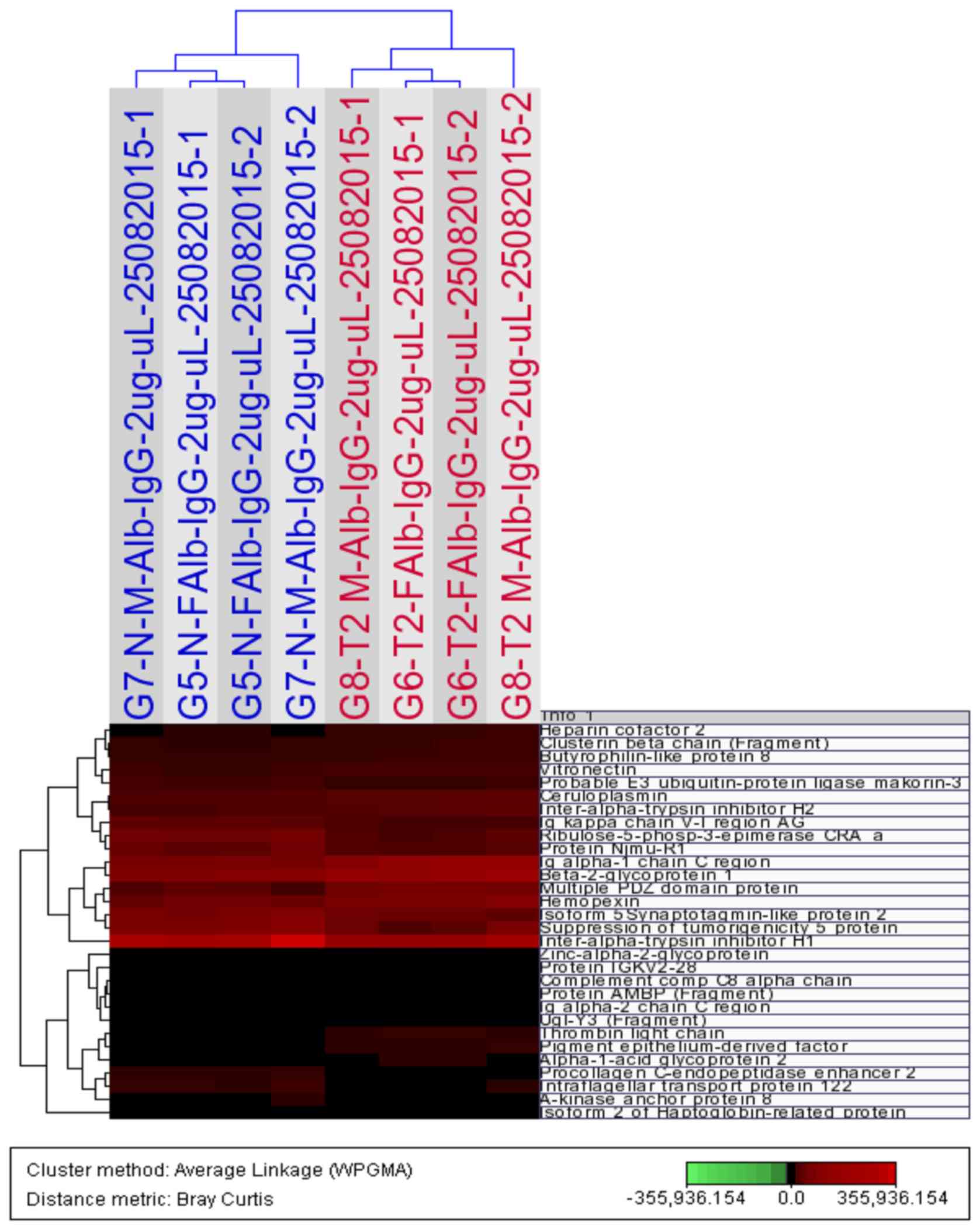
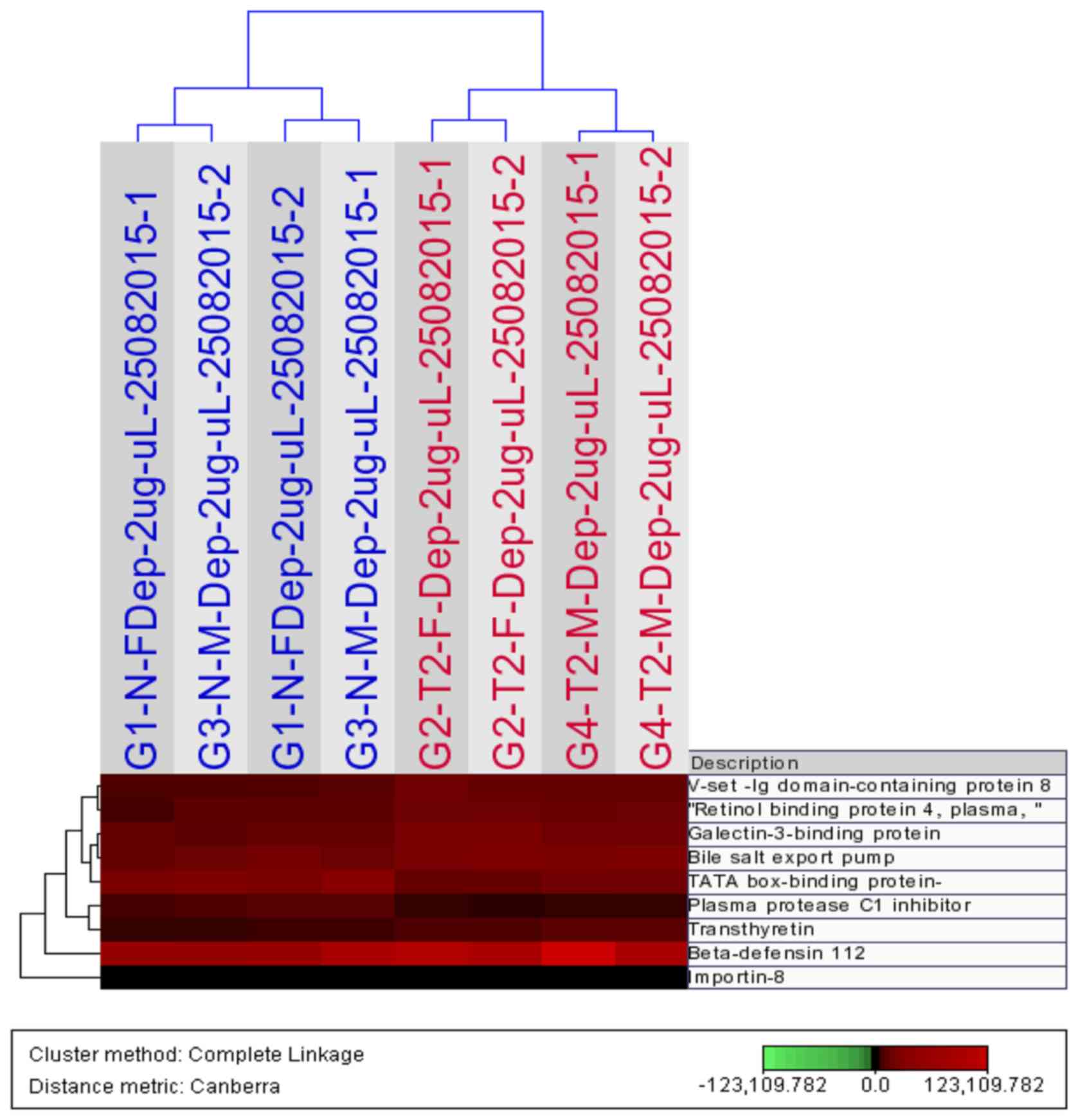
|
1
|
American Diabetes Association: Diagnosis
and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 32(Suppl
1): S62–S67. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
World Health Organization: Global Report
on Diabetes. World Health Organization; Geneva, Swizerland: 2016,
http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/204871/1/9789241565257_eng.pdf.
