell RC, Kim JH,
Fan W, Liu R, Zhong Q and Guan KL: Differential regulation of
distinct Vps34 complexes by AMPK in nutrient stress and autophagy.
Cell. 152:290–303. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B and Guan KL:
AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of
Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 13:132–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Liu D, Tang H, Li XY, Deng MF, Wei N, Wang
X, Zhou YF, Wang DQ, Fu P, Wang JZ, et al: Targeting the
HDAC2/HNF-4A/miR-101b/AMPK pathway rescues tauopathy and dendritic
abnormalities in alzheimer's disease. Mol Ther. 25:752–764. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Liu P, Ye F and Xie X, Li X, Tang H, Li S,
Huang X, Song C, Wei W and Xie X: mir-101-3p is a key regulator of
tumor metabolism in triple negative breast cancer targeting AMPK.
Oncotarget. 7:35188–35198. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|