|
|
3
|
Al-Mahroos F: Diabetes mellitus in the
Arabian peninsula. Ann Saudi Med. 20:111–112. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
International Diabetes Federation: IDF
Diabetes Atlas. 7th edition. IDF; Brussels, Belgium: 2015
|
|
5
|
Van JA, Scholey JW and Konvalinka A:
Insights into Diabetic Kidney Disease Using Urinary Proteomics and
Bioinformatics. J Am Soc Nephrol. 28:1050–1061. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
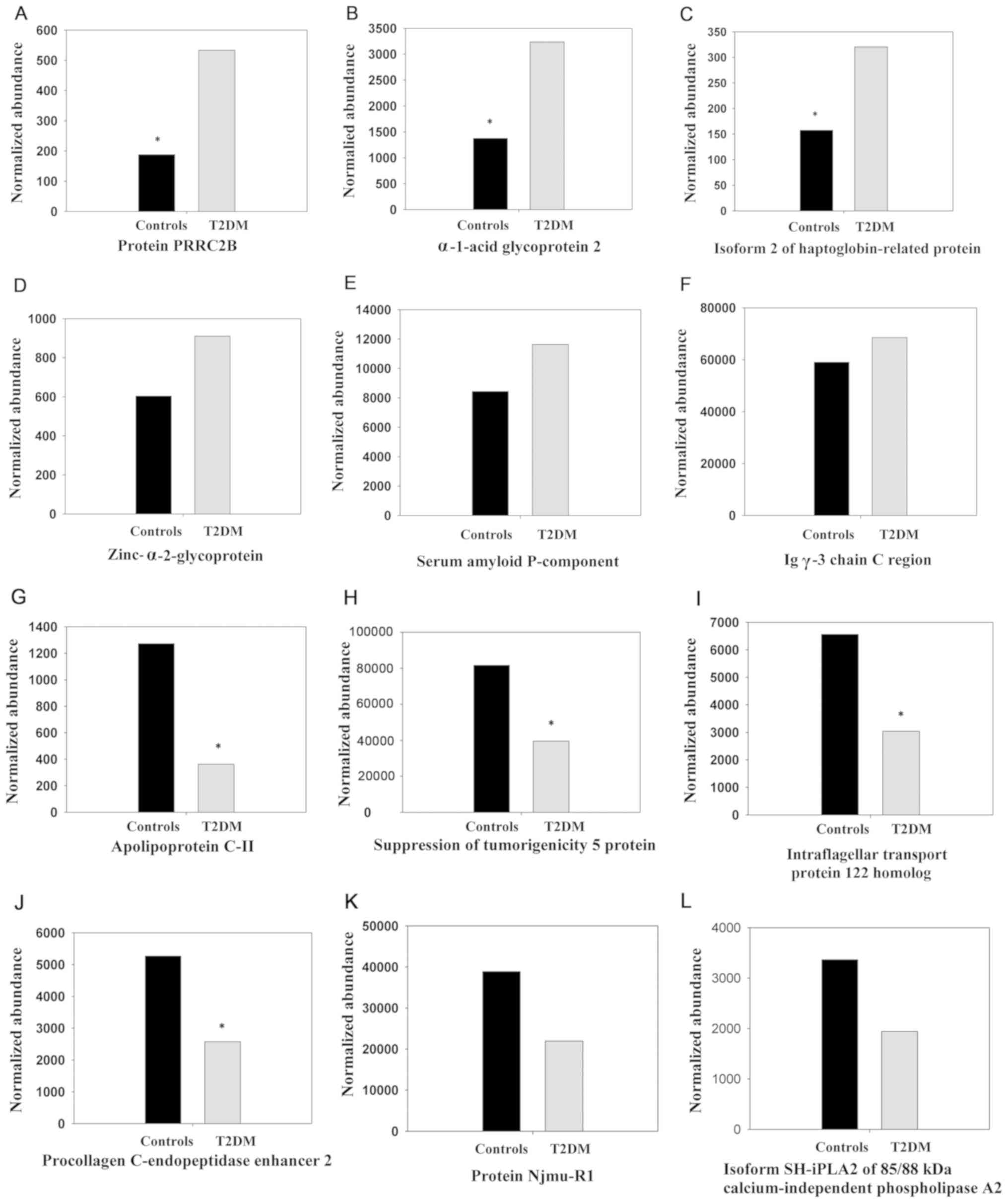
|
6
|
Cottrell JS: Protein identification using
MS/MS data. J Proteomics. 74:1842–1851. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bukowiecka-Matusiak M,
Chmielewska-Kassassir M, Szczesna D and Wozniak LA: Metabolomic
insight into lipid and protein profile in diabetes using mass
spectrometry. Mini Rev Med Chem. 16:1167–1174. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Doria A, Patti ME and Kahn CR: The
emerging genetic architecture of type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab.
8:186–200. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kahn CR: Banting Lecture. Insulin action,
diabetogenes, and the cause of type II diabetes. Diabetes.
43:1066–1084. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Knox SS: From 'omics' to complex disease:
A systems biology approach to gene-environment interactions in
cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 10:112010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ponomarenko EA, Poverennaya EV, Ilgisonis
EV, Pyatnitskiy MA, Kopylov AT, Zgoda VG, Lisitsa AV and Archakov
AI: The size of the human proteome: The width and depth. Int J Anal
Chem. 2016:74368492016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E, Zimmet P,
George KM and Alberti M: International Textbook of Diabetes
Mellitus. 4th edition. John Wiley and Sons; New York, NY: 2015,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Anderson NL and Anderson NG: The human
plasma proteome: History, character, and diagnostic prospects. Mol
Cell Proteomics. 1:845–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Anderson NL, Anderson NG, Pearson TW,
Borchers CH, Paulovich AG, Patterson SD, Gillette M, Aebersold R
and Carr SA: A human proteome detection and quantitation project.
Mol Cell Proteomics. 8:883–886. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
World Health Organisation: Definition and
diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and intermediate hyperglycemia:
Report of a WHO/IDF consultation. World Health Organisation;
Geneva, Swizerland: 2002, https://www.idf.org/webdata/docs/WHO_IDF_definition_diagnosis_of_diabetes.pdf.
|
|
16
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Alaiya A, Fox J, Bobis S, Matic G,
Shinwari Z, Barhoush E, Márquez M, Nilsson S and Holmberg AR:
Proteomic analysis of soft tissue tumor implants treated with a
novel polybisphosphonate. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 11:39–49.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Alaiya A, Assad L, Alkhafaji D, Shinwari
Z, Almana H, Shoukri M, Alkorbi L, Ibrahim HG, Abdelsalam MS,
Skolnik E, et al: Proteomic analysis of Class IV lupus nephritis.
Nephrol Dial Transplant. 30:62–70. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li GZ, Vissers JP, Silva JC, Golick D,
Gorenstein MV and Geromanos SJ: Database searching and accounting
of multiplexed precursor and product ion spectra from the data
independent analysis of simple and complex peptide mixtures.
Proteomics. 9:1696–1719. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Alaiya AA, Aljurf M, Shinwari Z, Almohareb
F, Malhan H, Alzahrani H, Owaidah T, Fox J, Alsharif F, Mohamed SY,
et al: Protein signatures as potential surrogate biomarkers for
stratifi-cation and prediction of treatment response in chronic
myeloid leukemia patients. Int J Oncol. 49:913–933. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Apweiler R, Bairoch A, Wu CH, Barker WC,
Boeckmann B, Ferro S, Gasteiger E, Huang H, Lopez R, Magrane M, et
al: UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids
Res. 32:D115–D119. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Weir GC and Leahy JL: Pathogenesis of
non-insulin- dependent (type II) diabetes mellitus. Joslin's
Diabetes Mellitus. 13th edition. Lea and Febiger; Philadelphia, PA:
pp. 240–264. 1994
|
|
23
|
Saltiel AR and Kahn CR: Insulin signalling
and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature.
13:799–806. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Meglasson MD and Matschinsky FM:
Pancreatic islet glucose metabolism and regulation of insulin
secretion. Diabetes Metab Rev. 2:163–214. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gersten DM, Khirabadi BS, Kurian P, Ledley
RS, Mahany T, Ramey ER and Ramwell PW: Albumin obscures sex
differences in blood protein patterns of rats and humans. Biochem
J. 191:869–872. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Al Kindi MA, Chataway TK, Gilada GA,
Jackson MW, Goldblatt FM, Walker JG, Colella AD and Gordon TP:
Serum SmD autoantibody proteomes are clonally restricted and share
variable-region peptides. J Autoimmun. 57:77–81. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Brooks-Worrell B and Palmer JP: Immunology
in the Clinic Review Series; focus on metabolic diseases:
development of islet autoimmune disease in type 2 diabetes
patients: potential sequelae of chronic inflammation. Clin Exp
Immunol. 167:40–46. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Geerlings SE and Hoepelman AI: Immune
dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM). FEMS Immunol
Med Microbiol. 26:259–265. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Murri M, Insenser M, Bernal-Lopez MR,
Perez-Martinez P, Escobar-Morreale HF and Tinahones FJ: Proteomic
analysis of visceral adipose tissue in pre-obese patients with type
2 diabetes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 376:99–106. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kimzey MJ, Kinsky OR, Yassine HN,
Tsaprailis G, Stump CS, Monks TJ and Lau SS: Site specific
modification of the human plasma proteome by methylglyoxal. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 289:155–162. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lepedda AJ, Lobina O, Rocchiccioli S,
Nieddu G, Ucciferri N, De Muro P, Idini M, Nguyen HQ, Guarino A,
Spirito R and Formato M: Identification of differentially expressed
plasma proteins in atherosclerotic patients with type 2 diabetes. J
Diabetes Complications. 30:880–886. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang HS, Woo JE, Lee SJ, Park SH and Woo
JM: Elevated plasma pentraxin 3 levels are associated with
development and progression of diabetic retinopathy in Korean
patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
55:5989–5997. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
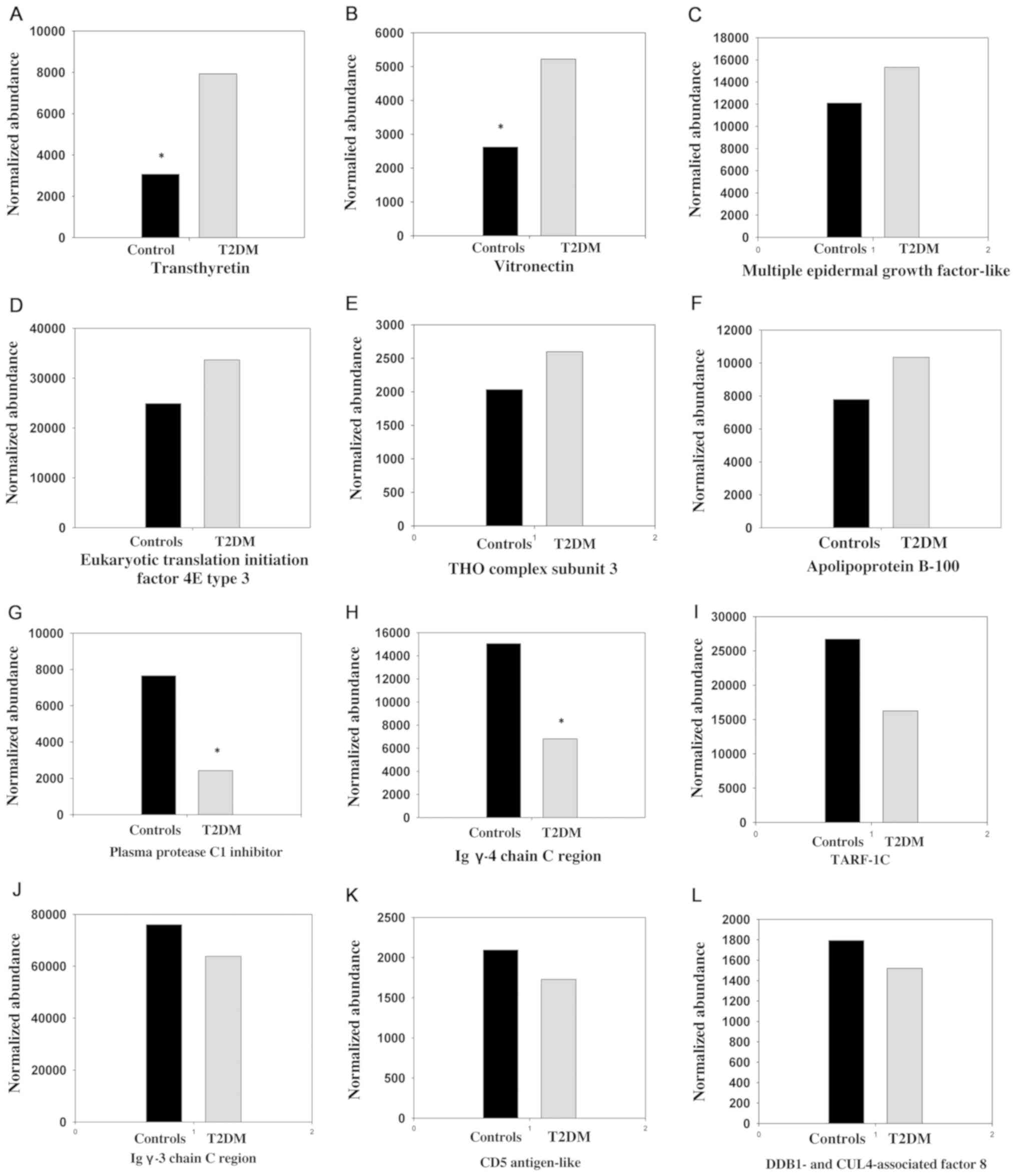
Karlsson E, Shaat N and Groop L: Can
complement factors 5 and 8 and transthyretin be used as biomarkers
for MODY 1 (HNF4A-MODY) and MODY 3 (HNF1A-MODY)? Diabet Med.
25:788–791. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zubiri I, Posada-Ayala M, Sanz-Maroto A,
Calvo E, Martin-Lorenzo M, Gonzalez-Calero L, de la Cuesta F, Lopez
JA, Fernandez-Fernandez B, Ortiz A, et al: Diabetic nephropathy
induces changes in the proteome of human urinary exosomes as
revealed by label-free comparative analysis. J Proteomics.
96:92–102. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Li TH, Qiu CJ, Yu XJ, Liu DD, Zhou PF and
Wu L: Increased serum pigment epithelium-derived factor in women
with gestational diabetes is associated with type 2 diabetes. Int J
Endocrinol. 2015:3469382015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kolberg JA, Gerwien RW, Watkins SM,
Wuestehube LJ and Urdea M: Biomarkers in Type 2 diabetes: Improving
risk stratification with the PreDx® Diabetes Risk Score.
Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 11:775–792. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Alessi MC, Nicaud V, Scroyen I, Lange C,
Saut N, Fumeron F, Marre M, Lantieri O, Fontaine-Bisson B,
Juhan-Vague I, et al DESIR Study Group: Association of vitronectin
and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 levels with the risk of
metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Results from the
D.E.S.I.R. prospective cohort. Thromb Haemost. 106:416–422. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang M, Liu R, Li S, Luo Y, Zhang Y, Zhang
L, Liu D, Wang Y, Xiong Z, Boden G, et al: Zinc-α2-glycoprotein is
associated with insulin resistance in humans and is regulated by
hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, or liraglutide administration:
Cross-sectional and interventional studies in normal subjects,
insulin-resistant subjects, and subjects with newly diagnosed
diabetes. Diabetes Care. 36:1074–1082. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee JH, Volinic JL, Banz C, Yao KM and
Thomas MK: Interactions with p300 enhance transcriptional
activation by the PDZ-domain coactivator Bridge-1. J Endocrinol.
187:283–292. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gupta RK, Gao N, Gorski RK, White P, Hardy
OT, Rafiq K, Brestelli JE, Chen G, Stoeckert CJ Jr and Kaestner KH:
Expansion of adult beta-cell mass in response to increased
metabolic demand is dependent on HNF-4alpha. Genes Dev. 21:756–69.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kelly P, Bailey CL, Fueger PT, Newgard CB,
Casey PJ and Kimple ME: Rap1 promotes multiple pancreatic islet
cell functions and signals through mammalian target of rapamycin
complex 1 to enhance proliferation. J Biol Chem. 285:15777–15785.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Christiansen MS, Iversen K, Larsen CT,
Goetze JP, Hommel E, Mølvig J, Pedersen BK, Magid E and
Feldt-Rasmussen B: Increased urinary orosomucoid excretion: A
proposed marker for inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in
patients with type 2 diabetes. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 69:272–281.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Pullakhandam R, Palika R, Ghosh S and
Reddy GB: Contrasting effects of type 2 and type 1 diabetes on
plasma RBP4 levels: The significance of transthyretin. IUBMB Life.
64:975–982. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gluhovschi C, Gluhovschi G, Petrica L,
Timar R, Velciov S, Ionita I, Kaycsa A and Timar B: Urinary
Biomarkers in the Assessment of Early Diabetic Nephropathy. J
Diabetes Res. 2016:46261252016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Watts GF, Ooi EM and Chan DC: Therapeutic
regulation of apoB100 metabolism in insulin resistance in vivo.
Pharmacol Ther. 123:281–291. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kei AA, Filippatos TD, Tsimihodimos V and
Elisaf MS: A review of the role of apolipoprotein C-II in
lipoprotein metabolism and cardiovascular disease. Metabolism.
61:906–921. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Rye KA, Barter PJ and Cochran BJ:
Apolipoprotein A-I interactions with insulin secretion and
production. Curr Opin Lipidol. 27:8–13. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Yarmolinsky J, Bordin Barbieri N, Weinmann
T, Ziegelmann PK, Duncan BB and Inês Schmidt M: Plasminogen
activator inhibitor-1 and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and
meta-analysis of observational studies. Sci Rep. 6:177142016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hasegawa Y and Ishigaki Y: Heparin
Cofactor II: A novel plausible link of obesity and diabetes with
thrombosis. J Atheroscler Thromb. 24:1202–1203. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bhandari BK, Feliers D, Duraisamy S,
Stewart JL, Gingras AC, Abboud HE, Choudhury GG, Sonenberg N and
Kasinath BS: Insulin regulation of protein translation repressor
4E-BP1 an eIF4E-binding protein, in renal epithelial cells. Kidney
Int. 59:866–875. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Rigor RR, Shen Q, Pivetti CD, Wu MH and
Yuan SY: Myosin light chain kinase signaling in endothelial barrier
dysfunction. Med Res Rev. 33:911–933. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
52
|
Funk C, Ponelle C, Scheuermann G and
Pantze M: Cholestatic potential of troglitazone as a possible
factor contributing to troglitazone-induced hepatotoxicity: In vivo
and in vitro interaction at the canalicular bile salt export pump
(Bsep) in the rat. Mol Pharmacol. 59:627–635. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Strässer K, Masuda S, Mason P, Pfannstiel
J, Oppizzi M, Rodriguez-Navarro S, Rondón AG, Aguilera A, Struhl K,
Reed R and Hurt E: TREX is a conserved complex coupling
transcription with messenger RNA export. Nature. 417:304–308. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Daimon M, Oizumi T, Karasawa S, Kaino W,
Takase K, Tada K, Jimbu Y, Wada K, Kameda W, Susa S, et al:
Association of the clusterin gene polymorphisms with type 2
diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 60:815–822. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|